carboxylic acids n derivatives - AQA chem
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
how are carboxylic acids produced? under what conditions?
oxidation of primary alcohols under reflux
are carboxylic acids strong or weak acids.
what does this mean in terms of their dissociation in solution
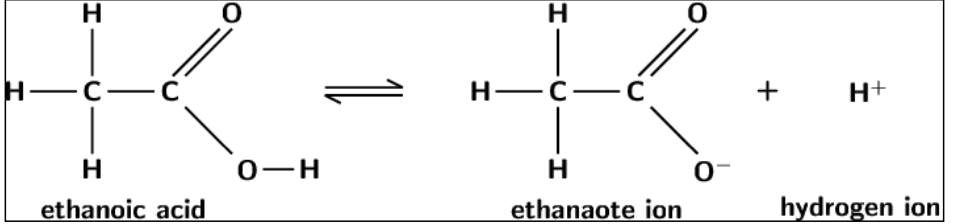
draw the dissociation of ethanoic acid in solution.
is it a reversible reaction or a regular reaction?
reversible
when carboxylic acids react with carbonates, what do they produce
carboxylate salt
water
CO2
carboxylic acids are ___ enough to _____ _____ form carbonates
strong enough to liberate CO2 to form carbonates
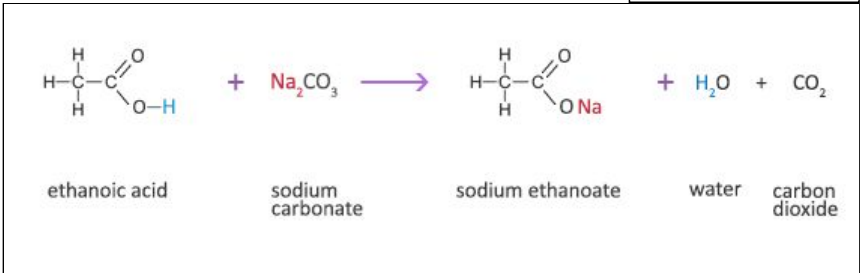
write the reaction (in words and in displayed formula) for ethanoic acid reacting with sodium carbonate
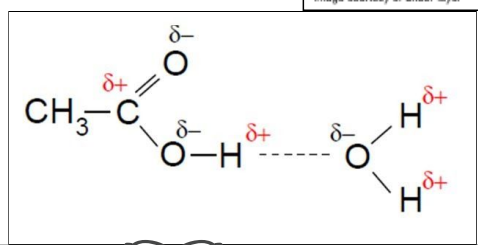
what are small chain carboxylic acids able to form with water molecules?
this makes them _______ in ________
can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
making them soluble in water
draw the hydrogen bonding between ethanoic acid and water molecule
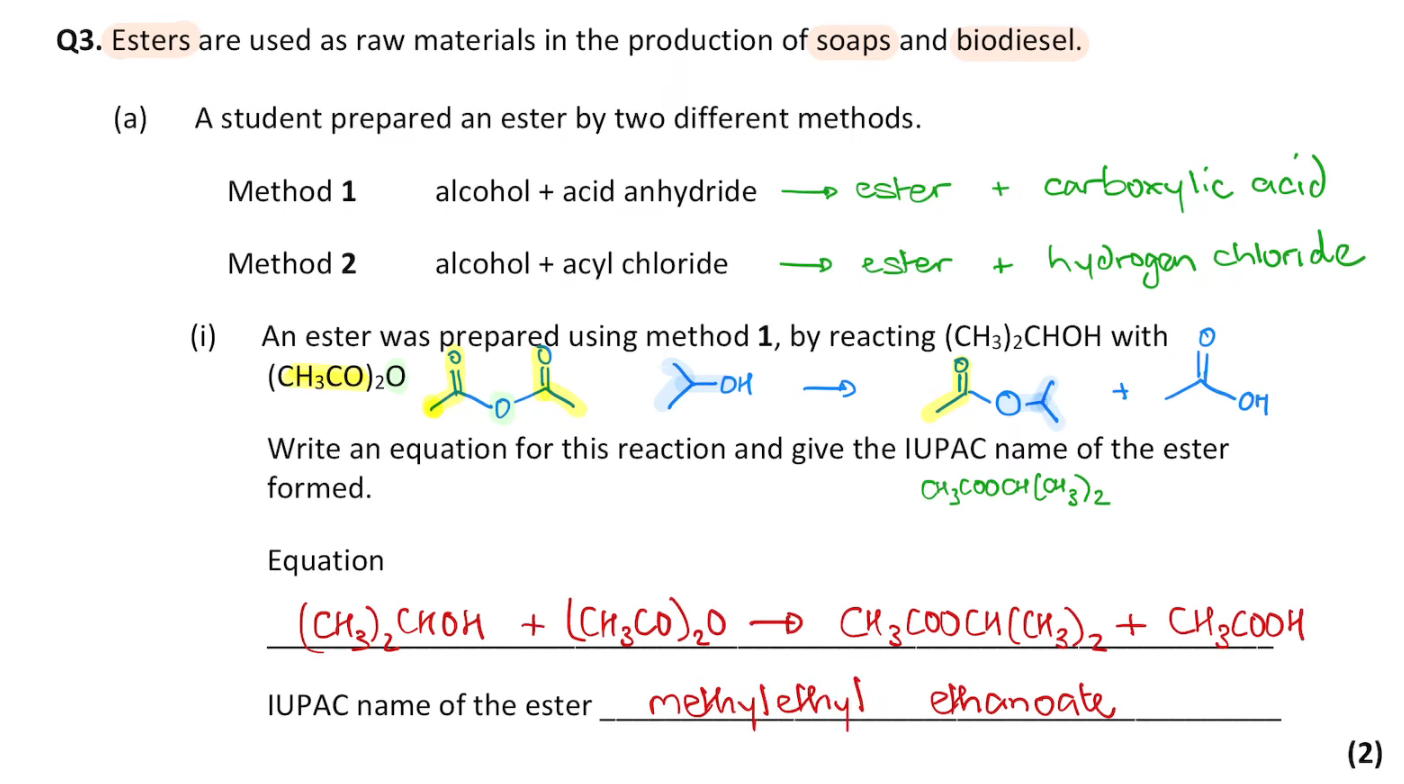
how are esters formed?
in the presence of what?
under what conditions?
when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol
in the presence of a strong acid catalyst
under reflux
what is the term for the reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols?
esterification
in esterification, what is lost form the carboxylic acid, and what is lost from the alcohol. what happens to the resultant of these losses
carboxylic acid loses its (OH) group within the carboxylate group (COOH)
the alcohol will only lose the hydrogen thats in the hydroxyl group (OH)
the resultant of these 2 will join to form an ester
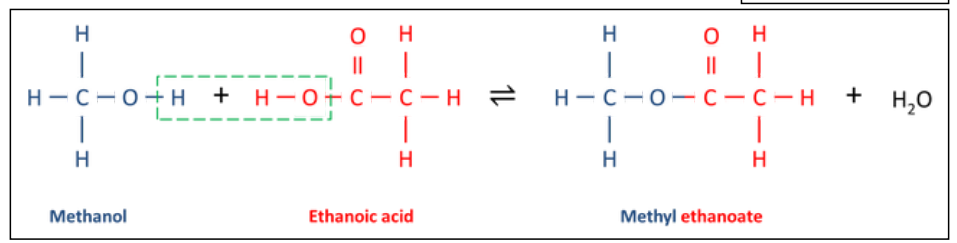
do the equation (displayed and written) of the esterification of methanol with ethanoic acid.
is it a reversible reaction, or is it a regular forward only reaction
it is a reversible reaction
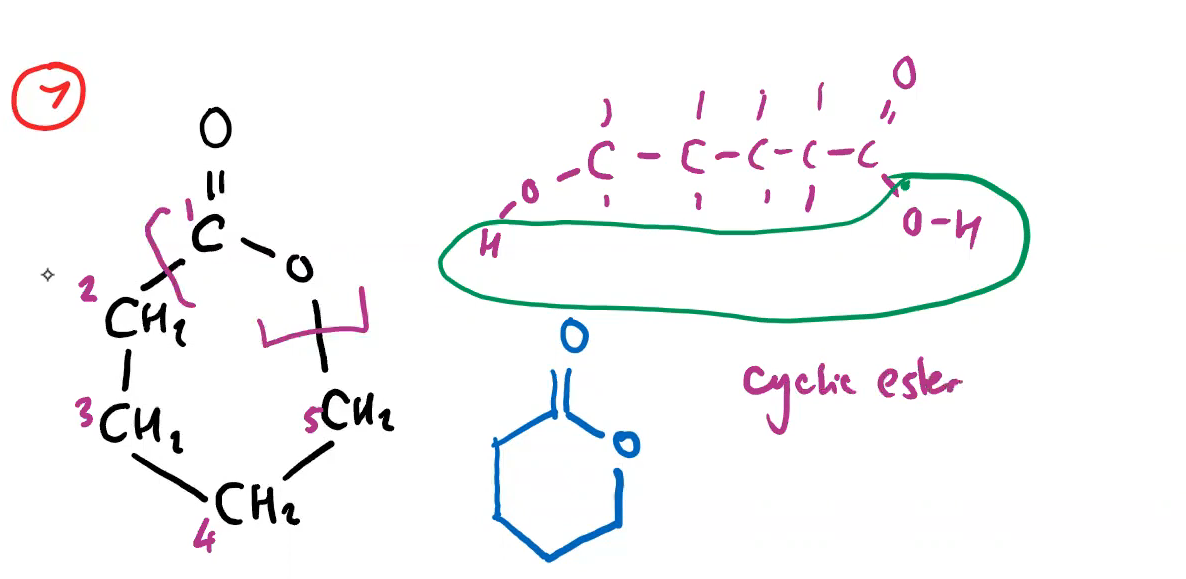
how are cyclic esters made from a hydroxy carboxylic acid (do it for 5-hydroxy pentanoic acid)
esters are ________ smelling compounds, used in _______ and ________. they have ________ boiling points, and also make ________ solvents for other ______ molecules
esters are sweet smelling compounds
used in food flavouring and perfumes
have low boiling points
make good solvents
for other polar molecules
what is the other use of esters, ( not solvents, flavourings, or perfume. whats the 4th)
used as plasticiser in polymers
what do plasticisers do in terms of flexibility, and in terms of intermolecular forces (IMF)
increases flexibility
decreases intermolecular forces (weakens them)
which has a lower boiling point, esters or C.A?
why?
esters
as carboxylic acids can form hydrogen bonds (with each other)
while esters cannot because the alkyl group prevents h bonding
are esters able to form hydrogen bonds with water?
yes
why does esterification need an acid catalyst, and what acid catalyst is used? what is the condition of the catalyst
because is a slow reaction
concentrated H2SO4
what is a more general term that esterification is referred to as (better to use esterification tho)
its a general “condensation reaction”
how are triglycerides formed?
esterification of glycerol with carboxylic acid
in the hydrolysis of esters, under acidic conditions, is it a reversible reaction, or is it just a regular forward only reaction? what are the products?
its a reversible reaction
the alcohol and C.A is reformed as the products
in the acidic hydrolysis of esters, what is the catalyst that is used, and what is its condition thats used
dilute HCl catalyst
what is the other name for the hydrolysis of esters in alkali conditions?
saponification
what is used and what is its condition for the saponification of an ester
excess dilute NaOH
what is the “functional group” for the saponification of an ester
COO- Na+
in COO- Na+, where is the negative charge located if using displayed formula
on the bottom Oxygen thats part of the ester link
how do you name the carboxylate salt that is formed from the saponification of an ester that has the COO- Na+ functional group
the same way u name an ester
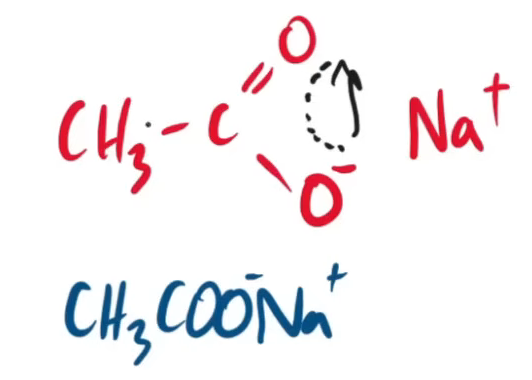
name this product form the saponification of ethyl ethanoate
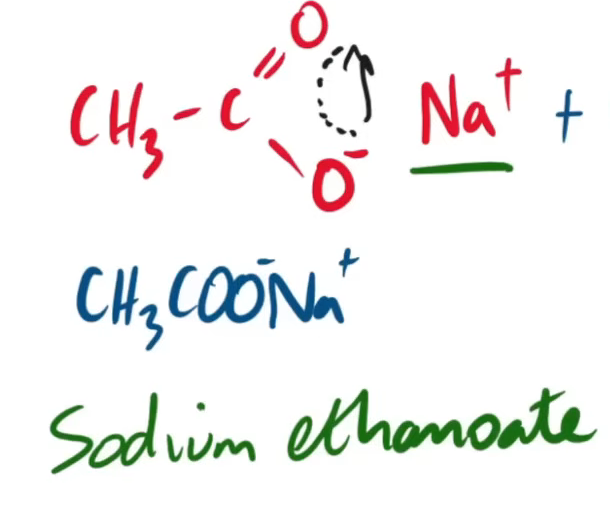
do the equation (written and displayed) for the saponification of ethyl ethanoate.
is it a reversible reaction or is it a regular just forward reaction?
just a regular forward reaction
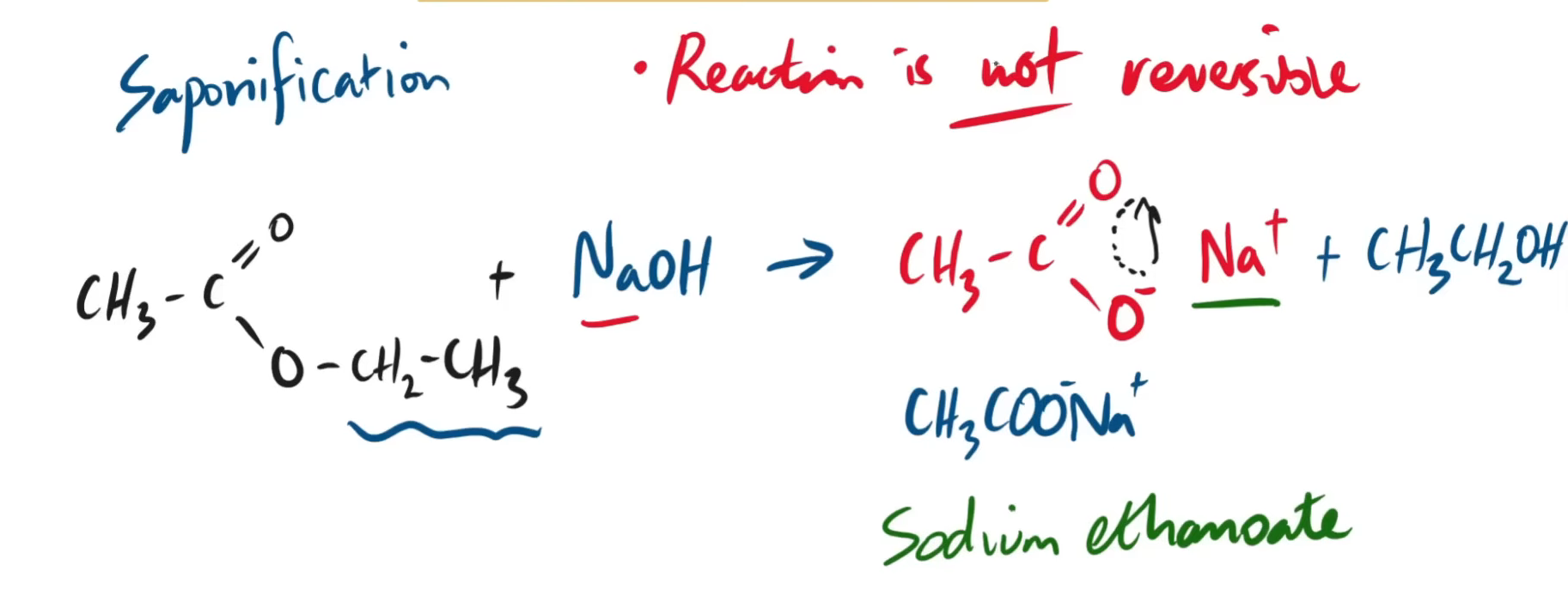
for both types of hyrdolysis of esters, what must it be heated under?
reflux
when u do the saponification of triglycerides, what is the carboxlyate salt used as / what is formed.
how is this possible (what 2 properties of the molecule is present)
soap
the chain is hydrophobic
the cabroxylate salt part (COONa) is hydrophilic
what does hyrdophobic and what does hydrophilic mean
hydrophobic = doesnt like water
hydrophilic = likes water
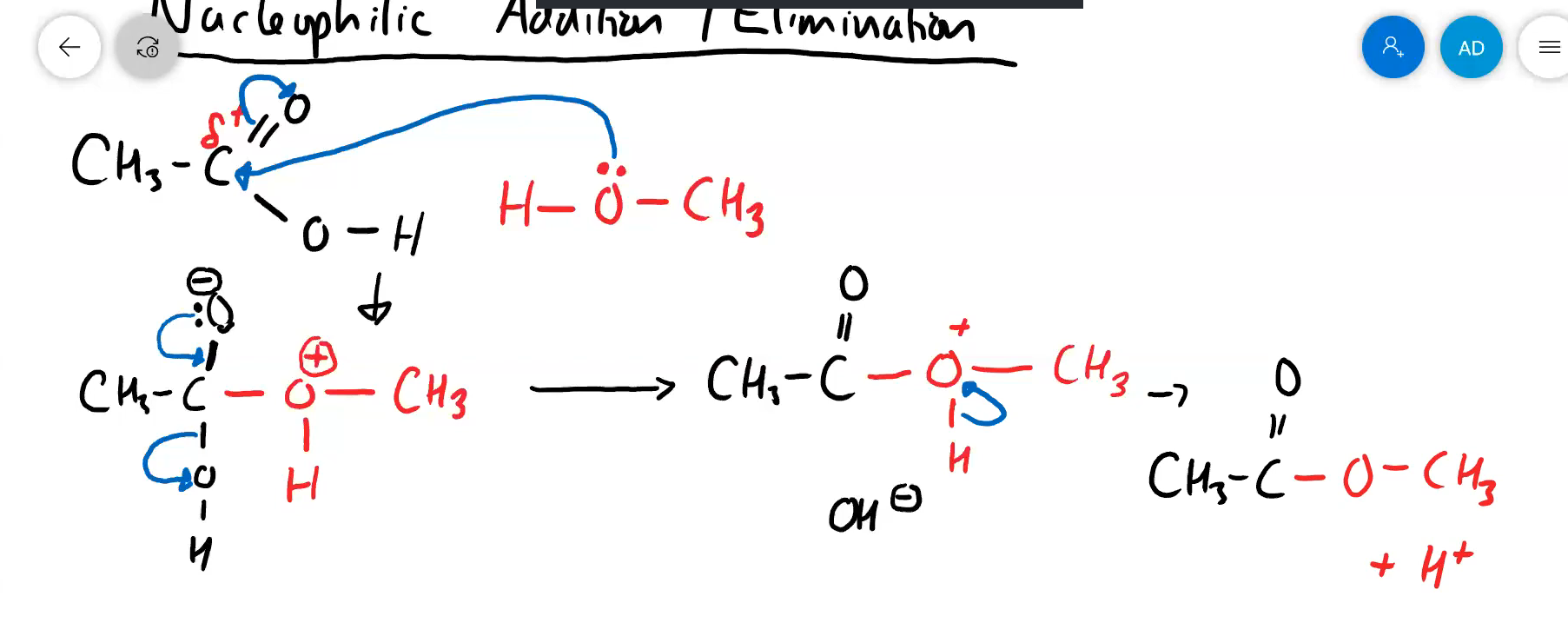
what is the name of the mechanism that is used in esterification (but not only just in esterification)
nucleophilic addition elimination
draw the NAE mechanism for the reaction of ethanoic acid with methanol
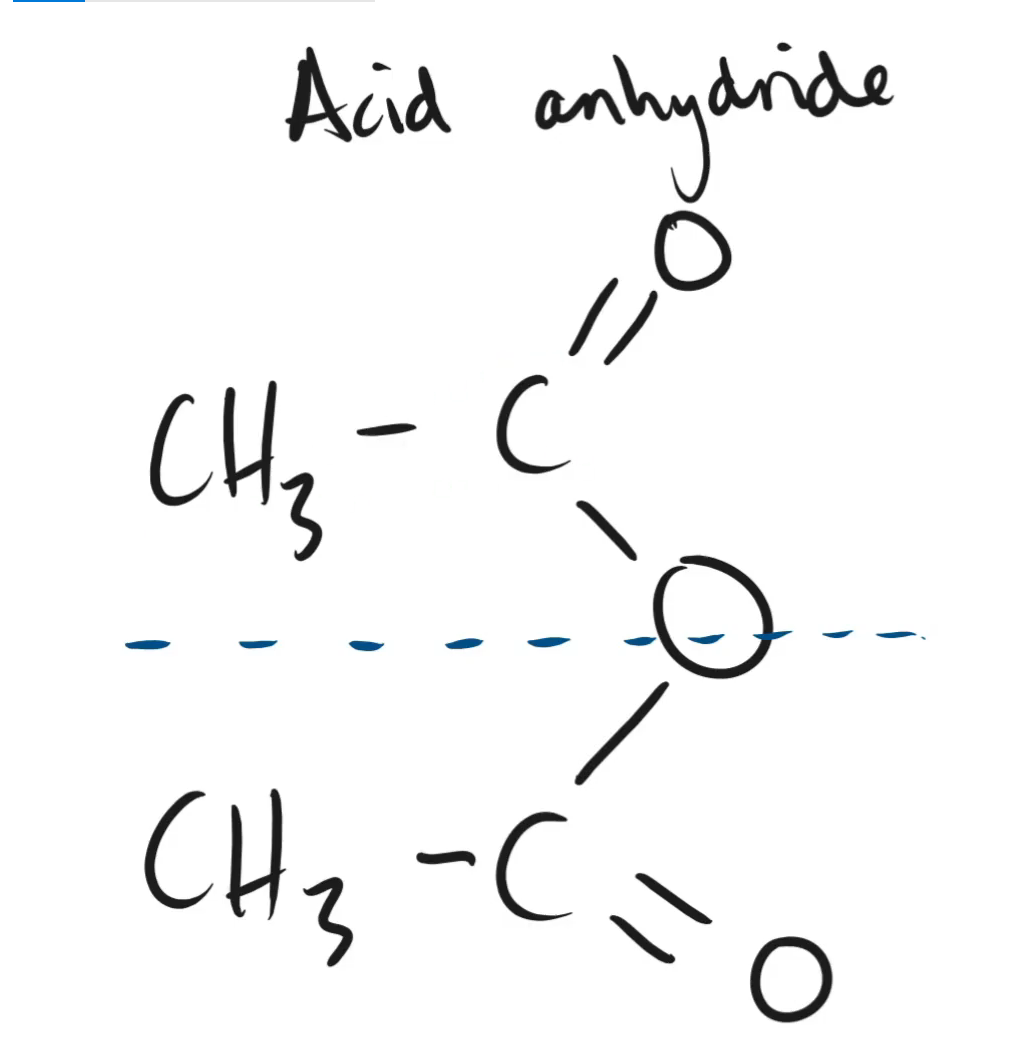
draw the displayed of a general acid anhydride
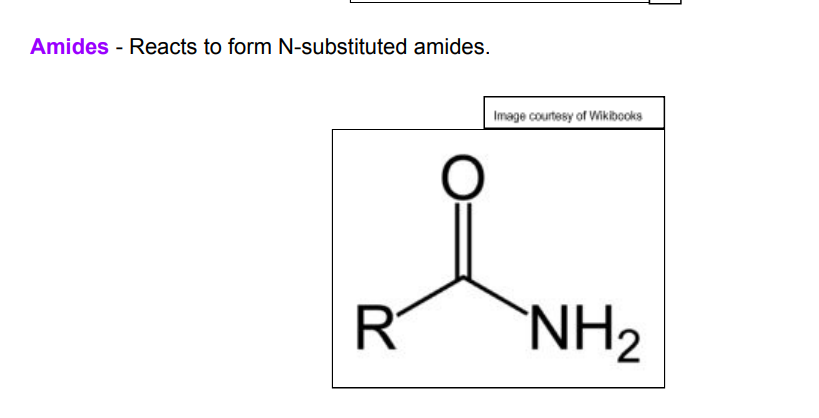
draw the displayed of a general amide (not N-substituted)
why is ethanoic anhydride used instead of ethanoyl chloride
ethanoyl chloride is more expensive, and produces harmful HCl fumes (as part of the reaction)
what does an acyl chloride + water form? (functional group)
at what conditions
what observation is produced.
What are the same 3 things, but for acid anhydride with water
acyl chlorides:
carboxylic acid
room temp
HCl gas (misty white fumes)
acid anhydride:
carboxylic acid
room temp
N/A
what does an acyl chloride + alcohol form? (functional group)
at what conditions
what observation is produced / what other product is formed.
What are the same 3 things, but for acid anhydride with alcohol
acyl chlorides:
ester
room temp
HCl gas (misty white fumes)
acid anhydride:
ester
room temp
carboxylic acid
what does an acyl chloride + ammonia form? (functional group product)
at what conditions
what observation is produced.
What are the same 3 things, but for acid anhydride with ammonia
acyl chlorides:
primary amide
room temp
NaH4Cl white smoke
acid anhydride:
primary amide
room temp
N/A
what does an acyl chloride + primary amine form? (functional group)
at what conditions
what observation is produced.
What are the same 3 things, but for acid anhydride with primary amine
acyl chlorides:
secondary amide
room temp
N/A
acid anhydride:
secondary amide
room temp
N/A
whats the difference between an amide and amine
the only difference is that an amide is when its in an “ester (link)”
whereas amine is just when its not in the ester link, e.g methyl amine

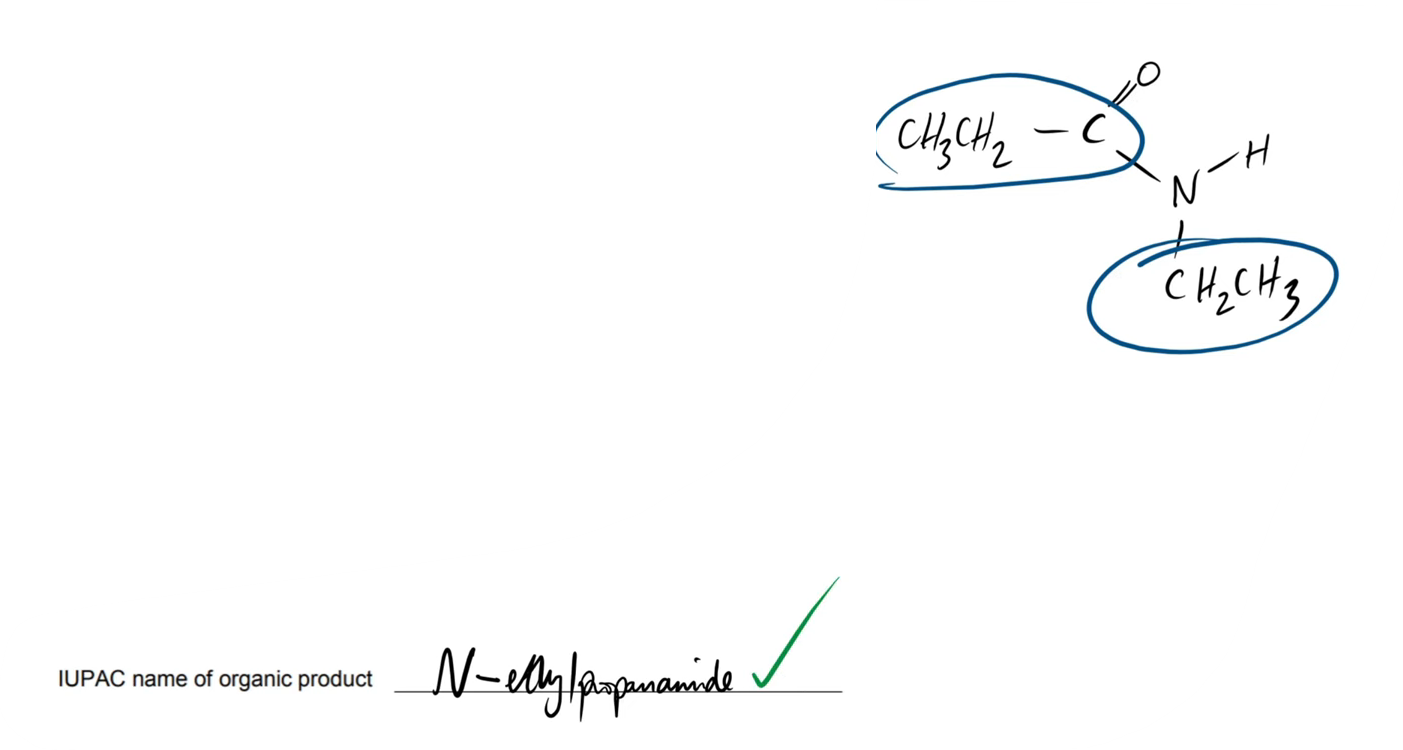
do this question
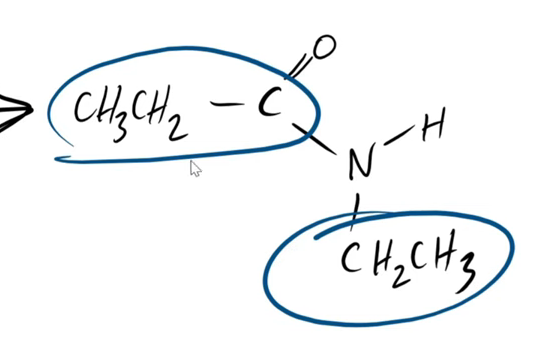
how would u name this molecule (produced from nucleophilic addition elimination), as in what are the steps?
when naming, do u have to use anything to add significance to the amine/amide?
what is its name
u name it like u would an ester
u have to add “N - “ to the IUPAC name to show that it is N-substituted
name:
N - ethyl propanamide