ch. 35 notes
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
plant tissue systems, types of cells in plants, plant structure + function
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
compound tissue
different cell types make it up
common cell types
parenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, sclerenchyma
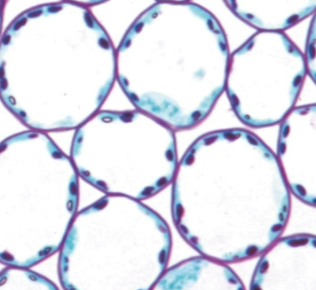
parenchyma cells
thin, 1’, primary cell walls
large vacuoles
space filling cells
lots of chloroplasts
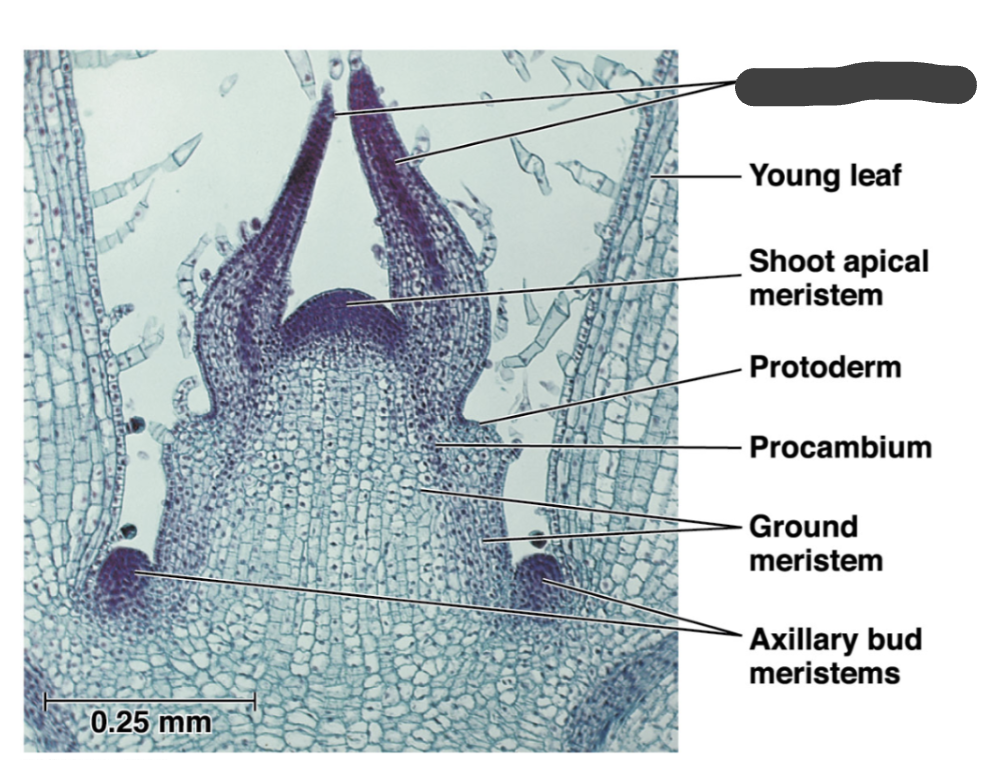
leaf primadora
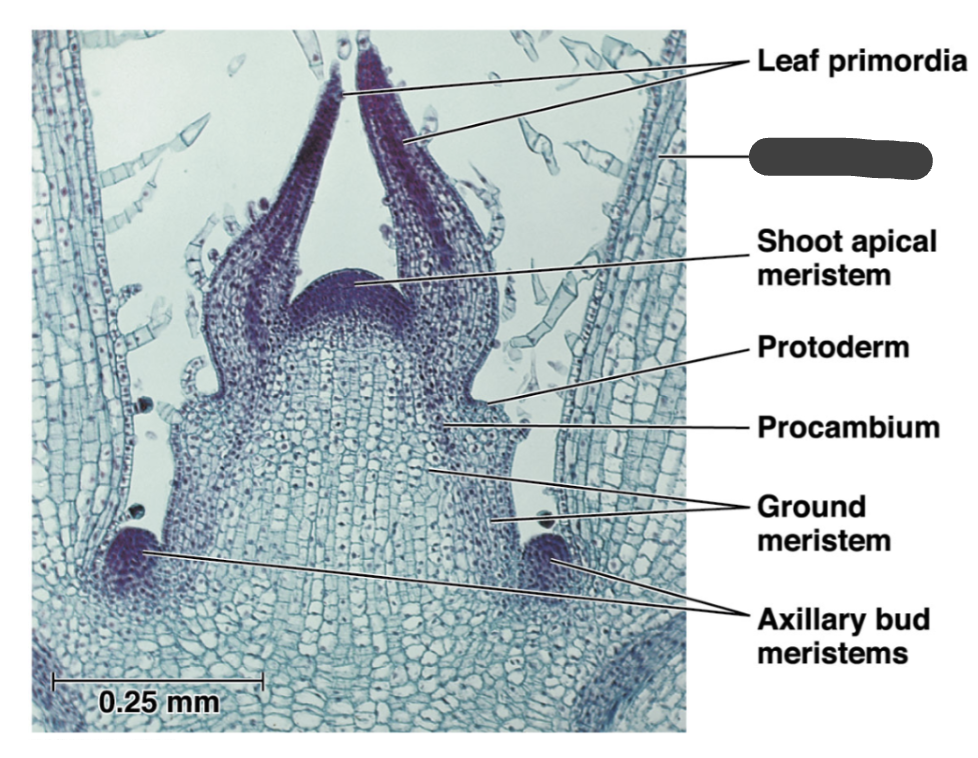
young leaf
meristem
cells maintain ability to divide adding to the plant body
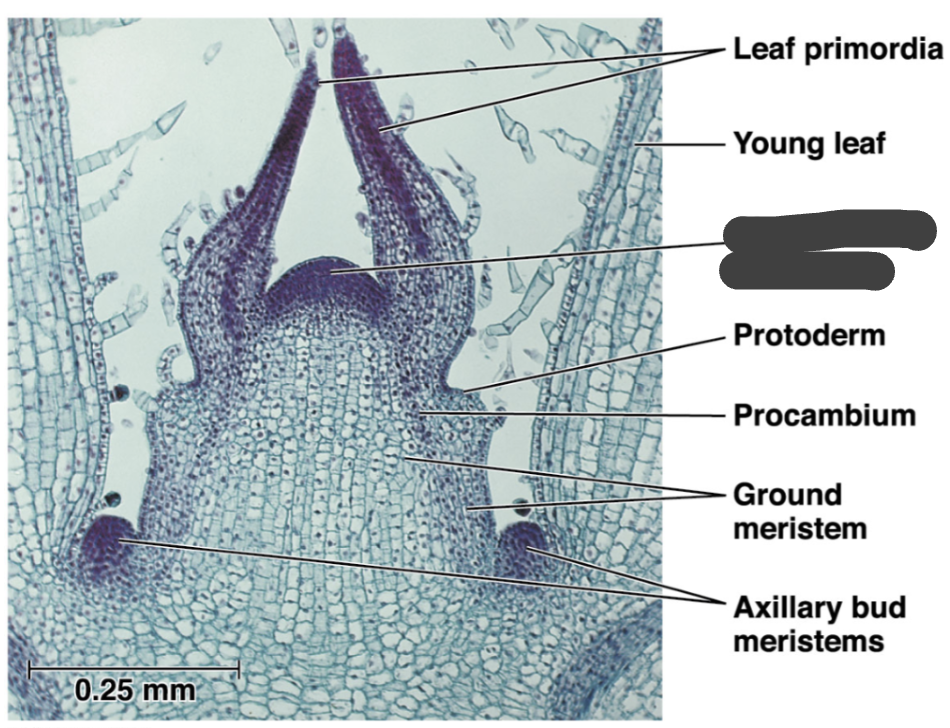
shoot apical meristem
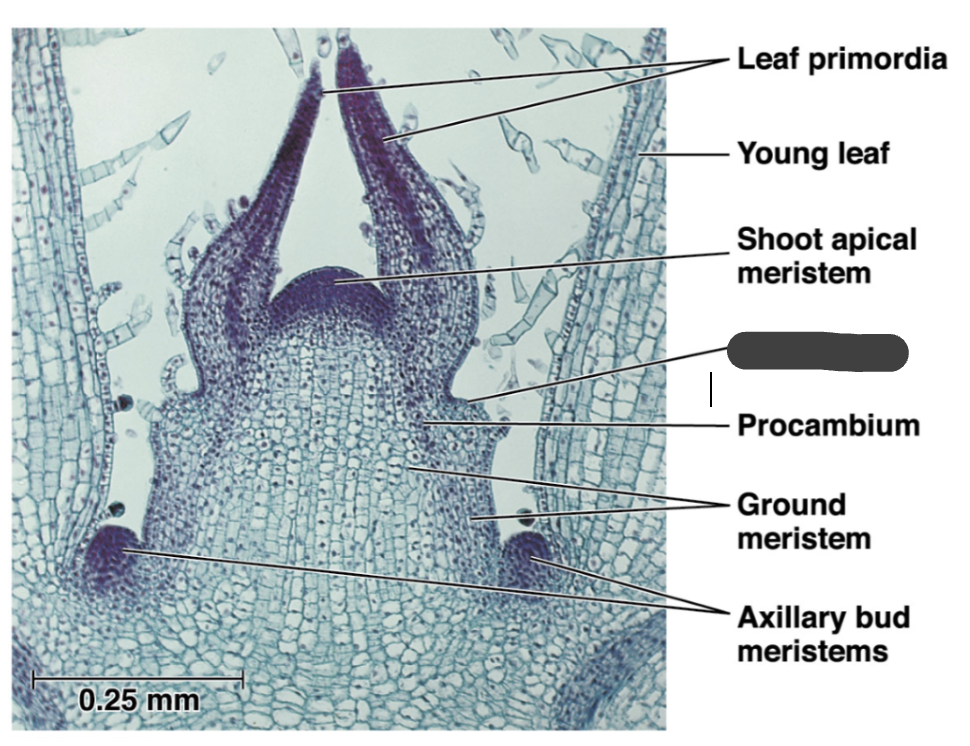
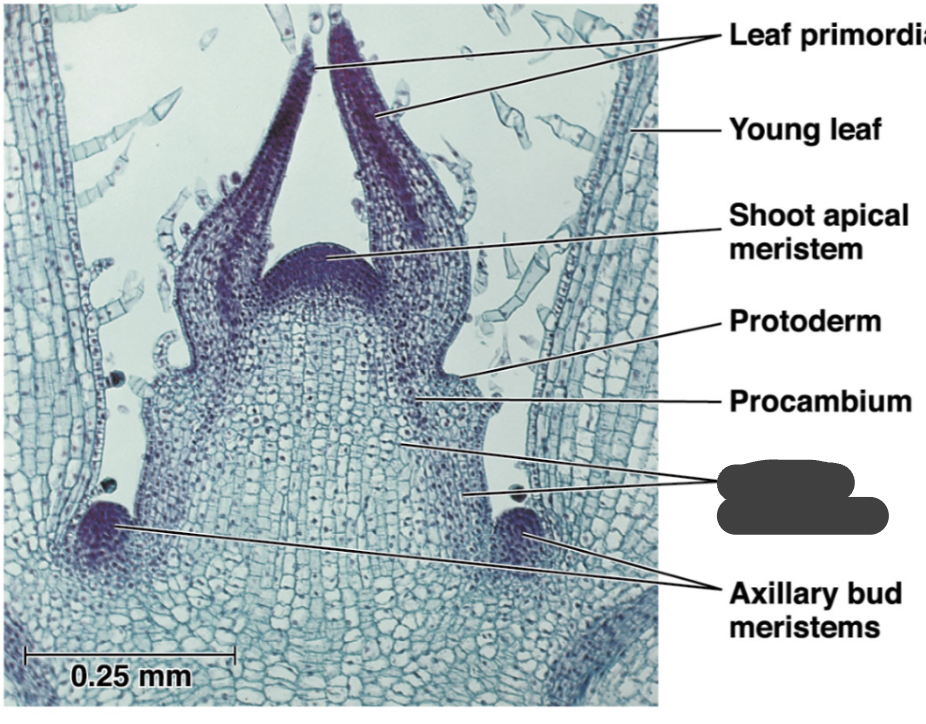
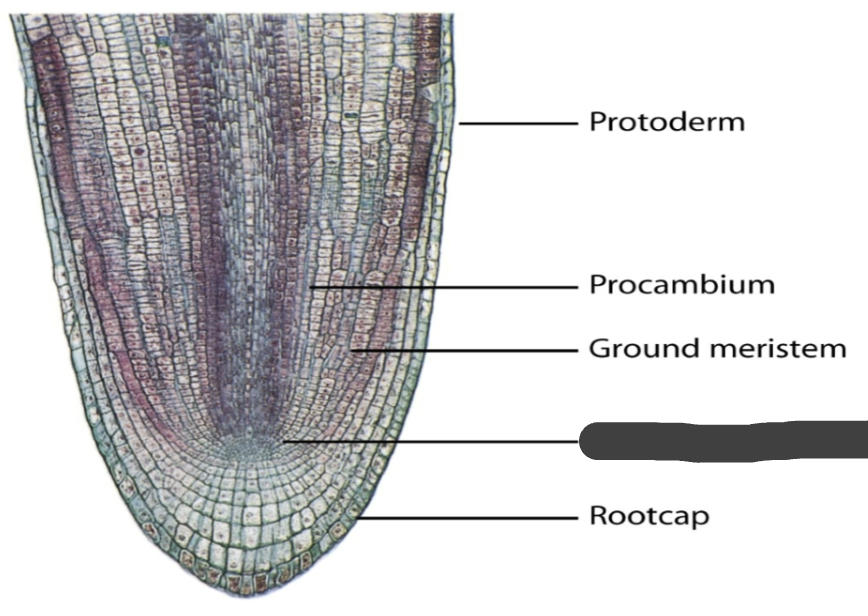
protoderm
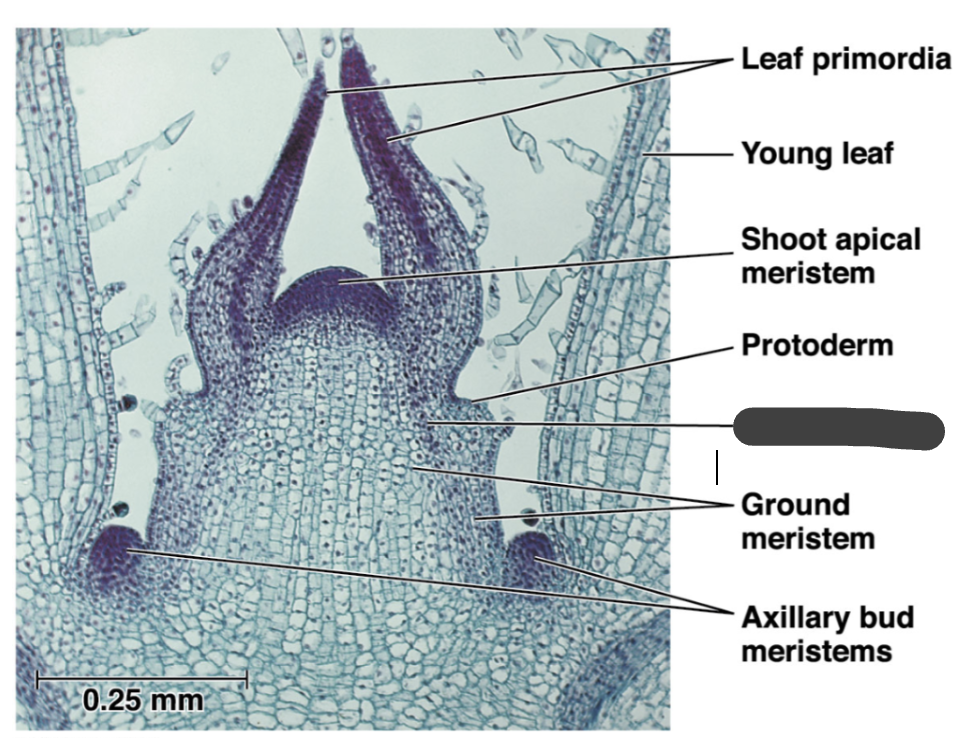
procambium
ground meristem
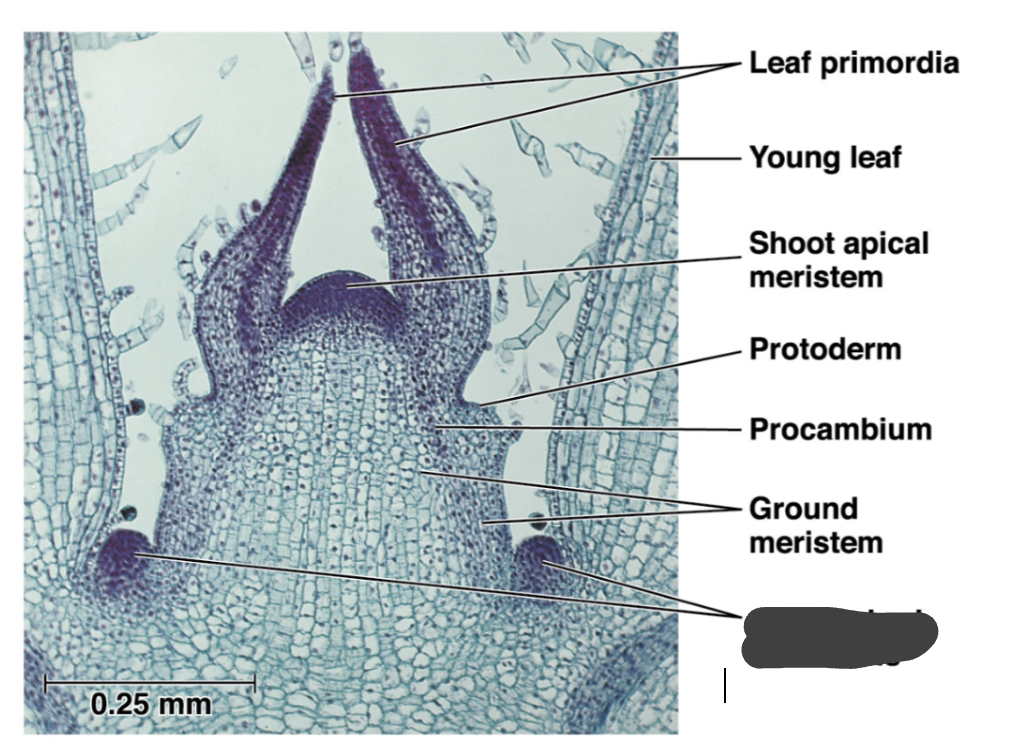
axillary bud meristems
sclerenchyma
dead @ maturity
thick 2’ cell wall
structural support
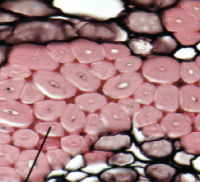
collenchyma cells
irregular 1’ cell walls
flexible supports
found in young plants
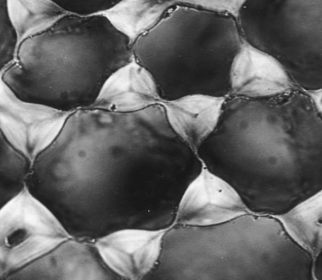
dermal tissues
aka the epidermis forming on the outermost layer of cells
flattened
outermost layer- protection
regulates exchange within the environment
trichomes- leaf hairs
ground tissue
fills spaces
parenchyma, collenchyma cells
vascular tissue
main roll is transport / conduction
rigid support
xylem / phloem
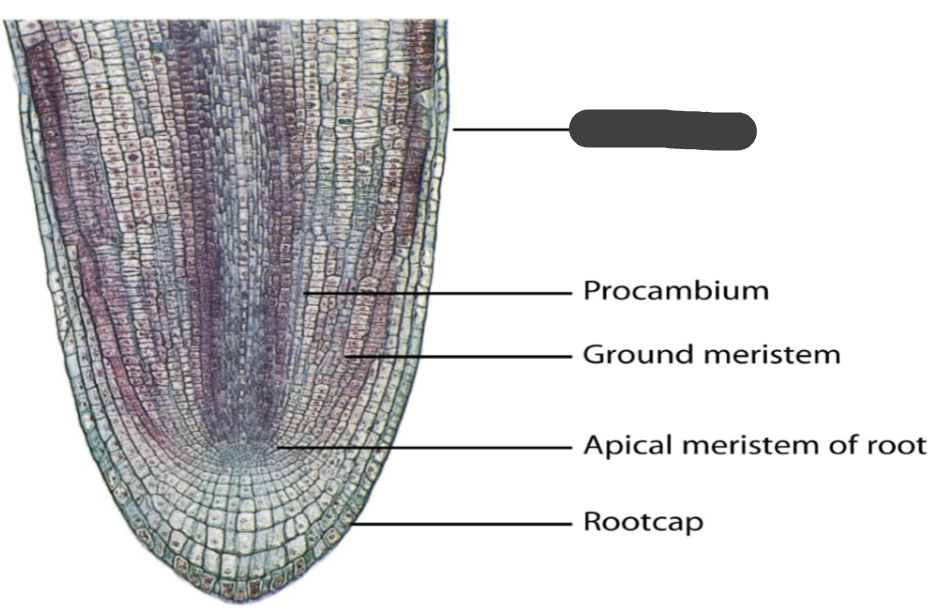
protoderm
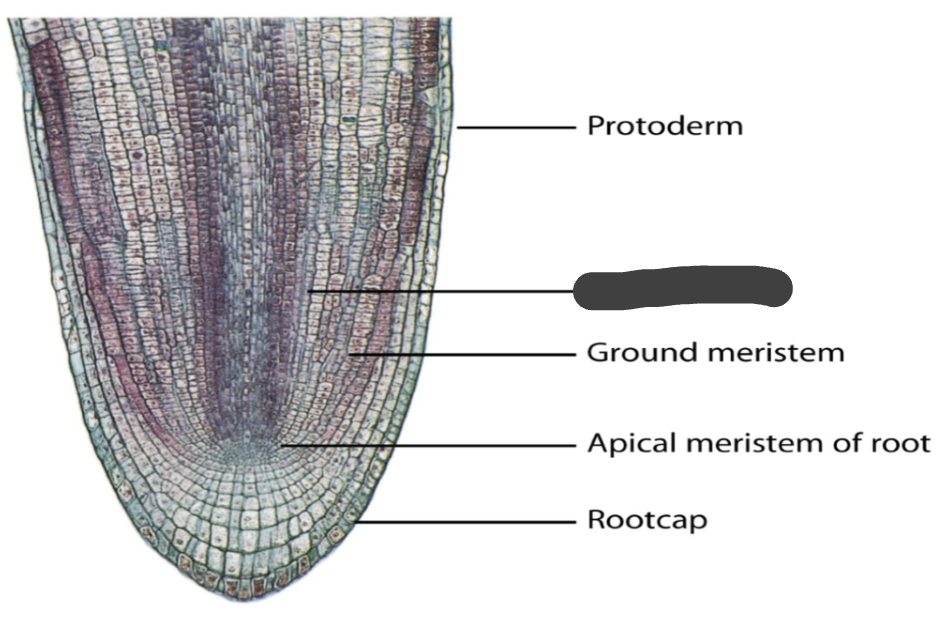
procambium
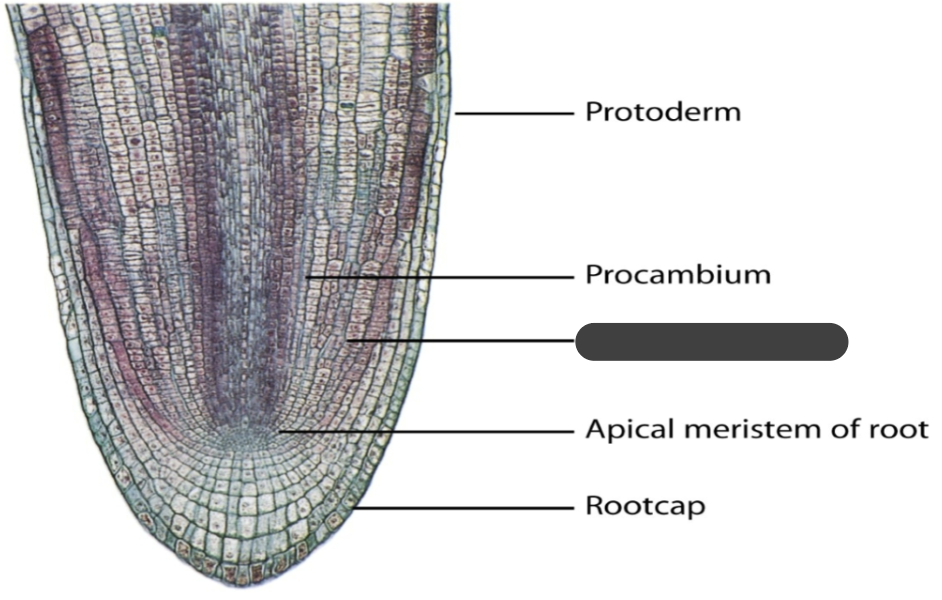
ground meristem
apical meristem of root
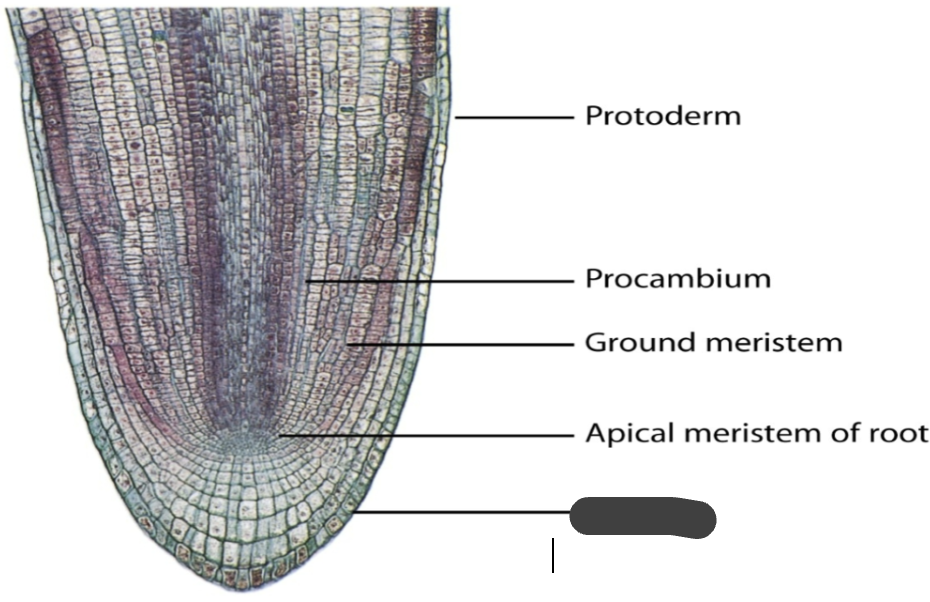
root cap
phloem
compound tissue- different cell types making it up
companion cell
sieve tube element = conducting
both of the above are always together
phloem fibers which are dead @ maturity
conduct sugar which are dissolved in water
xylem
compound tissue
tracheids- long and hollow (only conducting cells in gymnosperms)
fibers- sclerenchyma cells
all 3 are dead @ maturity