consequences of interventions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
definition of price controls?
legal restrictions on how high or low a market price may go
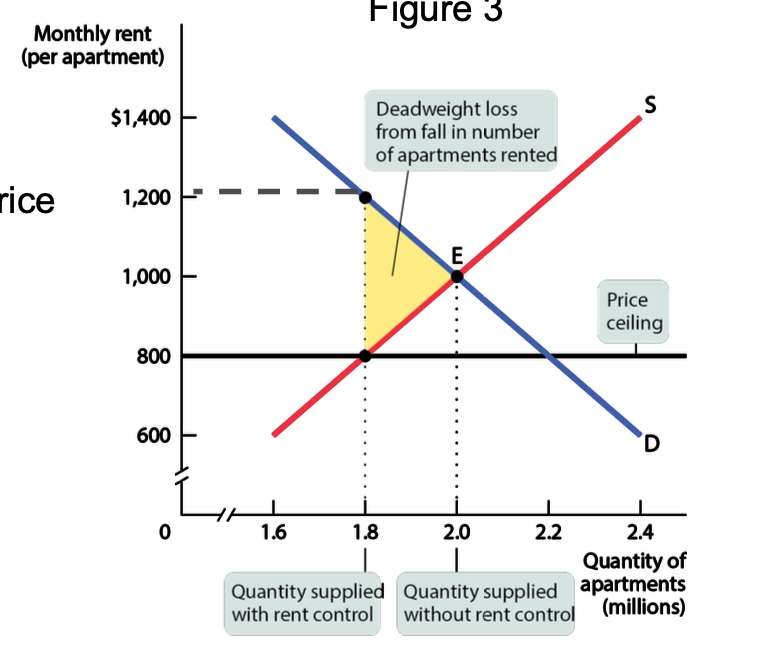
definition of a price ceiling?
maximum price sellers are allowed to charge for a good or service (usually set BELOW equilibrium)
definition of a price floor?
minimum price buyers are required to pay for a good or service (usually set ABOVE equilibrium)
what are the side effects of price ceilings?
– Inefficiently low quantity
– Inefficient allocation to customers
– Wasted resources
– Inefficiently low quality
– Black markets
– Can affect other related markets
draw an inefficiently low quantity graph?
definition of a shadow market?
is a market in which goods or services are bought and sold illegally—either because they are prohibited or because the equilibrium price is illegal
Because sellers cannot raise the price when the price is controlled, how do they respond?
reduce quality
reduce service
what is the purpose of price floors?
to push market prices up rather than down
what side effects do price floors cause?
• Deadweight loss
• Inefficient allocation of sales among sellers
• Waste of resources
• Inefficiently high quality
• Temptation to break the law by selling below the legal price
• Affect the markets of other good
draw a graph for inefficiently low quantity?
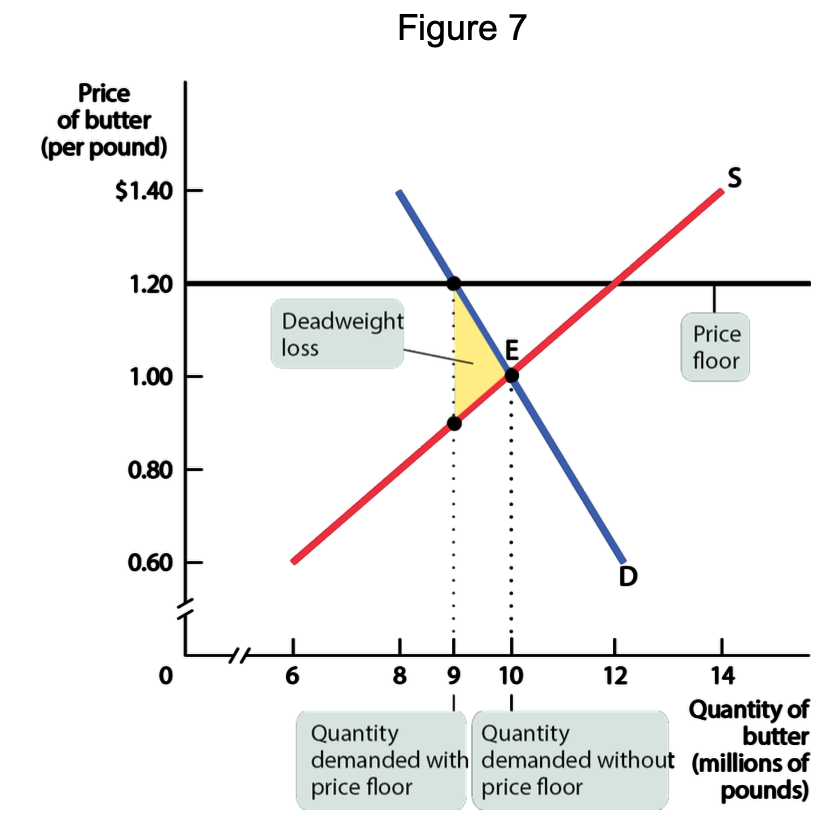
why can price floors lead to inefficient allocation of sales among sellers?
• Sellers who are willing to sell at the lowest price are unable to make sales.
• Sales go to the sellers who are only willing to sell at a higher price.
what do price floors encourage sellers to do?
offer goods of inefficiently high quality—the quality that is higher than buyers are
willing to pay for
why are there price floors?
• They do benefit some people (who are typically better organized and more vocal than those who are harmed by them).
• Government might wish to support some industries or firms which cannot survive at the equilibrium price (need a higher price).
• Government officials maynot understand supply and demand analysis.
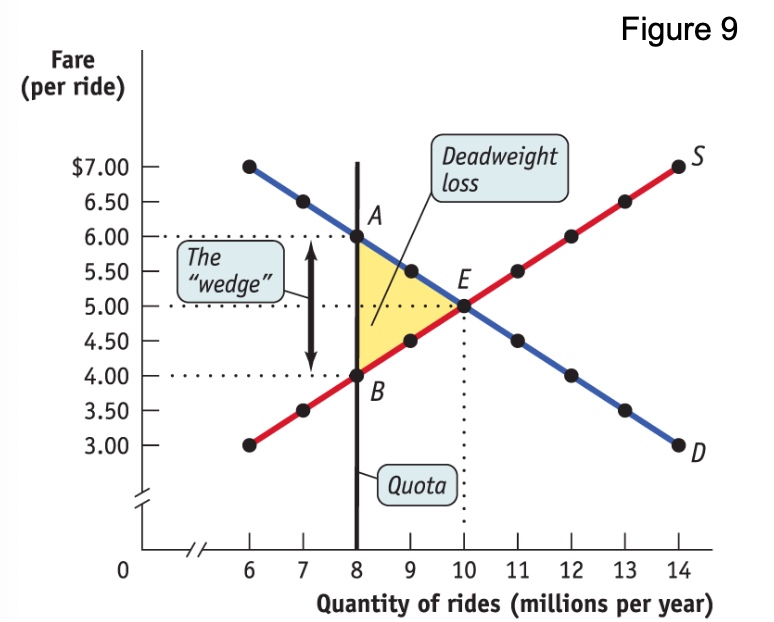
definition of a quota?
an upper limit, set by the government, on the quantity of some good that can be bought or sold; also referred to as a quantity control.
definition of a quota limit?
the total amount of a good that can be legally transacted under a quota or quantity control.
definition of license?
the right, conferred by the government, to supply a good
why do quotas impose losses on society?
deadweight loss
can result in illegal activities of selling without required licence
what happens if a licence fee is imposed?
it increases the cost to seller. This shifts the supply curve to the left. If the licence fee is appropriately set, it will shift so that the new equilibrium quantity is at the point which the government set as a quota
draw a graph for a quota on the market?