Respiratory 1: Intro, Pathology of Nasal Passages
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
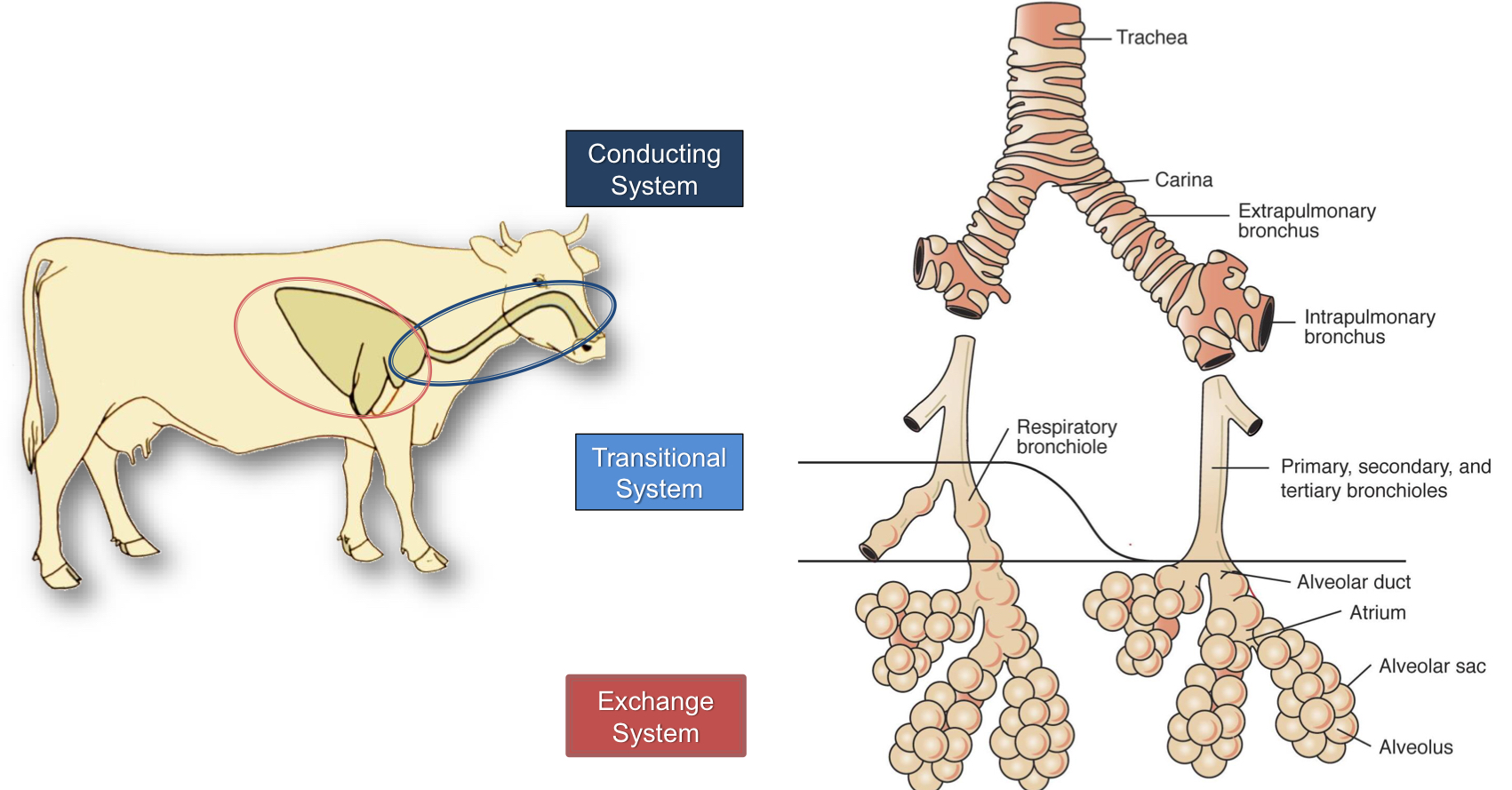
The Respiratory system can be broken down into 3 parts, what are they?
Conducting System
Trachea
Transitional System
Bronchioles
Exchange System
Alveoli
T/F: Bacterial normally exist in the respiratory tract
True
What are the 5 different ways that the respiratory system “defends“ itself
Air filtration
Mucociliary Clearance
Phagocytosis
Immunity
Detoxification
Air filtration can prevent the passage of particles _ 10 micrometers
<
The mucociliary defence can prevent the passage of what sized particles?
10-2 micrometers

What is done with particles that are caught by the mucociliary clearance in the nose?
They are moved towards the trachea
There they will be coughed out or swallowed
What performs phagocytosis in the respiratory system?
Pulmonary Alveolar Macrophages (PAMs)
When chronic damage to the respiratory sytem occurs, what particularcell undergoes hyperplasia?
Goblet cells
They mass produce mucus
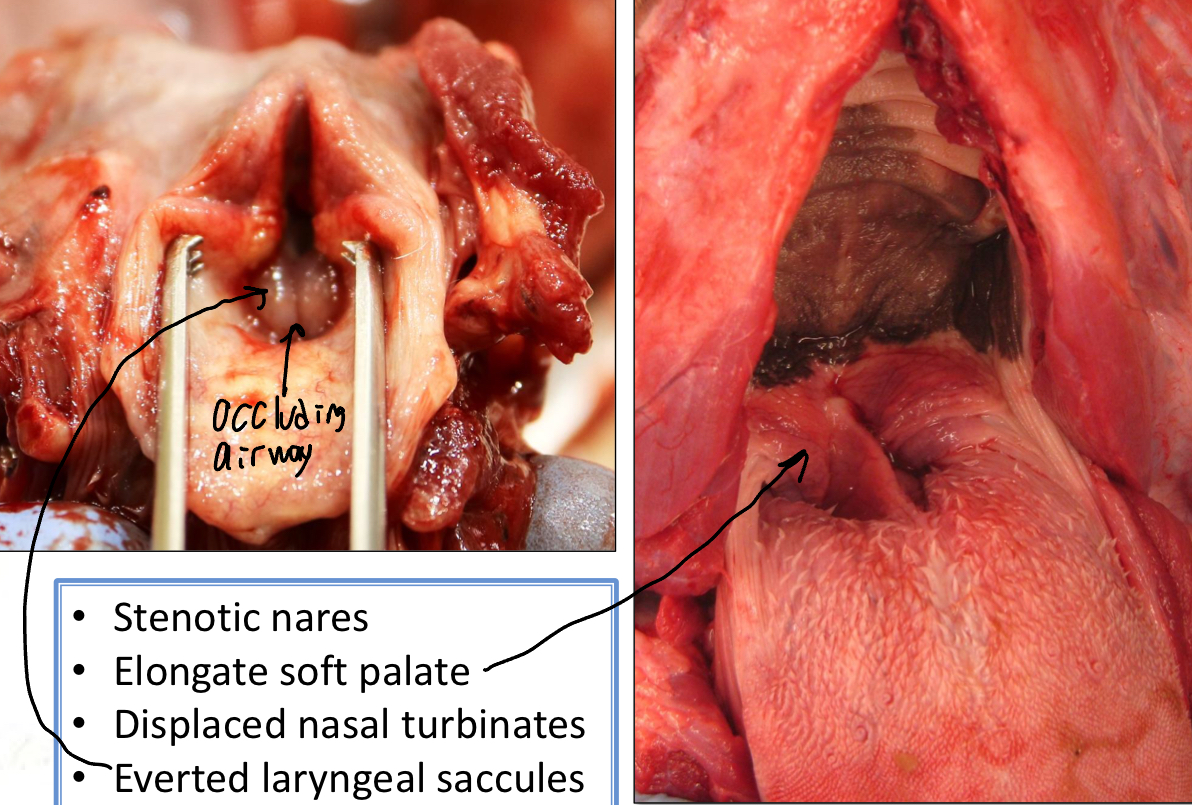
What is Brachycephalic Airway Syndrome?
Found in brachycephalic dogs
Characterized by
Stenotic Nares
Elongated nasal turbinates
Displaced nasal turbinates
Everted laryngeal saccules
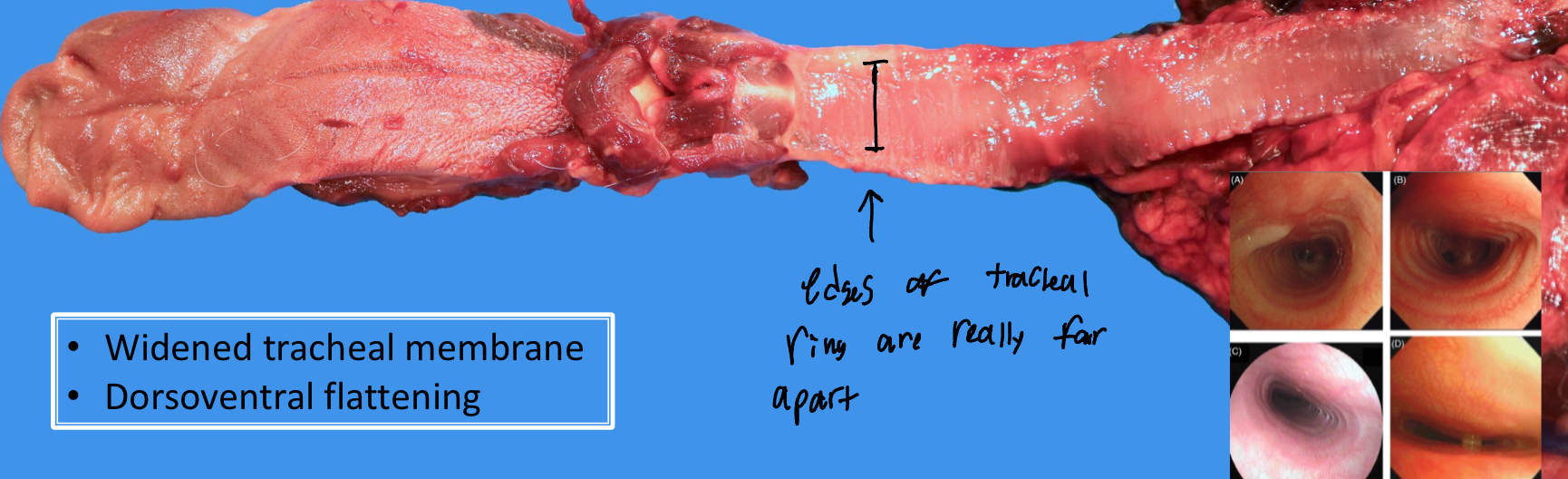
What is Tracheal Collapse Syndrome?
A congenital anomaly that is caused by the degradation of cartilage in the trachea
The degeneration results in the dorsoventral flattening of the trachea
What is Epistaxis?
Bleeding from the nose

What are differentials for Epistaxis in any species?
Trauma
Foreign body
Nasal Neoplasia
Rhinitis
Pulmonary Hemorrhage
Bleeding diathesis
What are some unique causes of Epistaxis in Horses?
Exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage (EIPH)
Guttural pouch mycosis
Progressive ethmoidal hematoma
Nasal Cysts

What is a Progressive Ethmoidal Hematoma?
A pedunculated blood-filled mass on the ethmoid
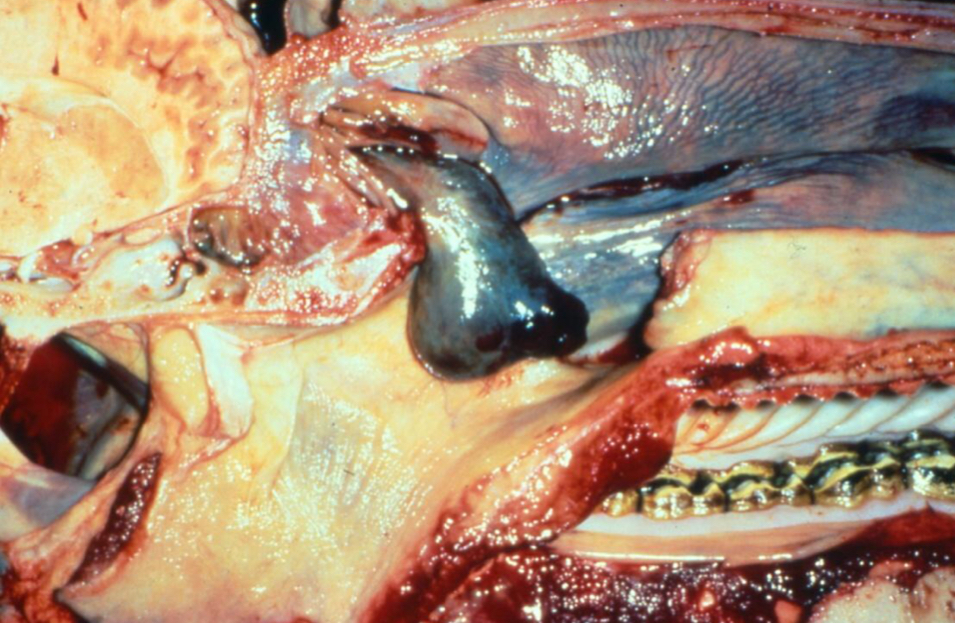
If a horse is presenting with unilateral epistaxis, what would be your first differential?
Progressive Ethmoidal Hematoma
Pyogenic bacteria cause ______ Rhinitis
Suppurative
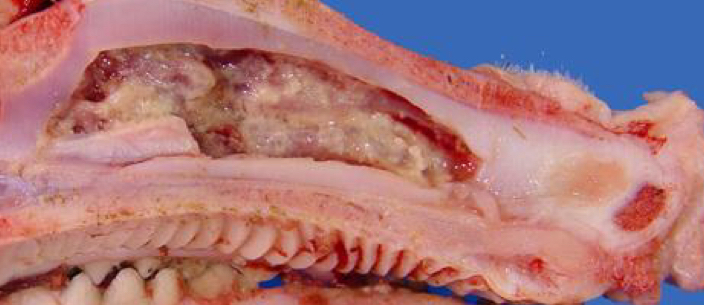
Toxin producing bacteria cause ________ Rhinitis
Fibronecrotizing
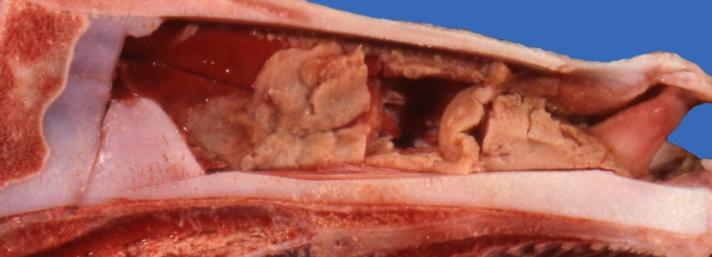
Fungus, Foreign Bodies, and Allergies cause ______ Rhinitis
Granulomatous
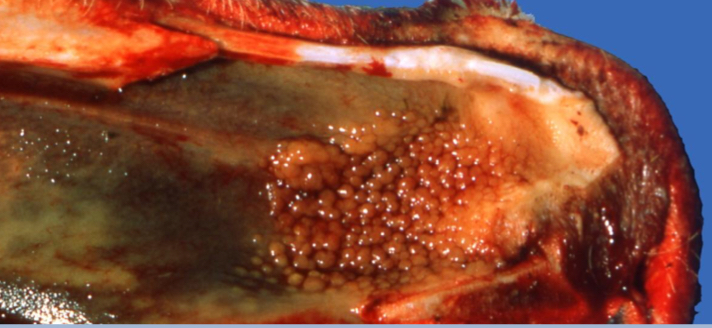

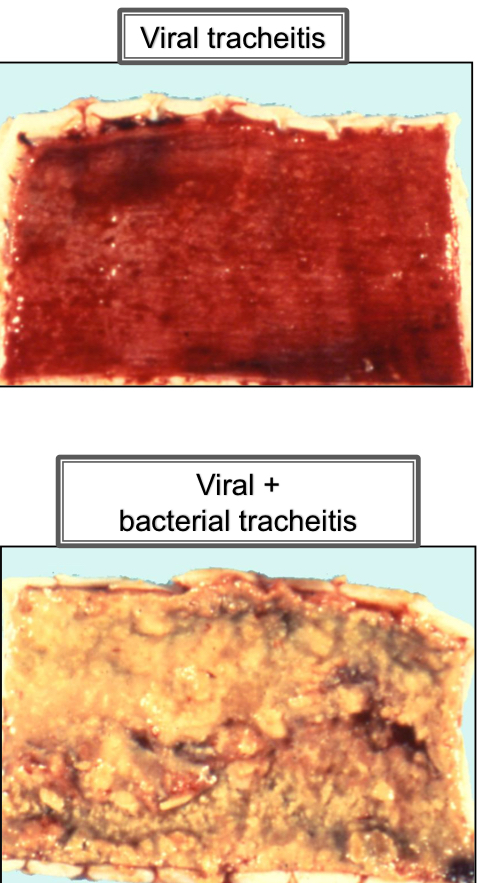
Identify the different types of Tracheitis
Purulent
Fibronecrotizing
Granulomatous
Regarding Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis, identify the…
Etiology
Species Affected
C.S
Associated Lesions
Bovine Herpesvirus-1 (BoHV-1)
Affects cattle
C.S
Fever, nasal discharge, salivation
Lesions
Hyperemia (excess of blood in vessels)
Nasal/Tracheal mucoal necrosis
Predisposes to 2° infections
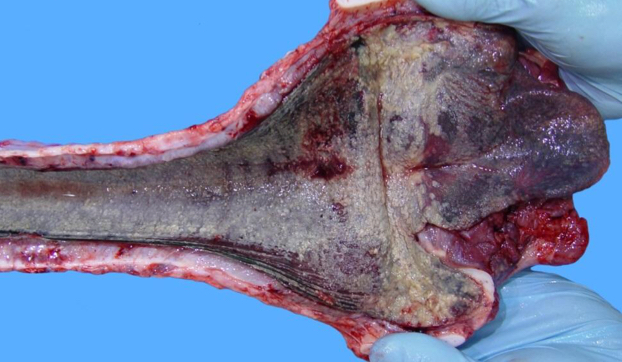
What is an important sequelae of IBR?
Bronchopneumonia
Regarding Necrotic Laryngitis, identify the…
Etiology
Species Affected
C.S
Lesions
Sequelae
More commonly known as Calf diptheria
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Calves
C.S
Fever, anorexia, depression
Halitosis (foul breath), moist cough, dyspnea
Lesions
Around the Larynx
Sequelae
Asphyxiation
Pneumonia
Sepsis
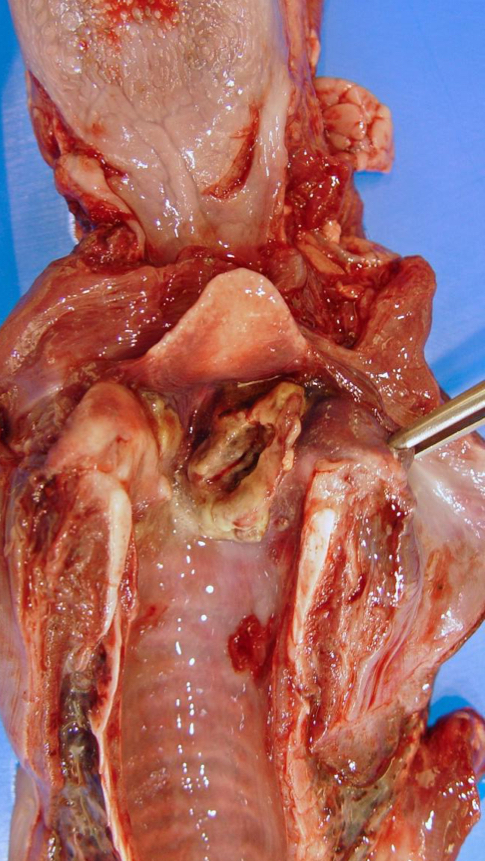
T/F: Necrotic Laryngitis only occurs as a 2° bacterial infection
True
Regarding Strangles, identify the…
Etiology
Species Affected
Associated Lesions
Sequelae
Streptococcus equi subspecies equi (SEE)
Horses
Lesions
Suppurative rhinitis
Regional Lymphadenitis
Visceral spread (Bastard strangles)
Spreads to other organs/LNs
Sequelae
Purpura Hemorrhagica
Immune mediated vasculitis
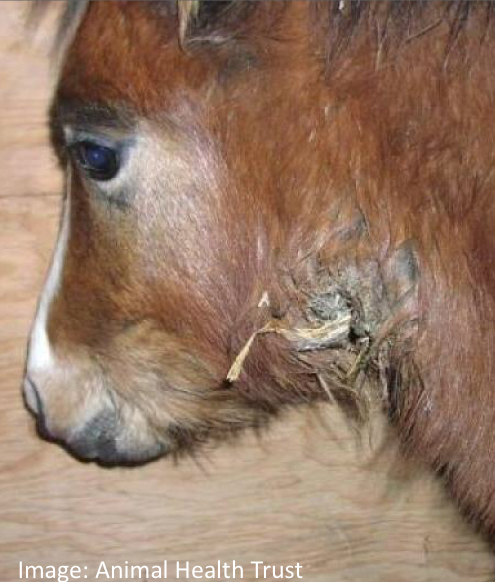
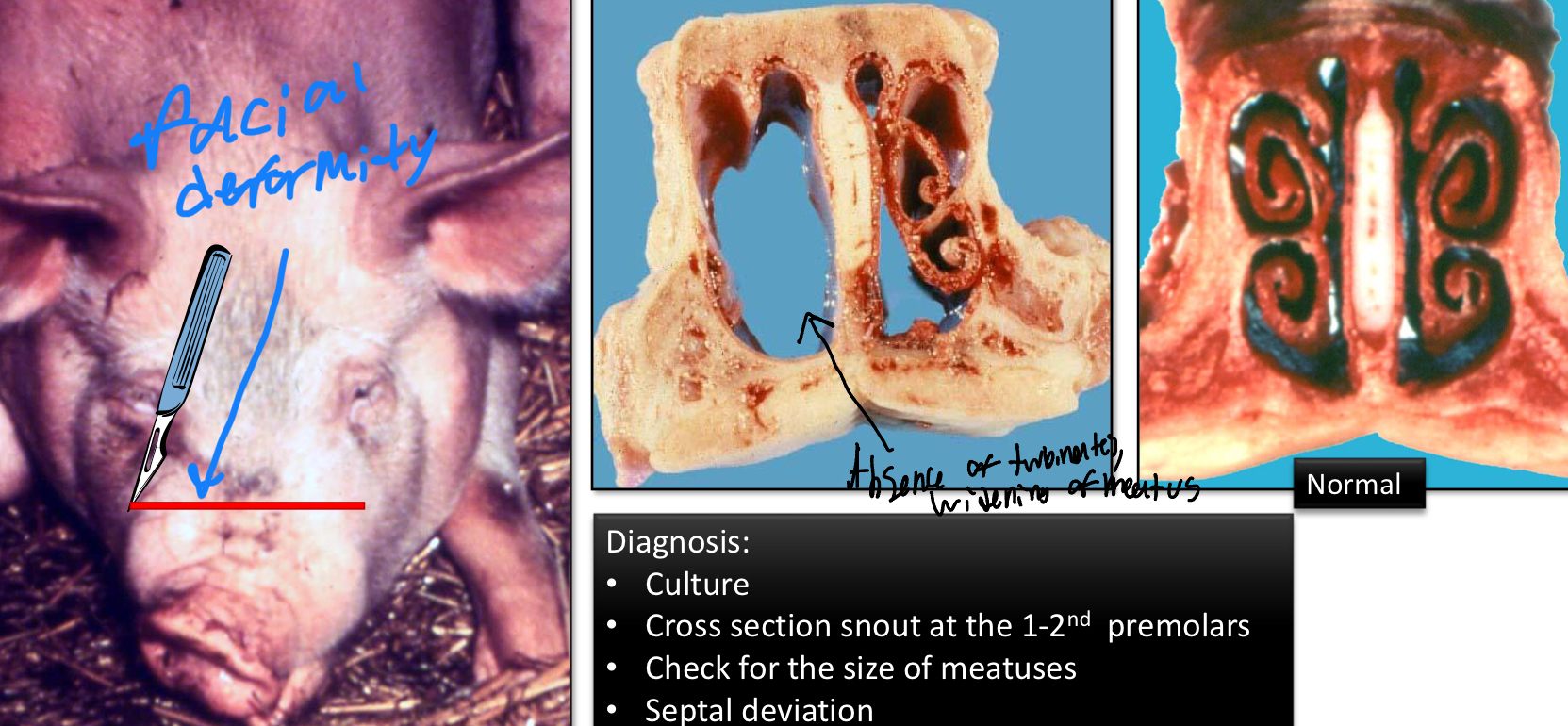
Regarding Progressive Atrophic Rhinitis, identify the…
Etiology
Species Affected
Associated Lesions
Pasturella multocida and Bordetella bronchiseptica
Pigs
Lesions
Atrophic conchae (destruction of conchae)
Facial deformities
No exudate
Regarding Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease Complex, identify the…
Etiology
Species Affected
C.S
Multifactorial etiology
Viral
Canine Adenovirus-2 (CAV-2)
Canine Parainfluenza virus
Secondary bacterial
Bordetella bornchiseptica
Dogs
C.S
Harsh dry cough
Retching
Sneezing
Productive cough
Purulent nasal discharge
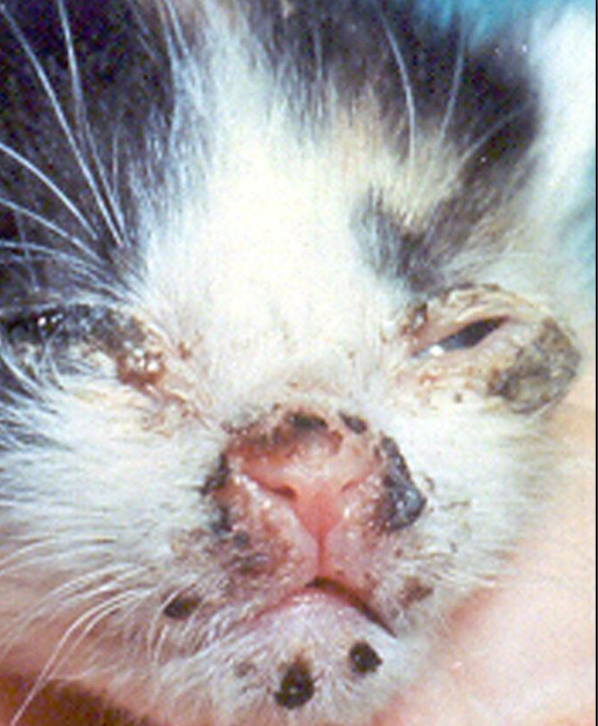
Regarding Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis, identify the…
Etiology
Species Affected
C.S
Sequelae
Felid Herpesvirus-1 (FeHV-1)
Cats
C.S
Keratitis and corneal ulcers (key indicator)
Sneezing
Nasal discharge
Mucopurulent rhinitis
Sequelae
Predispose to 2° bacterial infections
B. bronchiseptica, P. multocida, Strep. spp.
Regarding Feline Calicivirus, identify the…
Etiology
Species Affected
Associated Lesions
C.S
Feline Calcivirus
Cats
Lesions
Oral ulcers (key differentiator)
C.S
Sneezing
Nasal/conjunctival discharge
Limping kitten syndrome (arthritis)

What virus is indistinguishable, via C.S, to Feline calcivirus?
Chlamydia felis
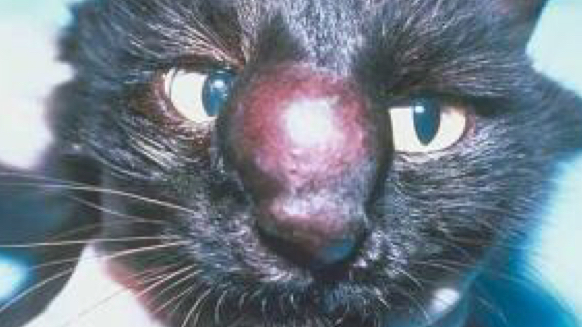
Regarding Cryptococcosis, identify the…
Etiology
Species Affected
Associated Lesions
Test
Cryptococcus neoformans and gatti (2 causes)
Many species susceptible, most common in cats
Lesions
Granulomatous rhinitis
Nasal dermatitis
Granumolatous pneumonia
Test
Cytology/biopsy
Squidward nose