1.2 ~ Opportunity Costs
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is Opportunity Cost?
the value of the next best alternative that is forgone when making a decision
Choice
eg. time
What do you consider when Making CHOICES?
Benefits must outweigh the costs
Rational Decision making
What is Self-Interest in Decicion Making?
choices you make that you think are best for you
What is Social Interest in Decision Making?
choices that are best for society as a whole
What are Incentives?
rewards and penalties for choices and you are more likely to choose actions with rewards and avoid actions with penalties
What is a Free Good?
Any good that isn’t scarce
Anything that can be obtained without sacrificing something else
Free goods have zero opportunity cost
There goods are rare
Consumers can obtain all they want of these goods at no charge
Ex. air, sunlight
Types of Free Goods?
Public Goods (provided by the government
Produced by scarce resources and paid by our taxes (opportunity cost)
Common Pool Resources
Certain natural resources not owns by anyone by becomes scarce due to overuse and depletion
eg. clean air, forests, fish
What is an Economic Good?
any good that is scarce
Can be naturally occurring
Can be produced by scarce goods
All economic goods have an opportunity cost greater than zero
Most goods are economic goods
What is a “trade-off”?
For every good a nation produces, it faces a “trade-off” in terms of some other good it can no longer produce
This is because production of goods is limited by the amount of resources that exist (labour, capital and materials)
Three Basic Economic Questions
WHAT?
All must decide what particular good or service to produce and in what quantities
HOW?
All must decide how to use their resources in order to produce goods and services
FOR WHOM?
All must make choices about how the goods and services produced are to be distributed among the population
For whom to produce? (3)
Distribution of Output
How much of what is produced do different individuals or groups of individuals in the population receive
Distribution of Income
The amount of output people get depends on how much of it they can buy
This, in turn, depends on how much income they have
Redistribution of Income:
When the distribution of income our output changes so that different social groups now receive more, or less, income and output
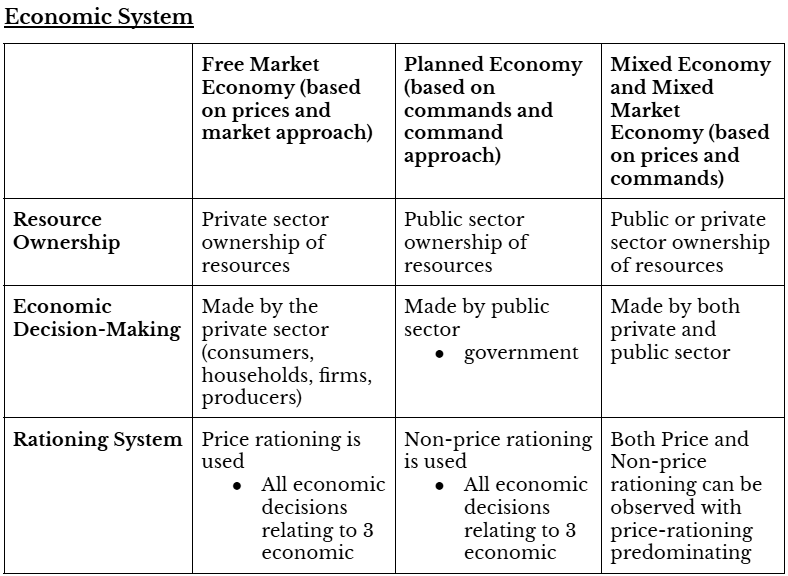
Market Method
Involves a private sector where resources are owned by private individuals or groups. Decisions are made by consumers and firms responding to prices determined in markets, about what, how, and for whom to produce.
Command Method
Involves a public sector where resources, particularly land and capital, are owned by the government. Decisions are made by commands from the government about what, how, and for whom to produce.
Mixed Economies
Real-world economies that combine elements of both market and command methods. The global trend is towards less government intervention, resulting in more reliance on market forces.
Economic System