Postpartum Period
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
after, delivery, 12
The Postpartum Period: Background
-The time _______ delivery when maternal physiologic changes related to pregnancy return to non-pregnant state
-The postpartum period begins upon __________ of the infant
-ACOG defines the end of the postpartum period as __ weeks after delivery
shivering, contraction, hemorrhage, fundus, two
Postpartum Physiologic Changes
-_________
Starts 1-30 minutes after delivery and can last for 2-60 minutes
-Uterine involution
The uterus begins to return to its non-pregnant size and condition
___________ of the interlacing myometrial muscle bundles constricts the intramyometrial vessels and impedes blood flow. This prevents ____________ at the placental site
The ______ recedes by approximately 1 cm/day after delivery and is not palpable abdominally by ___ weeks postpartum
shedding, mucous, shed, discharge, pinkish, white, dilated, normal
Postpartum Physiologic Changes
-Lochia → normal _________ of the blood and decidua
Decidua → the thick layer of modified _______ membrane which lines the uterus during pregnancy and is ____ after delivery
Lochia rubra → red/red-brown _________ for the first few days following delivery
Lochia serosa → ________-brown discharge for 2-3 weeks
Lochia alba → ____ discharge up to 6-8 weeks after delivery
-Cervix → remains 2-3 cm _________ for the first few days after delivery, and is less than 1cm dilated at one week postpartum
-Abdominal wall → initially very lax, but regains most ________ muscular tone over several weeks
Diastasis rectus abdominis may persist

fall, menstruation, engorgement, loss
Postpartum Physiologic Changes
-hCG levels _____
-Hot flashes
-Return of ____________ 45-64 days postpartum
-Return of ovulation 45-94 days postpartum
-Breast _____________
-Striae fade from red to silvery but are permanent
-Hair ____ 1-5 months after delivery, which is usually self-limited and returns to normal by 6-15 months after
hemorrhage, fundal, perineal, VTE, positive, pain
Maternal Care
-Monitoring → vital signs and postpartum __________
Perform ______ checks to assess uterine tone and _______ checks to assess for excessive vaginal bleeding
-Labs → hemoglobin
-Perineal care
-Prevention of ___ → prophylaxis for women at high risk
-Anti-D immune globulin for RhD-negative mothers of RhD-________ infants
-Pelvic muscle exercises
-_____ management
-Postpartum contraception
car seat, sleep, retention, varicose, dryness, pain, headache
Postpartum Counseling and Complications
-Counseling
____ ______ instructions, safe _____ counseling, follow-up appointments for mom and baby, and education on signs and symptoms of potential complications
-Complications
Postpartum urinary ________, hemorrhoids, incontinence, lower extremity _______ veins, mild vulvar edema, surgical site infection, endometritis, mastitis, UTI, septic pelvic thrombophlebitis, C. diff infection, neuropathy, vaginal ________, pelvic girdle and musculoskeletal ____, and postdural puncture ___________ after epidural
headache, seizure, bleeding, pain
Postpartum women with __________, new hypertension, _______, excessive _________, dyspnea or chest pain, severe abdominal ____, or vulvar symptoms should be evaluated promptly
perineum, 6, low, 1, delivery, hypothyroidism
More Postpartum Issues
-Sexual Dysfunction
Safe to resume sexual activity when the woman’s ________ is comfortable and bleeding is diminished, usually around _ weeks
However, sexual health issues can last for months, especially ___ libido
-Postpartum thyroiditis
Higher risk in women with type _ diabetes
Hyperthyroidism usually within 1-4 months after delivery and lasts 2-8 weeks
Followed by ____________ that lasts 2 weeks-6 months
bleeding, hypovolemia, mortality, 24, 12, atony, rupture
Postpartum Hemorrhage: Background
-Obstetric emergency characterized by _________ that is greater than expected and results in signs/symptoms of _________
Cumulative blood loss > 1000 mL or blood loss with signs/symptoms of hypovolemia within 24 hours
-One of the top five causes of maternal __________
-Primary PPH = within __ hours after delivery
-Secondary/late/delayed PPH = 24 hours - __ weeks after delivery
-Most common cause is uterine _______, which is a lack of effective contraction of the uterus after delivery
-Can also be caused by trauma due to lacerations, uterine ________, incisions, placental disorders, and coagulopathy
retained, second, instrumental, large, demise, trauma, thrombin
Postpartum Hemorrhage: Risk Factors and Etiology
-Risk Factors
__________ placenta/membranes, failure to progress during the _______ stage of labor, morbidly adherent placenta, lacerations, ____________ delivery, _____ for gestational age newborn, hypertensive disorders, induction of labor, prolonged first or second stage of labor, placental abruption, and intrauterine fetal _______
-Etiology
4 Ts of tone, _______, tissue, and thrombin
Tone → Atonic uterus
Trauma → lacerations, hematomas, inversion, rupture
Tissue → retained tissue, invasive placenta
Thrombin → coagulopathies
lightheadedness, tachycardia, pallor, lethargy
Postpartum Hemorrhage: Signs and Symptoms
-EBV 500-1000 mL → palpitations, _____________, no or mild increase in heart rate
-EBV 1000-1500 mL → weakness, sweating, ___________, tachypnea
-EBV 1500-2000 mL → restlessness, confusion, _______, oliguria, tachycardia, cool and clammy skin
-EBV 2000-3000 mL → ______, air hunger, anuria, collapse, tachycardia
massage, evacuation, oxytocin
Postpartum Hemorrhage Management: Uterine Atony (Tone)
-Fundal/uterine ________
-Bimanual compression/__________ of clots
-Uterotonic medications → __________, misoprostol, methergine, hemabate, cytotec, tranexamic acid
-Tamponade of uterus via bakri balloon or packing with gauze
-Uterine artery ligation
-Hysterectomy
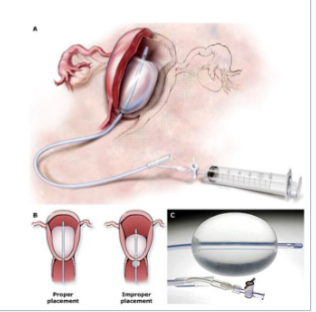
lacerations, repair, conservatively, inspect, retained, D&C, coagulation, DIC, transfusion
Postpartum Hemorrhage: Management of Trauma, Tissue, and Thrombin
-Trauma
Assess for __________, expanding hematomas, or uterine rupture
_______ any actively bleeding laceration as soon as possible
Most hematomas managed ___________, but if rapidly expanding and abnormal vital signs, consider I&D
-Tissue
Visually _______ placenta for completeness
Manual examination for __________ placenta or bedside US evaluation of uterine cavity
If suspected, try to remove retained portion manually or consider ___
-Thrombin
Evaluate a patient’s ___________ status
Consider possible etiologies leading to ___ like placental abruption and amniotic fluid embolism
Correct with replacement of clotting factors, fibrinogen, or other replacement sources (massive __________ protocol)
oxytocin, massage, umbilical
Postpartum Prevention
-Active management of 3rd stage of labor → __________ administration
Substantially reduces the incidence of PPH due to atony
-Uterine ________
-_________ cord traction
pituitary, infarction, failure, amenorrhea, hypotensive, adrenal
Sheehan Syndrome
-A rare but potentially life-threatening complication of postpartum hemorrhage
-The ________ gland is normally enlarged in pregnancy and therefore prone to __________ from hypovolemic shock
-Hypovolemic shock from PPH → resulting pituitary damage
-Hypopituitarism can range from mild to severe → can reduce secretion of one, several, or all of its hormones
-Common presentation → ________ to lactate postpartum and ___________/oligomenorrhea
However, any manifestations of hypopituitarism can occur at any time from the immediate postpartum period to years after birth
-Patients who remain ____________ after control of PPH and volume replacement should be evaluated and treated for _______ insufficiency in the immediate postpartum period
Evaluation of other hormonal deficiencies can be deferred until 4-6 weeks postpartum
6, cesarean, history, immobility, early, compression, LMWH
Postpartum Thromboembolism
-Highest risk period → first _ weeks postpartum
-Risk factors → ________ delivery, obesity, advanced maternal age, smoking, personal or family ________ of VTE, thrombophilia, and prolonged _________ or hospitalization
-Prevention and Management → ______ ambulation encouraged after delivery, ___________ devices for cesarean patients or high-risk individuals, pharmacologic prophylaxis (____) in high-risk patients, and risk assessment should be performed for every postpartum patient
endometrium, fever, cesarean, migrate, sterile
Postpartum Endometritis: Background
-Infection of the pregnancy _____________ (decidua)
-Common cause of postpartum _____ and uterine tenderness
-Significantly more common after ________ delivery than vaginal delivery
-Pathogenesis → During labor and delivery, endogenous cervicovaginal flora ________ into the uterine cavity and contaminate its normally _______ contents
cesarean, antibiotic, amniotic, DM
Postpartum Endometritis: Risk Factors
-_________ delivery → need ________ prophylaxis
-Other risk factors → chorioamnionitis, prolonged labor, prolonged rupture of membranes, multiple cervical examinations, internal fetal or uterine monitoring, large amount of meconium in ________ fluid, manual removal of the placenta, low socioeconomic status, maternal __ or severe anemia, preterm or postterm birth, operative vaginal delivery, obesity, HIV infection, colonization with group B streptococcus, nasal carriage of staph aureus, and heavy vaginal colonization by E. coli
fever, pain, soft, bleeding, malodorous, WBC, tenderness, purulent
Endometritis Clinical Findings and Diagnosis
-Signs and Symptoms → _____, uterine tenderness, tachycardia, and midline lower abdominal ____
-Physical exam → slightly ____ and subinvoluted uterus, which may cause excessive uterine ___________. ____________ purulent lochia can be seen too.
-Lab → elevated ___ count and bacteremia
-The diagnosis is made in patients with at least two of the following signs or symptoms → fever (>100.4 F), uterine or abdominal pain/____________ with no other recognized cause, and _________ drainage from the uterus
Clindamycin, gentamicin, 60
Endometritis Treatment and Prevention
-Broad spectrum antibiotics → ____________ + ____________
-Prophylactic antibiotics within __ minutes prior to making the skin incision for all cesarean deliveries
transient, week, hormonal, neurotransmitter, anxiety, decreased, 2-3
Postpartum Blues: Background
-Differentiating factor between other mental health issues → _________
-Develops in approximately 40% of women within a _____ of delivery
-Pathogenesis → unknown, but may be due to postnatal _________ changes that lead to abnormal _____________ levels or activity
-Symptoms → sadness, crying, irritability, _______, insomnia, exhaustion, __________ concentration, mood lability
-Symptoms typically develop within ____ days of delivery, peak over the next few days, and resolve within two weeks
spontaneously, reassurance, sleep, night, CBT, suicidal
Postpartum Blues: Management
-Generally resolves ____________ and does not require treatment
-Watchful waiting as well as ____________ and support for the woman and her family
-Adequate time for the patient to _____ and rest is essential
-Recruiting someone else to care for the baby at _____ is often sufficient to manage insomnia
-If insomnia persists, ___, pharmacotherapy, or both may be indicated
-If symptoms worsen or persist beyond two weeks, or if there is ________ ideation, patients should be evaluated for postpartum depression and referred for indicated treatment
stress, fear, hemorrhage, PTSD
Postpartum PTSD
-Prevalence of 4% in the general obstetric population
-Risk factors
Pre-pregnancy ______ → sexual/physical trauma, history of PTSD
Negative pregnancy experience → _____ of childbirth, low support, perceived lack of control, maternal morbidity, pregnancy complications
Delivery issues and complications → lack of social support, emergency C-section, instrumental vaginal birth, postpartum ___________, and poor neonatal outcomes
-Typical ____ symptoms and treatment
genetic, stressful, depressive, 12
Postpartum Depression: Background
-Prevalence is approximately 9% in the US
-Pathogenesis → unknown, but may involve _______ susceptibility, hormonal changes, psychological and social problems, and ________ life events
-Symptoms of major _________ episodes during the postpartum period, generally considered as the first __ months after birth
health, bonding, development, suicide, death, history, single, violence, fear, stress
Postpartum Depression: Consequences and Risk Factors
-Consequences
Impaired maternal functioning, poor nutrition and ______ in the offspring, impaired _________, abnormal infant and child _____________, cognitive impairment and psychopathy in the child, strained marital relationships, _______ (increases in the first year after childbirth and is the leading cause of maternal _____ in the general population), infanticide
-Risk Factors
_______ of depression prior to pregnancy, stressful life events during pregnancy or after delivery, poor social and financial support, young age, ______ marital status, multiparity, family history, intimate partner _________, unintended pregnancy, negative attitudes towards pregnancy, ____ of childbirth, poor perinatal physical health, body image dissatisfaction, history of PMS/PMDD, perinatal anxiety, perinatal sleep disturbance, season of delivery, adverse pregnancy/neonatal outcomes, postpartum blues, breastfeeding difficulties, and childcare ______ such as colic or infant sleep disturbance
Edinburgh, 6, 1, CBT, SSRI
Postpartum Depression: Screening and Treatment
-Screening should be performed by PCPs, OBGYNs, and pediatricians
-____________ Postnatal Depression Scale
Recommended at _ week postpartum visit
Also done at pediatrician offices at _, 2, 4, and 6-month well-infant visits
-Treatment
___, couples/family therapy, group therapy, ____ (sertraline or paroxetine), brexanolone, zuranolone, ECT
mania, decreases, mood, younger, hospitalization, suicidal, substance, lithium
Postpartum Bipolar Disorder
-Episodes of major depression, ______, and hypomania during the postpartum period
-Etiology is unknown → may be due to __________ in estrogen and progesterone, decreased or erratic sleep, increased stress associated with caring for the newborn, social issues, genetics
-Risk Factors → prenatal ____ symptoms and episodes, ________ age at delivery, unplanned pregnancy, primiparity, history of previous postpartum mood episodes, and family history of mood disorder
-Treatment → inpatient ____________ may be required for severely ill patients
_______ or homicidal ideation or behavior, aggressive behavior, psychotic features, __________ dependence, impaired functioning, and poor judgement that places the patient or others at risk of being harmed
_______ or lamotrigine
emergency, reality, sleep, two, insomnia, history, first
Postpartum Psychosis: Background
-Medical ___________
-A disturbance in an individual’s perception of _______
-Pathogenesis → unknown, but research points to genetic, immunologic, and hormonal factors, as well as ______ deprivation
-Most commonly presents within ____ weeks of childbirth
-Persistent severe __________ is often the first indication of an incipient postpartum psychosis
-Risk Factors → _______ of postpartum psychosis, family history, history of BPD/schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder, family history of bipolar disorder, _____ pregnancy, and discontinuation of psychiatric medications
hallucinations, mood, less, harming, thought, insomnia, agitation
Postpartum Psychosis: Symptoms
-___________ → command auditory hallucinations may be present, instructing the mother to harm the baby or herself
-Delusions → tend to be related to the patient’s _____ state. Typically involve their baby and are ____ bizarre than typically seen in schizophrenia
9% of women hospitalized for postpartum psychosis had thoughts of _________ their infants
-_______ disorganization, bizarre behavior, manic or depressed mood, severe ________, rapid mood changes, anxiety, irritability, psychomotor ________ may be present, and disorientation to person/place/time
hospitalization, alone, lithium, psychotherapy, benzodiazepine
Postpartum Psychosis: Treatment
-___________ → do not leave the mother _____ with their children
-Preferred pharmacologic treatment → an antipsychotic and ______
-Adjunctive ____________ focusing on education and encouraging adherence to medication
-if there is prominent insomnia, add a ______________
-ECT is also an option
Postpartum hemorrhage
What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A 26 y/o woman is 1 hour postpartum after a prolonged labor with oxytocin augmentation. She suddenly develops heavy vaginal bleeding and soaking of pads within minutes. Her uterus feels boggy on exam. BP is 90/58, HR 128.
Postpartum thromboembolism
What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A 32 y/o woman, 5 days after an uncomplicated vaginal delivery, presents with unilateral leg swelling, warmth, and tenderness. She notes the pain worsens when she walks. She has a history of obesity and was mostly immobile at home due to fatigue.
Postpartum endometritis
What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A 29 y/o woman is 3 days postpartum after a cesarean delivery for prolonged rupture of membranes. She develops fever, lower abdominal pain, and foul-smelling lochia. Her uterus is tender to palpation.
Postpartum blues
What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A 25 y/o first-time mother, 4 days postpartum, reports sudden episodes of tearfulness, feeling overwhelmed, and mild anxiety. She is sleeping poorly but denies suicidal thoughts. Her symptoms are intermittent and she feels bonded to the baby.
Postpartum PTSD
What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A 30 y/o woman, 6 weeks after a traumatic emergency C-section for fetal distress, reports nightmares, flashbacks to the delivery, and avoidance of anything related to the hospital. She becomes panicked when hearing beeping sounds similar to monitors.
Postpartum depression
What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A 33 y/o woman, 4 weeks after delivery, reports persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, severe fatigue, and feelings of worthlessness. She struggles to bond with her baby and has trouble concentrating. She denies psychosis or mania but says, “I don’t feel like myself at all”
Postpartum bipolar disorder
What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A 27 y/o woman with no prior psychiatric history presents 3 weeks postpartum with periods of elevated mood, increased energy, decreased need for sleep, rapid speech, and impulsive spending, followed by episodes of deep depression. Her symptoms fluctuate dramatically within days.
Postpartum psychosis
What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A 24 y/o woman, 2 weeks postpartum, is brought in by family for bizarre behavior. She reports hearing a voice telling her the baby is “possessed”, has paranoia, disorganized thoughts, and visual hallucinations. She has not slept for 3 days.