BIOSC 0150 FUNCTIONAL GROUPS and Macromoles Functions
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
aldehyde
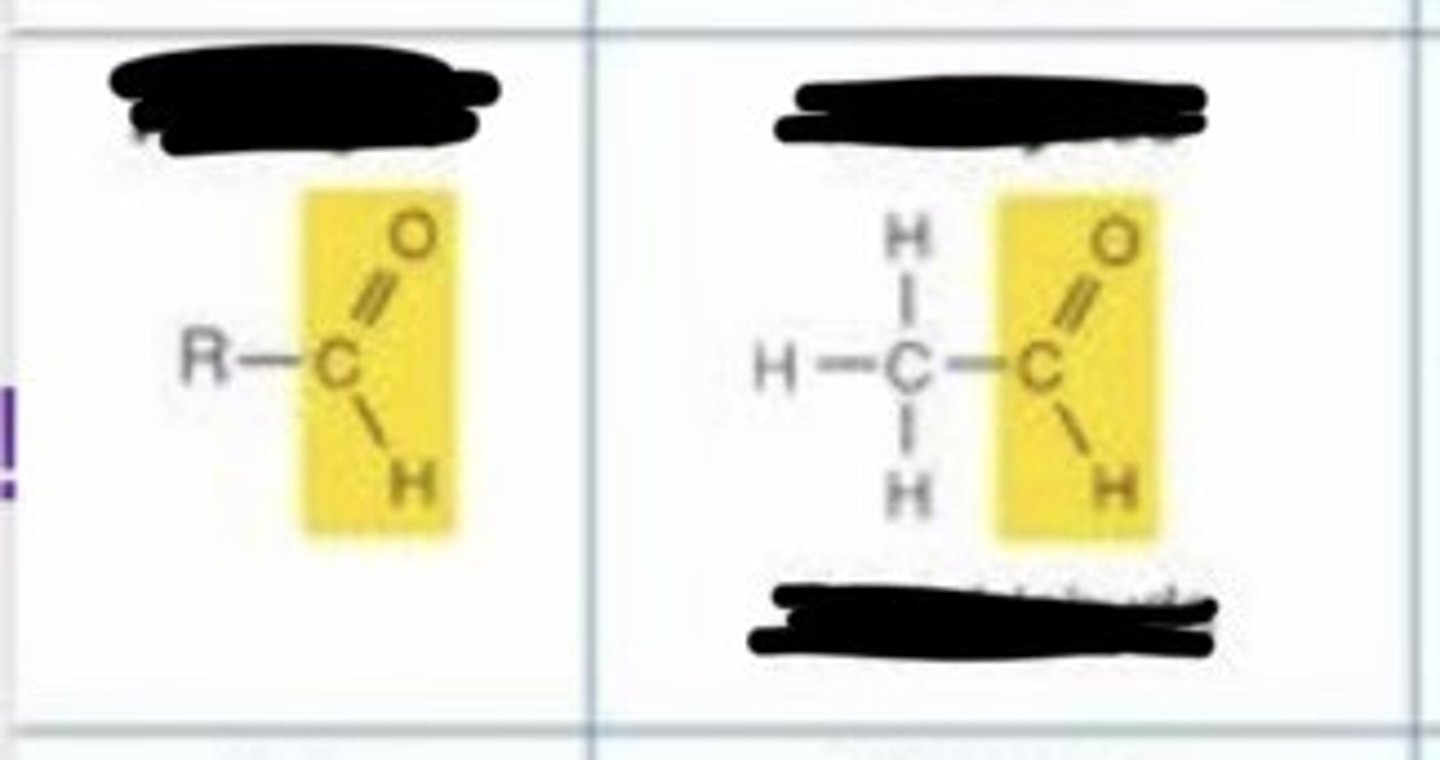
keto
- polar
- c=o group is very reactive
-is important in building/creating carbohydrates and in energy-releasing reactions
keto
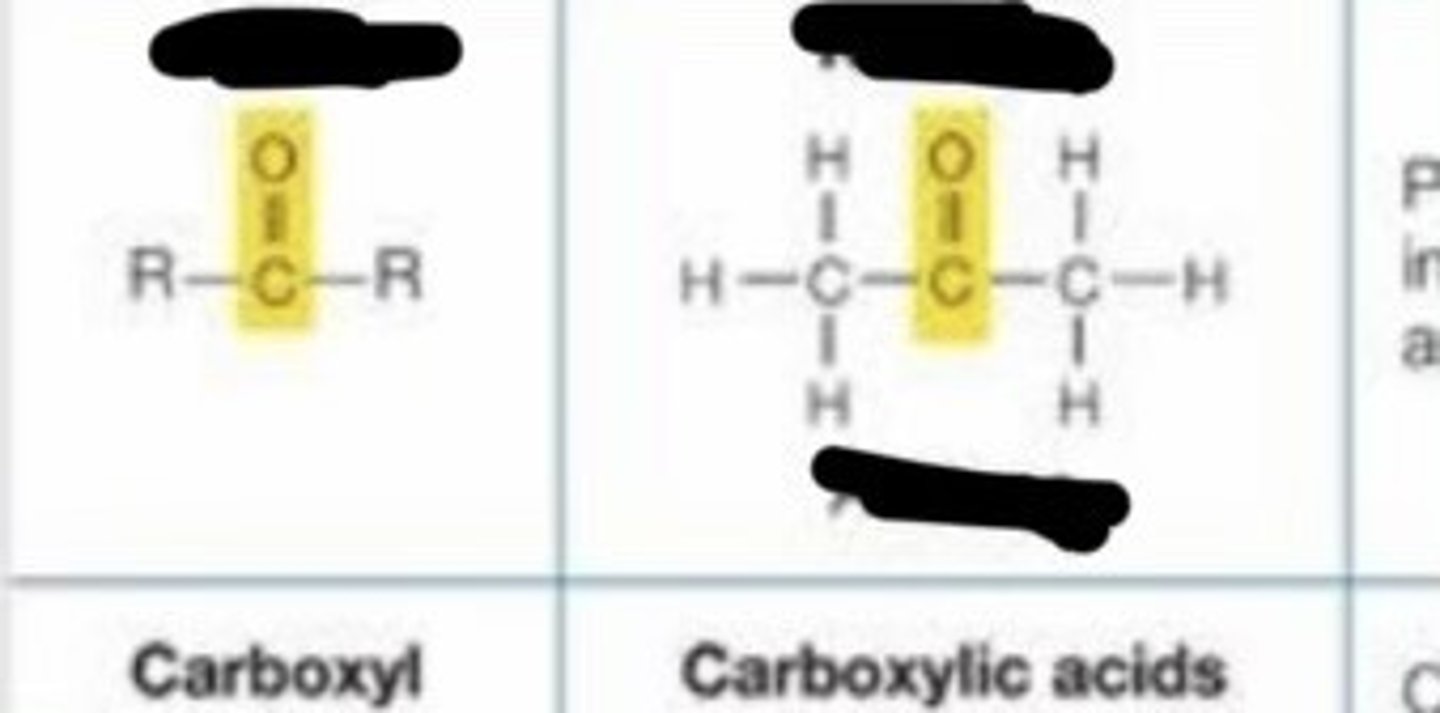
carboxyl
- charged
- acidic
- ionizes in living tissues to form -COO- and H+
- enters into condensation reactions by giving up -OH making H20
- some carboxyic acids important in energy releasing reactions
carboxyl
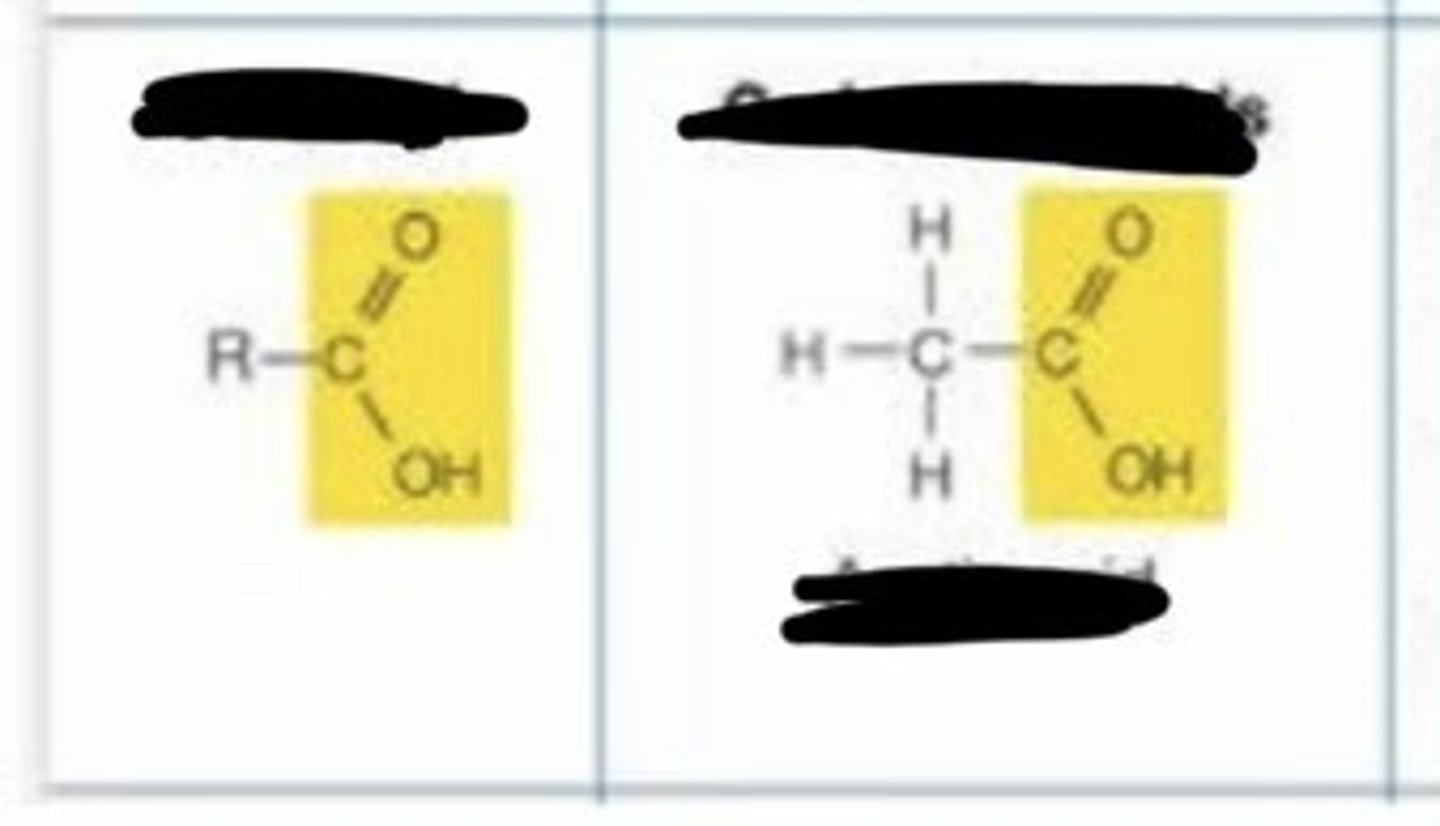
amino
- charged
- basic: not acidic
- accepts H+ in living tissues to form -NH3+
- enters into condensation reactions by giving up H+
amino
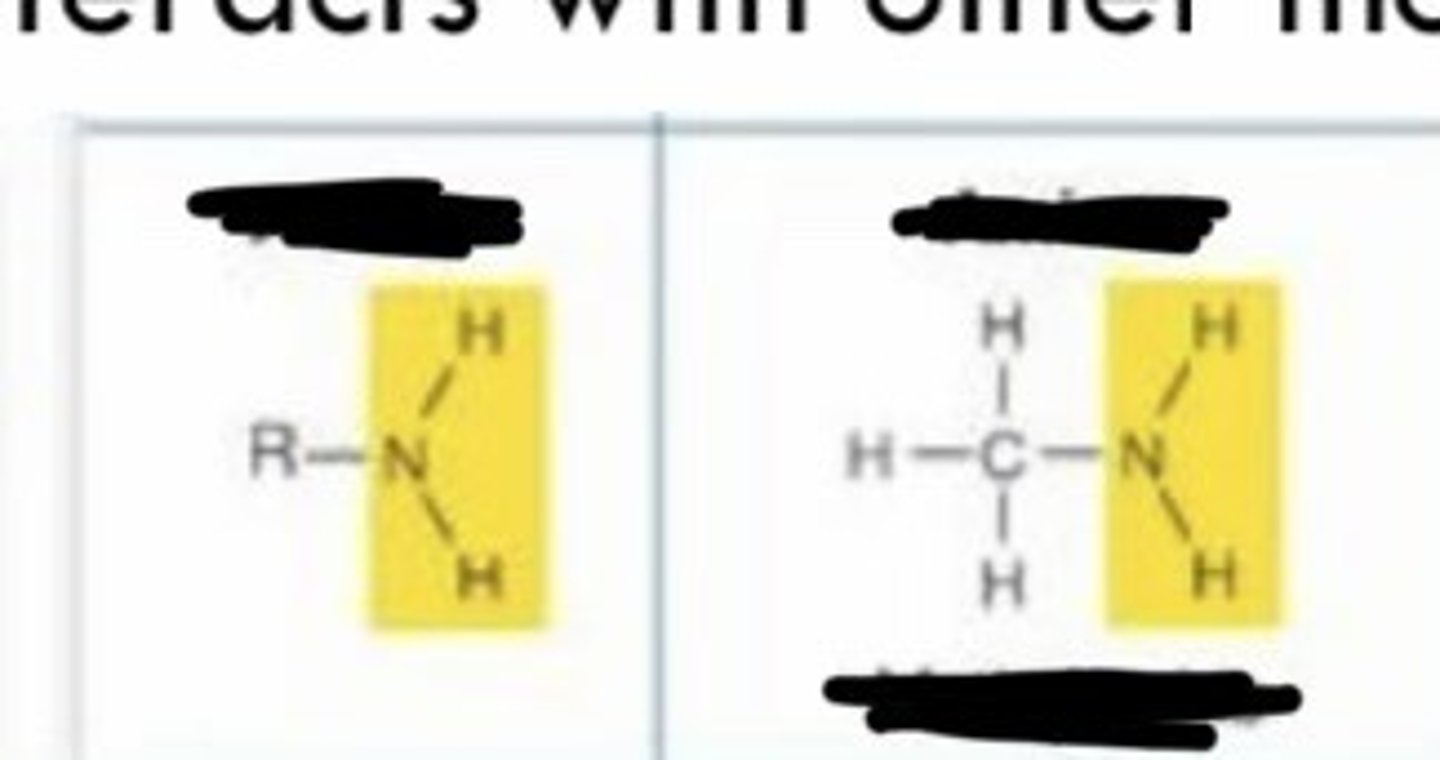
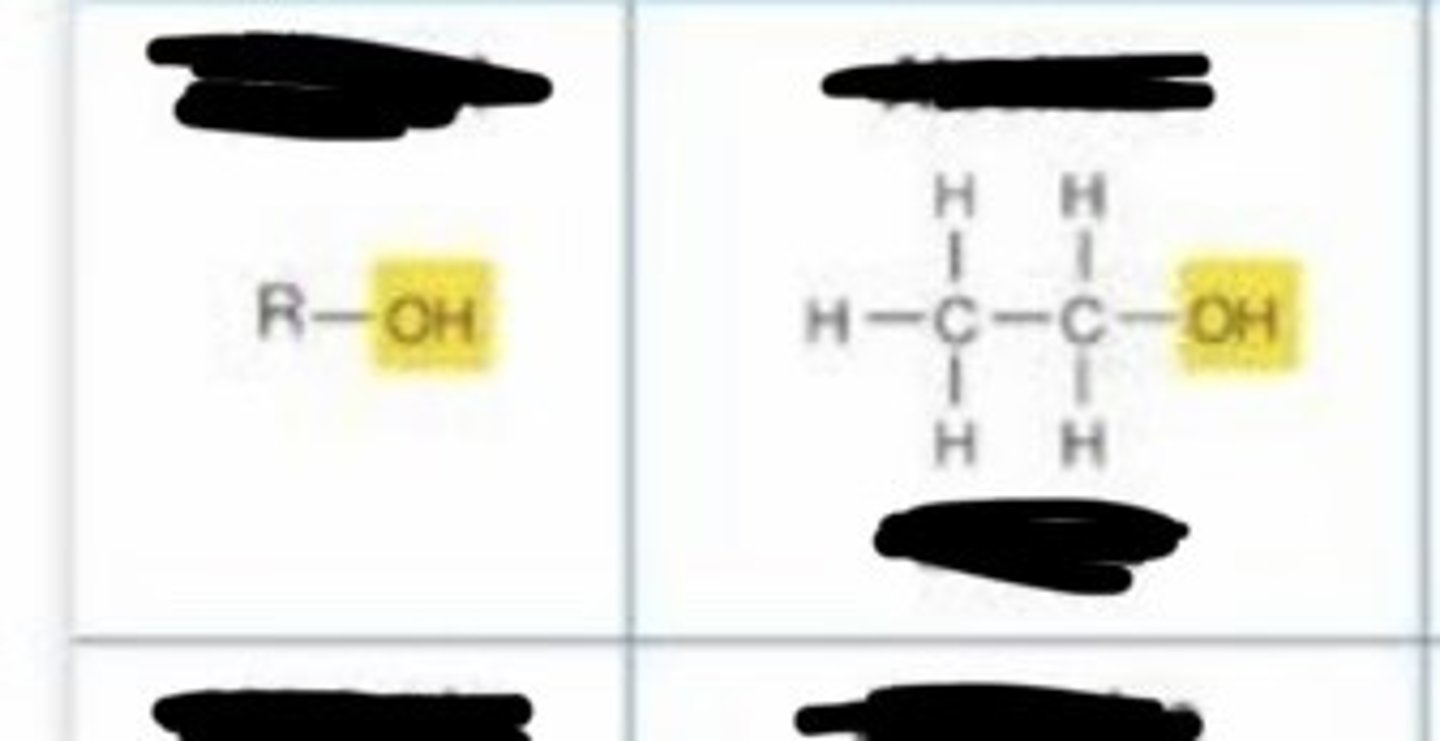
hydroxyl
- polar
-forms hydrogen bonds with water to help dissolve molecules.
-enables linkage to other molecules by condensation
hydroxyl
aldehyde
- polar
- c=o group is very reactive
- important in building molecules and in energy-releasing reactions
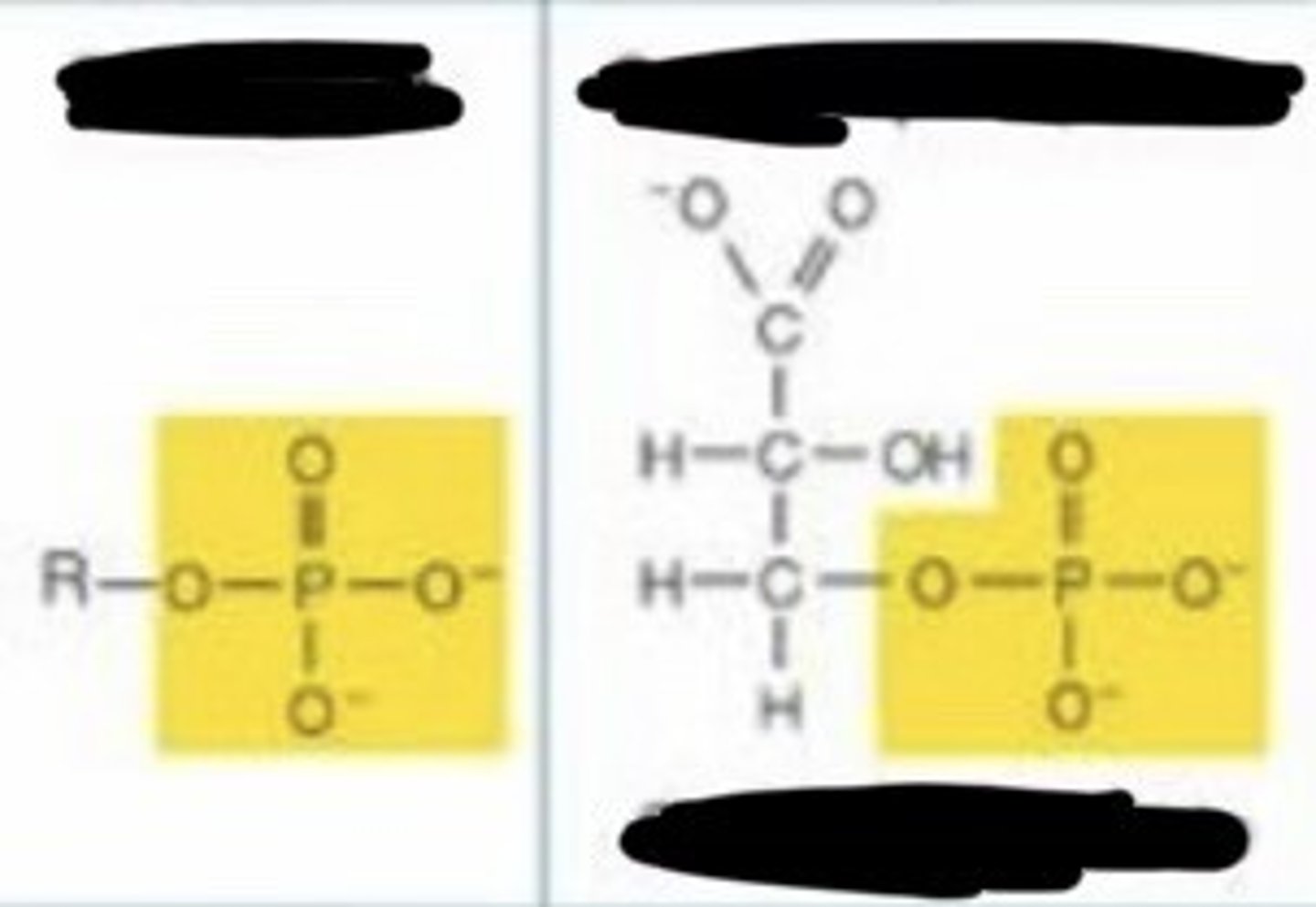
phosphate
- charged
- acidic
- enters into condensation reactions by giving up -OH
- when bonded to another phosphate, hydrolysis releases a lot much energy
phosphate
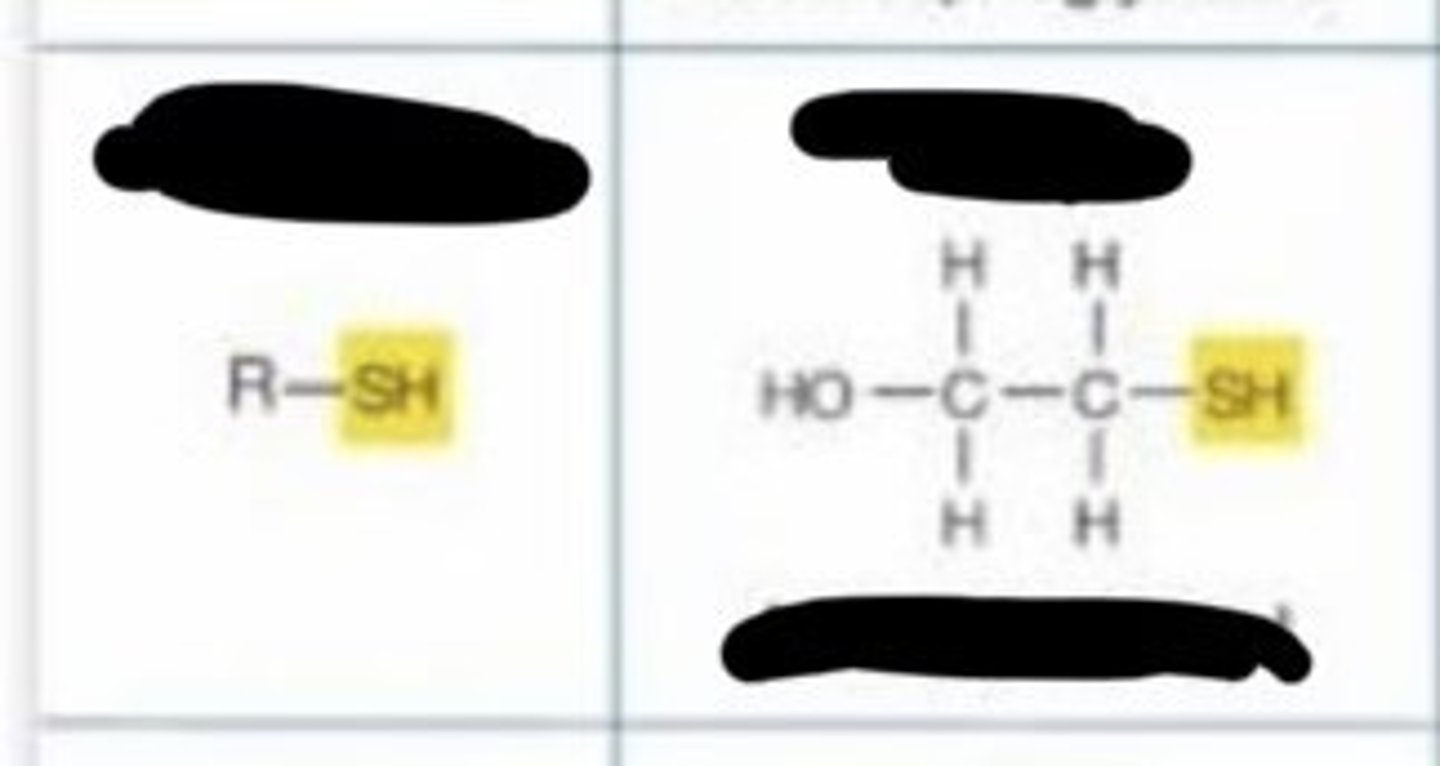
sulfhydryl
- gives up H
-Allows two -SH groups allows the reaction to create a disulfide bridge, thus stabilizing protein structure
sulfhydryl
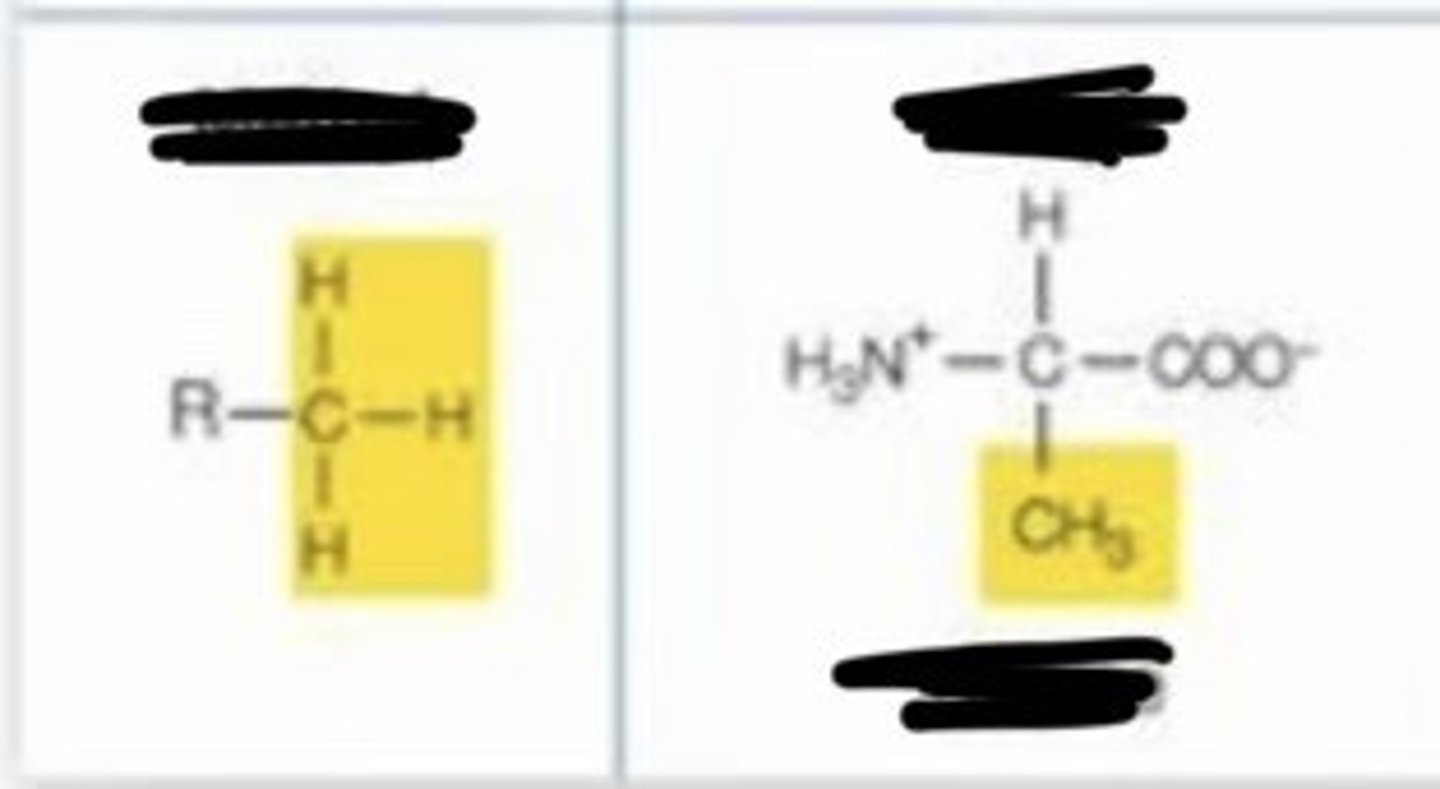
methyl
- nonpolar
- important in interacting with other nonpolar molecules and in energy transfer
methyl
Amino Acids
-Protein Function
-Neurotransmission
-Nitrogen Metabolism
Nucleotides
-made up of a pentose sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base
-Nucleic Acid Function
-Energy Conversion
-Signal Transduction
-Enzyme catalysts
carbohydrates
-energy conversion
-cell wall structure
-cell recognition
-nucleotide structure
-follows the same 1:2:1 CH2O ratio. every 1 carbon, 2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen
fatty acids
-Cell membrane
-Energy converter
-Cell signaling
-Long chain of C-H molecules