AP Euro art styles
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
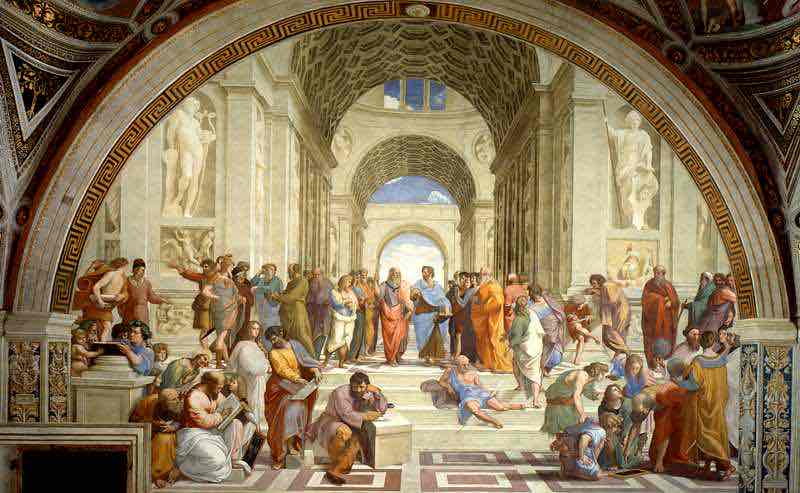

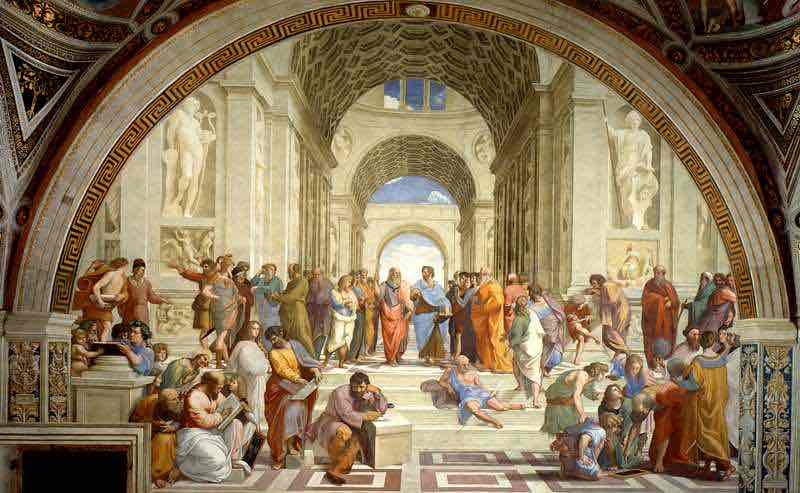
Italian Renaissance (14-16th century)
Return to the ideals of Greek and Roman period. (Re-birth of Greco-Roman style). Man as a noble, perfect creature combined with Biblical themes. Mostly religious art. Humanism.
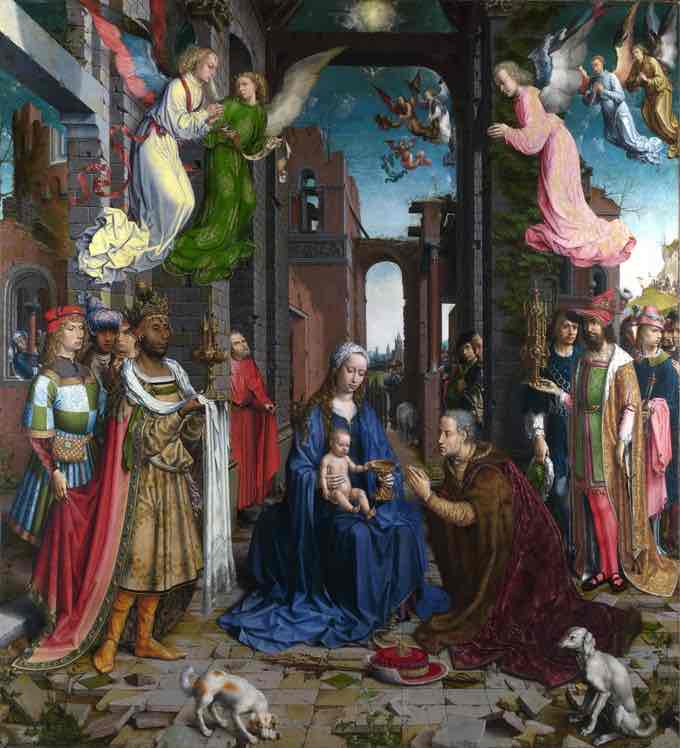


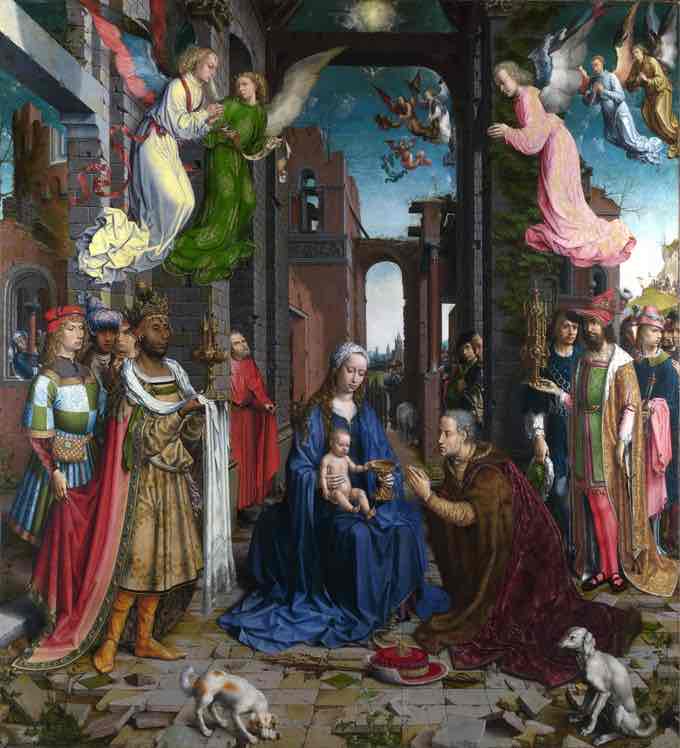
Northern Renaissance (14th-16th century)
Dutch, Flemish, and German Renaissance. Move towards greater realism and more emotion. Influenced by the Reformation (Protestant).


Mannerism (1520-1600)
It is characterized by the embracement of artificiality, elegance, and distortion of the human figure. It often depicts elongated limbs, small heads, and stylized facial features. It includes intense and unnatural colors, sometimes embracing heightened emotional narratives.
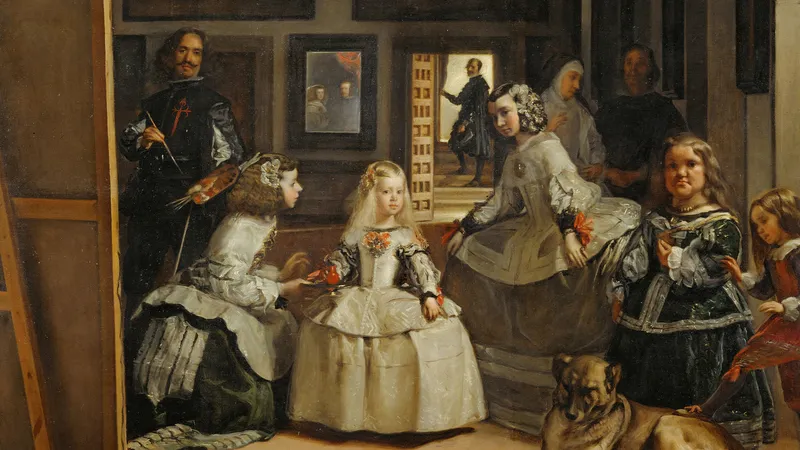


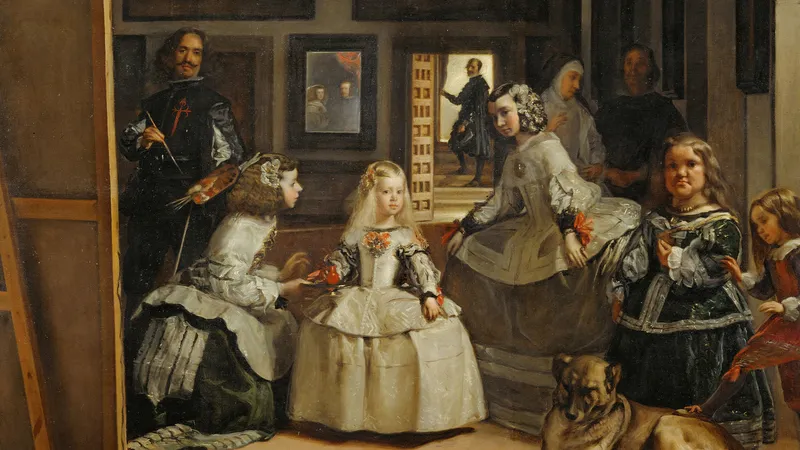
Baroque (17th century)
Takes realism from Renaissance and adds more movement, drama, energy, light, passion.

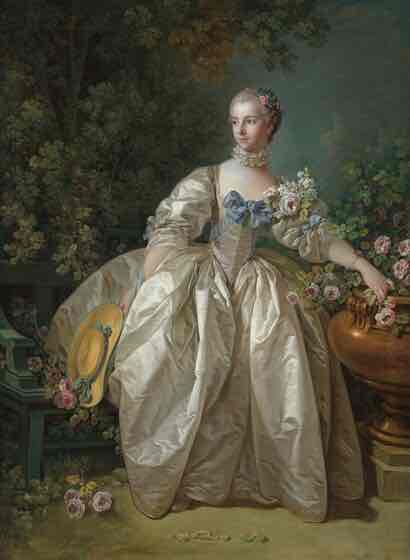
Rococo (18th century)
Highly ornamental, busy, light-hearted, rich. (Pink, fluffy, clouds and cherubs.) Style of the aristocracy.
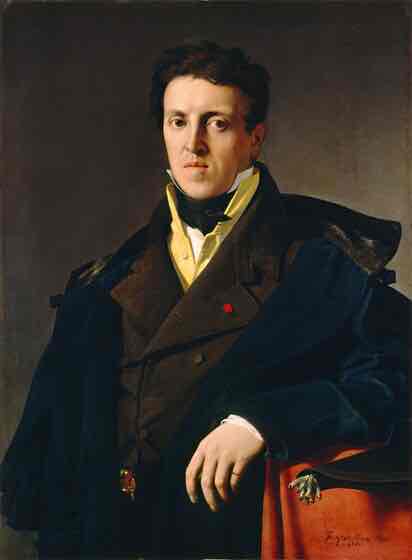

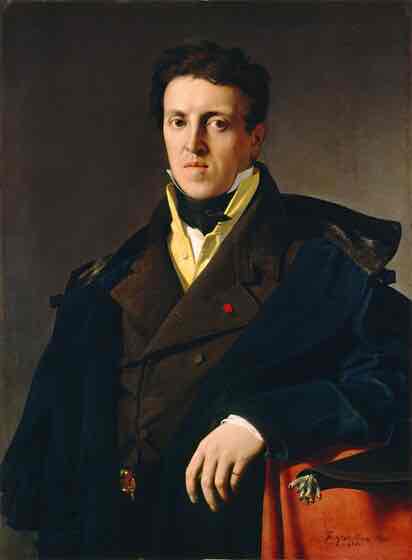
Neo-Classicism (19th century)
Severely linear style - precise line. Cool, calm, classical. (Style of the French and American Revolutions.)
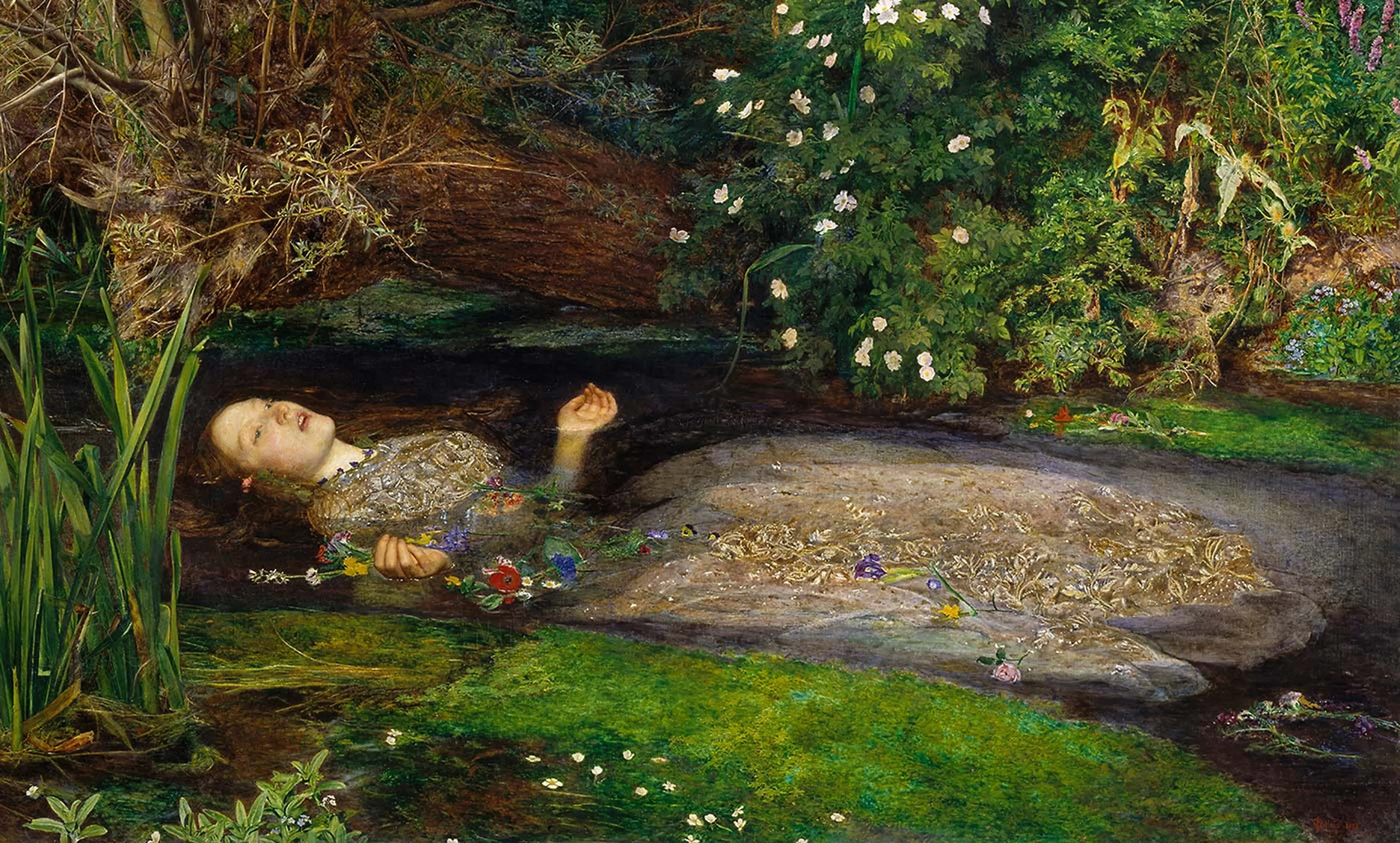


Romanticism (19th century)
Highly emotive, sometimes horrific or sublime imagery. Images from the mind or psyche - often a literary connection. Nature over man.
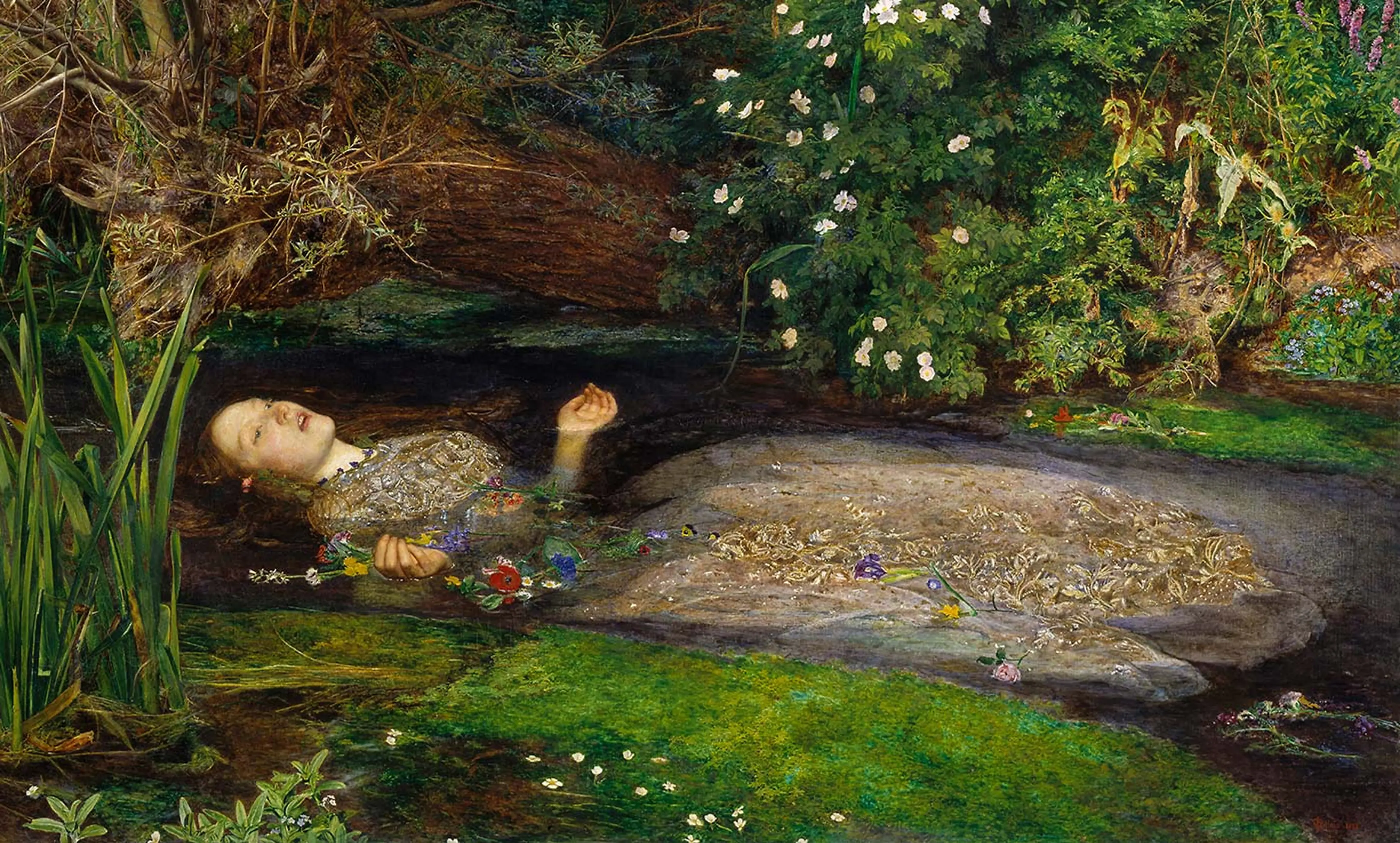


Realism (19th century)
New subject matter: current events and the modern world. Landscapes, still lifes, genre scenes.
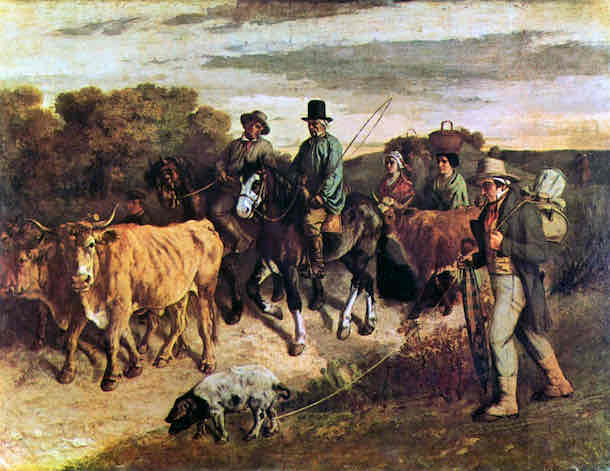


Impressionism (19th century)
Capturing the effects of light on surfaces, especially in landscape motifs. Brush work more loose, painterly effects giving a sensation or "impression" of the image. Subject matter: Nature and the newly created middle-class


Post-Impressionism (19th century)
Inspired by Impressionism. Two wings: One interested more in form and structure, the other interested more in emotion and symbolism. 1. Cezanne, Seurat. 2. Gauguin, van Gogh.


Expressionism (1905) Fauvism
French form of Expressionism, intense color. Flattened space, little or no linear perspective. Leader: Matisse.
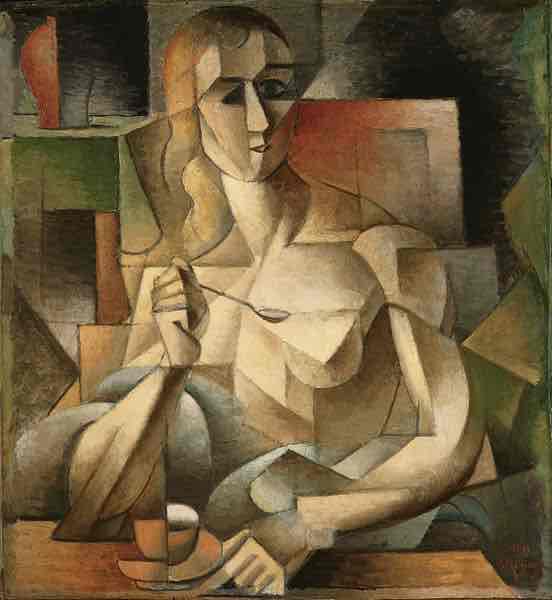


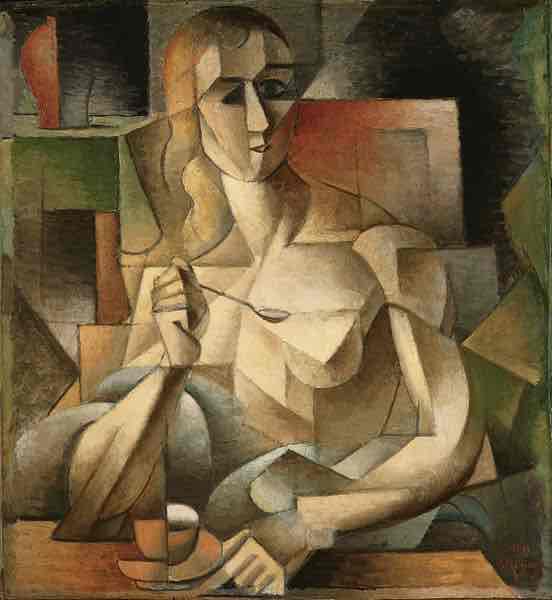
Cubism (1907)
Faceted, broken forms, showing many sides at once. Some African and Oceanic influences. Leader: Picasso.
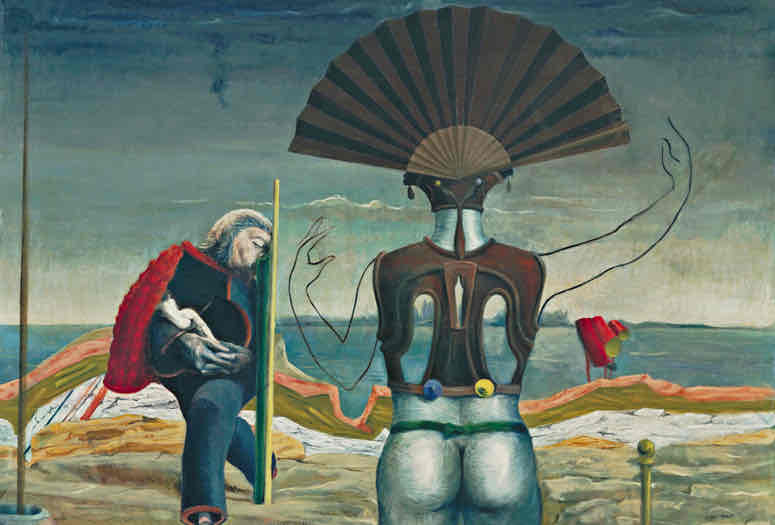


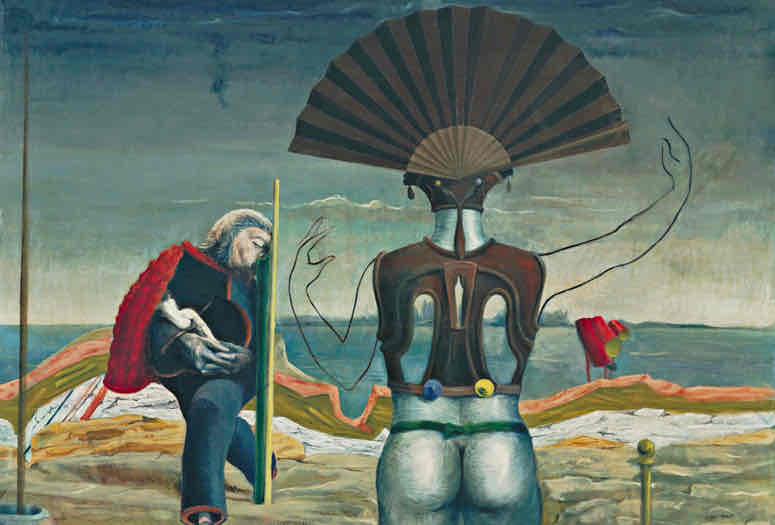
Surrealism (1924)
Focus on the subconscious and the world of dreams and visions. Utilized elements of chance and the accidental. Influenced by modern psychology: Freud and Jung. Leaders: Andre Breton, Dali, Miro.

Italian Renaissance Key Concepts
Perspective, chiaroscuro (light and shadow), anatomical accuracy, and classicism.
Northern Renaissance Key Concepts
Detailed realism, oil painting techniques, individualized portraiture, and a focus on domestic interiors.
Mannerism Key Concepts
Distortion of proportion, complex compositions, exaggerated poses, embrace of elegance, and intricate symbolism.
Baroque Key Concepts
Tenebrism (dramatic illumination), dynamic compositions, emotional intensity, movement, and grandeur.
Rococo Key Concepts
Asymmetrical designs, playful themes, intricate details, light-heartedness, and rich ornamentation.
Neo-Classicism Key Concepts
Clarity of form, classical themes, moral narratives, precise lines, and a focus on reason.
Romanticism Key Concepts
Emphasis on emotion, dramatic landscapes, themes of the sublime, idealism, and a connection to nature.
Realism Key Concepts
Everyday subject matter, focus on social issues, unembellished depiction of life, and direct observation.
Impressionism Key Concepts
Light effects on surfaces, loose brushwork, capturing the 'impression' of the moment, and common life subjects.
Post-Impressionism Key Concepts
Bold colors, structural painting, emotional symbolism, influence of personal expression, and experimentation with form.
Expressionism Key Concepts
Vivid colors, emotive forms, bold outlines, distortion of reality, and an emphasis on emotional experience.
Cubism Key Concepts
Fragmented objects, multiple perspectives, geometric shapes, abstraction, and the elimination of depth perception.
Surrealism Key Concepts
Dream-like scenes, unexpected juxtapositions, irrational imagery, focus on the subconscious, and use of chance.