Micro Unit 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:52 PM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
1
New cards
Virion
Extracellular complete virus particle; includes nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
2
New cards
nucleocapsid
nucleic acid, protein coat (capsid), maybe some additional components
3
New cards
helical symmetry
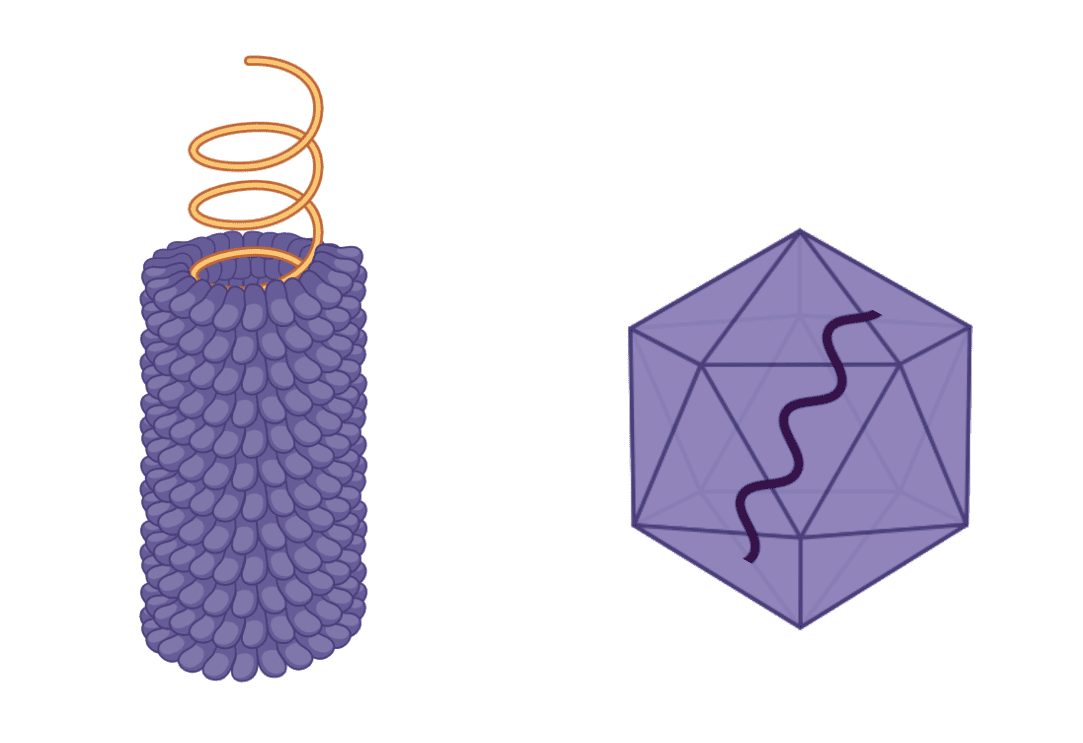
4
New cards
icosahedral symmetry
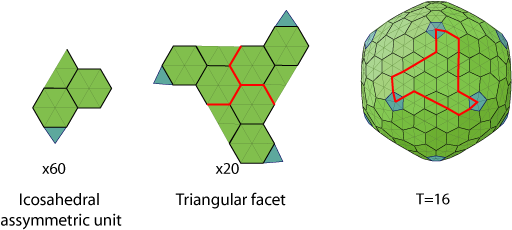
5
New cards
binal symmetry
T4 bacteriophage
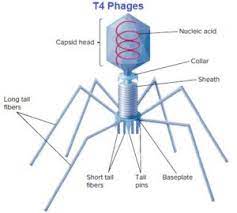
6
New cards
positive sense virus
viral genome and mRNA are the same sequence
7
New cards
negative sense virus
viral genome and mRNA are compliments
8
New cards
Negative sense dogma
RNA genome --> mRNA --> protein
9
New cards
Positive sense dogma
1) genome used as mRNA
or
2) RNA --> DNA --> mRNA --> protein
or
2) RNA --> DNA --> mRNA --> protein
10
New cards
viral envelopes
outer flexible membranous layer around the capsid that is usually host derived
11
New cards
Envelope proteins
spikes or peplomers for attachment to host, enzymatic activity, nucleic acid replication, identification
12
New cards
viral replication
attachment, entry, uncoating, synthesis, assembly, release
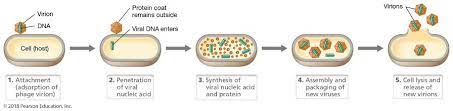
13
New cards
One step growth curve
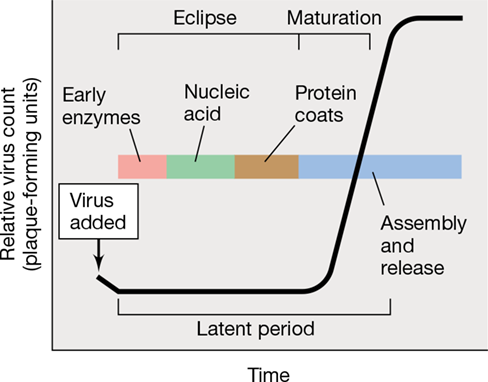
14
New cards
bacteriophage characteristics
infect bacteria, diverse and structurally complex, contain dsDNA, naked
15
New cards
Virulent
lytic
16
New cards
temperate
lysogenic
17
New cards
Lytic cycle
multiplies immediately after entering the host, lyses host cell for release; ex: T4
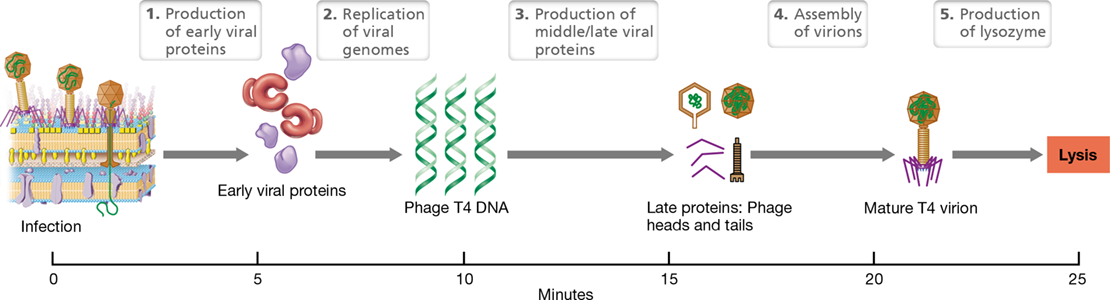
18
New cards
lysogenic cycle
integrate with host genome and remain in the host cell without killing it, may switch to lytic at any time; ex: lambda
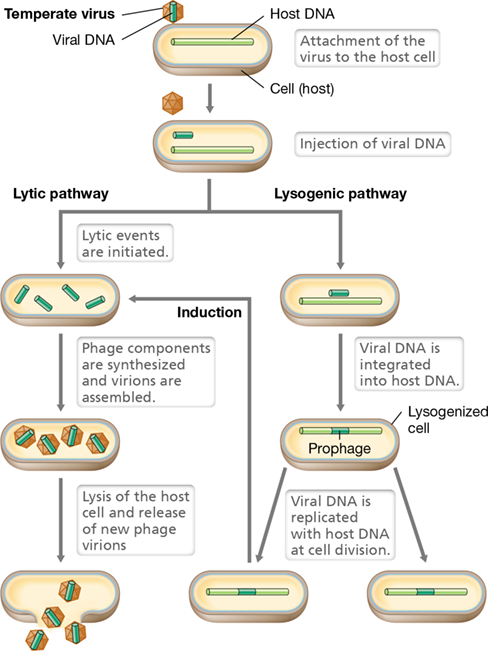
19
New cards
lysogeny
nonlytic relationship between host genome and integrated viral genome
20
New cards
prophage
integrated bacteriophage genome
21
New cards
lysogeny enzyme
integrase
22
New cards
lysogenic attachment sites
between galactose and biotin operons
23
New cards
lysogenic conversion
prophage changes the phenotype of hose
24
New cards
induction
when a phage switches from lysogenic to lytic cycle
25
New cards
What causes a drop in lambda repressor?
exposure to UV light or chemical mutagen that causes DNA damage
26
New cards
What is triggered by a drop in lambda repressor?
switch to the lytic cycle
27
New cards
excisionase
binds integrase enzyme and enables integrase to reverse integration process; SOS response
28
New cards
latent viral infection
virus stops reproducing and remains dormant for some time; ex: HSV
29
New cards
persistent viral infection
virus almost always detectable, clinical symptoms mild or absent for long periods; ex: hepatitus B, HIV
30
New cards
oncoviruses
1) pick up oncogene and transfer it
2) alter protooncogenes
3) incorporate directly into tumor suppressor gene and inactivate it
2) alter protooncogenes
3) incorporate directly into tumor suppressor gene and inactivate it
31
New cards
retroviruses
replicate through a DNA intermediate using reverse transcriptase, released by budding
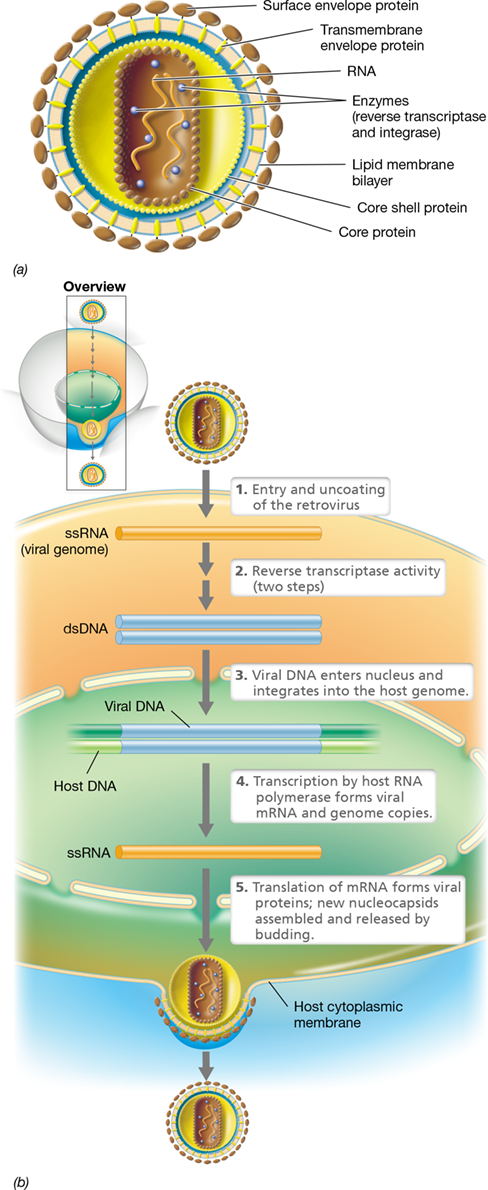
32
New cards
SARS-CoV-2
positive sense, ssRNA, helical capsid symmetry, spike glycoprotein
33
New cards
Covid Infection and Transmission
spike protein attaches to host receptor on lung epithelial cells, fuses with cell membrane, virions released by exocytosis, zoonotic and person to person through droplets
34
New cards
nucleiod
location of bacterial chromosome and proteins
35
New cards
plasmid
small closed circular DNA that exist and replicate independently of the chromosome
36
New cards
gene
DNA segment that codes for a polypeptide, rRNA or tRNA
37
New cards
genotype
specific set of genes an organism possesses
38
New cards
phenotype
set of observable characteristics denoted with a + or -
39
New cards
wild type strain
strain isolated from nature
40
New cards
mutation
stable, heritable change in nucleotide sequence that alters the genotype, may or may not have an effect on the phenotype
41
New cards
forward mutation
wild type becomes mutant form
42
New cards
reverse mutations
mutant phenotype becomes wild type phenotype
43
New cards
auxotroph
lost the ability to synthesize essential compounds
44
New cards
prototroph
can synthesize essential compounds
45
New cards
screening
detects mutants via observation
46
New cards
selecting
placing organisms under conditions where the growth of those with a particular genotype will be favored
47
New cards
transformation
take up of DNA from a lysed donor cell
48
New cards
transduction
take up of DNA from a viral injection
49
New cards
conjugation
sharing of plasmid DNA between living cells
50
New cards
homologous recombination
DNA is nicked, single stranded binding protein and RecA complex formed, recipient DNA invaded, crossover leads to exchange which is then ligated to form two recombinant DNA molecules
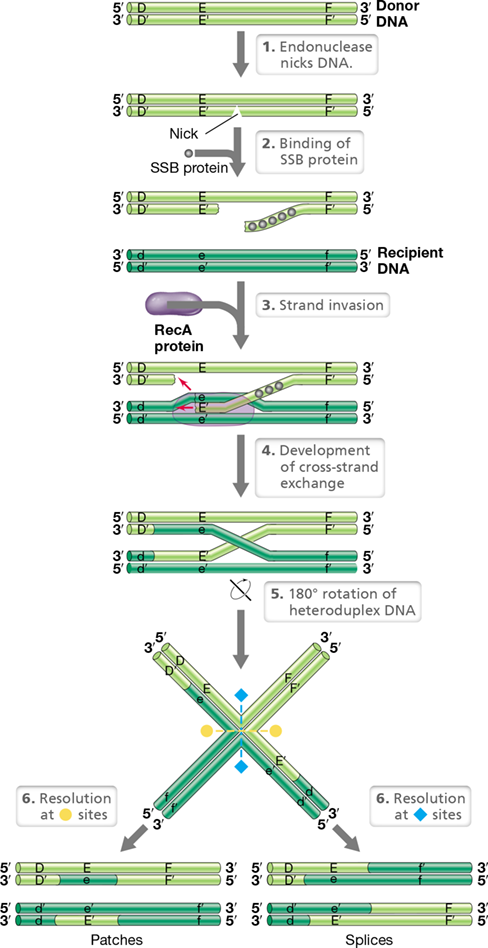
51
New cards
RecA
gene required for homologous recombination
52
New cards
F+
contains the fertility plasmid
53
New cards
F-
does not contain the fertility plasmid
54
New cards
tra
encode for conjugation
55
New cards
ori
independent origin of replication
56
New cards
λdgal
carries genes for galactose utilization
57
New cards
generalized transduction
host DNA mistakenly packaged into phage head
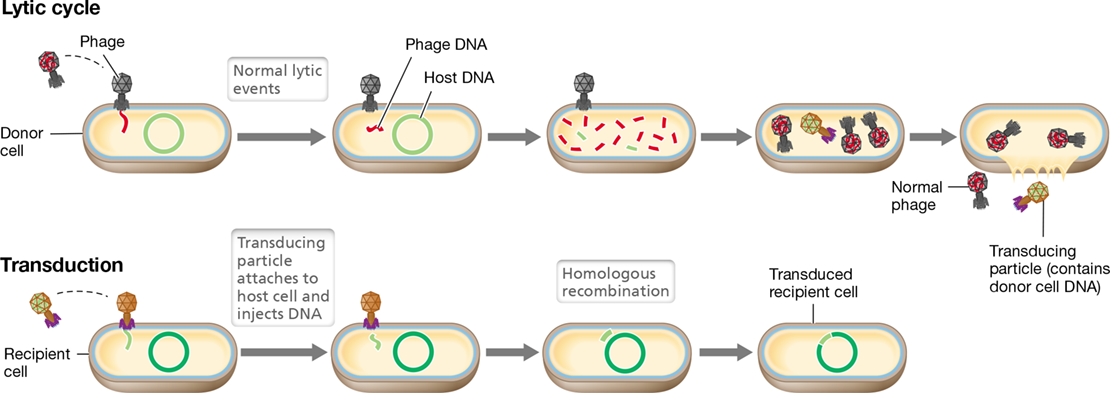
58
New cards
specialized transduction
temperate phages with established lysogeny are incorrectly excised, host DNA exchanged for phage DNA and makes way into new phages
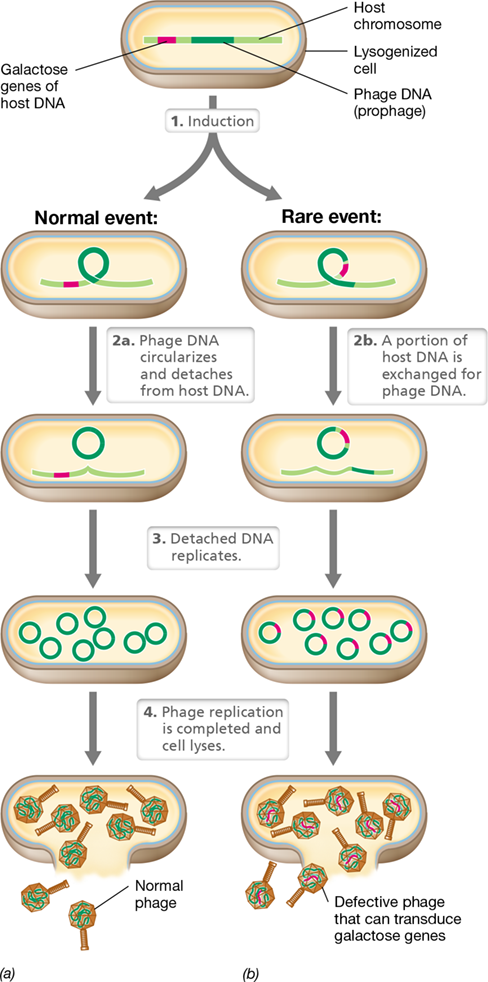
59
New cards
PCR
synthesis of large quantities of DNA
60
New cards
PCR Ingredients
target DNA, primers, taq polymerase (thermostable), dNTPs
61
New cards
PCR Steps
1. denaturing
2. annealing
3. extension
4. repeat
2. annealing
3. extension
4. repeat
62
New cards
denaturing
denature target DNA with heat
63
New cards
annealing
primers bind to target DNA
64
New cards
Extension
copies of target DNA are synthesized
65
New cards
PCR Protocol
95 C for 1 min
30 cycles of
- 95 C for 30 sec
- 55 C for 1 min
- 72 C for 1 min
Hold at 4 C
30 cycles of
- 95 C for 30 sec
- 55 C for 1 min
- 72 C for 1 min
Hold at 4 C
66
New cards
Steps of Molecular Cloning
1. isolation and fragmentation of source DNA
2. Insertion of DNA fragment into cloning vector
3. Introduction of cloned DNA into host organism
2. Insertion of DNA fragment into cloning vector
3. Introduction of cloned DNA into host organism
67
New cards
restriction enzymes
cut DNA at specific sequences
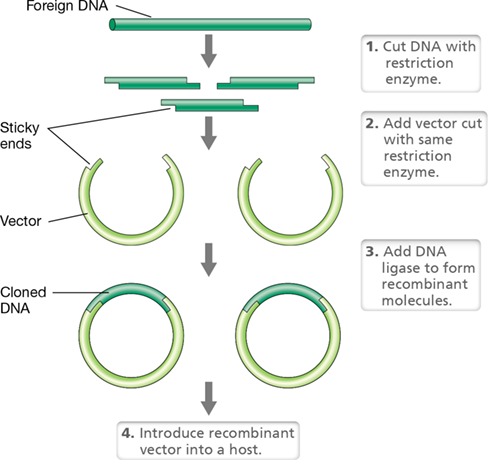
68
New cards
plasmid vector
take up foreign DNA and replicate independent of chromosome
69
New cards
DNA ligase
joins DNA
70
New cards
why are plasmids good as cloning vectors?
easy to purify, small size, independent origin of replication, multiple copy number, presence of selectable markers, unique cloning sites
71
New cards
Locations of normal microbiota
surfaces and mucous membranes; eyes, ears, nose, mouth/throat, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, skin, urethra, vagina
72
New cards
Skin bacteria
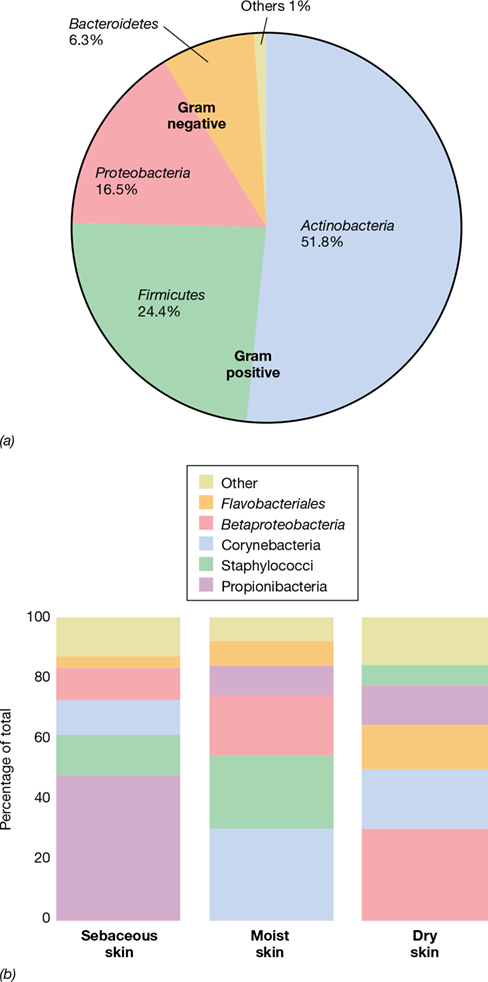
inhospitable environment, both transient and resident, influenced by environment and host factors, cause acne and body odor
73
New cards
Mouth bacteria
antimicrobial enzymes in saliva, streptococcus colonize on teeth and gums, biofilm forming,
74
New cards
Stomach bacteria
hard to survive in acidic conditions, some survive if pass through quickly or ingested in food particles, helicobacter pylori
75
New cards
Intestinal bacteria
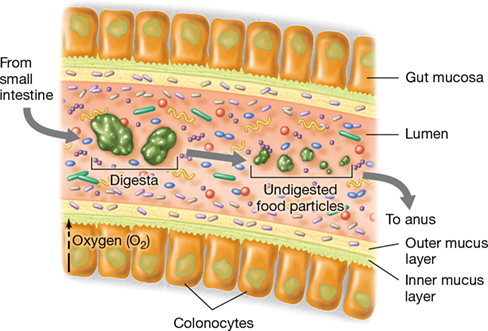
small- increasing pH has increasing microbes, E faecalis, lactobacilli
large- most microbes in body, obligate anaerobes, bacteroides, clostridium, produce vitamins and gas
large- most microbes in body, obligate anaerobes, bacteroides, clostridium, produce vitamins and gas
76
New cards
respiratory bacteria
staphylcocci/streptococci in upper tract, no normal microbiota in lower tract, lysozyme in mucous
77
New cards
Urogenital bacteria
kidneys/ureter/bladder may have residential, few microbes in distal portions of urethra (E coli can cause UTI), lactobacilli in vagina
78
New cards
Infection vs disease
infection means there are bacteria present, disease means they are causing damage to host tissues
79
New cards
5 rings of infectous disease
agent, virulence, exposure, dose, susceptibility
80
New cards
direct disease transmission
infected host to susceptible host
81
New cards
indirect disease transmission
fecal-oral, airborne, fomites
82
New cards
vector disease transmission
through insect bites
83
New cards
reservoir disease transmission
animate or inanimate place pathogens reside or propagate
84
New cards
zoonosis
disease occurs primarily in animals but is occasionally transmitted to humans
85
New cards
common source curve
rapid rise to peak, moderately rapid decline
86
New cards
propagated cruve
slow, progressive rise and gradual decline
87
New cards
immune system
recognizes foreign substances or microbes and acts to neutralize or destroy them
88
New cards
immunity
ability of a host to resist a particular disease or infection
89
New cards
immunology
study of immune response
90
New cards
innate response
nonspecific natural response
91
New cards
adaptive response
specific and acquired-- cell mediated or antibody mediated
92
New cards
innate barriers to pathogen invasion
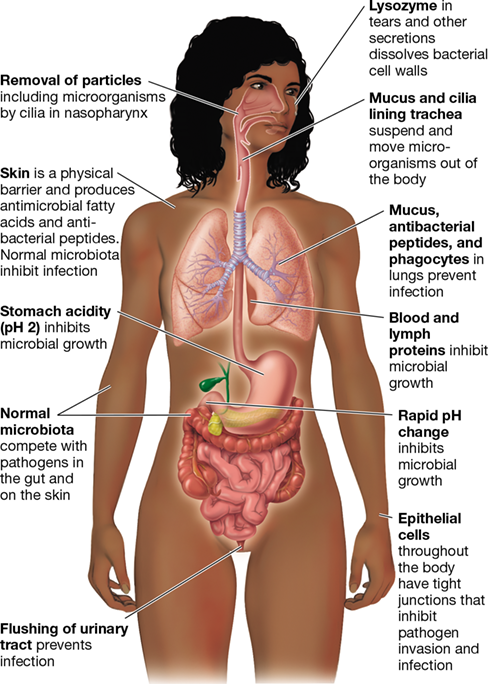
first line of defense, no memory, does not rely on previous exposure
93
New cards
phagocytes
engulfs and destroys foreign substances, results in inflammation
94
New cards
cell mediated immunity
T cells, mobile, require antigen binding to T cell receptors
95
New cards
antibody mediated immunity
B cells, not very mobile, activated by some binding but mostly need T cell triggering
96
New cards
Acquired immunity
Natural- active from being sick, passive from breast feeding
Artificial- active from vaccination, passive from nonhuman sources
Artificial- active from vaccination, passive from nonhuman sources