3.1 - shoulder general tx. & anatomy
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
GH
AC
SC
scapulothoracic
what are the joints of the shoulder
coracoid process
what bony landmark does the brachial plexus run under
greater tuberosity
what is the most common landmark for shoulder pain
internal; external
the lats does active (internal or external) rotation and could limit (internal or external) rotation
bent
the lats more tight if the legs are (bent or straight), this can lead to limited shoulder flexion if they are tight
serratus anterior
the __________ muscle is the main muscle that provides scapular thoracic stability
anterior; winging
a tight pec minor that result in the scapula having a ___________ tilt and __________ winging
motor control
scapular dumping is a ___________ problem
upper trap and levator scap
what are the common muscles for shoulder trigger point pain
GH
SC
AC
ST
thoracic spine
cervical spine
joint mobs for the shoulder
posterior capsule/cuff (most common)
pec minor
upper trap/levator scapula
common STM for shoulder pain
IR
_______ motion is limited with a tight posterior cuff
teres minor
infraspinatus
what muscles are the contributors to a tight posterior cuff
SC
whats better to mob? SC or AC joint
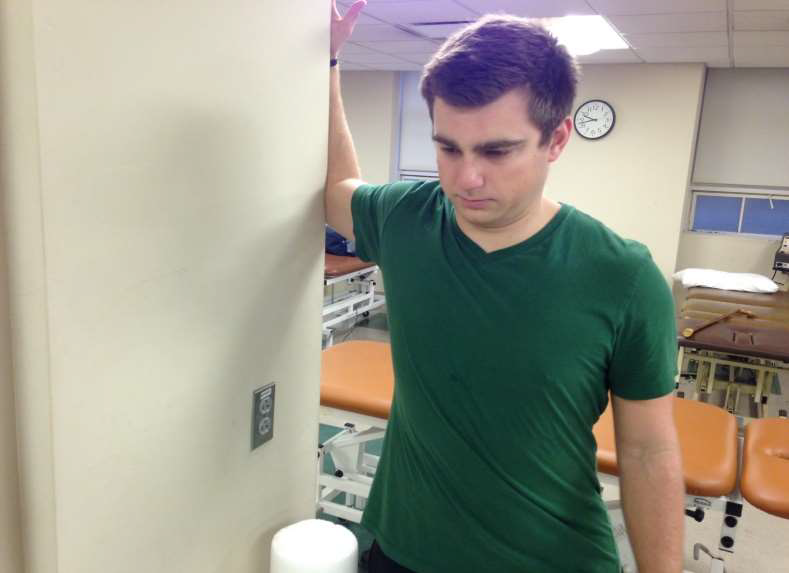

door stretch with elbow bent
whats the best stretch for the pec minor
retraction (pulling down and back → open up chest)
after stretching the anterior shoulder, follow it up with scapular ______ exercises
cross body abduction - inc. shoulder ROM more
sleeper stretch
stretch options for posterior shoulder tightness, which increases shoulder ROM more
posterior
perform __________ glides to improve posterior shoulder tghtness
anterior
lying on a foam roller addresses (anterior or posterior) shoulder tightness
pulleys
codman’s/pendulums
wall walks
examples of shoudler AROM/AAROM
shoulder instability/hypermobile
what pt diagnosis shouldn’t be given codman’s/pendulums
tactile cueing
visual feedback
scapular assist test
ways to teach pt to elevate shoulder without substitution
allows shoulder to be in scapular plane
what is the benefit to adding a towel under the arm for a patient in supine
central
T-spine and C-spine manipulations are theorized to increase ROM, BUT _______ effects are the likely cause
extension and IR (because painful position,threat to shoulder)
what is the last motion we do to with the shoulder in PT
manips
which is better for improving shoulder pain, manips or mobs?
supine towel
supine roller
seated thoracic and cervical extension over chair
active thoracic extension
posture correction
cat camel
c-spine/upper t-spine retraction (chin tuck)
c-spine/upper t-spine rotation
self mob examples
flexion; extension
during a chin tuck; the upper cervical spine goes into _________ and the lower cervical spine goes into _________
stabilizers; NM
exercises for shoulder pain should emphasize on ___________ and ___________ control
focus on rotator cuff and scap muscles (middle trap, lower trap, serratus anterior)
minimize
upper trap
levator scap
when exercising the shoulder, which muscles should you focus on and which muscles should you minimize
supraspinatus
what muscle does full can exercises target
smaller
when rehabbing the shoulder, start with the (smaller or larger) muscles
OKC
OKC or CKC shoulder exercise:
functional
CKC
OKC or CKC shoulder exercise:
stability
OKC
OKC or CKC shoulder exercise:
isolate muscle activity
lower trap and serratus
what muscles get shut down with shoulder pain
T (perfer pain free but if the minimal pain subsides when exercise is over it is okay)
T/F: you can exercise the shoulder when there is minimal pain during the exercise
isotonics
which type of exercise is preferred for strengthening/motor the rotator cuff?
isometric
isotonic
isokinetic
provides better blood flow to the cuff and reminder for stability
what is the purpose for the towel being under the elbow during RC strengthening
rotate; elevate
when rehabbing the shoulder, the rule of thumb is __________ before __________
sidelying
which position is better for shutting down the upper trap…
standing er
sidelying er
increases; decreases
full can exercise (decreases or increases) moment arm and (decreases or increases) the supraspinatus force
abduction; flexion
GH elevation during ___________ is not functional and has potential for impingement and GH elevation during ___________ is more functional with less chance of impingement
IR and ER
shoulder elevation (flexion, scap, abduction)
what exercises are best to activate the RC
serratus anterior and lower trap
the ____________ and _____________ muscles are commonly implicated to activate scapular exercises
prone Y
what is the testing position for lower trap
serratus anterior; levator scap
during AROM of exercise/strengthening of the shoulder, reduce muscle activity or scap muscles __________ and ___________
I → T → Y
what is the progression with prone Ys, Is, and Ts
down (shuts down the lats)
palm (up or down) is harder during prone I’s
upper trap
the shoulder W exercise shuts off the __________ muscle
level 1
is it shoulder or not - clear the neck
level 2 - category…
rotator cuff/impingement
frozen shoulder
GH instability
level 3
high, moderate, or low irritability
what are the levels and sublevels of the “complaint of shoulder sx” level pyramid
key positives
impingement signs
painful arc
pain with isometric resistance
weakness
atrophy
key negative
significant loss of motion
instability signs
key positives and key negatives of the level 2 classification specific exam for rotator cuff/impingement
key positive
spontaneous progress pain
Loss of motion in multiple planes
Pain at endr ange
key negative
normal motion
age < 40
key positives and key negatives of the level 2 classification specific exam for frozen shoulder
ER
the hallmark sign of frozen shoulder is significant loss of _______ motion
key positive
Age < 40
Hx d/l or sublux
Apprehension
Generalized laxity
key negative
no history d/l
no apprehension
key positives and key negatives of the level 2 classification specific exam for GH instability
High pain (≥7/10)
Night or rest pain
Consistent
Pain before end ROM
AROM < PROM
High disability
DASH
ASES
signs/sx of high irritability of the level 3 irritability classification
pain reducaiton
if a patient is in the high irritability category, the focus should be on _________
pain reduction
impairments
basic function
if a patient is in the moderate irritability category, the focus should be on _________
functional activity
if a patient is in the high low category, the focus should be on _________
Mod pain (4- 6/10)
Night or rest pain
Intermittent
Pain at end ROM
AROM ~ PROM
Mod disability
DASH,
ASES
signs/sx of moderate irritability of the level 3 irritability classification
Low pain (≤3/10)
Night or rest pain
None
Min pain with overpressure
AROM = PROM
Low Disability
DASH
ASES
signs/sx of low irritability of the level 3 irritability classification
3; 5
need at least ______ out of the ______ signs/sx to categorize someone into an irritability rating
:)
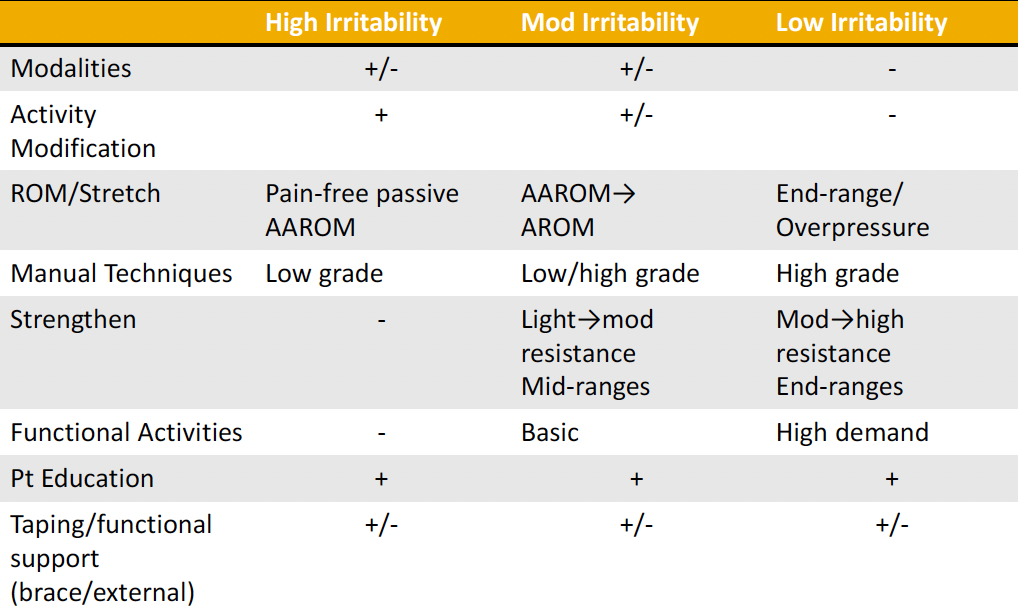
write out the treatment strategy for irritability categories (high, moderate, low)
here are the treatment strategies…
modalities
activity modification
ROM/stretch
manual techniques
strengthen
functional activities
pt education
taping/functional support (brace/external)
extrinsic
extrinsic or intrinsic cause of rotator cuff disease:
compression in the subacromial space
intrinsic
extrinsic or intrinsic cause of rotator cuff disease:
tendon is worn down, common with age
extrinsic (posture, shoulder kinematics)
can PT fix intrinsic or extrinsic causes of rotator cuff disease
posterior/internal
_______________ impingement is a category of rotator cuff disease where compression of the tendons between the posterior rom of the glenoid and the humeral head
posterior/internal or subacromial pain
______________ impingement is common in overhead athletes
anterior lateral
people with subacromial pain 'impingement’ syndrome with have pain located in the ____________ shoulder with OH activities
hawkin’s
neer
painful arc
special test for compression/extrinsic subacromial pain ‘impingement’ syndrome
resisted ER
full can
empty can
painful arc
special test for tension to the cuff causing subacromial pain ‘impingement’ syndrome
apprehension test and shoulder relocation
special test for internal SAIS subacromial pain ‘impingement’ syndrome
F
T/F: general exercise is better than specific exercise
function; pain
exercise vs surgery:
exercise is better for __________
surgery is better for ___________
resistance; proprioceptive
______________ and _____________ exercises are better than movement based exercises
decrease OH/provocative activities (dec pain)
AROM
stretching
strength/motor control
posture correction
manual therapy
modalities
MEDS: NSAIDS, injections
address risk factors with job/ADLs/hobbies
pt education
genertal treatment during the acute phase of SA impingement
T
T/F: isotonic exercises is the preferred choice as the muscle functions through the ROM for strengthening/motor control during the acute phase of SA impingement
shrug
__________ is defined as early or excessive upward rotation
dump
__________ is defined as a rapid downward rotation during lowering
chin tucks/retractions
stretch
strengthen
exercises to reduce forward head posture
extension
when address posture for SA impingement, focus on thoracic __________
posterior; lower trap
the theory behind elastic taping for SA “impingement” is increasing __________ tilt and increasing activity of the ____________ muscle
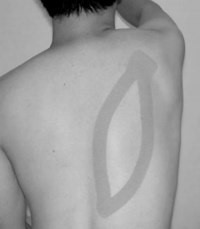
leukotape
is kinesiotape or leuoktape better for posture correction
facilitatory = bottom, facilitates lats
inhibitory = top, inhibiting upper trap
which tape is facilitatory and which is inhibitory
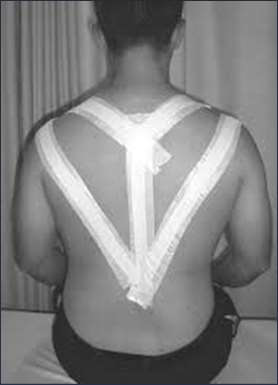
sub-acute/chronic
will a patient in the (acute or sub-acute/chronic) phase of SA ‘impingement’ tolerate more stretching
acute = arm is at their side
sub-acute chronic = arm is getting in front, 45-90 degrees
what is the main difference between strengthening treatment between acute and sub-acute chronic
6 weeks
it takes a minimum of _________ for bone to heal