Lecture #2 | Terminology and Epidemiology of Cancer
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Carcinogen
Anything that causes cancer
things in the environment that act on DNA, RNA, or proteins
Also hereditary causes to cancer
Epidemiology
Provides clues about heritable and non heritable causes of cancer through the study of incidence, distribution and determinants of disease in human population
Concept: Tumors are clonal
Tumors arise from one ore more cells that grow uncontrollably, creating a clone
while all cancer cells are derived from one cell, they are all not the same due to a mixture of cell types
Tumors are heterogenous
This causes difficulties in controlling it
How do tumors come about
From a series of events affecting one cell
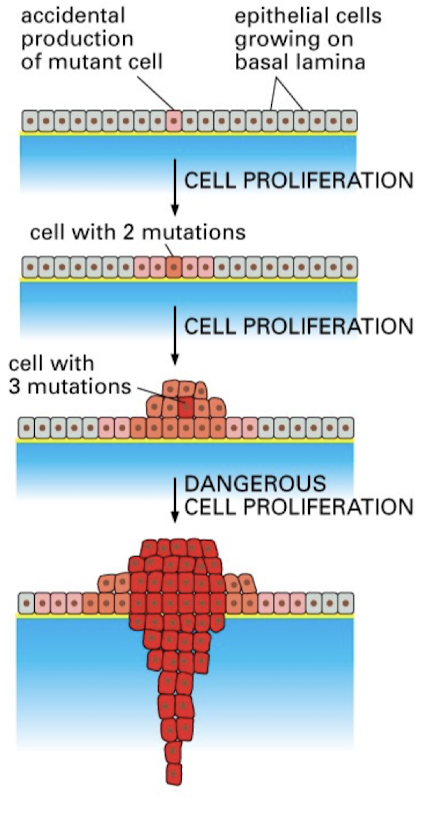
cell with mutation clones itself
cells with mutations are more likely to develop further mutations
will continue to clone cell with larger and larger amount of mutation
Concept: Tumors arise from a series of events
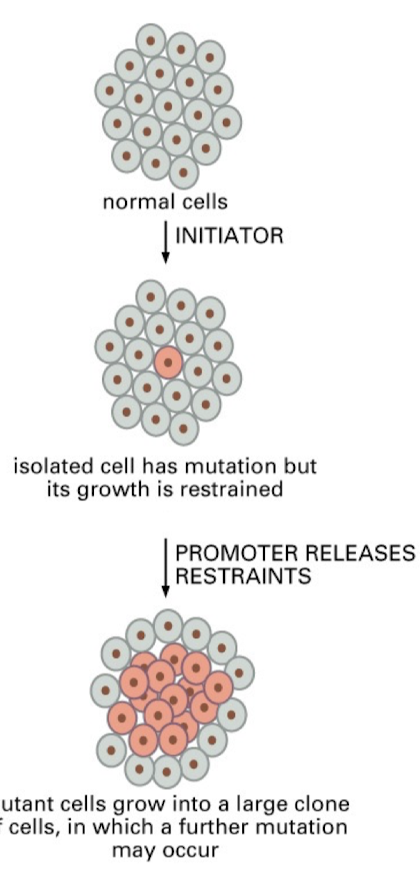
Initiator
Promoter events
Initiating event
Creation of a mutation in a cell
mutagens
90% of all mutagens are carcinogen
not all though as some mutations are beneficial
a single event can be sufficient to cause a mutant
inherited mutations
Promoter event
Compounds applied to an organism previously treated with an initiator that cause cancer, promotes cell proliferation
not direct mutagen but may cause mutations indirectly
induce cells to proliferate (replicate DNA)
anything that encourages cells to grow: hormones, phorbol ester (TPA), saccharin (rodents)
Promoter
Compound that induces “initiated” cells (mutants) to replicate in an un restricted fashion
so almost anything that causes cells to replicate can be a promoter
come in all shapes and sizes, many are man made, others are naturally occurring
Complete carcinogen
Acts as both initiator and promoter
ex: cigarette smoke contains >1000 chemicals
Concept 3: Timing and repetition of promoters are important
Promoters follow initiators
Promoters must reach a certain threshold
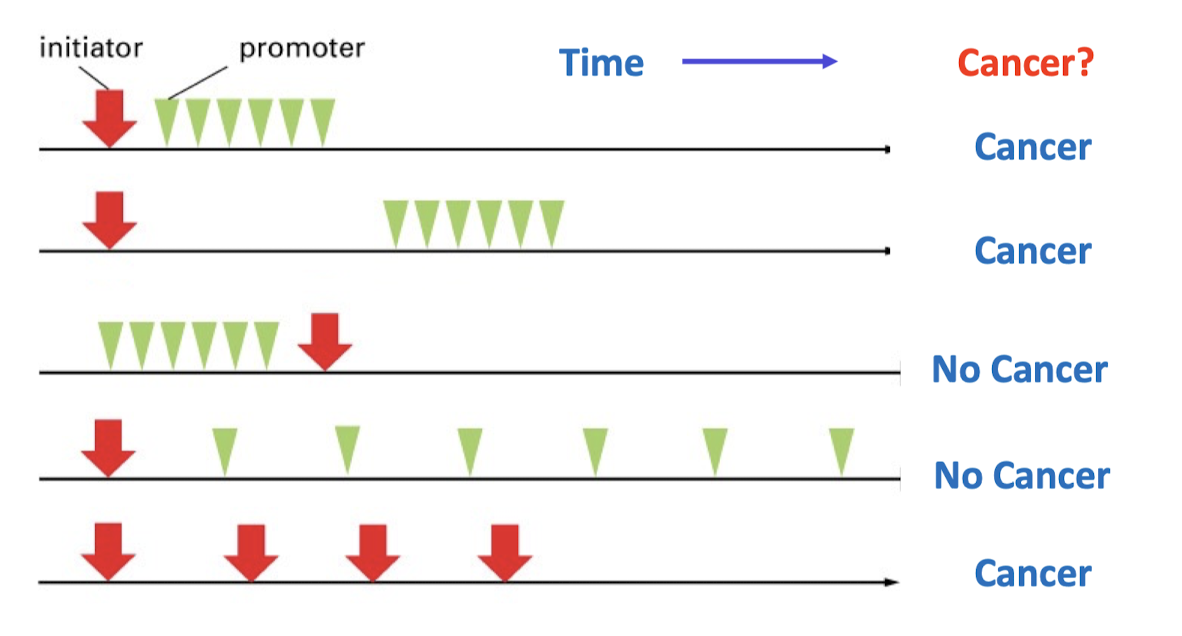
Scenario 2: While time elapsed, an initiator event is permanents
Scenario 4: Promoters must reach a certain threshold
Scenario 5: A lot of mutations means that there is no promoter is needed
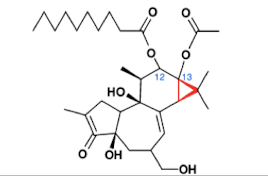
Phorobol ester (TPA)
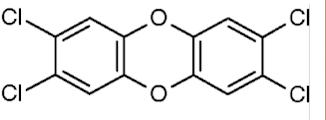
Dioxin (TCCD)
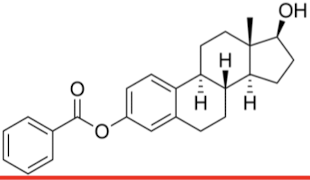
Estradiol benzoate
Concept #4: Progression follows initiation and promotion of the tumor
Progression can reduce the time that a mutation can take to proliferate
from 10-20 years with initiation + promotion to months-years with just progression
Why does it take years to form a tumor?
Because their are checkpoints in cell growth
Concept #5: There is a delayed onset from the initial exposure to a carcinogen and when the cancer/tumor is first observed
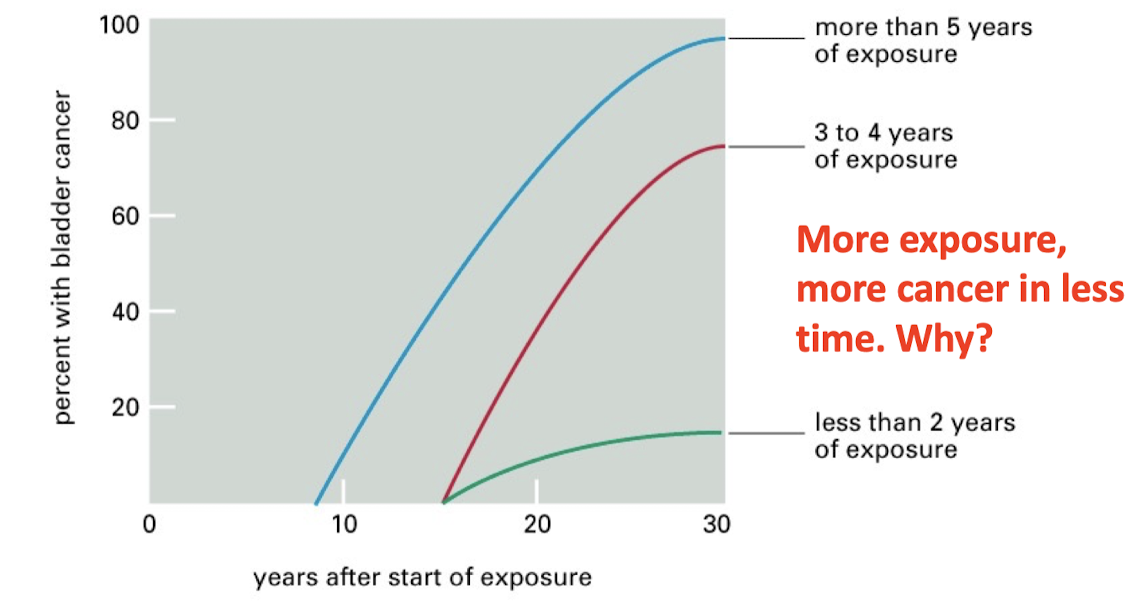
Concept #6: Cancer is a multistep process that arises from multiple initiating and promoting events
Require steps (grouped into 6 categories) for cancer cells to undergo all the necessary changes to be fully malignant
each step takes time
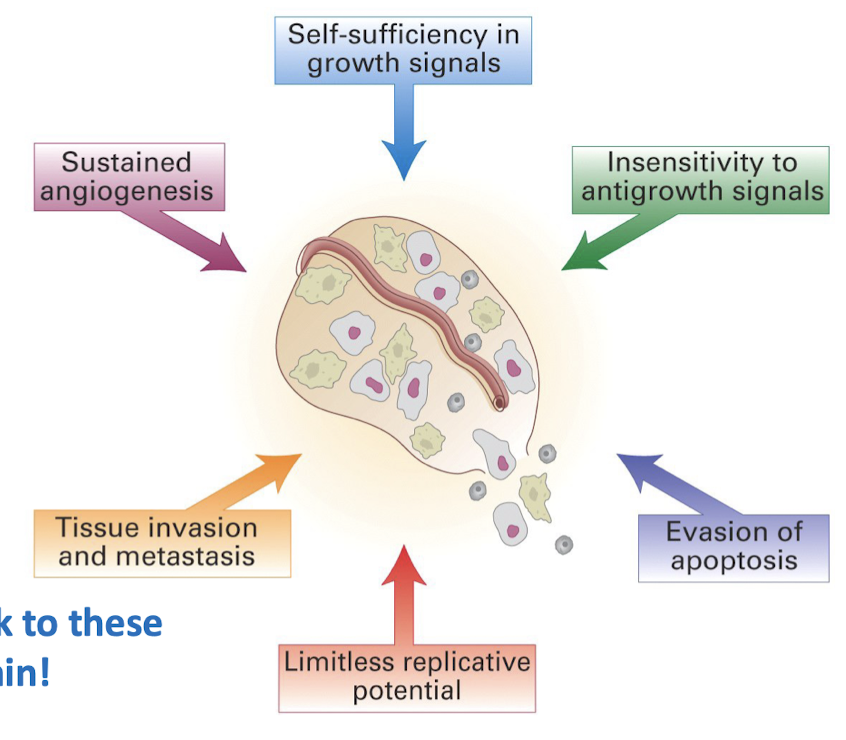
all steps need to keep happening
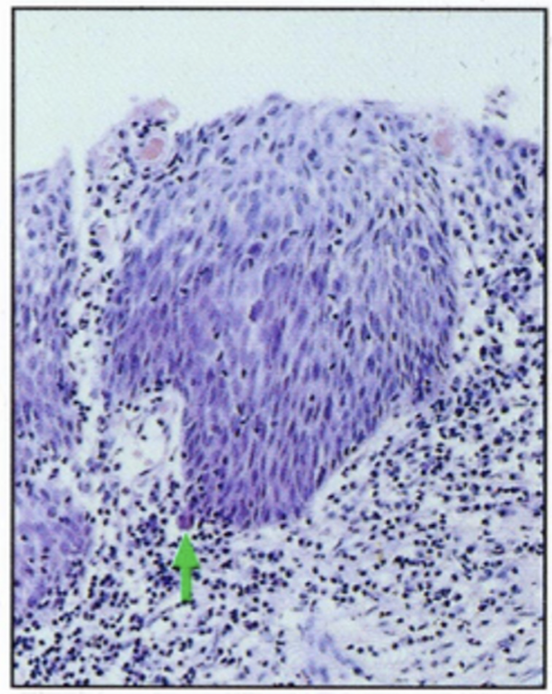
Concept #7: Classification of tumors depends on the stage of the tumor and its tissue of origin
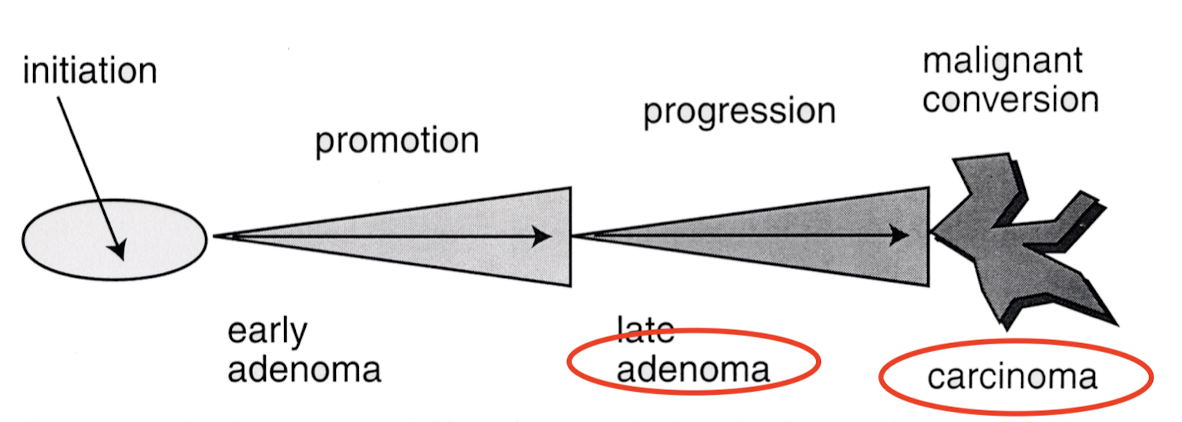
if promotion is removed in early adenoma, it can regress
Benign (adenoma)
Differentiated
Normal structure, look like surrounding cells
Slow, progressive growth, few mitoses
Encapsulated
Not metastatic (not traveling)
Seldom harm to the host
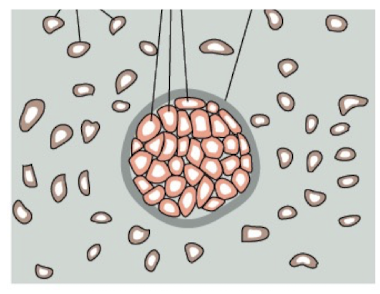
well formed
Malignant (carcinoma)
Will keep growing
• Dedifferentiated
• Atypical structure, embryonic-like
• Rapid growth, very mitotic (identify spindle formation and condensation of chromatin)
• Not encapsulated
• Metastatic (invades other tissue)
• Significant harm to the host, due to metastases