Physics EOY
1/320
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
321 Terms
A physical quantity:
can be measured
has its own unit
expressed as numerical value with a unit
Physical quantity Formula
Physical quantity = numerical value x unit
Physical quantities can be classified into
base qualities
derived qualities
Precision of an instrument
smallest unit that the instrument can measure
Base Quantities (7)
Mass
Length
Time
Electric Current
Temperature
Amount of Substance
Luminous Intensity
SI Base Units (7)
kilogram
metre
second
ampere
kelvin
mole
candela
Mass Base Unit
kg
Length Base Unit
m
Time Base Unit
s
Electric Current Base Unit
A
Temperature Base Unit
K
Amount of Substance Base Unit
mol
Luminous Intensity
cd
Derived Quantities (7)
Force
Pressure
Work Done
Power
Electric Charge
Electromotive Force
Frequency
Define Derived Quantities
Quantities that are obtained with a formula that comprises operations of base quantities
Force Formula
F = Mass x Acceleration
Pressure Formula
P = Force/Area
Work Done Formula
Work = Force x Distance
Power Formula
Power = Work/Time
Electric Charge
Electric Charge = Current x Time
Force SI unit
Newton, N
Pressure SI unit
Pascal, Pa
Work SI unit
Joule, J
Power SI unit
Watt, W
Frequency SI unit
Hertz, Hz
Express unit of kinetic energy in terms of base units.
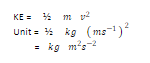
Prefixes
Tera
Giga
Mega
Kilo
Deci
Centi
Milli
Micro
Nano
Pico
To get more kisses, daddy cooks mommy more nice pancakes
Tera (T)
1012
Giga (G)
109
Mega (M)
106
Kilo (k)
103
Deci (d)
10-1
Centi (c)
10-2
Milli (m)
10-3
Micro (micro)
10-6
Nano (n)
10-9
Pico (p)
10-12
Stuff I should know
Unit Conversion
Standard Form
Estimation
Common instruments to measure length
Tape Measure
Metre Rule
Calipers
Digital Calipers
Digital Micrometer Screw Gauge
Precision of metre rule
0.1 cm
Precision of tape measure
0.1 cm
Precision of digital calipers
0.01 mm
Precision of digital micrometer screw gauge
0.001 mm
Parts of a digital caliper
Outside Jaws
Inside Jaws
Digital Display
Zero Button
Depth Rod or Tail
Parts of a digital micrometer screw gauge
Anvil
Spindle
Thimble
Ratchet
Zero Button
Stop Watch Precision
0.01 seconds but only record 0.1
Define period of oscillation
Time taken by the pendulum to complete one oscillation
What is an oscillation
One full swing, back and forth
Period of oscillation is independent on:
the mass of pendulum bob
initial angle of displacement
Period formula
Total time/Number of oscillations
Define scalar quantities
physical quantity which has magnitude only
Scalar = magnitude, unit → speed = 10 ms-1
Define vector quantities
physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction
Vector = magnitude, unit, direction → velocity = 10 ms-1 due west
Scalar quantity example
distance
speed
mass
energy
Vector quantity example
displacement
velocity
weight
acceleration
Define kinematics
motion of a body or a system of bodies, without consideration of its mass or the forces which cause the motion
Define Distance
total length travelled by a body regardless of the direction of motion
Distance = scalar, metre (m)
Define displacement
distance measured in a straight line in a specified direction
Displacement = vector, metre (m)
Define speed
body defined as the distance travelled per unit time
Speed = scalar, metre per second (m s-1)
Define average speed
total distance travelled divided by the total time
Define instantaneous speed
speed of the body at any given point in time
Define velocity
change in displacement per unit time
Velocity = vector, metre per second (m s-1)
Define acceleration
change in velocity per unit time
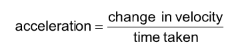
Acceleration = vector, metre per second squared (m s-2)
When does velocity change?
When a body accelerates, decelerates or changes direction
Define rectilinear motion
two possible directions for body to move, must be opposite
Displacement-Time Graph Uniform Velocity
Gradient Formula
Change in y/Change in x
Gradient of a displacement-time graph is the ______
velocity
Describe motion of Uniform Velocity D-T Graph: Answer format
velocity of object from t1 to t2 is constant at [velocity]
direction (positive/negative)
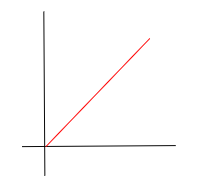
displacement-time
constant velocity, positive
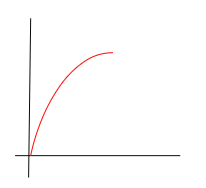
displacement-time
deceleration, positive
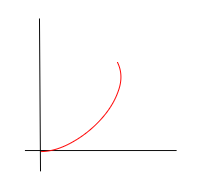
displacement-time
acceleration, positive
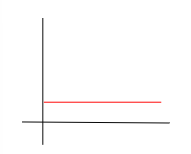
displacement-time
zero acceleration, zero velocity
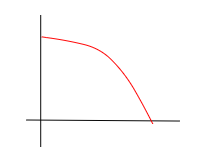
displacement-time
acceleration, negative
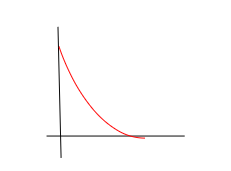
displacement-time
deceleration, negative
When describing curves: Answer Format
Sign of gradient of curve (positive, negative, zero)
Changes in magnitude of gradient (increasing/acceleration, decreasing/deceleration, constant)
The gradient of a velocity-time graph is the _________
acceleration
Area under velocity-time graph is ____________
change in displacement
Example of Answer Format for Velocity Time
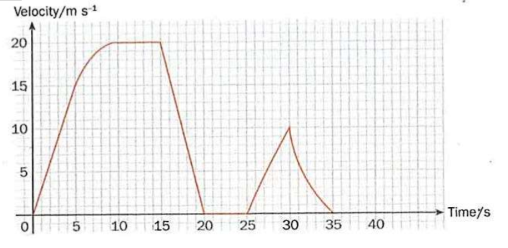
From t = 0 to t = 5, the body is traveling with a constant acceleration at 3 ms-2. Direction of acceleration is in the positive direction, or velocity of the body increases proportionately with time from ms-1 to 15ms-1.
From t = 5 to t = 10, the body is accelerating at a decreasing rate, reaching a velocity of 20 ms-1. Direction of acceleration is in the positive direction.
From t = 10 to 1 = 15, the body is traveling at a constant velocity of 20 ms-1.
From t = 15 to t = 20, the body is decelerating uniformly at 4ms2. The direction of acceleration is in the negative direction and body comes to a stop at t = 20s.
From t = 20 to t = 25, the body is stationary.
From t = 5 to t = 30s, the body is traveling with a constant acceleration at 2 ms-2. Direction of acceleration is in the positive direction.
Finally, from t = 30 to t = 35, the body is decelerating at a decreasing rate. The direction of acceleration is in the negative direction and body comes to a stop at t = 35s.
Define a freely-falling body
a body that moves under the influence of gravitational force of attraction only
falls with a constant acceleration of 9.81 ms-2
What is terminal velocity?
body accelerate downwards → velocity increase
velocity increase = air resistance increase → acceleration downwards decreases
air resistance becomes equal to weight → net acceleration becomes zero
body travels at uniform velocity = terminal velocity
Air resistance is _________ on velocity.
dependent
For the equations of motion to be valid, what conditions need to be fulfilled?
acceleration is constant
motion is rectilinear
Kinematic Equation Formulas
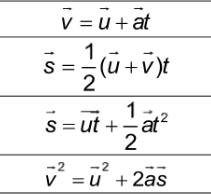
Define constant force and provide examples
act when two objects have physical contact
applied
normal contact
frictional
elastic
viscous
Define non-constant force and provide examples
act over a distance without physical contact between two objects
gravitational
magnetic
electric
non-contact forces are also called ____
field forces
Define gravitational field
a region in which a mass experiences a force due to gravitational acceleration
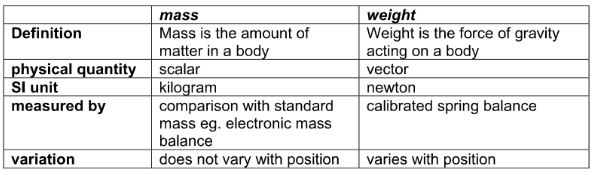
Compare mass and weight
Define inertia
Inertia refers to the resistance of a body to resist a change in the state of rest or motion of the body.
Greater mass = _______ inertia
greater
Define normal contact force
perpendicular force extended by the surface of one object on the surface of another when they are in physical contact and it prevents objects from passing through each other
Characteristics of the normal contact force (4)
only exists when an object is in contact
always perpendicular to contact surface and its direction is through object of interest
normal force does not always pass through the CG of the object
magnitude can change; not always equal to weight of object
When magnitude of normal contact is equal to weight, the object is said to be in __________
equilibrium
Define friction
contact force that acts between objects that opposes or tends to oppose or resist motion
always act opposite to direction of motion at point of contact
Characteristics of friction
When contact surfaces are smooth → little to no friction
When contact surfaces are rough → friction
Parallel to surface
Magnitude of friction is proportional the normal force
Viscous force is also called ___ and ____
drag, air resistance
Viscous force _____ with speed of the object and ____ with the surface area of the object.
increases, linearly
Greater speed = ___ viscous
larger
Greater surface area = _____ viscous force
larger
Viscous force depends on __________
nature of fluid