7. Temperature
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Methods of temperature measurement
pressure/volume(thermal expansion)
contact potential btw diff metal
resistance of metal/semiconductor
energy radiation
Working mechanism of a thermoelectric temperature sensor (thermocouple)
2 different metal joint at both end
Seebeck effect: when junctions of the metal experience different temperature, electric current flows
contact potential (difference in electric potential difference) increases with temperature
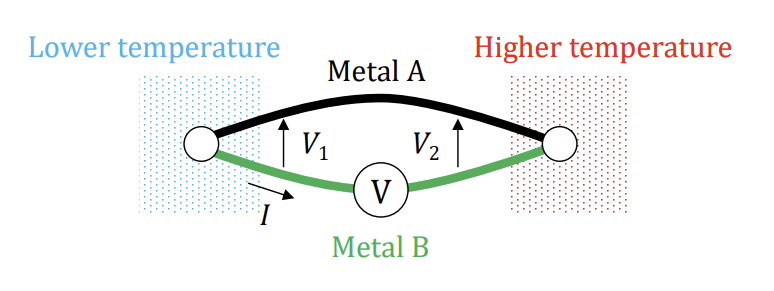
how does contact potential occur
junction of 2 different metal always produces contact potential
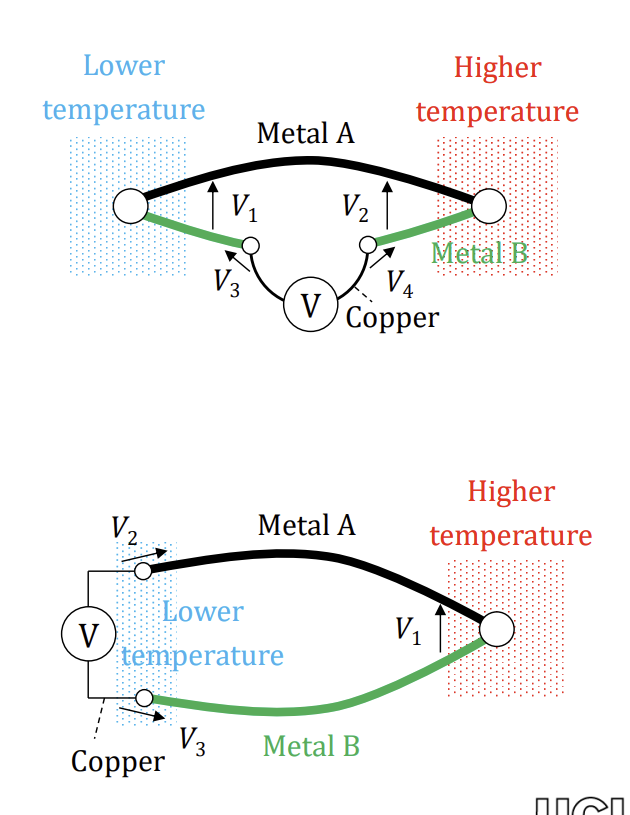
How to account for contact potential of wires connecting the voltmeter (2 ways)
ensure junction of wire and voltmeter wire is kept at same temperature, therefore the contact potential produced cancels out
connect in second configuration, such that V1=V2-V3
Factors to consider when choosing type of thermocouple
sensitivity and temperature range
application to corrosive environment
withstand thermal and mechanical stress
accuracy
price
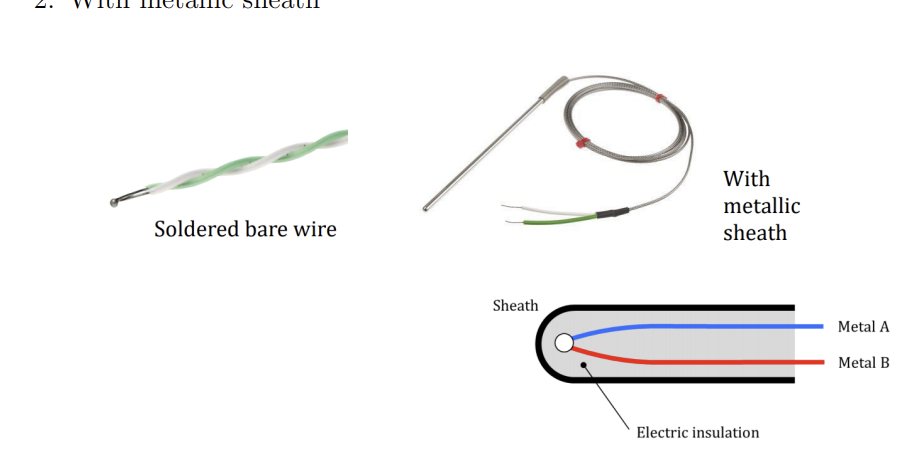
Difference between thermocouple probe ends:
soldered bare wire
metallic sheath
Metallic sheath:
can touch conductive surface due to inner insulation
longer response time as sheath and insulation has to be heated up before it reaches junction
Insulation material has high resistance and thermal conductivity

Working mechanism of basic metallic resistance thermometer + formula
resistance of certain metal changes with temp
α: temperature coeff of resistance
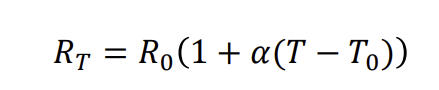
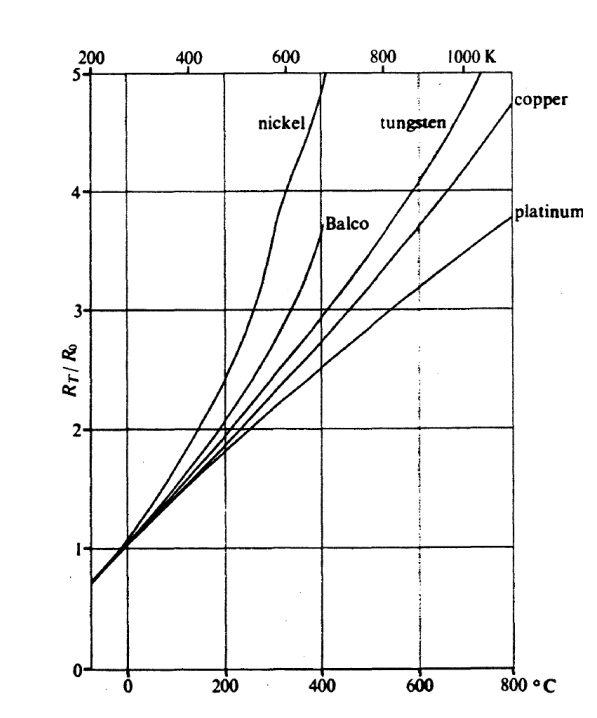
Reasons platinum is commonly used for metallic resistance thermometer + 1 disadvantage
platinum typically used for
stability
reproducibility(linear relationship)
inert and resistant to contamination
disadvantage: less sensitive compared to other metals
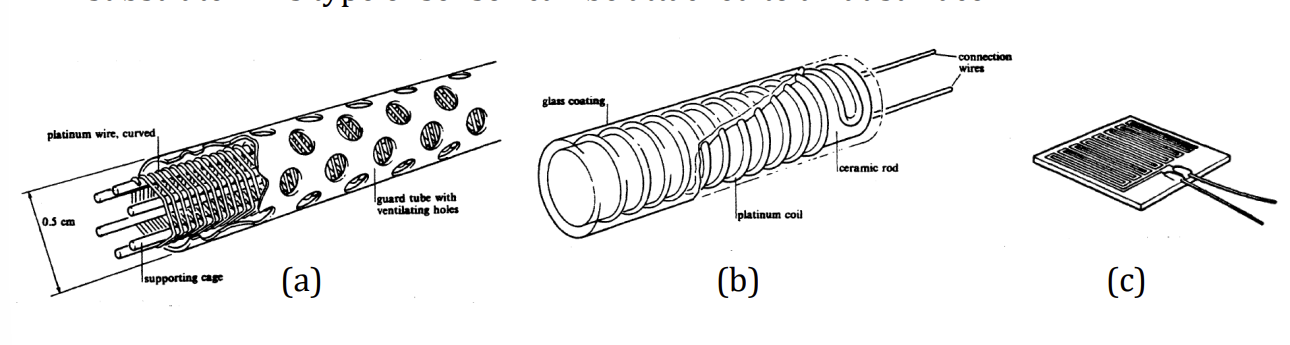
3 types of metallic resistance thermometer construction
a. wire directly exposed to fluid measured
b. isolated by ceramic rod to prevent contamination that could change relationship to temeperature
c. metal deposited as thin film pattern on insulating substrate and attached to flat surface
2 Potential errors occur in metallic resistance thermometer
self heating effect-electric current heats up wire due to energy dissipation
Thermoelectric effect(seebeck effect): if resistance wire and lead wire is made of different material, additional current will flow
Relationship of resistance and temperature of a thermistor (semiconductor resistance thermometer)
resistance decrease with temperature increase
larger negative temperature coefficient of resistance
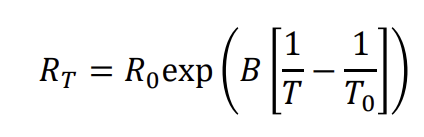
difference between thermistors and metallic resistance thermometer
smaller
responds to temperature variance more quickly
BUT
self heating effect is greater→ should operate at lower current levels
How does resistive thermometer be converted into voltage
due to small current levels, thermistor x is large, and approximation of small x does not apply
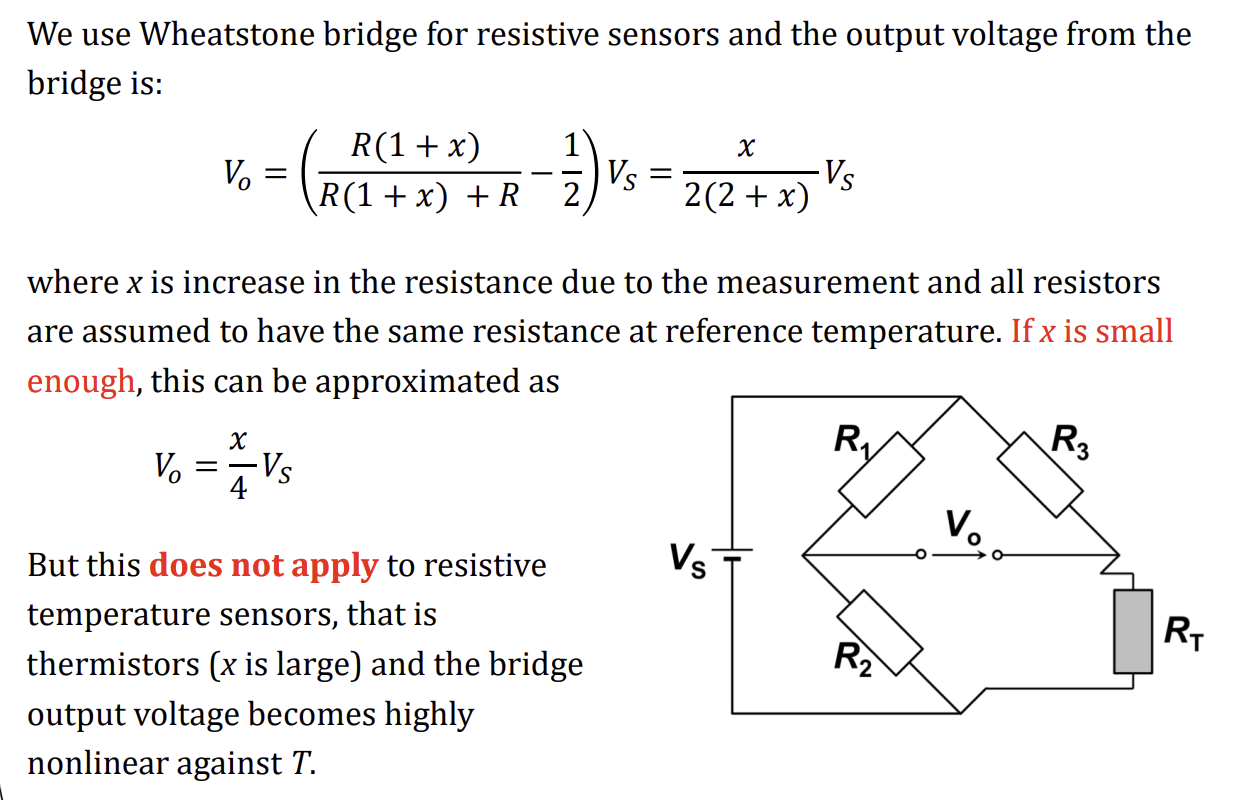
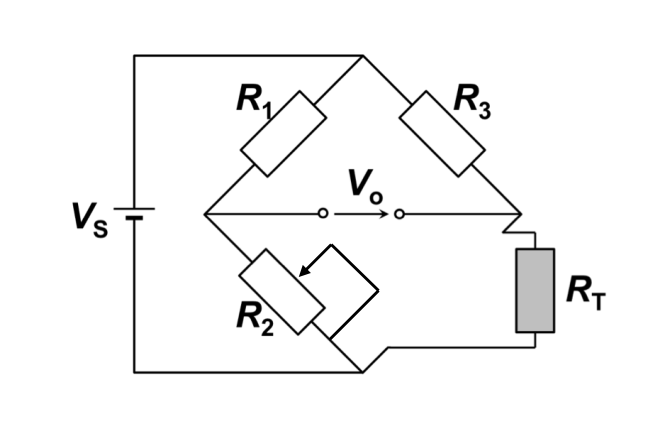
How to determine temperature by varying R2
change R2 to ensure V0=0
therefore R2=RT
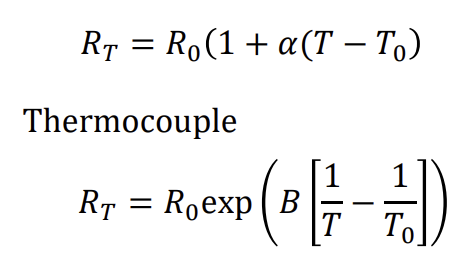

Working principle of radiation pyrometer
detect infared radiation given by object measured
temperature transducer used in detector (e.g. thermopile) is converted to radiation energy using Stefan-Boltzmann law - detect temperature from radiation NOT surface temperature)
energy converted to temperature of measured surface using black body energy plot
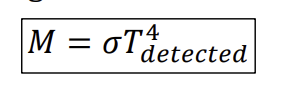
Definition of black body
black body emit radiation in all wavelengths
a ‘body’ at a certain temperature emits certain amounts of enerhy at certain spectrum
any object that temperature is not absolute zero will emit radiation
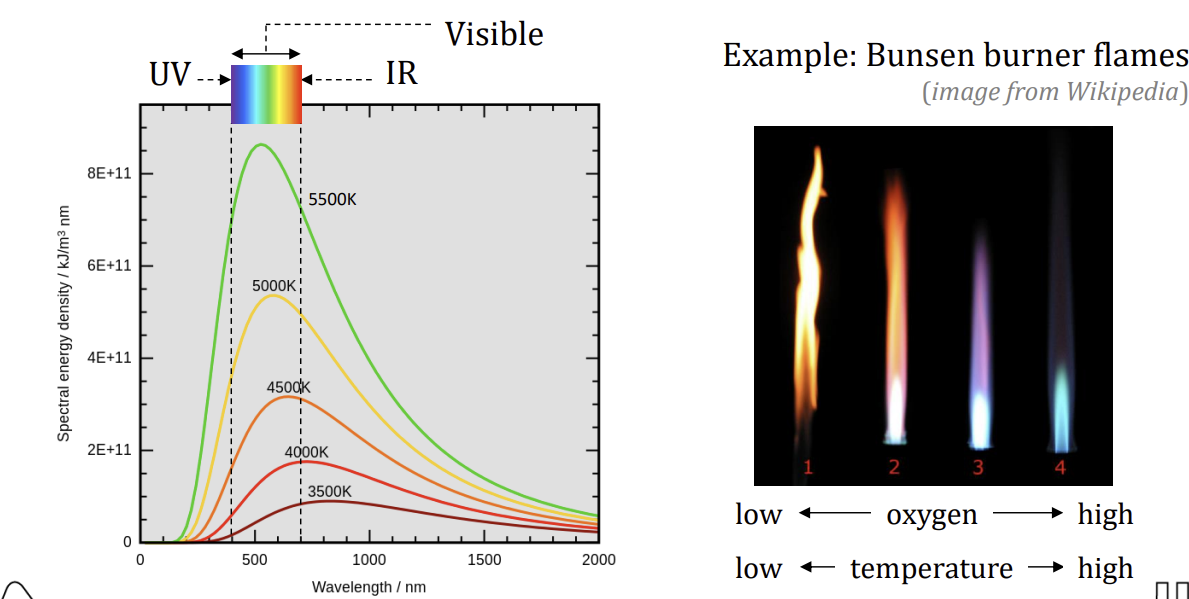
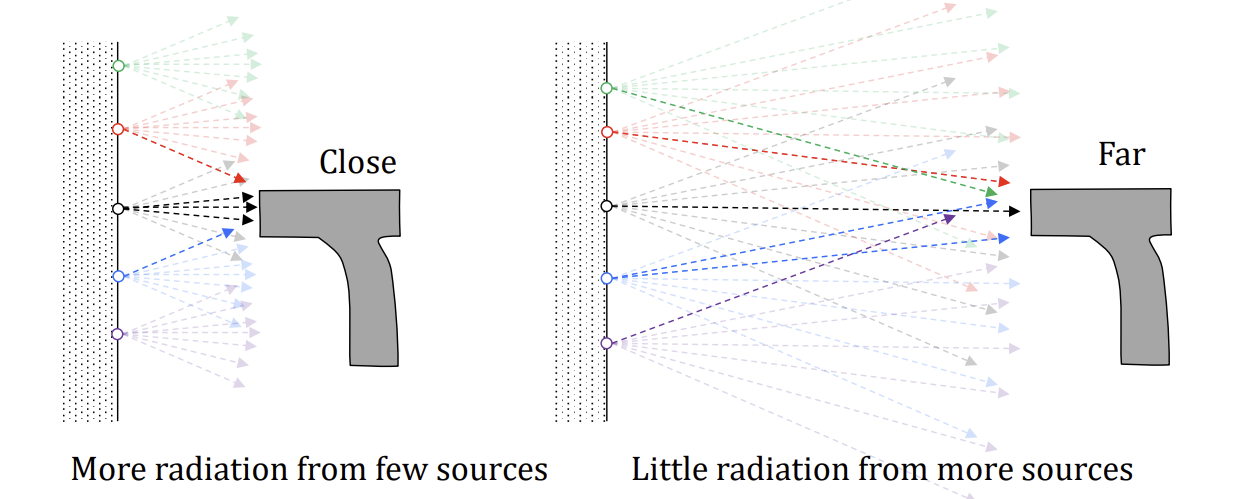
Advantages and disadvantages of pyrometers
GOOD:
short response time
distance independent measurement
BAD:
error for reflective or transparent/translucent surface
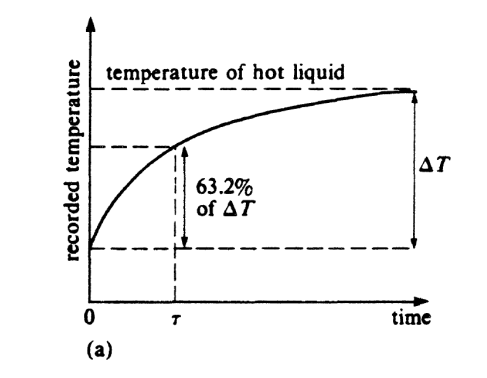
Equation of temperature response time for a constant temperature
speed of change is categorised by time constant (1/K) or time when it reached 0.63(Tf-T0)
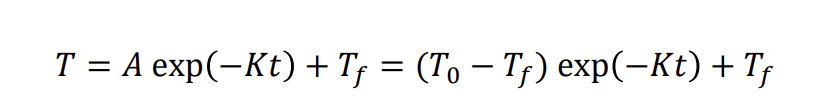
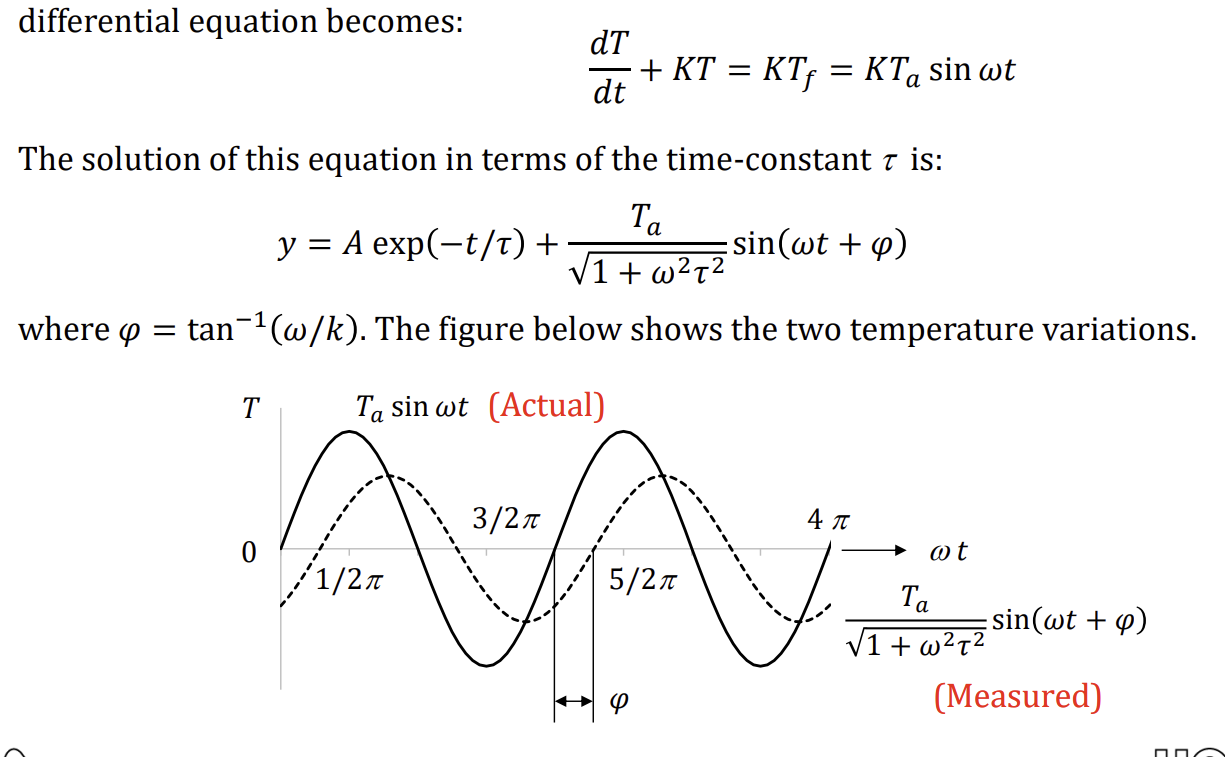
Equation of temperature response time for a sinusoidally varying temperature
the lag causes the measured temperature to not accurately measure the maximum temperature