Midterm OB/GYN ~ Sept 2025
1/317
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 41 - 52
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
318 Terms
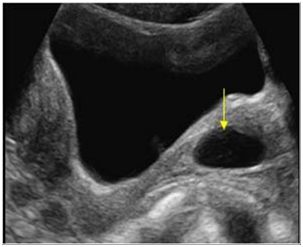
MC benign cyst in vagina
Gartner Duct Cyst
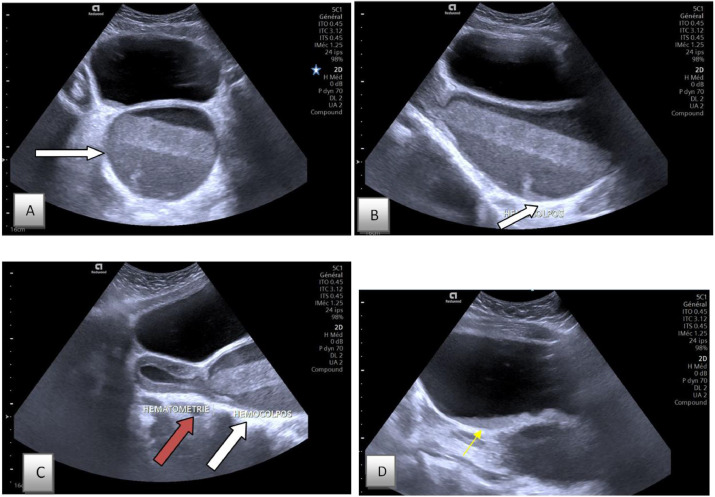
MC congenital abnormality in the female GI TRACT
results in
hydrometra
hematometra
pyometra
Imperforated Hymen
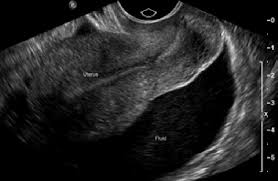
MC area of intraperitoneal fluid collection
can happen in anterior cul-de-sac
Posterior Cul-de-sac
Cervix normal measurement
2- 4 CM
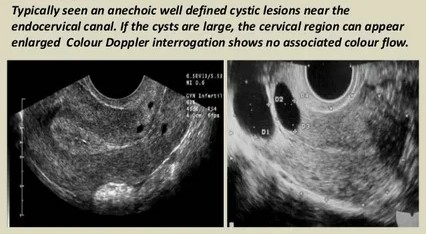
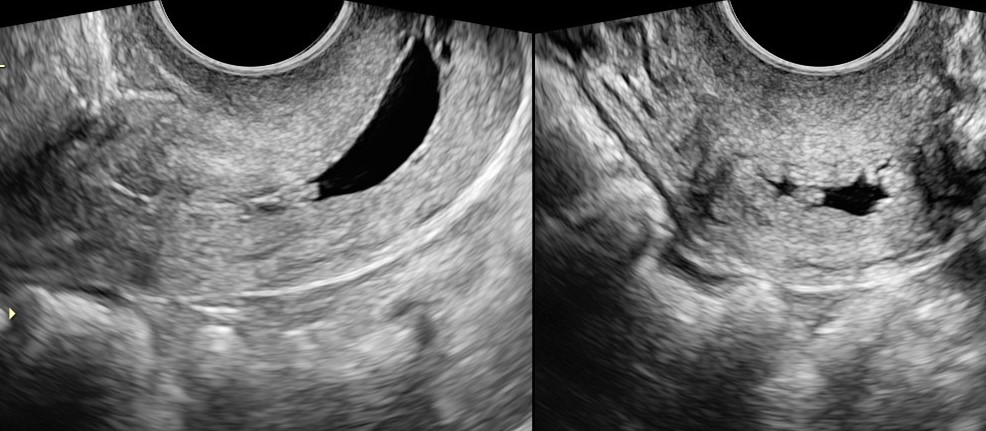
MC benign cystic lesion
caused by
chronic cervitis
<2 cm cysts
Nabothian Cyst
Irregular bleeding
benign
may be pedunculated
45 - 60 yrs (late middle ages)
Cervical Polyp
caused by
radiation
surgery
infection
menopause
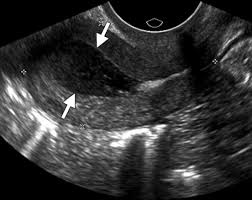
post meno - hydro/hemato/pyo metra
pre meno - inferility, cramps, irregular or no period
Cervical stenosis
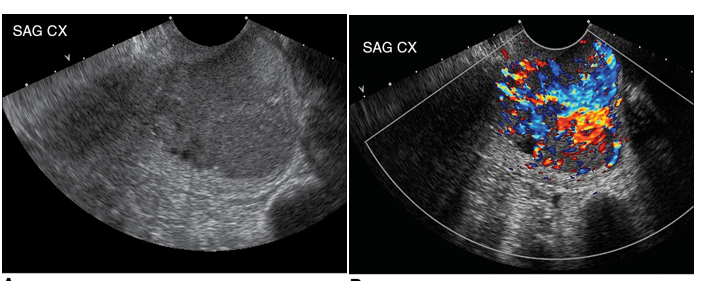
Mc cervical malignancy
vaginal discharge/bleeding
Cervical Carincoma (MC: squamous cell carcinoma)
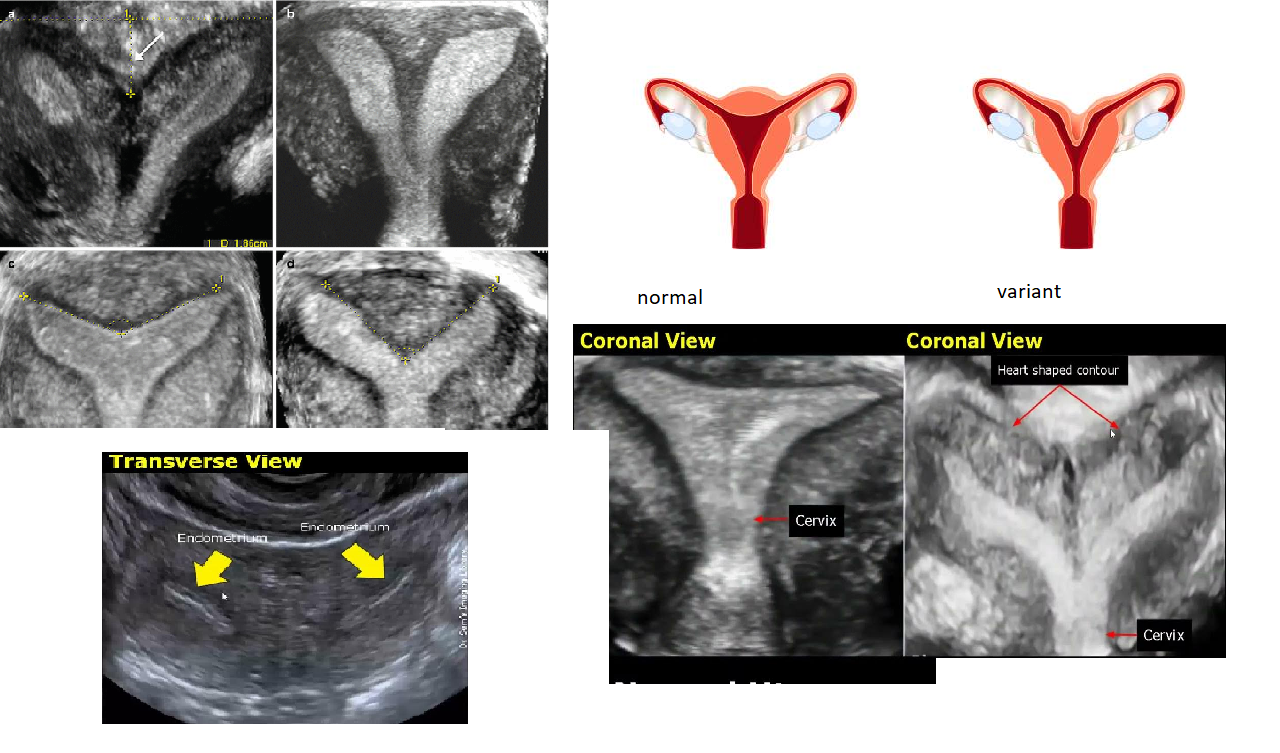
congenital anomaly
incomplete mullerian duct fusion
Bicornuate uterus
2 uterus
2 cervix
Failure of mullerian duct fusion
congenital anomaly
Uterus Didelphys
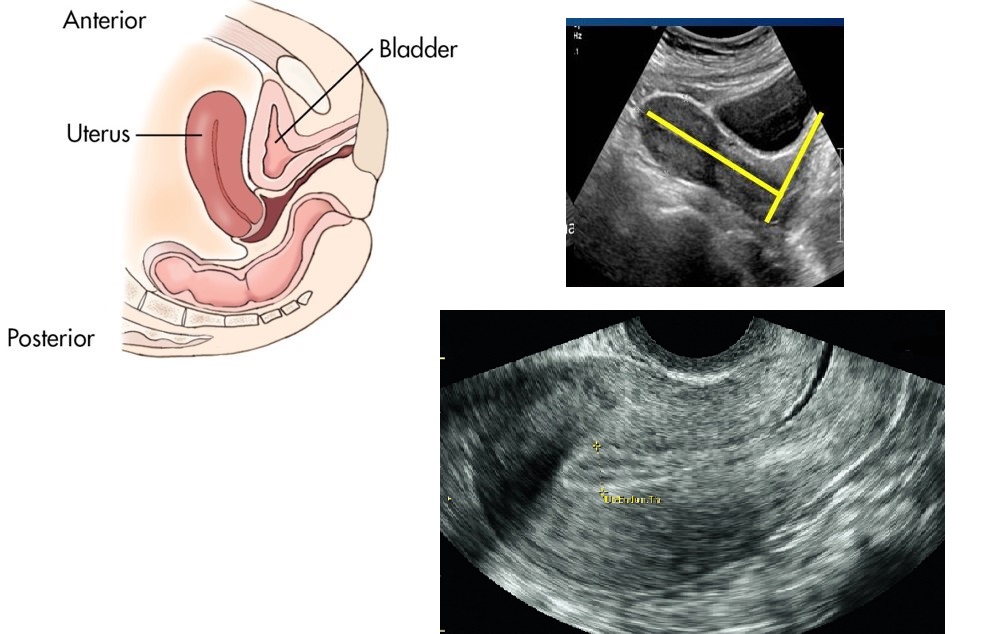
MC uterine position
Anteverted
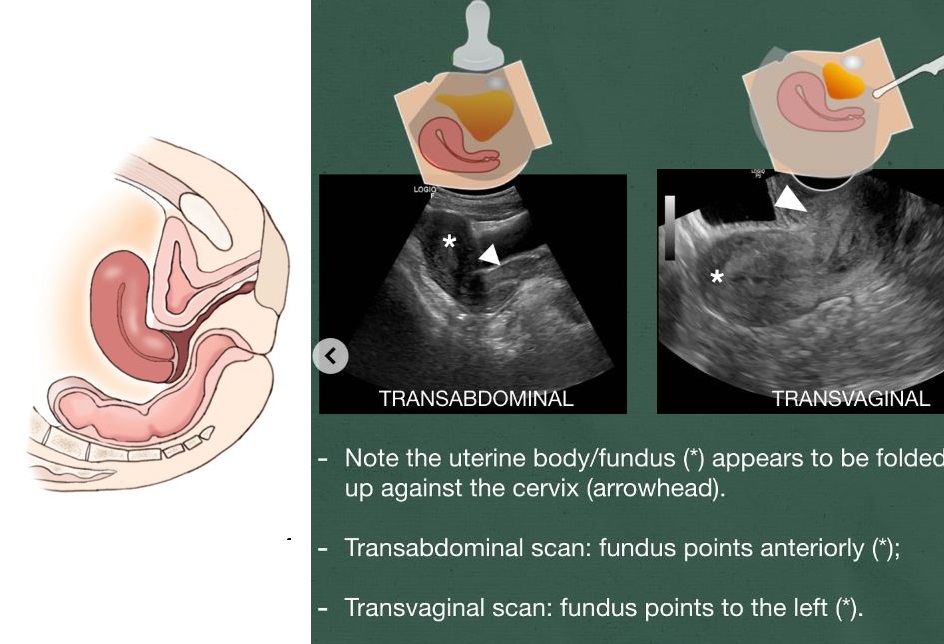
Anteflexed
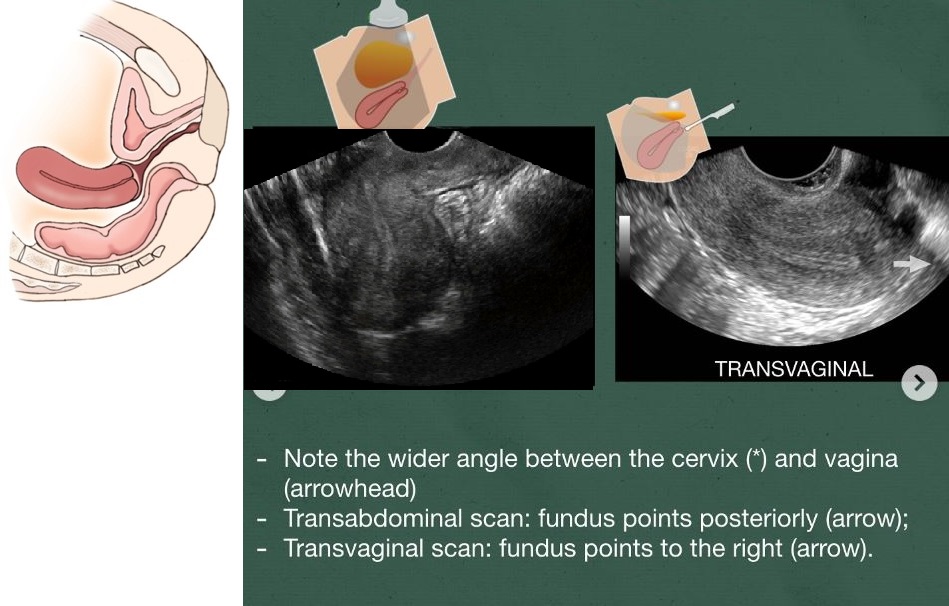
Retroverted
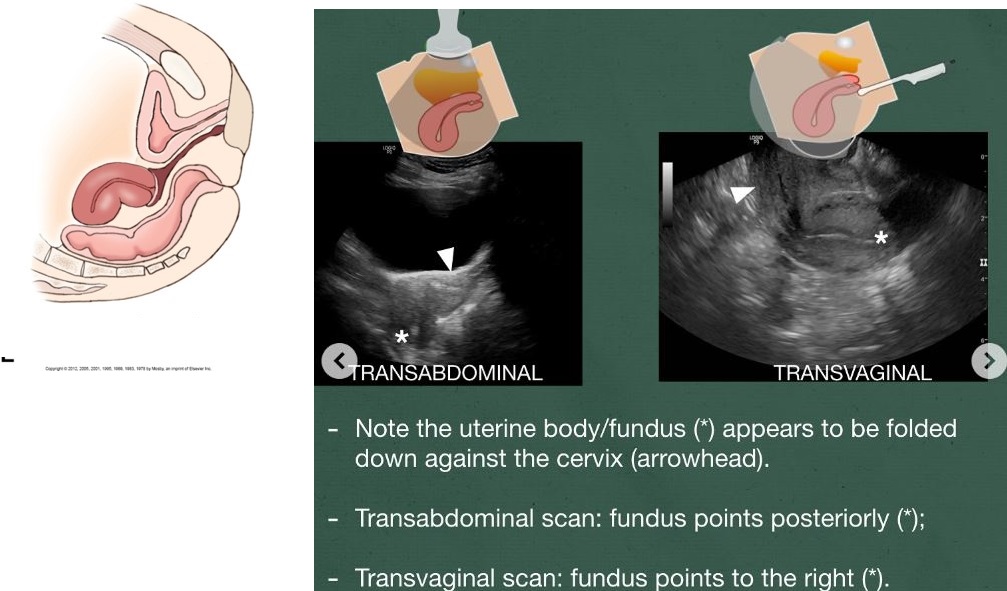
Retroflexed
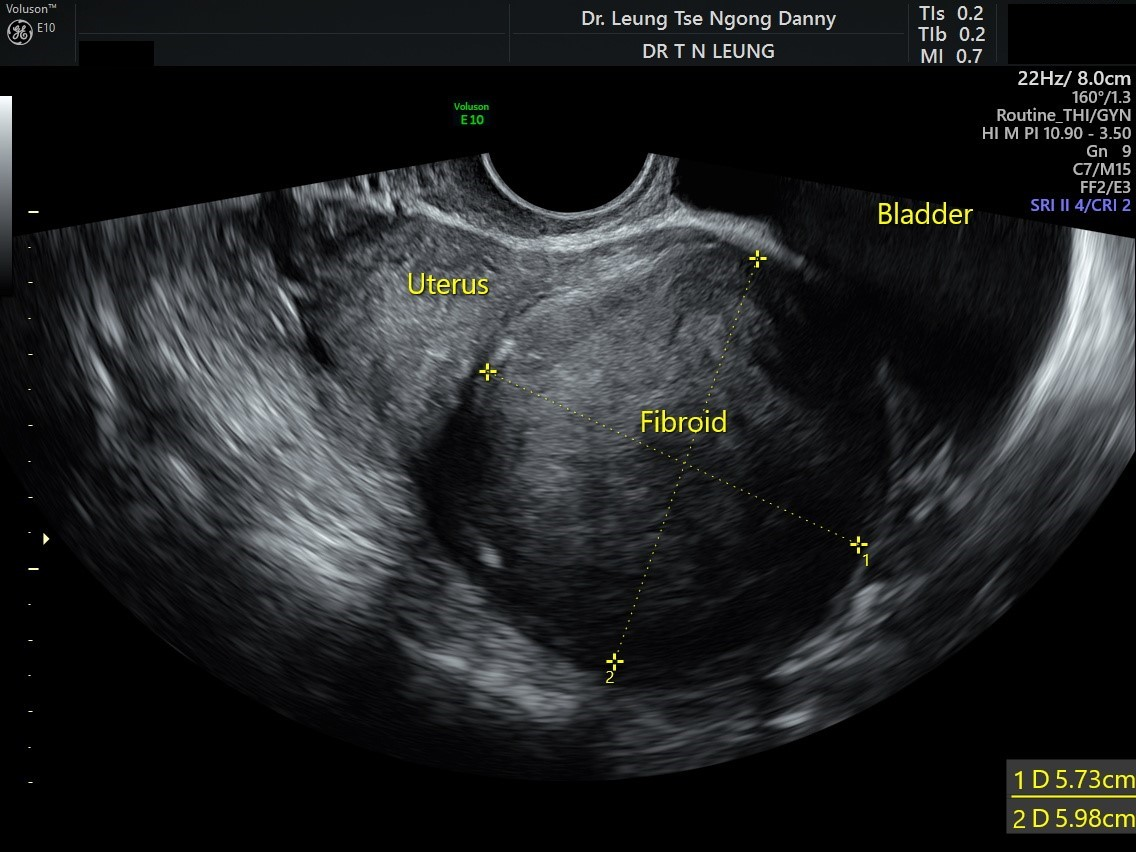
MC uterine pelvic tumor
> 30 yrs
Black women
estrogen-dependent
pelvic pain
pain
heavy or irregular bleeding
Leiomyoma (Fibroid)
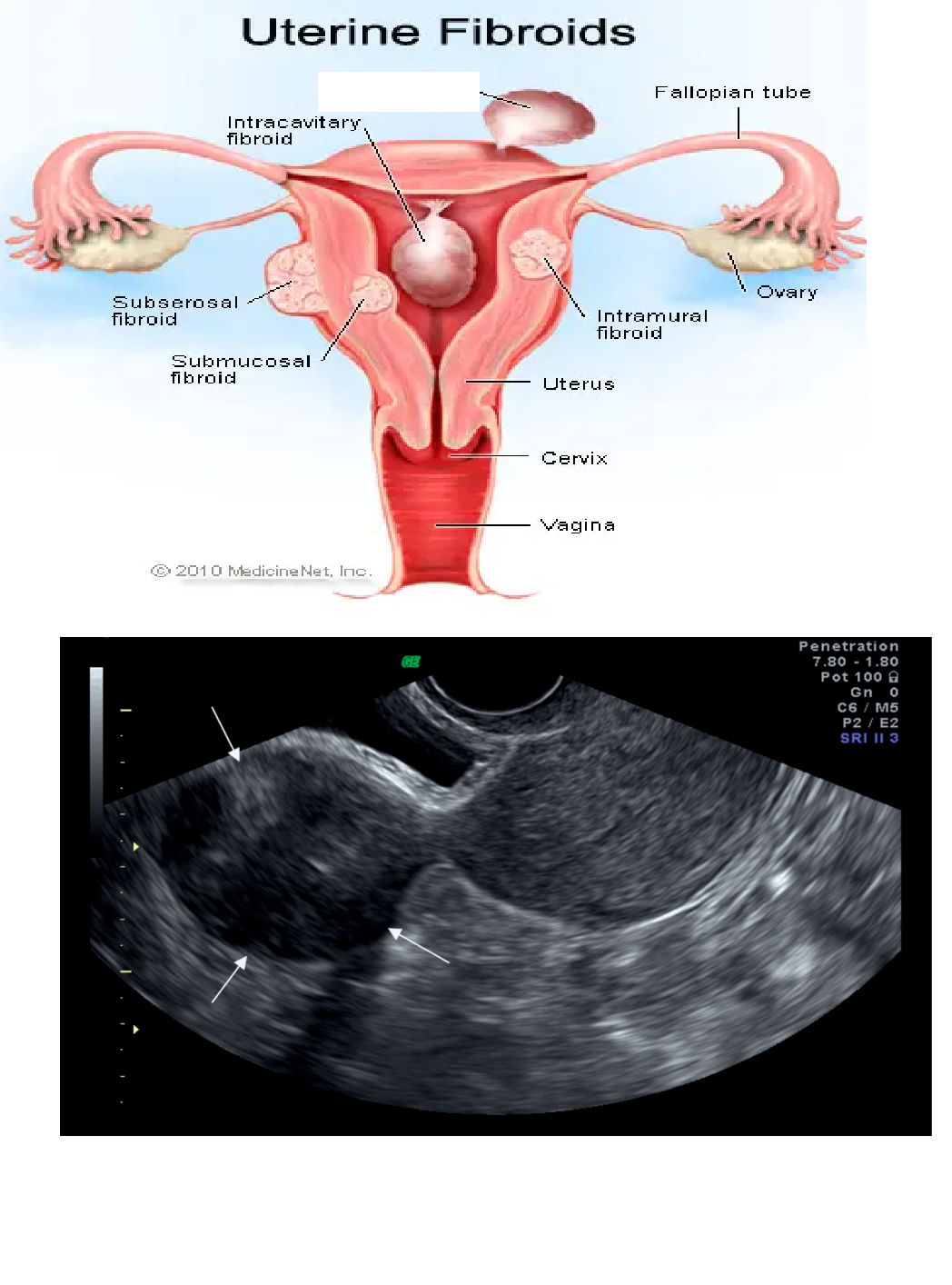
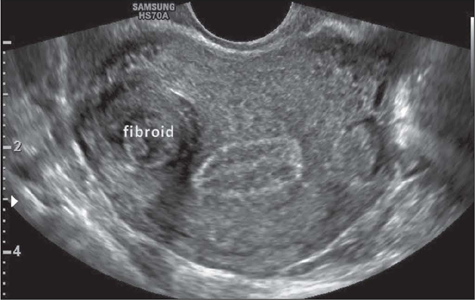
What kind of fibroid is this?
Has a stalk
Pedunculated Fibroid
Heavy bleeding
pregnancy loss
Infertility
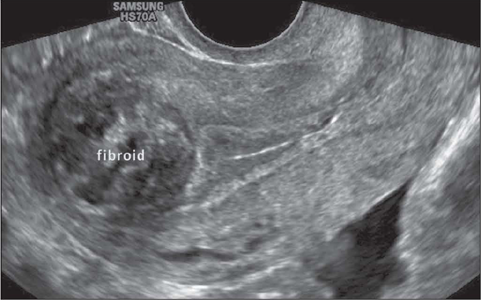
wha location is this?
Intramural (within myometrium)
Fil in blank
Intramural Fibroid
Fill in blank
Submuosal Fibroid
bleeding
ANEMIA
fertility issues
what location is this
Submucosal (in endo)
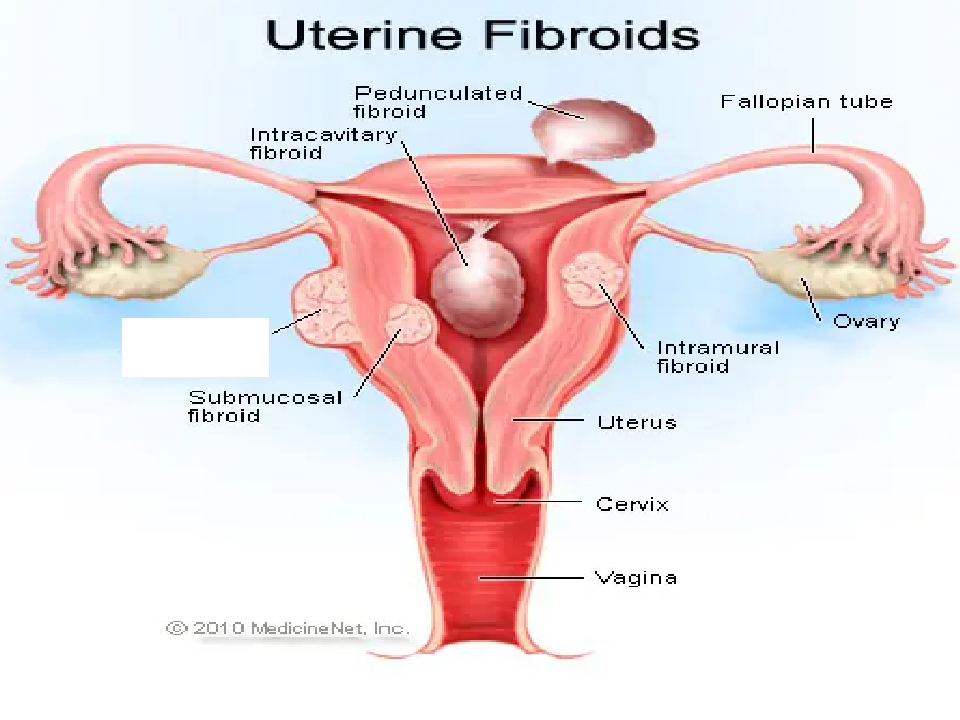
Fill in blank
Subserousal Fibroid
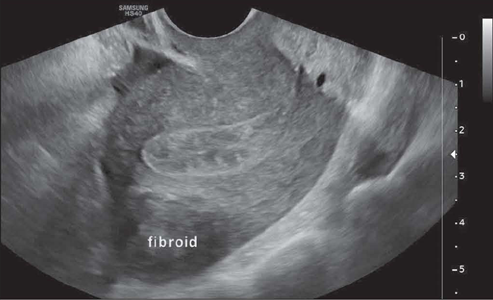
sometimes pedunculated (stalk)
Subserousal (outside)
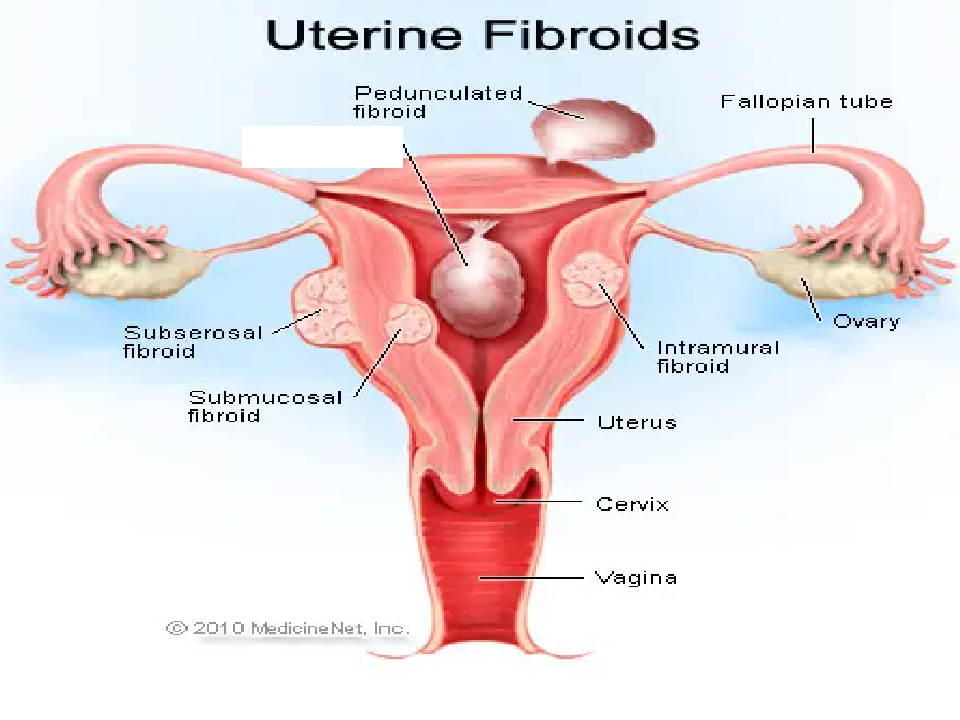
Fill in blank
Intracavitary Fibroid
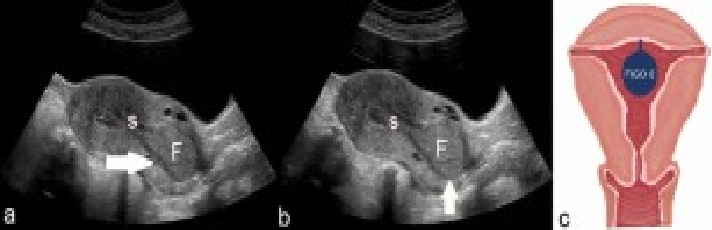
what location is this fibroid in ?
Intracavitary
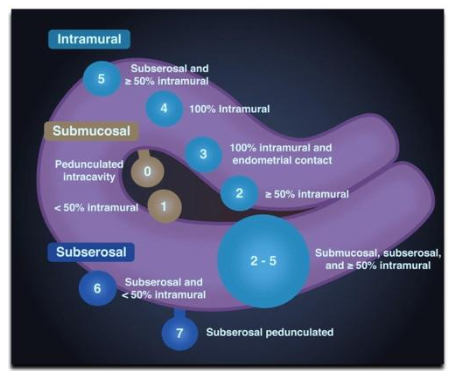
Fibroid location chart
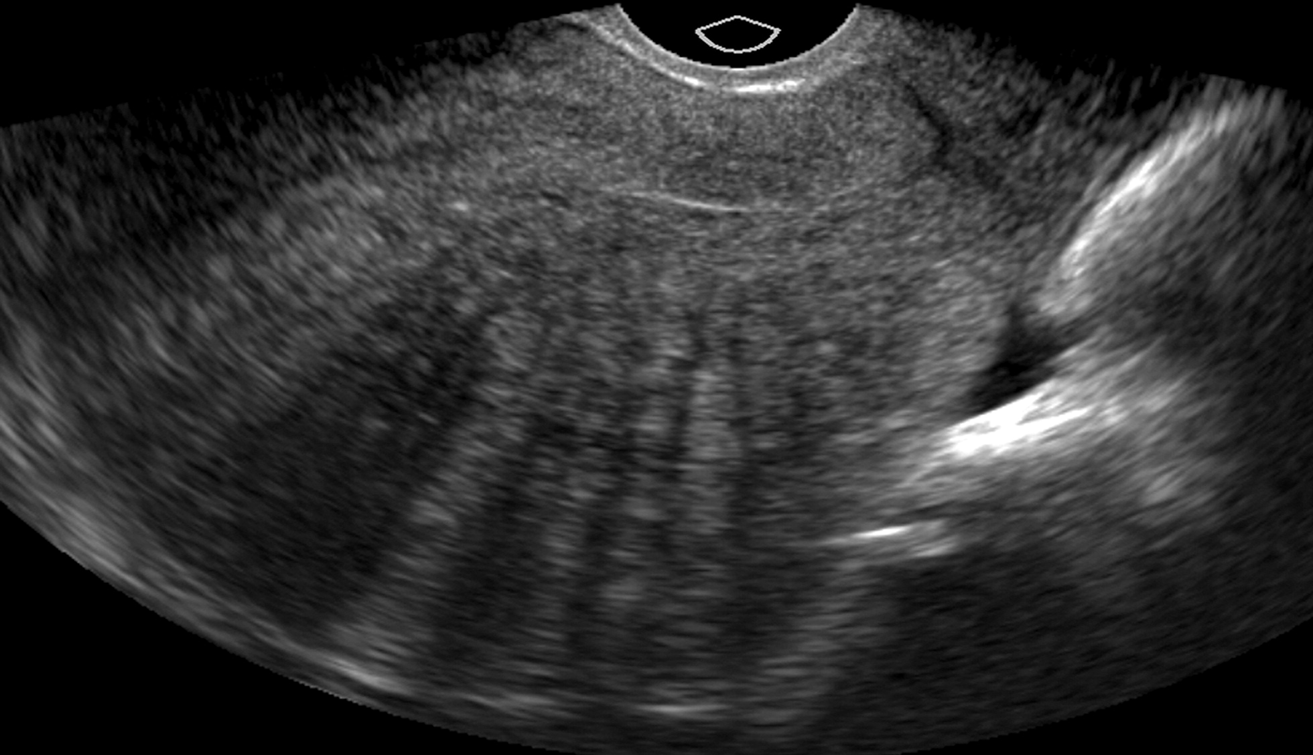
form of endometriosis (WITHIN MYOMETRIUM)
benign, ectopic occurrence of endometrial tissue invasion
OLDER WOMEN
MULTIPARIOUS
heavy, painful periods
tenderness
Hypermenorrhea (heavy bleeding)
metorrhea (irregular bleeding)
Adenomyosis
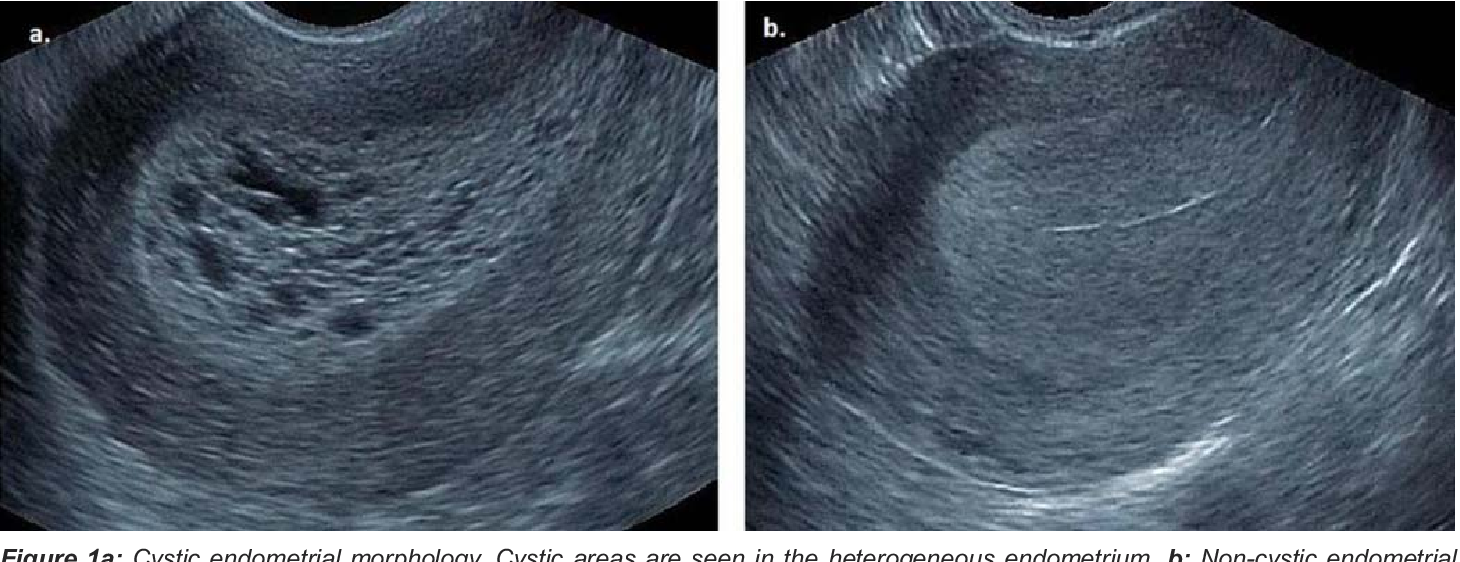
MC cause of abnormal uterine bleeding in PRE and POST menopausal
estrogen stimulation (PCOS, obesity)
pre meno > 14mm
post meno > 8 mm
precursor to cancer
Endometrial Hyperplasia
In menstrual phase, how thick is endo
2 -3 mm
In proliferative phase, how thick is endo?
4 -6mm
In periovulatory phase, how thick is endo?
6-8 mm
In secretory phase, how thick is endo?
8-15 mm
peri/post meno
(Premenopause → Perimenopause → Menopause → Postmenopause)
Menometrorrhagia (heavy, long, irregular bleeding)
infertility
Use color = highly vascular
Use sonohysterography
attached to the endometrium by a narrow or sometimes broad stalk.
Endometrial Poylp
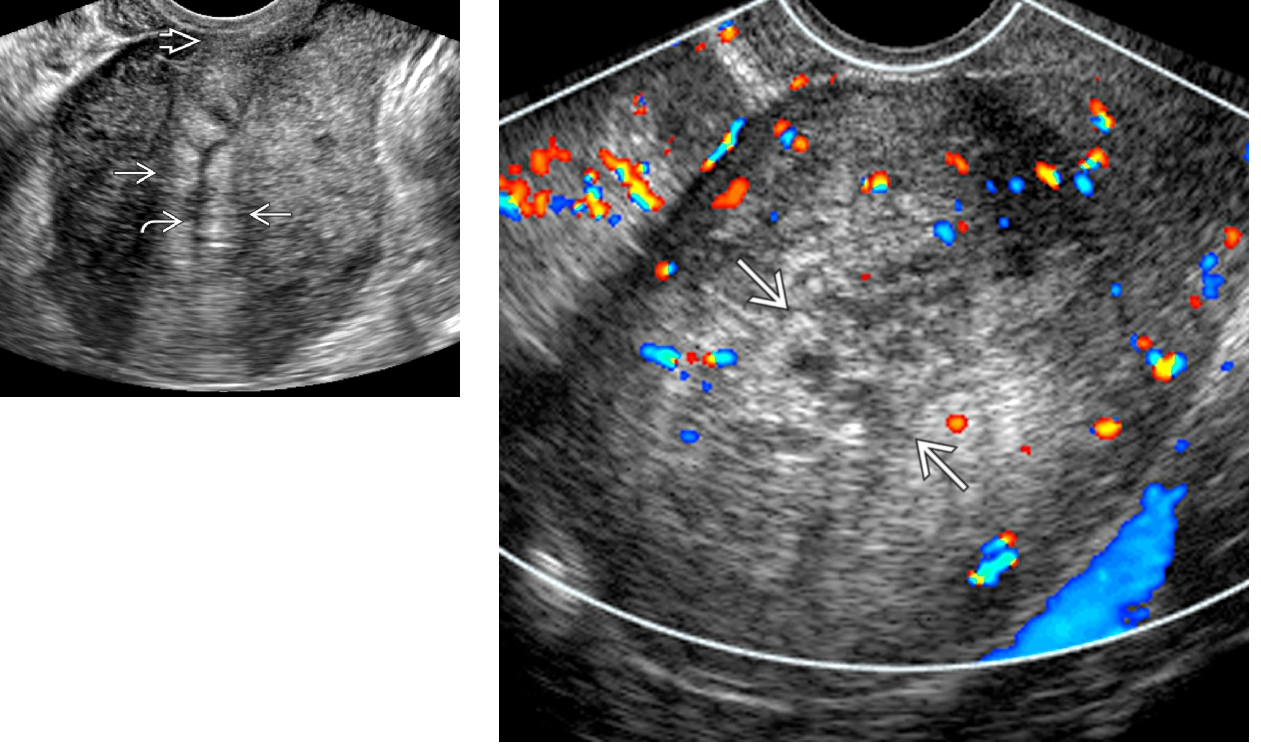
POSTPARTUM patients
PID pts
use of instrumentation causing infection
fever / HIGH WBC
pelvic pain
low back pain
vaginal bleeding
Endometritis
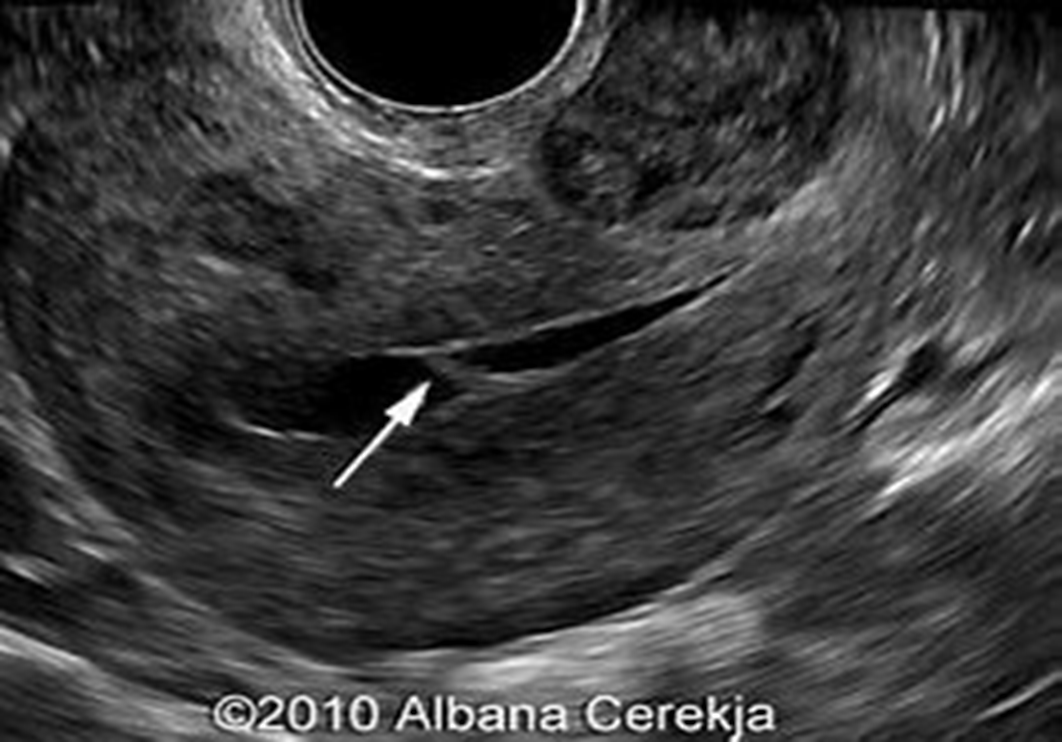
results from
trauma
surgery
D&C
C-section
Postpartum curettage
Synechiae
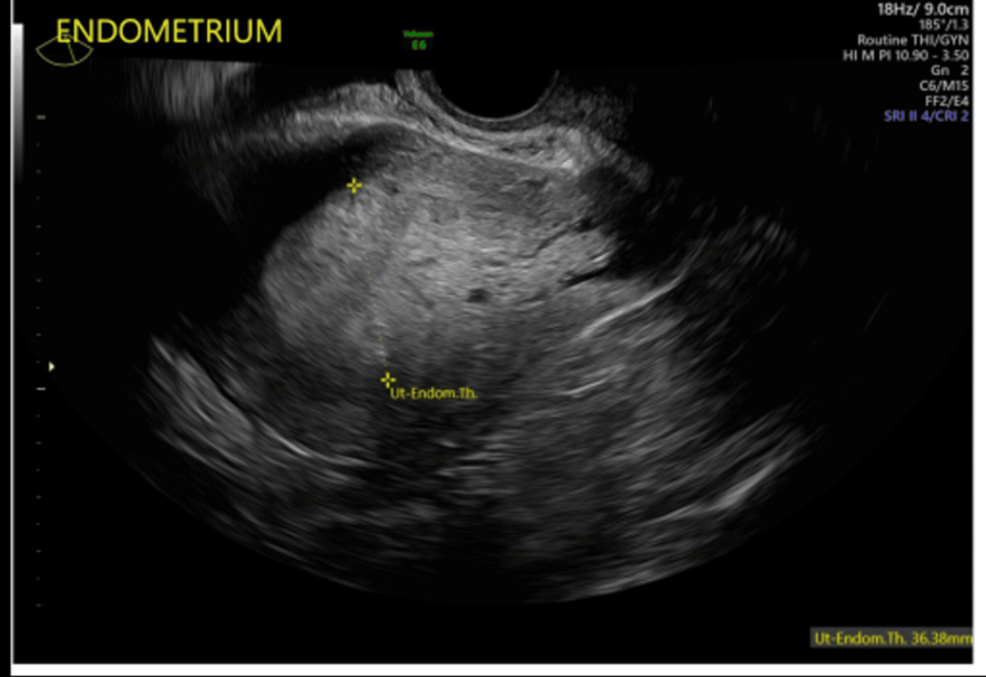
MC gynecologic MALIGNANCY in North America
postmeno
estrogen-therapy
tamoxifen
pre meno
anovulatory cycles
obesity
pelvic pain
Endometrial Carcinoma
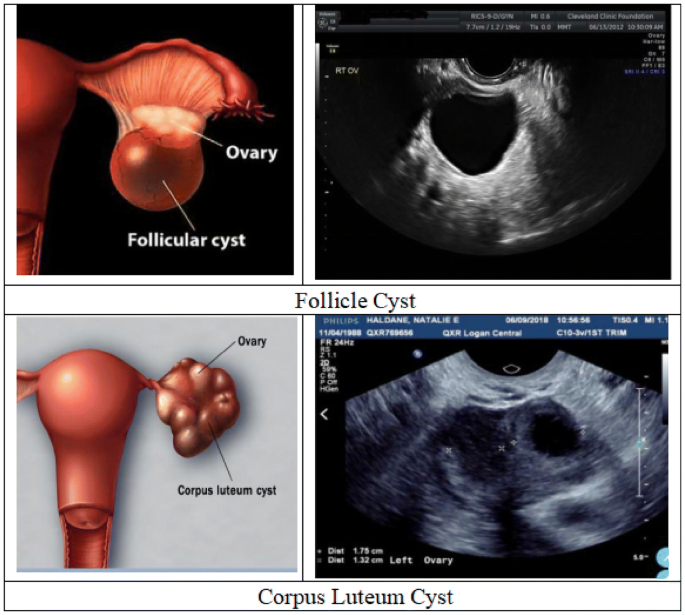
Happens when a dominant follicle fails to rupture or reseals (failed ovulation)
Usually >2.5 cm, typically up to 8–10 cm
Simple cyst
anechoic
clear thin walls
posterior enhancement
asymptomatic
dull, adnexal pressure
adnexal pain
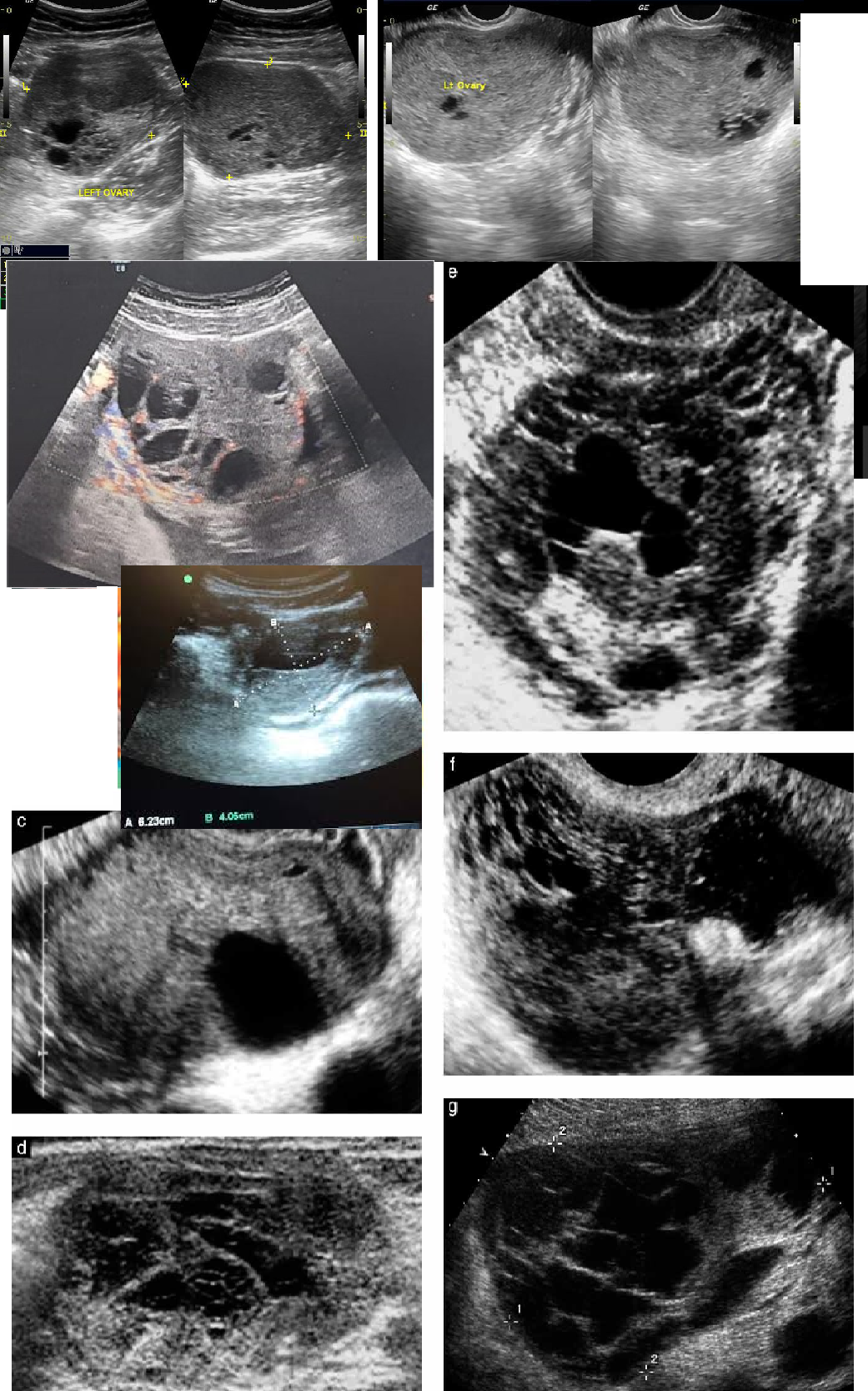
Follicular cyst(Functional cyst)
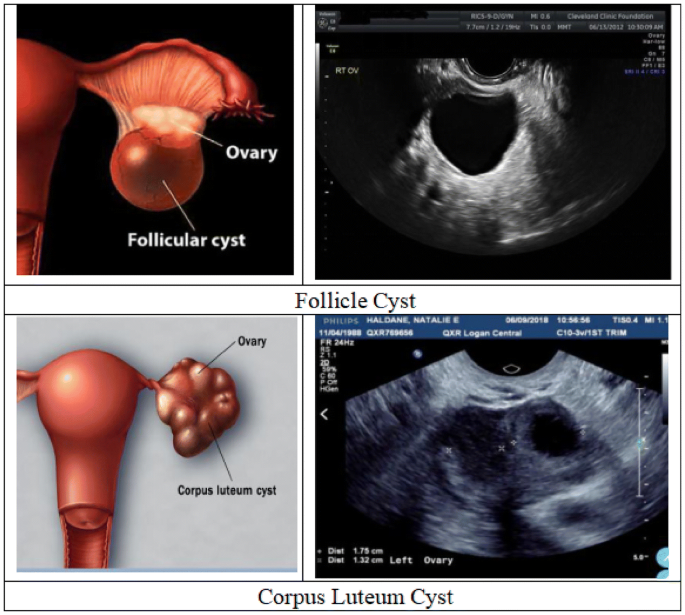
Ruptured dominant follicle normally becomes this.
Complex cyst
thick walls
1- 10 cm
“Ring of Fire”
Internal echoes with cystic fluid / blood
irregular mens cycle
pain
mimic ectopic pregnancy
rupture
Corpus Luteum Cyst
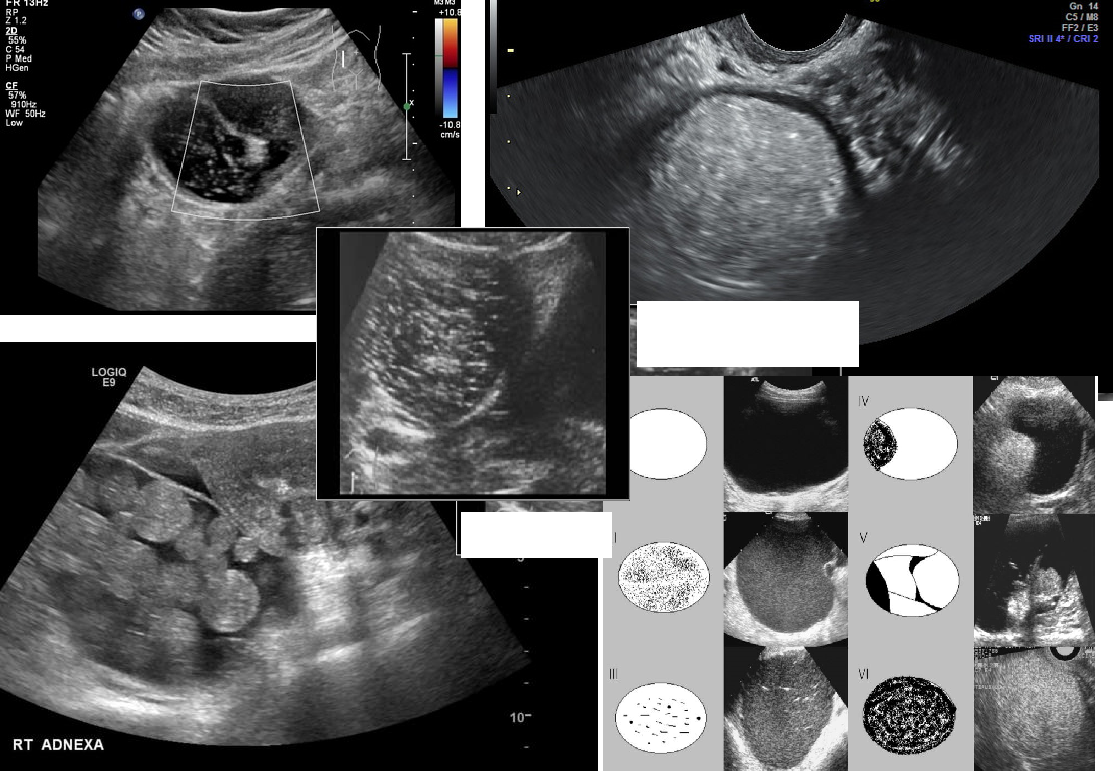
MC benign tumor of the ovary
abdominal pain / enlargement / pressure
complex solid mass with fat, teeth, hair, cartilage, bone
“tip of iceberg"
Immature type-
malignant, rare
10 - 20 yrs
AFP = HIGH
Teratoma (Dermoid Cyst)
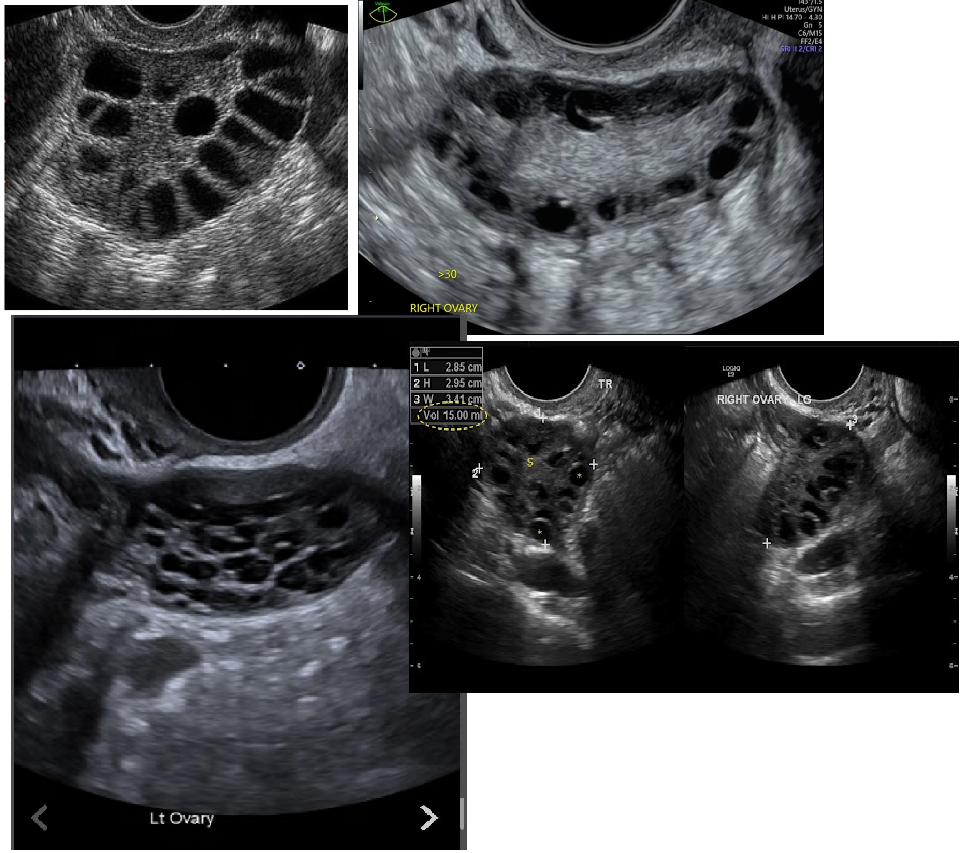
endocrine disorder
Chronic anovulation
late teens - 20’s
hirsutism
obesity
infertility
irregular periods/no period
high LH
low FSH
Includes stein- leventhal syndrome
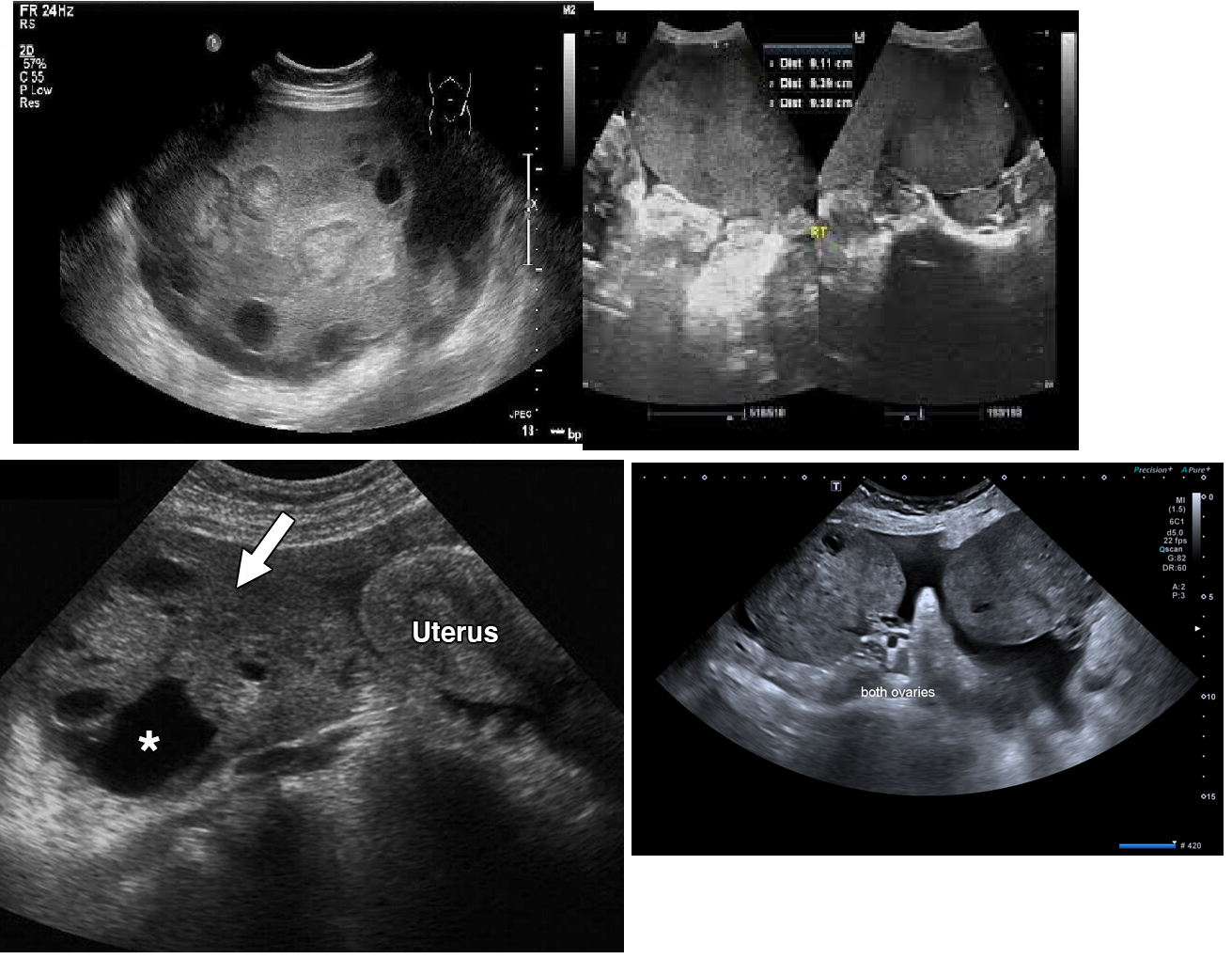
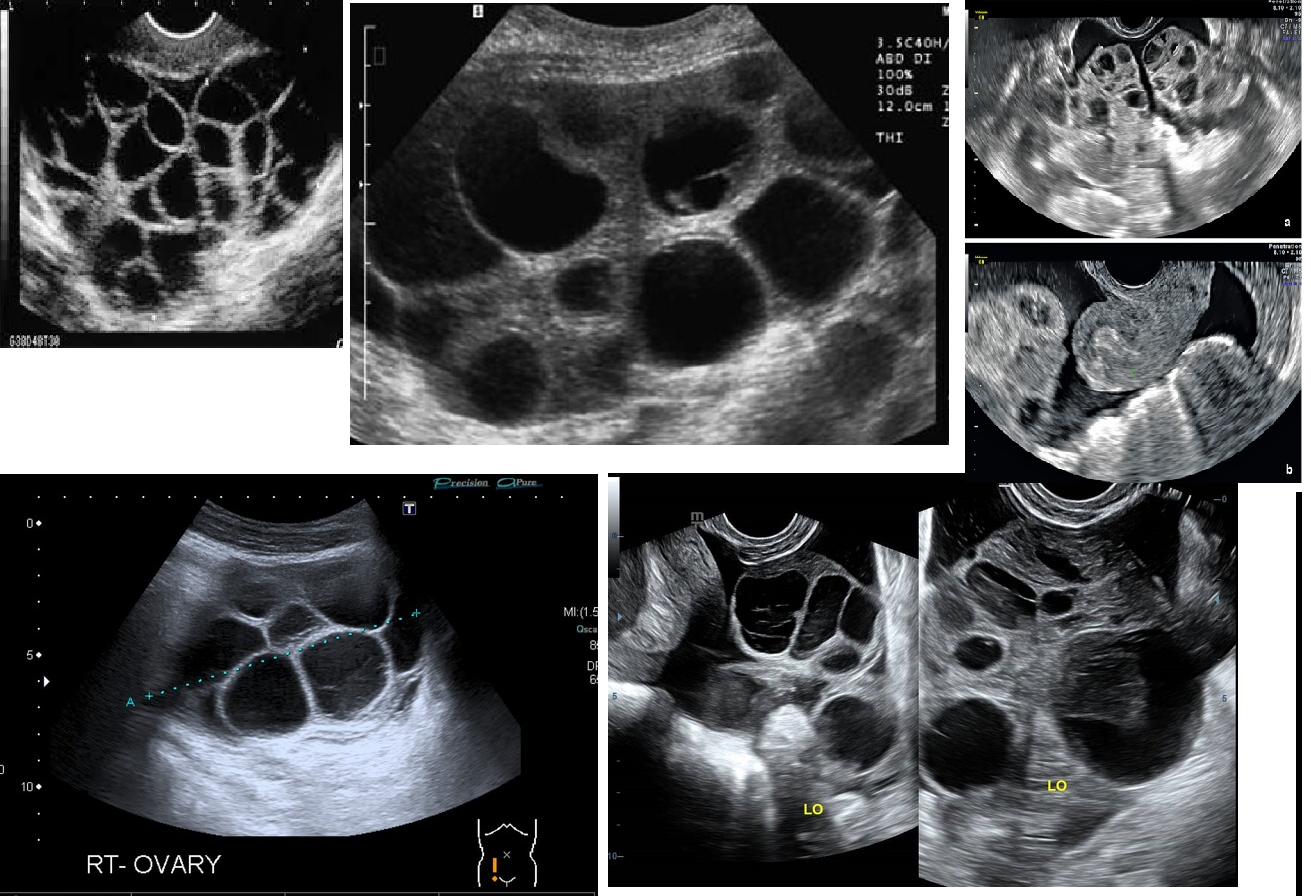
“string of pearls” appearance
ENLARGED CYSTS
PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome)
2nd MC epithelial malignancy
1st MC is serous cystadenocarcinoma (also epithelial)
50 - 60 yrs
Endometroid
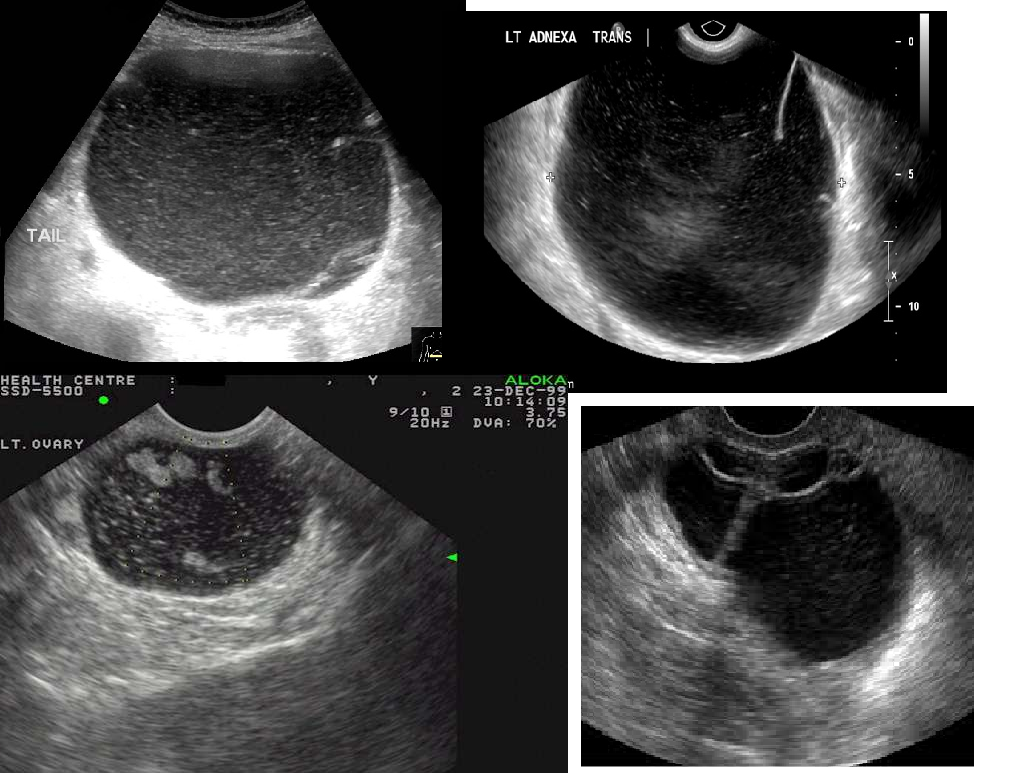
elements from endocervix or bowel
100 LBS
often in 40-70 yrs old
benign, common
large complex mass
20-25% of all benign ovarian neoplasms
5-10% of all malignant ovarian neoplasms
15-20% bilateral when malignant
Mucinous Cystadenoma
Definition: middle cycle pain
“Mittelshmerz”
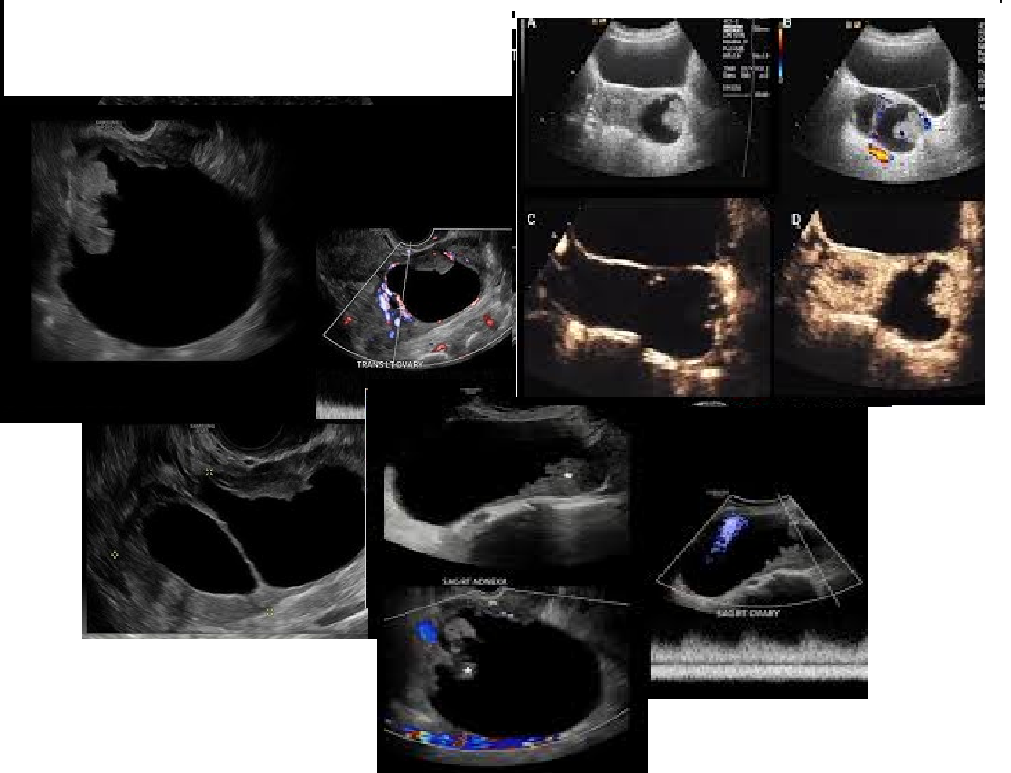
MC ovarian MALIGNANCY
Serous Cystadenocarcinoma
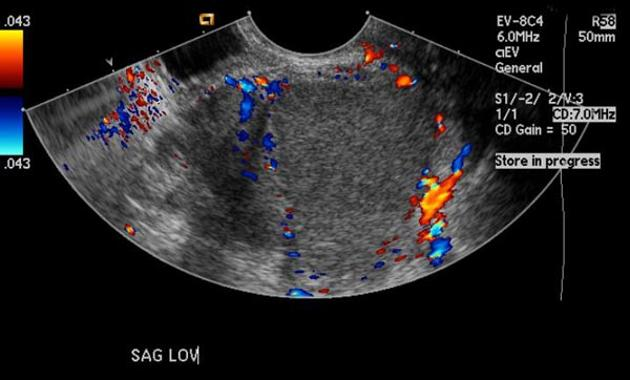
invades OUTSIDE THE UTERUS
15% are pre-meno
chronic pelvic pain
DYSMENORRHEA = painful menses
Infertility
painful sex
irregular bleeding
lower, abd pain
Endometriosis
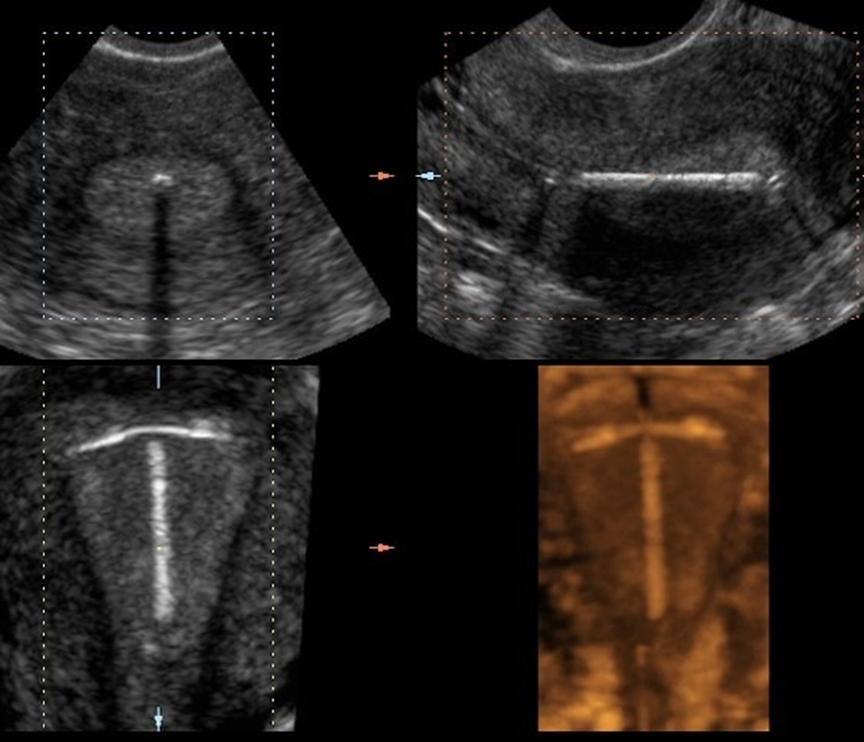
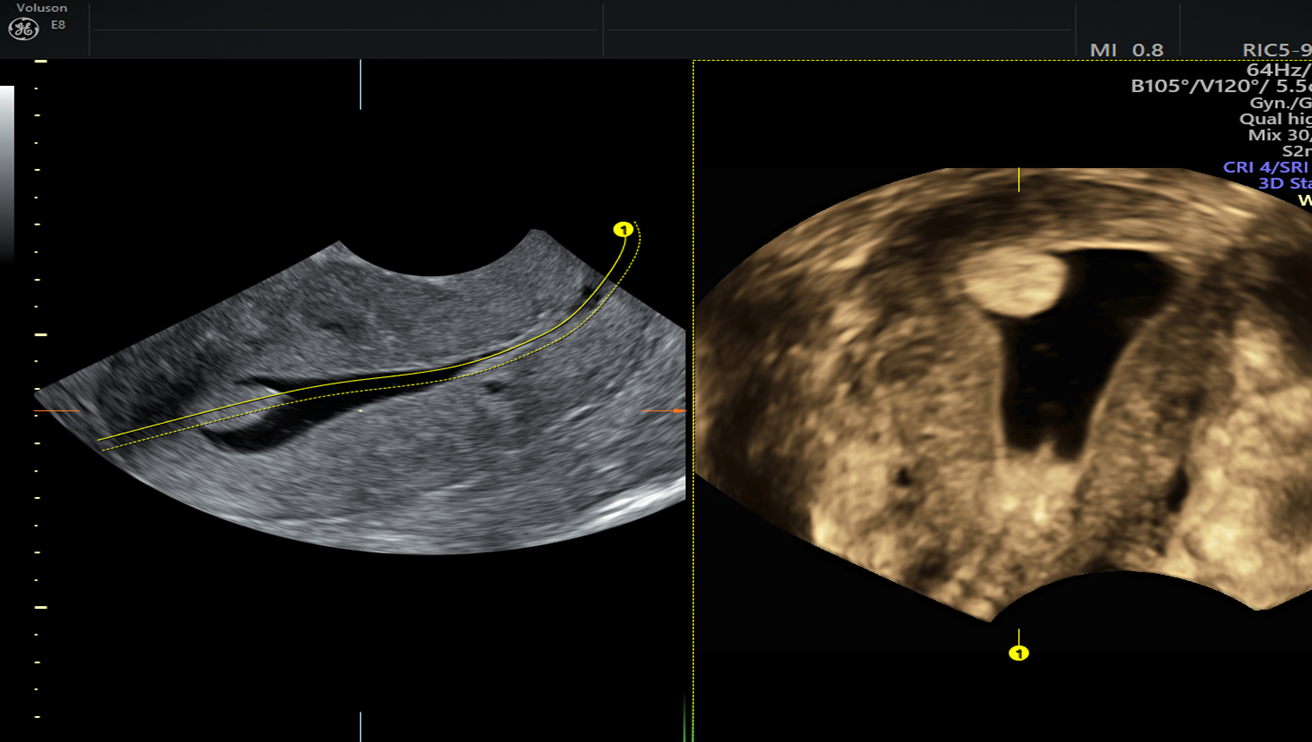
What is seen here
IUCD (Intrauterine Contraceptive Device)
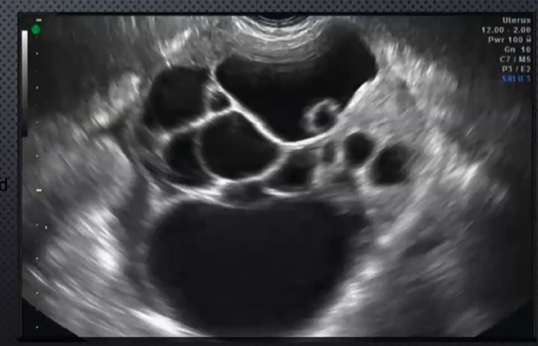
40 - 70 yrs
leads to pseudomyxoma peritone (ascites thick)
large, multiloculated, THICK, irregular walls
menopausal women 10%
pelvic pressure
pain when ruptured
bloating
weight loss
Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma
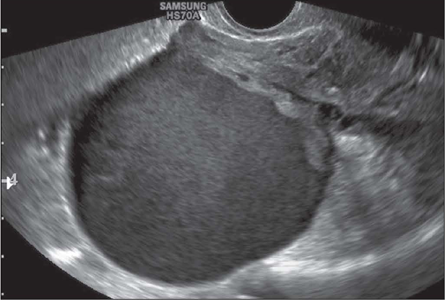
“Chocolate cyst”
heavy menses
well-defined
infertility
spotting
chronic lower back pain
Endometrioma
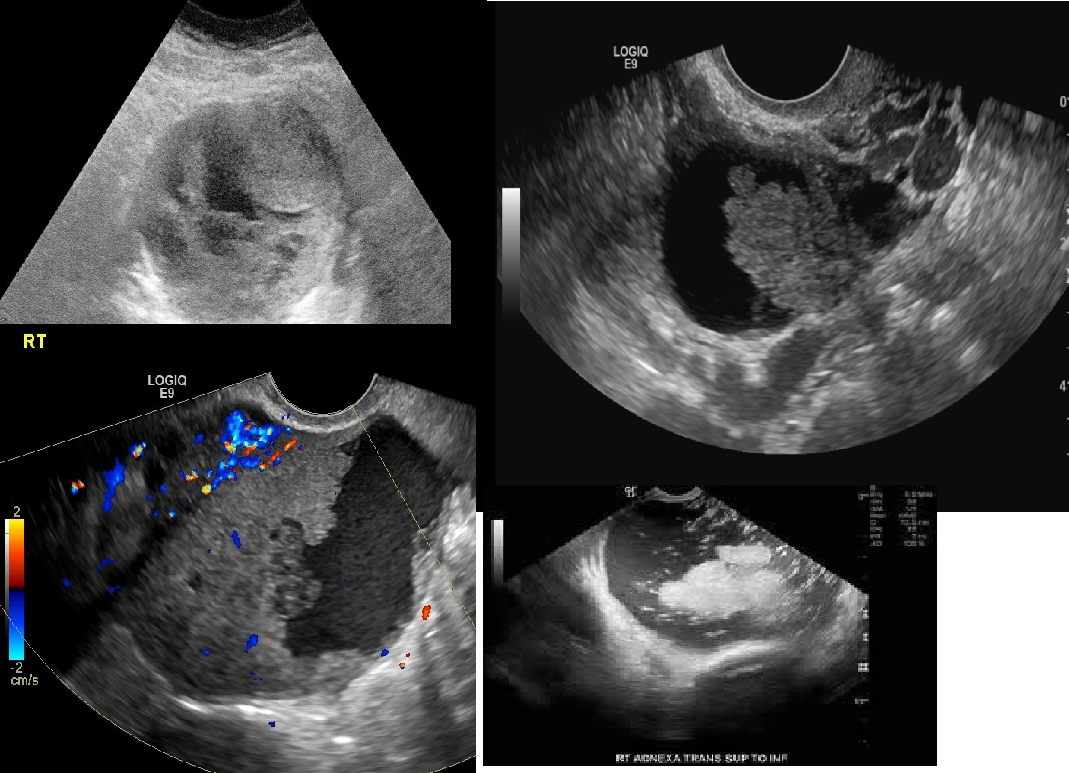
4th leading cause of death
40 - 60 yrs
Family HX
Infertility
NULLIPARITY
abdominal pain
abdominal swelling
Indigestion
weight change
urinary urgency
Ovarian Carcinoma
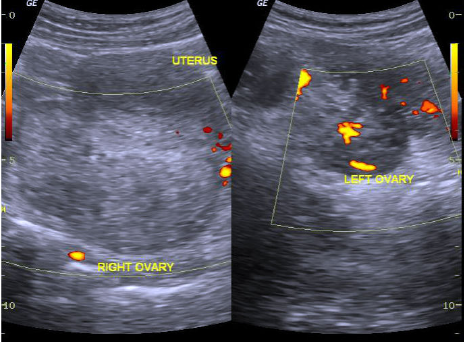
MC in children + adolescents
Rt ovary 3 x more likely
Sudden, severe pain
nausea/vomiting
fever
palpable mass
Ovarian Torsion
Masculinization is taken over by anovulation
< 30 yrs
LOW menses
NO menses
Produces Androgens
benign
Virilization (deep voice)
Arrhenoblastoma / Androblastoma
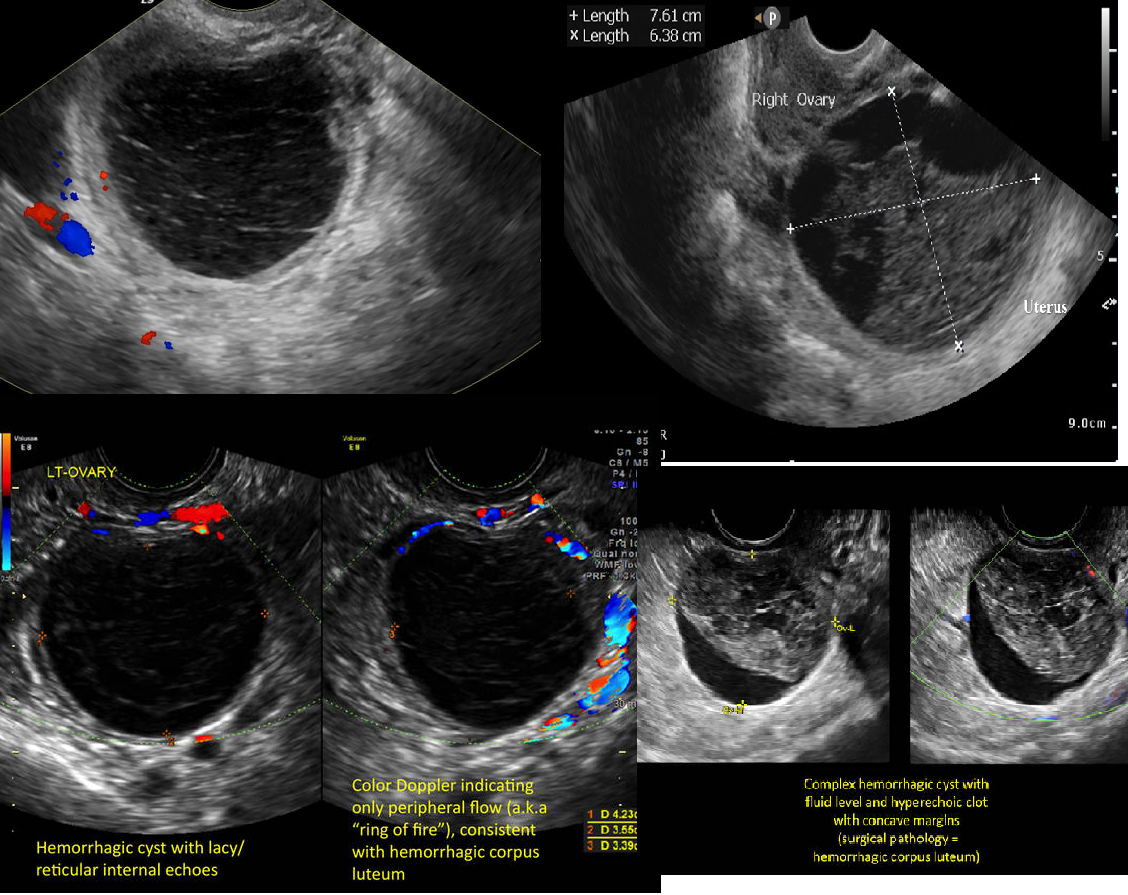
sudden pelvic pain
causes internal bleeding into a follicular cyst or corpus luteum cyst
Hours/days after:
highly echogenic due to clot formation
Several days after
increasingly complex appearance
Hemorrhagic Cyst
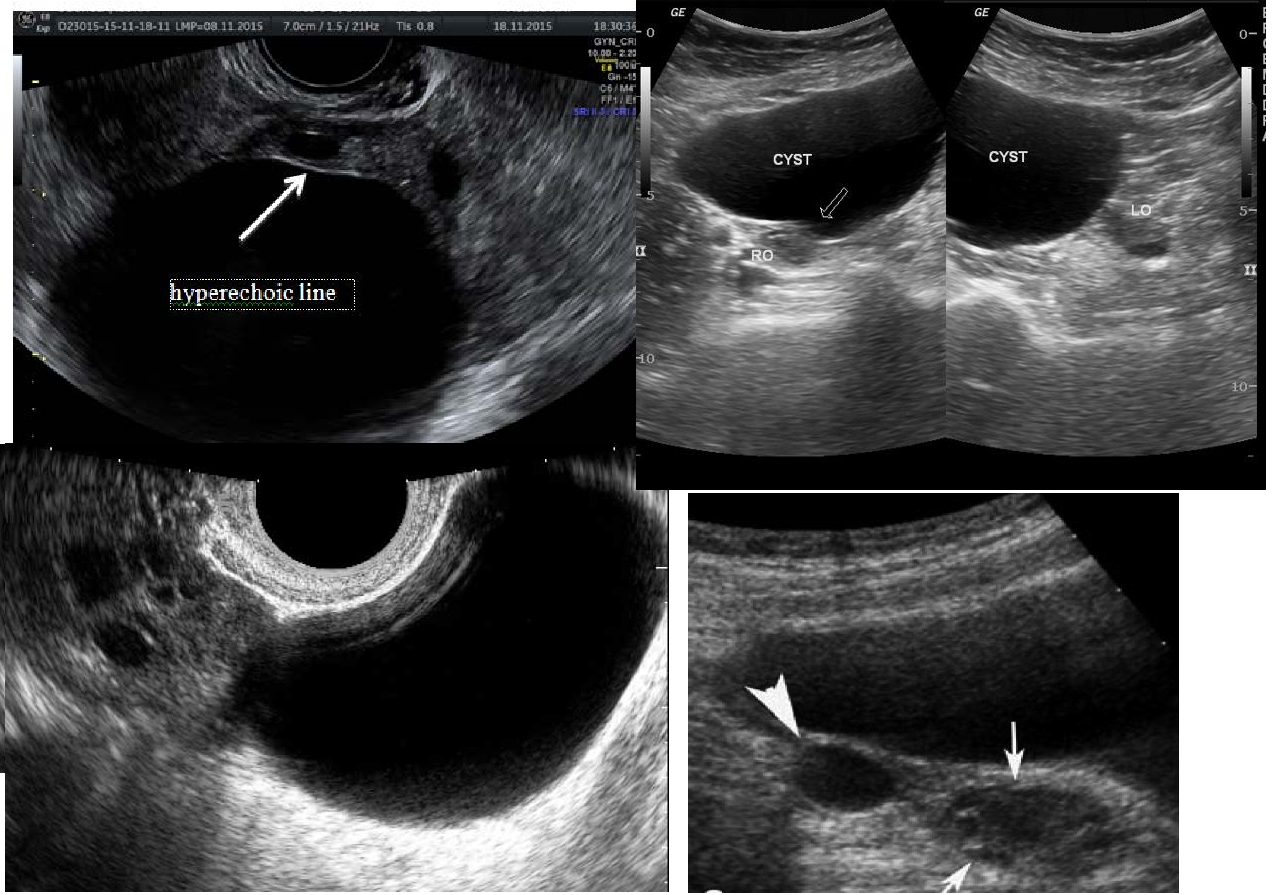
Wolfian duct remnants
10% of all adnexal masses
BROAD LIGAMENT location
benign cyst
20 -40 yrs
mesothelial/paranephric origin
asymptomatic
Para-ovarian Cyst
MC malignancy in CHILDHOOD
high AFP and beta HCG
Dysgerminoma
BENIGN Small, solid, hypoechoic tumor
ASSOCIATED W/ MIEG'S
No internal cystic structures
(u) No calcifications, but possible
*Very similar to granulosa cell tumor
Brenner's Tumor
Gastric adenocarcinoma with ovarian metastases
Krukenberg Tumor
Iatrogenic (treatment-caused) complication from ovulation induction
Mild - pelvic discomfort
Severe - severe pelvic pain + abdominal distention
5-10 cm
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
20-24 yrs
intense pelvic pain
dull, aching tenderness
fever
DISCHARGE
RUQ pain
Risk factors
early sex
multiple partners
STD
IUCD
douching
postsurgical/post abortion
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
PID caused by GONORRHEA
RUQ pain
related to PID
Fitz- Hugh Curtis Syndrome
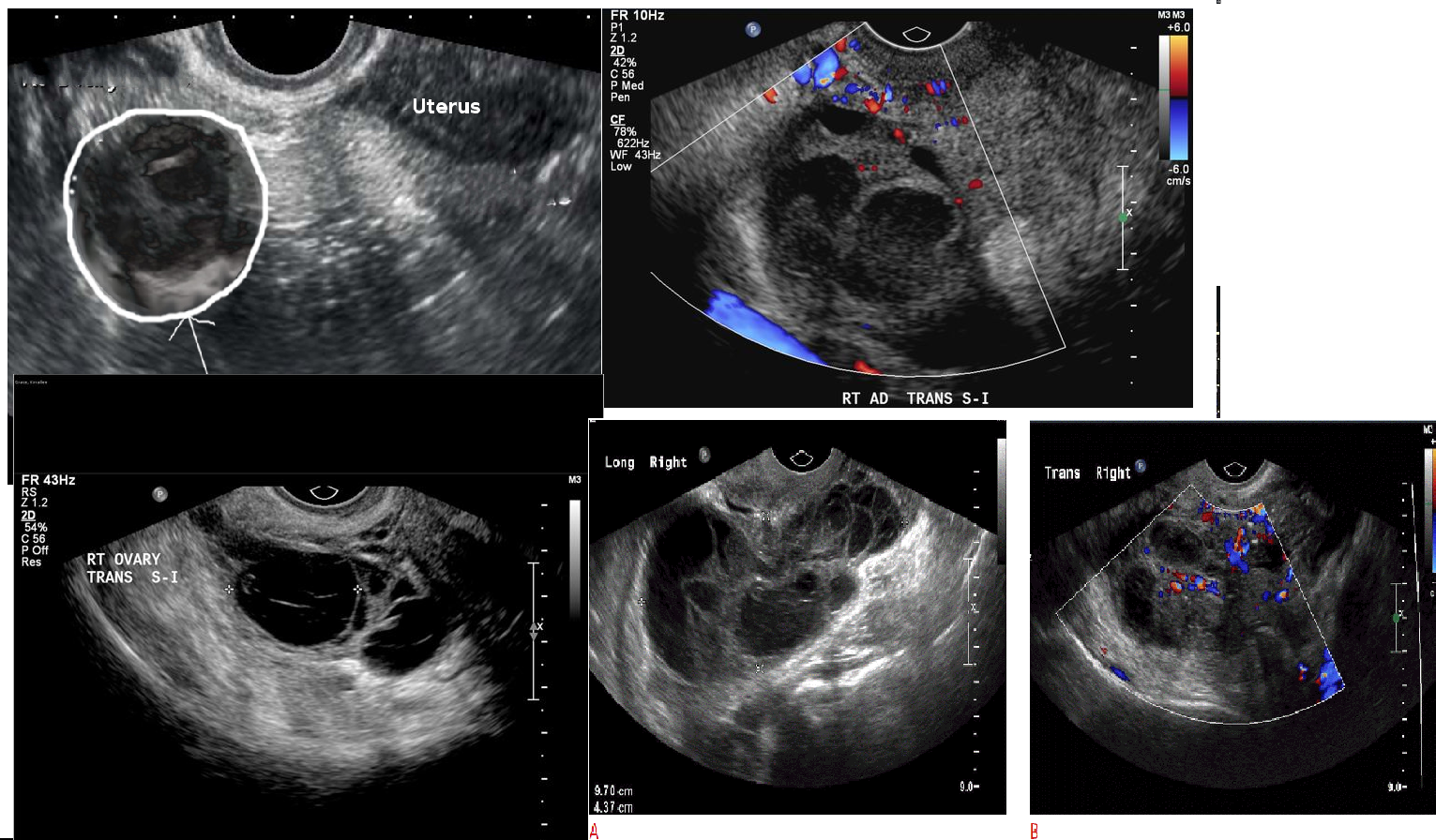
pelvic pain
fever
adnexal tenderness
PID complication
Tubo-ovarian Abscess
secondary to PID, endometriosis
infertility
pelvic pain
Hydrosalpinx (Fluid in Fallopian tube)
Chronic PID
SEVERE pelvic pain
fever
Pyosalpinx (Pus in fallopian tube)
pelvic discomfort
fullness
LOW-grade fever
pelvic tenderness
related to PID
Salpingitis
Total # of pregnancies (including current)
Gravidity
Total # of births given
Parity
3rd parameter after Gravity and Parity
Preterm & Stillborn
4th parameter after Gravity and Parity
Losses & Abortions
5 parameter after Gravidity and Parity
Living children
1st Trimester is how long
13 weeks and 6 days
2nd Trimester is how long
14 wks - 26 2ks + 6 days
3rd Trimester is how long
27 wks → delivery
< 90 BPM is considered what
Bradycardia
> 160/170 BPM is considered what
Tachycardia
What two measurements are taken in the 1st Trimester?
CRL (crown to rump)
Yolk Sac
What is measured that is should be < 3.5 mm in the first trimester?
Nuchal Translucency
Gestational Age (Menstrual age / LMP) is 2 weeks after or before the conceptual age (embryonic age)
If your gestational age is 8 weeks, the actual embryo is about 6 weeks old.
After
Conception → 12 days is considered what
Zygote
Implantation → 10 wks is considered what
Embryo
10+ weeks → delivery is considered what
Fetus
Menses cycle,
days 1-14 is considered what phase?
Menstruation phase
Menses cycle,
days 5-14 is considered what
Proliferative Phase
Proliferative phase is aligned with what ovarian phase?
see TRI -laminar sign (three line sign)
THIN ENDO
high estrogen
ovulation occurs on day 14
Follicular phase
Menses cycle,
Days 15-28 is considered what phase?
Secretory phase
The secretory phase is aligned with what ovarian phase?
ruptured follicle becomes Corpus luteum
produces progesterone
ENDO THICKENS
if no pregnancy, estrogen and progesterone DECLINE
Luteal phase
The next period starts on _____ which is the end of the cycle
Day 28
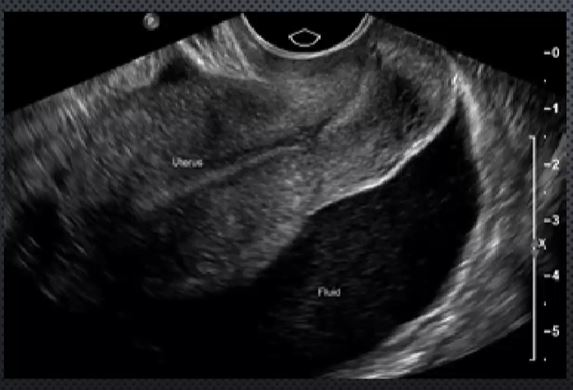
Positive HCG, but there’s fluid + adnexal mass =
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
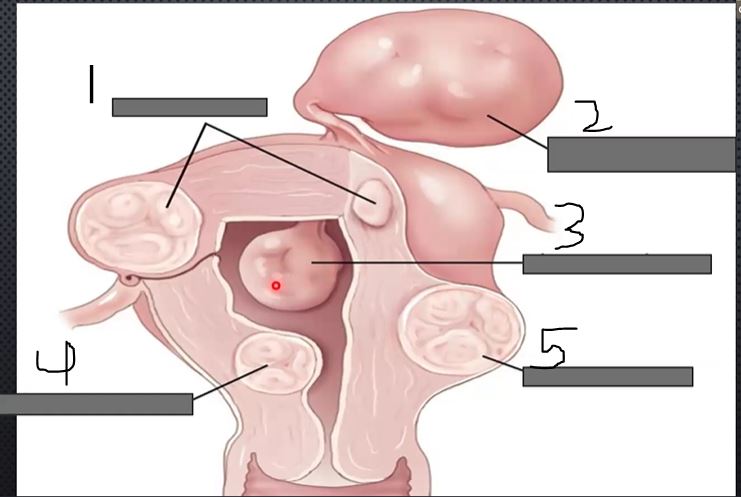
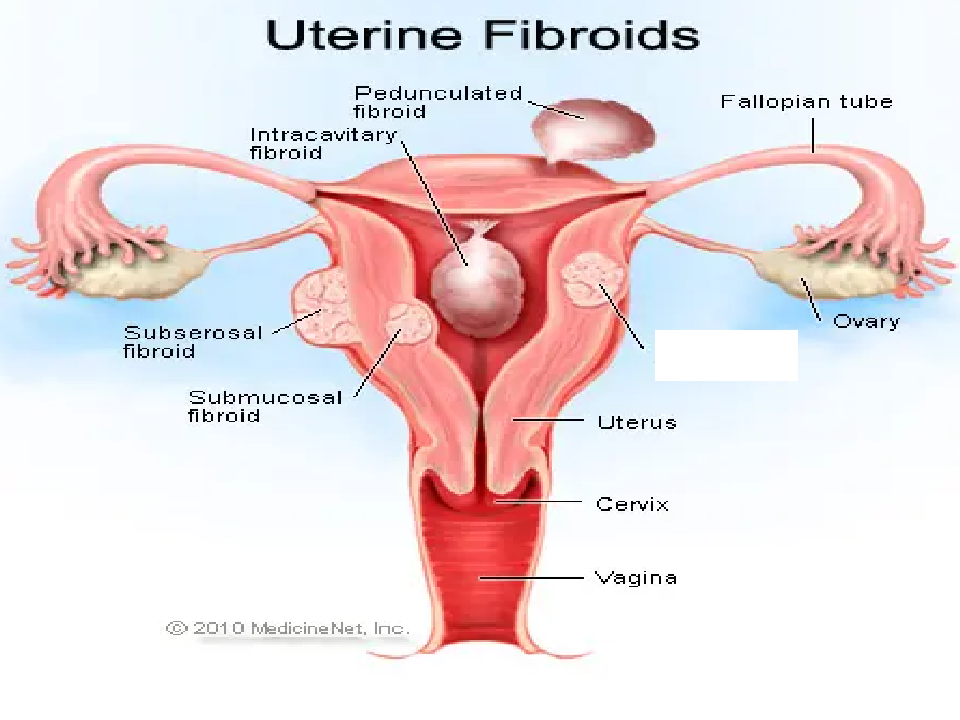
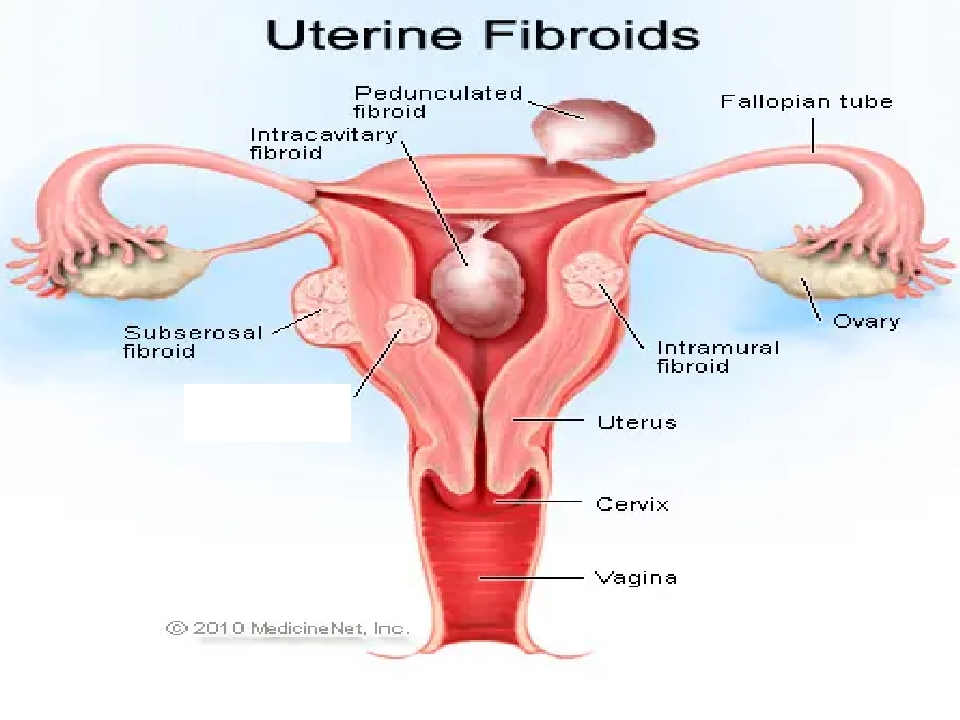
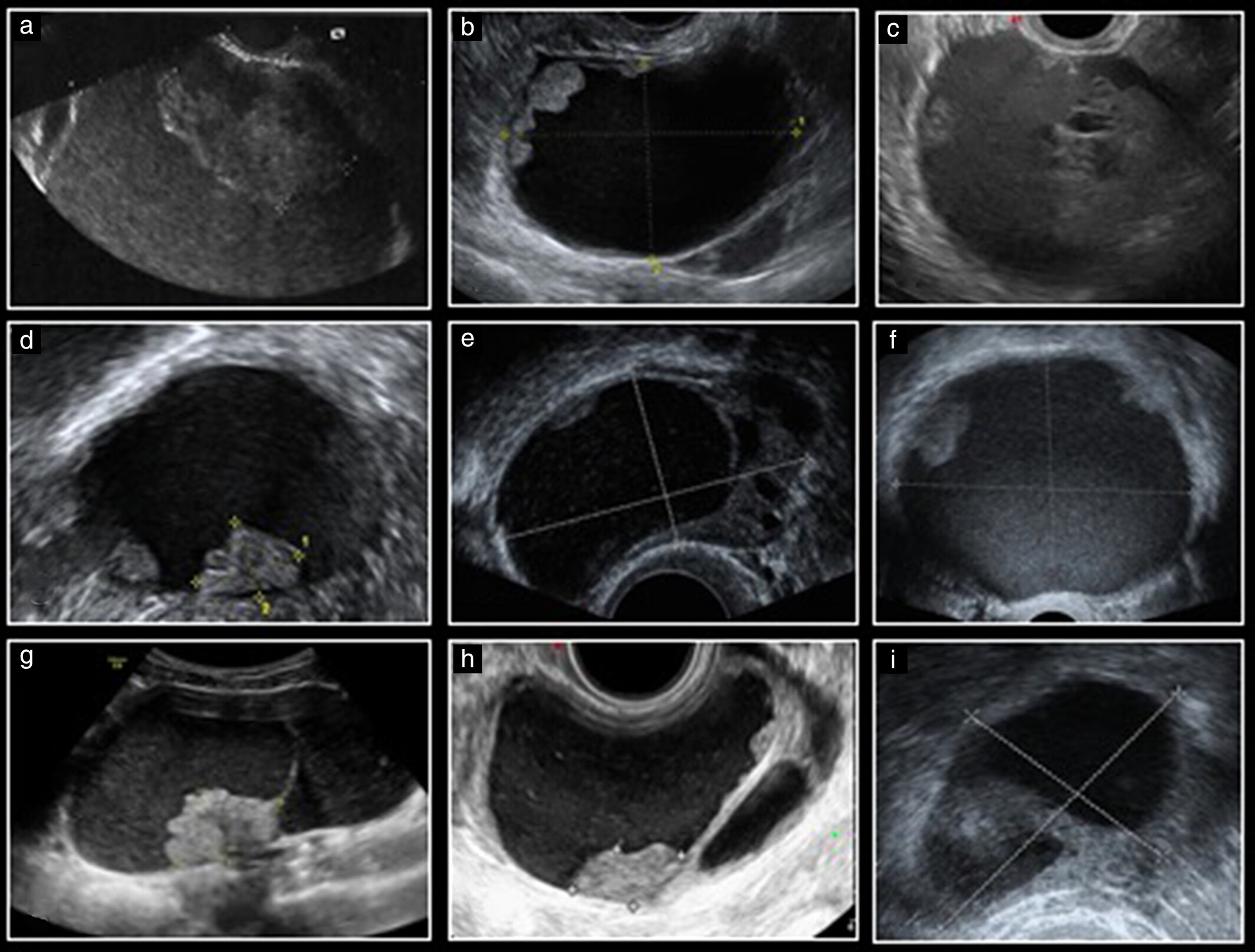
What is 1?
Intramural
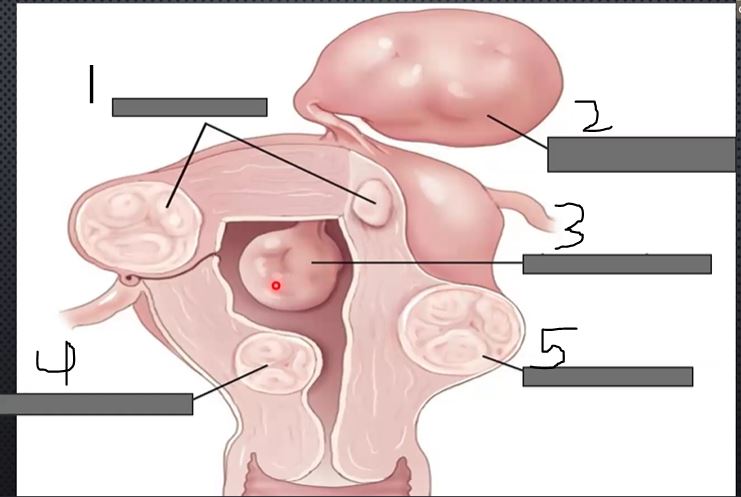
what is 2?
Pedunculated
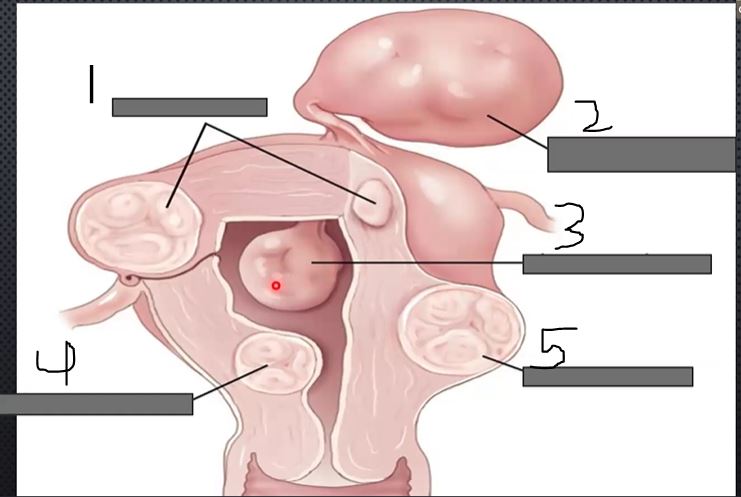
What is 3?
Intracavitary
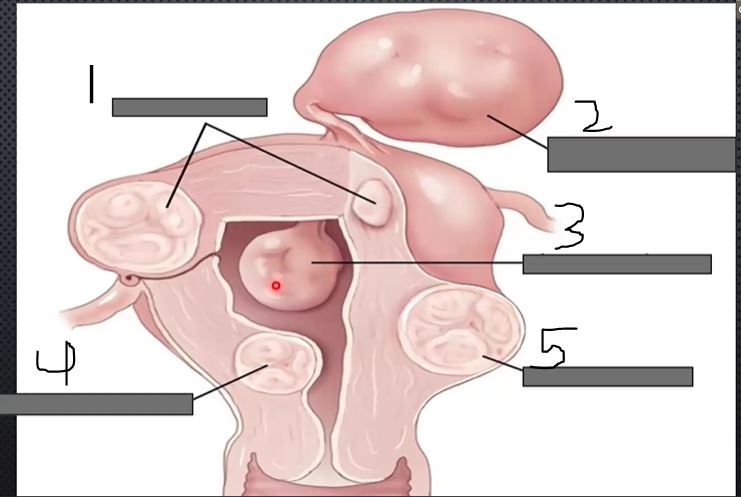
what is 4?
submucosal
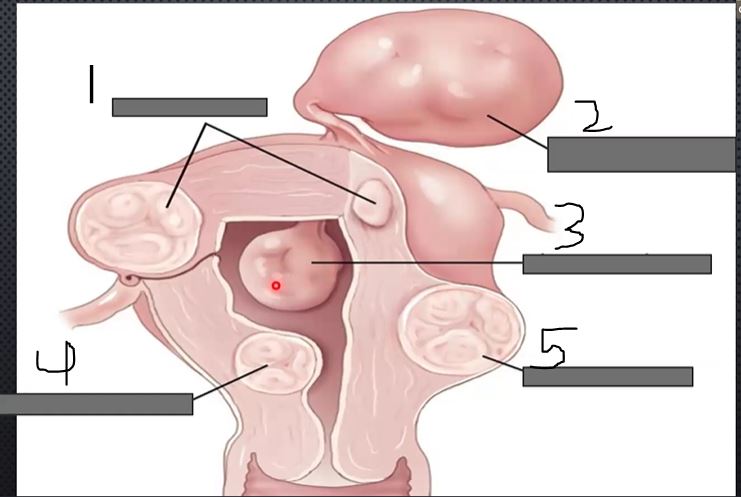
what is 5?
subserousal
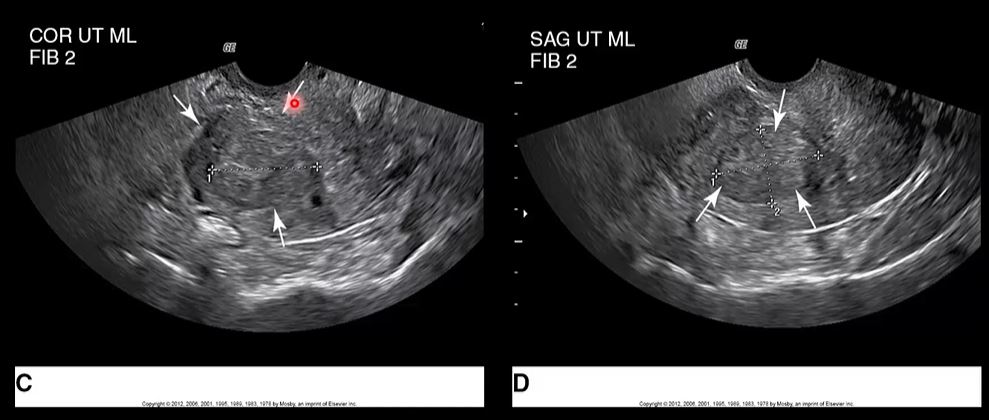
How to write this ?
SAG UTERUS ML, Fibroid 2
intramural fibroid is seen within the myometrium of the uterus
up to ~2.5 cm (normal)
aka graafian follice
normal ovulation
Dominant follicle
Greater than what measurement is considered a surgical consult for an follicular cyst?
> 5 cm
Menstrual week 3 = how much beta hcg?
35-50 miu/ml
Menstrual week 4, how much beta hcg?
45-426 miu/ml