New Penguin Russian Grammar Chapters 1-5
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
How does the Russian 'o' sound when stressed vs unstressed?
'о' is pronounced as 'a' is it is unstressed in the word
ex:
тóт [toh] - 'that'
ктó-то [ktoh-ta] - 'someone'
What is the effect of the hard sign ъ?
It makes the letter before it hard instead of soft ands acts like a slight break in the middle of the word/creates two syllables
ex: Подъезд
What is the effect of the soft sign ь?
Softens the sound of the consonant before
Does Russian have a present conjugation of to be and what is it?
есть - to be, and it is NOT conjugated into the present tense
If the sentence has nouns in the subject and predicate, a hyphen is used
ex: Мзри—англичанка
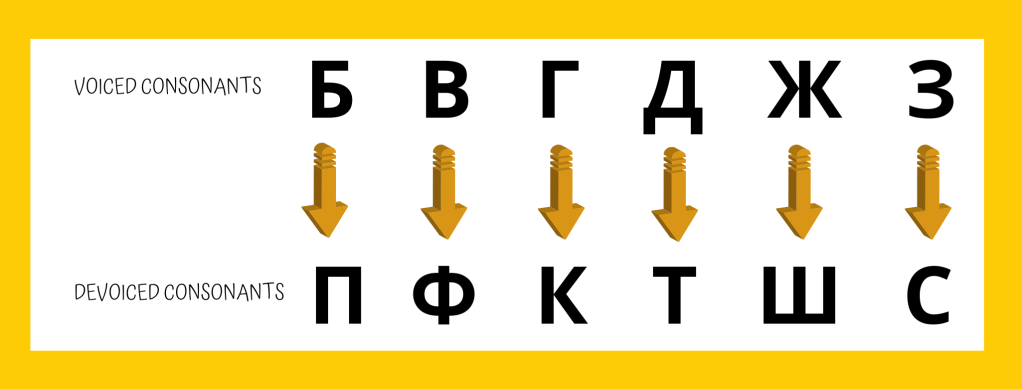
Voiced vs Voiceless/Devoiced Consonants
When a voiced consonant comes before a voiceless consonant or being located at the end, it becomes its voiceless counterpart.
Водка sounds like вотка (д in front of к = т)
Заказ sounds like Закас (з at the end = с)
В пути sounds like ф пути (voiced в before voiceless п takes on the sound of voiceless ф)
Likewise, a voiceless consonant becomes its voiced counterpart when precedes a voiced one (except for voiced в) - a voiceless consonant stays voiceless at the end of a word.
• сделать sounds like зделать (с in front of д = з)
ЙЭ sound
Е (yeh)
ЙО sound
Ё
ЙУ sound
Ю
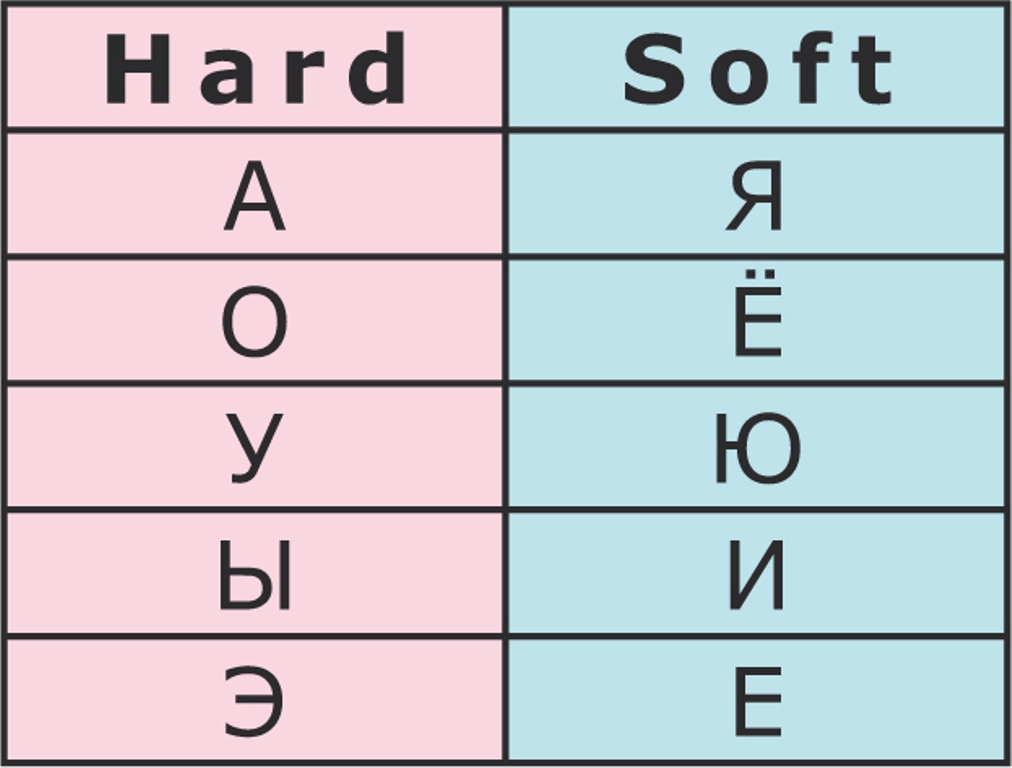
Hard vs Soft vowels
the hard consonants before a soft vs hard vowel changes
Ex: Дом and День pronounce the Д differently
How to (usually) identify if a noun is masc., fem., or neutral
Masc. nouns: end in consonants or й
Fem. nouns: end in -а/-я
Neuter nouns: end in е/ё/о
Это uses
means “this” and “that” and also “it” when replacing “this/that”
ex:
A: Что это? - What is this/that/it?
B: Это вино - It/This/That is wine
Gender of nouns ending in ь
Most are feminine, but there are many masculine ones too
Это vs Вот
When you are talking about something that has already been named, Вот is used
Ex: Где чай? Вот он.
What is the infinitive ending?
-ть
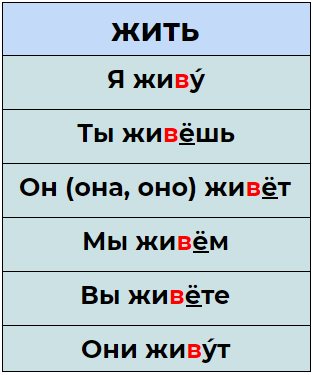
Present Tense Type 1 Verb Conjugation: знать
Majority of verbs have this type of conjugation

Present Tense Type 1B Verb Conjugation:
Similar endings to Type 1 знать, but the stem is unpredictable
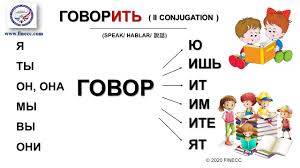
Present tense Type 2 Verb Conjugation: говорить
How to make verbs negative in Russian
Simply put ‘не’ before the verb
Ex: Я не знаю (I don’t know)
Prepositional Case use(s)
words that come after prepositions в (in), на (on), о (about, concerning) need the prep. case endings
Prepositional case endings for Masculine nouns
add an -e, while the й changes to an -e
ex: автобус → на автобусе (on a/the bus)
музей → в музее (in a/the museum)
Prepositional case endings for Feminine nouns
Change their -а/-я ending to -e
ex: Москва → в Москве (in Moscow)
Prepositional case endings for ь nouns
if Feminine, the -ь turns into и, if Masc., it turns into -е
ex)
царь (m) - о царе
Сибирь (f) - в Сибири
Exception to case ending rule for -я/-e endings that have an и before them
The final -я/-e actually turns into another и
ex) Англия → в Англии (in England)