Physics Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:09 PM on 3/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
The small energy values of quanta or **photons** are usually expressed in ______ (eV)
electronvolts
2
New cards
a particle representing a quantum of light or other __electromagnetic__ radiation; carries energy proportional to the radiation frequency but has zero rest mass.
photon
3
New cards
1 eV = ?
1\.60 X 10^-19 J
4
New cards

Which decay equation is this?
alpha; ***charge and number of nucleons must be conserved, must be the same on right and left sides of the equation***
5
New cards
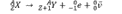
Which decay equation is this?
beta minus
6
New cards
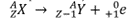
Which decay equation is this?
beta positive; the **positron** is ejected from the nucleus; the neutron remains in the nucleus so the atomic mass remains the same, but the atomic number decreases by one
7
New cards
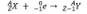
Which decay equation is this?
electron capture
8
New cards
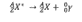
Which decay equation is this?
gamma
9
New cards
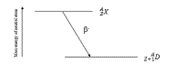
Which decay scheme is this?
beta minus
10
New cards
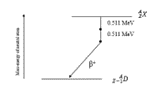
Which decay scheme is this?
beta positive; the difference between mass-energy of parent neutral atom and daughter neutral atom must be at least two times the electron mass energy (1.02 MeV) for positron emission; parent atom emits a positron and must rid itself of an atomic electron to become a neutral atom
11
New cards
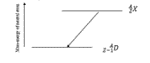
Which decay scheme is this?
electron capture
12
New cards
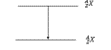
Which decay scheme is this?
internal conversion
13
New cards

•Suppose that a radioactive parent isotope X decays to a daughter product D with a half-life Tp
• D decays to G with a half-life Td
If Tp>Td then after some period of time the ratio of the activity of D to the activity of X will approach a constant value
• D decays to G with a half-life Td
If Tp>Td then after some period of time the ratio of the activity of D to the activity of X will approach a constant value
radioactive equilibrium
14
New cards
Which type of equilibrium is Tp≫Td?
secular
15
New cards
Which type of equilibrium is Tp≳Td?
transient
16
New cards
•occurs when Tp >> Td
•After some time, the activity of the daughter becomes equal to the activity of the patient
•After some time, the activity of the daughter becomes equal to the activity of the patient
secular equilibrium
17
New cards
•Occurs when the half-life of the daughter is somewhat less than the parent
•After a long time the decay curves become almost parallel to one another and the apparent half-life of the daughter becomes the same as the half-life of the parent and the ratio of the activities reaches a constant value
•After a long time the decay curves become almost parallel to one another and the apparent half-life of the daughter becomes the same as the half-life of the parent and the ratio of the activities reaches a constant value
transient equilibrium
18
New cards
nuclei are composed of nucleons, which are what?
protons and neutrons
19
New cards
__ have a single unit of positive charge and _____ are neutral
protons, neutrons
20
New cards
atomic number (Z)= ?
number of protons
21
New cards
mass number (A)= ?
number of protons - number of neutrons
22
New cards
___ can only have specific discrete energies. __ in different shells have different energies that are unique to each element. ___ are bound to atom, so energies are negative
electrons
23
New cards
It takes a _____ amount of energy to free the electrons from the atom (ionization)
positive
24
New cards
Electrons in inner shells are ____ tightly bound to atom than outer shell electrons
more
25
New cards
Higher Z means more or less tightly bound inner electrons?
more
26
New cards
Ground state of an atom is the ____ possible energy configuration of electrons
lowest
27
New cards
occurs when 1 or more electrons occupy a higher energy state than they would if in ground state
excited state
28
New cards
occurs when 1 or more electrons receive so much energy (at least the atomic binding energy for the shell) that they are removed from the atom
ionization
29
New cards
•Electrons can make transitions between shells
•Transition from lower to high energy state occurs if atom absorbs energy equal to difference between energy levels
•Atom is left with excess energy à excited state
•Transition to lower energy states are possible if vacancy in lower energy shell
•Electron in higher energy shell will rapidly drop down and fill vacancy
•Energy is released as a ____ ______
•Transition from lower to high energy state occurs if atom absorbs energy equal to difference between energy levels
•Atom is left with excess energy à excited state
•Transition to lower energy states are possible if vacancy in lower energy shell
•Electron in higher energy shell will rapidly drop down and fill vacancy
•Energy is released as a ____ ______
photon emission
30
New cards
The number of electrons and their configuration determines the ____ _____ of an element
chemical properties
31
New cards
____ _____ involve the sharing or exchange of outer electrons between atoms
chemical reactions
32
New cards
dense, positively charged body consisting of protons and neutrons (called nucleons)
nucleus
33
New cards
Mass of proton and neutron are _______
comparable
34
New cards
Mass of electron is about ____ times smaller
2000
35
New cards
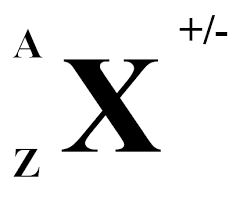
A= ?
atomic mass number (number of nucleons)
36
New cards
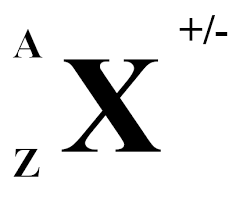
Z= ?
atomic number (number of protons)
37
New cards
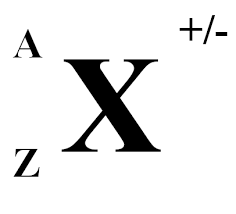
X= ?
chemical symbol
38
New cards
How do you find the number of neutrons?
N=A-Z
39
New cards
Number of _____ determines chemical identity of element
protons
40
New cards
Number of ____ determines its chemical behavior
electrons
41
New cards
•Same A (number of __**p**__rotons) but different N (number of neutrons)
isotope
42
New cards
•Same __**A**__ (number of nucleons) but different Z (number of protons)
isobar
43
New cards
Same A and Z, but nucleus is in an excited state called a __**m**__etastable state that has a long lifetime
isomer
44
New cards
same number of __**n**__eutrons
isotone
45
New cards
•The atomic mass unit (*u*) corresponds to an energy of ______
931MeV
46
New cards
•1 *u* is roughly the mass of a ______
nucleon
47
New cards
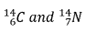
What is this an example of?
isobar
48
New cards
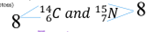
What is this an example of?
isotone
49
New cards
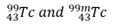
What is this an example of?
isomer
50
New cards
***an excited state that has a relatively long lifetime***
metastable
51
New cards
*If the percentage change in distance from the source is small, the percentage change in the intensity of a radiation beam is approximately _____ the percentage change in distance*
twice
52
New cards
well-collimated beam, detector placed far from attenuating material so that no scattered photons may enter the detector
narrow beam attenuation
53
New cards
___ is the linear attenuation coefficient; has units of inverse distance and depends on the energy of the radiation and the attenuating medium
µ
54
New cards
•The thickness of specified material necessary to attenuate intensity of beam to half its original value for narrow beam geometry; depends on energy of beam and material that beam traverses
half value layer
55
New cards
•The ______ HVL (HVL2) is the additional thickness necessary to reduce beam intensity by another factor of 2
second
56
New cards
•As a _______ beam penetrates the material, it usually becomes “hardened” and so it is generally true that HVL2 > HVL1
polyenergetic
57
New cards
•For a _______ beam, HVL2 = HVL1
monoenergetic
58
New cards
tera (T)
10^12
59
New cards
giga (G)
10^9
60
New cards
mega (M)
10^6
61
New cards
kilo (k)
10^3
62
New cards
hecto (h)
10^2
63
New cards
deka (da)
10^1
64
New cards
deci (d)
10^-1
65
New cards
centi (c)
10^-2
66
New cards
milli (m)
10^-3
67
New cards
micro (µ)
10^-6
68
New cards
nana (n)
10^-9
69
New cards
pico (p)
10^-12
70
New cards
*____ _____* are based on the metric system since most countries use the metric system
SI units
71
New cards
An x-ray machine has two major components
x-ray tube and generator
72
New cards
X-rays are produced inside tube and exit tube through the
window
73
New cards
Generator supplies __ and ___ to the tube
current, voltage
74
New cards
_____ are created when a beam of electrons, accelerated inside the evacuated x-ray tube, strikes a target at the end of the tube
x-rays
75
New cards
When electrons strike the target, a fraction of their kinetic energy is converted to x-rays and the remaining KE is converted to _____
heat
76
New cards
Electrons have to be accelerated through a large potential difference because they have to gain enough KE to produce ____ ____
energetic x-rays
77
New cards
•_______ are produced when electrons are accelerated between the cathode (negative electrode) and anode (positive electrode) in an evacuated metal or glass tube, and strike the anode at the end of the tube
x-rays
78
New cards
•When electrons strike the target (which is embedded in the anode) a large fraction of their energy is dissipated as _____
heat
79
New cards
•The remainder is converted to _____
x-rays
80
New cards
The _____ has a heated filament that gets very hot, like a toaster wire
cathode
81
New cards
The electrons are boiled off the cathode filament and are accelerated toward the _____
anode
82
New cards
•Most diagnostic tubes use _____ (W) for the target material
tungsten
83
New cards
Why is the high melting point of tungsten (3370C) beneficial?
the electron beam produces a high heating rate
84
New cards
Why is the high Z of tungsten beneficial?
it has a high efficiency for x-rays production
85
New cards
the _____ is commonly made of copper with tungsten target embedded in it
anode
86
New cards
•Copper is a _____ heat conductor
good
87
New cards
When an electron strikes the target of an x-ray tube (or in a linac), it interacts with the ______ in the target. It can interact with either atomic electrons or the atomic nucleus
matter
88
New cards
•______ electron interacts with an outer or an inner shell electron
incoming
89
New cards
•_____ shell electrons can be excited to higher-level energy states
outer
90
New cards
•They will then drop back to their original states and emit low-energy photons. These photons will be absorbed quickly in the target, and their energy converted to _____
heat
91
New cards
•Outer shell electron could be ejected from the atom, and the atom is ____
ionized
92
New cards
•Ejected electron will move through target material, interacting with other atoms, and will find another atom missing an outer shell electron and “______” with that atom and a low energy photon, whose energy will be absorbed
recombine
93
New cards
•Occasionally a high-energy bombarding electron will eject an inner shell electron (K or L shell)
•There will be a vacancy that can be filled by outer shell electrons dropping down
•Inner shell electrons are very tightly bound, so the energy released when outer shell electrons drop down to fill an inner shell vacancy will be high (classified as x-rays)
•Some of the higher energy x-rays may escape from the target without being absorbed
•They will have discrete energies that are characteristic of the atom from which they are emitted (unique for each element)
•There will be a vacancy that can be filled by outer shell electrons dropping down
•Inner shell electrons are very tightly bound, so the energy released when outer shell electrons drop down to fill an inner shell vacancy will be high (classified as x-rays)
•Some of the higher energy x-rays may escape from the target without being absorbed
•They will have discrete energies that are characteristic of the atom from which they are emitted (unique for each element)
characteristic x-rays
94
New cards
Incident electron with kinetic energy E0 ejects an orbital electron and leaves from the collision with energy E0 – ΔE, where ΔE is the sum of the energy imparted to the ejected electron and the energy used to overcome the binding energy of that electron
A hole is left by the departed orbital electron and a higher shell electron drops to fill that vacancy in the lower shell, giving off a characteristic photon with energy equal to the difference in the binding energies for the shells
A hole is left by the departed orbital electron and a higher shell electron drops to fill that vacancy in the lower shell, giving off a characteristic photon with energy equal to the difference in the binding energies for the shells
characteristic x-rays
95
New cards
When a bombarding electron passes close to an atomic nucleus in the target, it will be accelerated as a result of the electrical attractions between the electron and the nucleus
Accelerated charges generate electromagnetic radiation
Radiation will be emitted by the electron over a wide range of energies
Maximum energy of the emitted x-rays is equal to the total kinetic energy of the bombarding electron
Accelerated charges generate electromagnetic radiation
Radiation will be emitted by the electron over a wide range of energies
Maximum energy of the emitted x-rays is equal to the total kinetic energy of the bombarding electron
Bremsstrahlung emission
96
New cards
bremsstrahlung radiation means what in German?
braking radiation
97
New cards
At large angles with respect to electron beam for low-energy x-ray beams (diagnostic) but strongly peaked in the forward direction for therapeutic energies
Bremsstrahlung directional dependence
98
New cards
In a typical target both ___ ___ and _____are produced
characteristic x-rays, bremsstrahlung
99
New cards
x-rays with discrete wavelengths that are uniquely characteristic of the distinct energy levels of the atom from which they come. these result when a bombarding electron ejects an inner shell electron in the target medium.
characteristic x-rays
100
New cards
when bombarding electron passes close to an atomic nucleus in the target, it will be accelerated as a result of the electrical attraction between the and the nucleus. accelerate charges generate electromagnetic radiation. radiation will be emitted by the electron in this process over a wide range of energies. this radiation is called bremsstrahlung, which means “braking radiation” in German. the maximum x-ray is eqaul to the total kinetic energy of the bombarding electron.
bremsstrahlung (continuous) x-rays