ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD, ASCENDING, DESCENDING, AND INTERSEGMENTAL TRACTS (PART 2)
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Tracts and shi
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
TRACTS REVIEW: ASCENDING PATHWAYS
The following slides will ask for everything in the tables of the WS Doc gave us, make sure u studied them before.

Lateral Spinothalamic Tract:
Good luck
Sensation
Pain and temperature
Lab: Pain can be fast pain or general pain
FAST PAIN
Within 0.1 sec
Sharp, acute, pricking pain
Almost confined to skin
Receptor
Free nerve endings
Chemical substances in damaged tissue (serotonin, histamine, bradykinin, acids like lactic acid and K+) excite nerve endings
1st order neuron
Ipsilateral Dorsal Root Ganglia
2nd order neuron
Ipsilateral Substantia Gelatinosa
3rd order neuron
Contralateral ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) of the thalamus
Lab: can also be ventral posteromedial (VPM)
Termination
Post Central gyrus of the cortex
Lab: Broddman area 312 , 57
Location in SC
Contralateral Lateral White Column
Extent in SC
All levels of the spinal cord
Follow up questions for lateral spinothalamic tract
1. Before synapsing at the 1st order neuron, the stimulus climbs which tract (Lec: 1-2 segments; Lab: 2-3 segments)
2. The Lateral spinothalamic tract is medial and anterior to what tract?
3. Which fibers are more anterior; Fibers carrying pain or Fibers carrying temperature?
4. What is the arrangement of fibers from medial to lateral?
5. At the level of the MEDULLA what is the tract called?
6. What is the sulcus that separates Motor and Sensory gyrus
Tract of Lissaur
Spinocerebellar tract
Fibers carrying pain
Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral
Spinal Lemniscus
Rolandic sulcus
Main excitatory Amino acid NT released by A δ fibers and C fibers; Fast-acting and localized
Neuropeptide; Released from C fibers, Slow release and diffuses widely in the posterior horn
Termination for FAST pain
Termination for SLOW pain
Gyrus for interpretation of pain
Gyrus for interpretation of emotional aspect of pain
Gyrus for interpretation of pain from internal organs and cause an autonomic response
Glutamate
Substance P
Cerebral cortex
Reticular formation
Postcentral Gyrus
Cingulate Gyrus
Insular Gyrus
Anterior Spinothalamic Tract
Good luck
Sensation
Light/Crude Touch and Pressure
Lab: Slow pain
SLOW PAIN
Felt 1.0 secs after stimulation
Burning, aching, throbbing pain
Produced by tissue destruction
Occur in any tissue of the body
Receptor
Free nerve endings
1st order neuron
Ipsilateral Dorsal Root Ganglia
2nd Order Neuron
Ipsilateral Substantia Gelatinosa
3rd Order neuron
Contralateral VPL of the Thalamus
Lab: Can also be VPM
Termination
Contralateral Postcentral gyrus
Lab: Broddman area 312, 57
Location in SC
Contralateral Anterolateral White Column
Extent in SC
All levels of the spinal cord
Extra Notes
Also has tract of lissaur
Also turns into spinal lemniscus at level of medulla
Together with lateral spinothalamic:
Level of pons : located at the posterior part of the spinal lemniscus
Level of midbrain : Located at tegmentum lateral to medial lemniscus
POSTERIOR/DORSAL COLUMN MEDIAL LEMNISCUS
Good luck
Sensation
Discriminative touch, Vibration sense, Conscious muscle joint sense
Lab: Spatial proprioception, kinesthesia
Receptors
Meissner Corpuscles, Pacinian Corpuscles, Muscle Spindles and GTO
1st Order neuron
Ipsilateral Dorsal Root Ganglia
2nd Order neuron
Ipsilateral Nucleus Gracilis and Nucleus Cuneatus
3rd Order neuron
Contralateral VPL of the thalamus
Lab: Or VPM
Termination
Postcentral gyrus of cerebral cortex
Lab: Broddman area 312, 57
Location in SC
Posterior white column
Medial = Gracilis
Lateral = Cuneatus
Extent in Spinal Cord
Fasciculus Gracilis = T6 below (meron pa above pero gracilis lng nasa baba)
Fasciculus Cuneatus = T6 above
Follow up questions:
At the 2nd order neuron of the DCML tract, what are the axons called?
As the tract ascends through the brainstem after decussation what is it called?
At the 3rd order neuron, where do the axons pass through?
What is the arrangement of the spinal nerves from medial to lateral?
Internal Arcuate Fibers
Medial Lemniscus
Posterior limb of the internal capsule of the corona radiata
Sacrum, Lumbar, Thoracic, Cervical.
CUNEOCEREBELLAR TRACT (READ)
Above T6 only
Originate in nucleus cuneatus and enter cerebellum through the ipsilateral inferior cerebellar peduncle
Known as the posterior external arcuate fibers
To convey information of muscle joint sense to the cerebellum
POSTERIOR and ANTERIOR SPINOCEREBELLAR TRACT
good luck
Sensation
Unconscious muscle joint sense
Receptors
Muscle Spindles, GTO and joint receptors
1st Order neuron
Ipsilateral DRG
2nd Order Neuron
Ipsilateral Nucleus Dorsalis / Clarke Nucleus
3rd Order Neuron

Termination
Ipsilateral Cerebellar Cortex
Location in SC
Posterior : Ipsilateral White Lateral Column
Anterior : Contralateral White Lateral Column
Only Anterior fibers decussate
Some anterior fibers go ipsilaterally
Extent in SC
above L2
Follow up questions:
Which cerebellar peduncle does the posterior spinocerebellar tract join?
Which cerebellar peduncle does the Anterior spinocerebellar tract join?
Since the nucleus dorsalis only extends from C8-L2, where does the axons below L2 pass?
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
Superior cerebellar peduncle
Posterior white column
SPINOTECTAL tract
Good luck
Sensation
Spinovisual reflexes
receptor
free nerve endings
1st order neuron
Ipsilateral DRG
2nd order neuron
Unknown; decussates at the level of the spinal cord
3rd order neuron
N/A
Termination
Contralateral superior colliculus
Location in SC
Anterolateral white column
extent in SC
All levels
SPINORETICULAR tract
Good luck
Sensation
Consciousness
Receptor
Free nerve ending
1st order neuron
Ipsilateral Dorsal Root Ganglia
2nd Order Neuron
Unknown; uncrossed
3rd order neuron
N/A
Termination
Reticular formation of brainstem
Location in SC
Lateral white column
Extent in SC
All levels
SPINO-OLIVARY TRACT (READ)
1st Order Neuron: DRG
Unknown 2nd order neuron
Axons cross midline and ascend as spino-olivary tract in junction of anterior and lateral columns
3rd Order: inferior olivary nuclei in medulla
Axons decussate and pass through inferior cerebellar peduncle to cerebellum
Conveys information from cutaneous and proprioceptive organs
VISCERAL SENSORY TRACTS (READ)
Receptor: pain and stretch receptor endings in viscera
1st Order Neuron: DRG
2nd Order Neuron: posterior or lateral gray horn
Axons join the spinothalamic tracts and ascend
3rd Order Neuron: VPL of thalamus
ASCENDING TRACTS DONE
Take a break and rehydrate

DESCENDING TRACTS REVIEW
The following slides will ask for everything in the tables of the WS Doc gave us, make sure u studied them before.

Anatomical Organization
Lower Motor Neuron (LMN)
Anterior horn motor neuron send axon to innervate the skeletal muscle through the anterior roots of spinal nerves
Upper Motor Neuron (UMN)
Supraspinal neurons and their tracts
Anatomical Organization
1st Order Neuron: cerebral cortex
2nd Order Neuron: anterior horn of spinal cord; axons are short
3rd Order Neuron: LMN; axons innervate the skeletal muscle through anterior root of spinal nerve
LATERAL AND ANTERIOR CORTICOSPINAL TRACT
good luck
Function
Rapid, Skilled, Voluntary movements, especially distal ends of the limbs
Origin
Primary motor cortex (1/3), secondary motor cortex(1/3), Parietal lobe (1/3)
More info:
⅓ from primary motor cortex (area 4) cortical layer 5, pyramidal cells
⅓ from secondary motor cortex (area 6)
⅓ from postcentral gyrus of parietal lobe (area 3,1,2)
Decussation
Lateral Tract : Junction of the spinal cord and medulla
Anterior Tract: Level of termination
Termination
Anterior Horn Cells
Location in spinal cord
Lateral : Descends into the contralateral white columns
Anterior: Descends into the anterior white column
RUBROSPINAL TRACT
Good luck
Function
Facilitates the activity of flexor muscles and inhibits activity of extensors
Origin
Red nucleus of the midbrain
Decussation
Immediately at the level of the red nucleus
Termination
Anterior horn cells
Location in SC
Lateral white column
Additional Notes
Receive afferent impulses with cerebral cortex and cerebellum
Indirect pathway by which the cerebrum and the cerebellum can influence a and y motor neurons
VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACT
Facilitates extensors and inhibits flexors
Lab: responsible for Balance as well
Origin
Vestibular nuclei
Decussation
N/A; uncrossed
Termination
Anterior Horn cells
Location in SC
Anterior column
RETICULOSPINAL TRACT
Good luck
Function
Inhibits or facilitates voluntary movement; hypothalamus controls sympathetic and parasympathetic outflows
Origin
Reticular formation of pons and medulla
Decussation
Some cross at various levels
Termination
α and 𝛾 motor neurons
Location in SC
Descends in anterior column
TECTOSPINAL TRACT
Good luck
Function
Reflex postural movements concerning sight
Origin
superior colliculus of midbrain
Decussation
Soon after origin
Termination
α and 𝛾 motor neurons or anterior horn cells (idrk)
Location in SC
Anterior white column
DESCENDING AUTONOMIC FIBERS (read)
From cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, amygdaloid complex and reticular formation
Cross midline in brainstem
Descend in lateral column
Synapse with autonomic motor cells in thoracic and upper lumbar levels for sympathetic and mid sacral levels for parasympathetic
ARRANGEMENT OF NERVE FIBERS IN WHITE MATTER
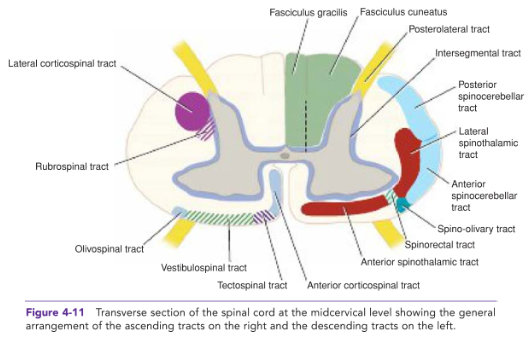
INTERSEGMENTAL TRACTS (read)
Short ascending and descending tracts that originate and end within the SC
In anterior, lateral and posterior columns
To interconnect neurons of different segmental levels
Important for intersegmental reflex
Does not go out of the SC
Tracts that start within the spinal cord and end within the spinal cord only at a different level
Connect different segments of the SC