Chapter 3- Separation and Purification
- A pure substance consists of a single element or compound.
- Pure substances have a constant and fixed boiling and melting point.
- Impurities cause variation in the melting and boiling points of the substance. Therefore, they can be used to determine if a substance is pure or not.
- Different purification techniques can be used to separate and purify substances.
| Method | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
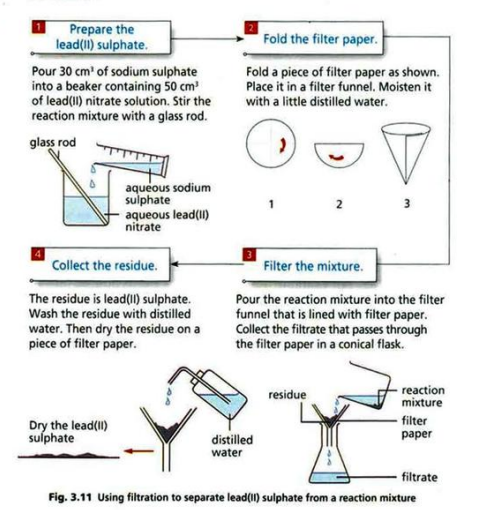
| Filtration | Insoluble solid from liquid | Sand and water |
| Evaporation to dryness | Soluble solid from a solution | To get salt from salt solution |
| Crystallization | Pure solid from a solution | To get Copper (II) sulfate from water |
| Solvent in which only one solid is soluble | A Mixture of two solids | Sand and salt |
| Sublimation | Solid that sublimes with one which doesn’t | Iodine and sand |
| Magnet | Magnetic substance from a non-magnetic one | Iron filings and sulfur |
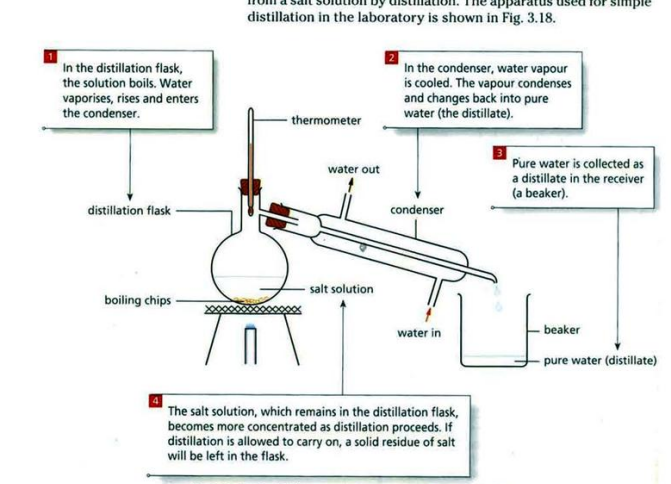
| Simple distillation | Pure solvent (liquid) from the solution | To get water from a salt solution |
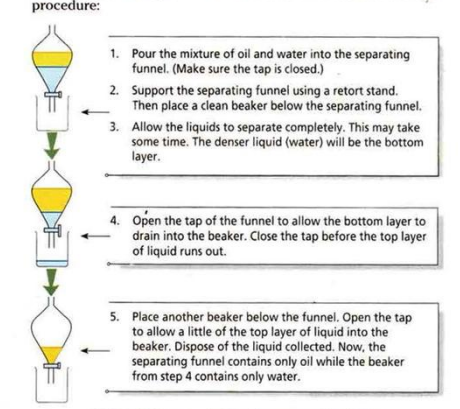
| Separating funnel | Immiscible liquids | Oil and water |
| Fractional distillation | Miscible liquids with different boiling points | Water and ethanol |
| Chromatography | Components that dissolve in the same solvent | Different dyes |
| Centrifugation | Mixtures by spinning | Blood cells from plasma |
| Decanting | Liquid and insoluble particles | Rice from water |
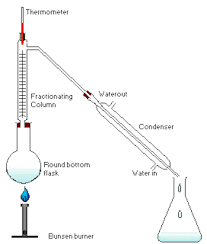
STEPS TAKEN DURING DISTILLATION:
Thermometer should be placed beside the sidearm of the distillation flask, not inside the liquid.
Water outlets should be positioned in the correct way with cold water in from the bottom and leaving from the top.
The condenser slopes downward so the pure solvent runs to the flask/beaker.
If the distillate is volatile, it has to be kept in a container containing ice so it doesn’t evaporate.
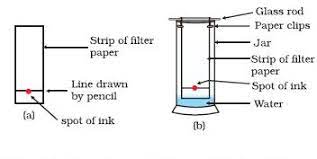
Chromatography
Different components separated using chromatography have distinct Rf values or Retention factors.
Rf value is calculated by dividing the distance moved by the solute by the distance moved by the solvent.
Rf values can be matched by the already known values to identify the component.
Sometimes, the components are transparent such as amino acids. A locating agent (e.g. Ninhydrin) is sprayed on the chromatogram to make them visible.