Repro Week 1
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
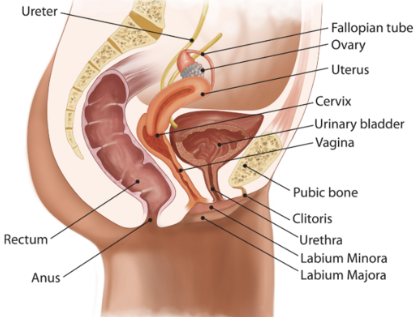
does the uterine system have direct contact with ovaries
no
what does the female duct/tube system include
1 vagina
1 uterus
2 uterine tubes (fallopian tubes)
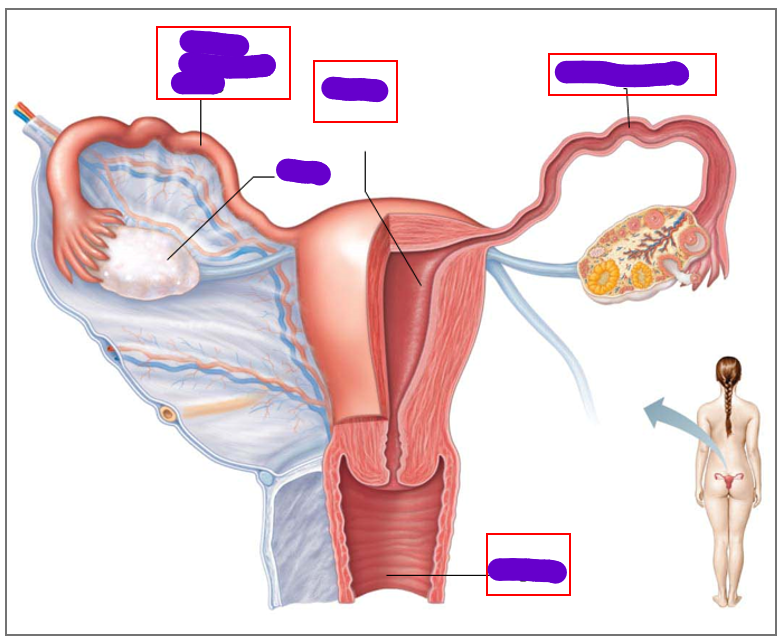
where are the follicles located
cortex of ovaries
what is an oocyte
immature egg cell
how many oocytes in each follicle
1
What surrounds the oocyte in a primordial follicle
A single layer of flat follicle cells
what surrounds more mature follicles
multiple layers of granulosa cells
what structure forms in mature follicles
antrum
what happens to the oocyte in ovulation
it is expelled from the ovary
what happens to the follicle after ovulation
it becomes a corpus luteum
what is the HPG axis
a hormonal feedback loop that regulates reproduction and cycles
what organs are involved in the HPG axis
hypothalamus
pituitary gland
gonads
what are the 3 key events in the female reproductive tract
ovarian cycle (in ovaries)
menstrual cycle (in uterus)
changes in cervical mucus composition
what is the ovarian cycle
Monthly series of events associated with maturation of the ovum
what are the phases of the ovarian cycle
follicular phase
ovulaton
luteal phase
what is the follicular phase
period of vesicular follicle growth
when does the follicular phase occur
days 1-14
what is the luteal phase
period of corupus luteum activity
when does the luteal phase occur
days 14-28
what do ovarian follicles do
house and nurture developing oocytes
what causes the ovary wall to rupture in ovulation
rising levels of LH
what do granulosa cells respond to
FSH
what do granulosa cells secrete in response to FSH
estradiol and inhibin
what do theca cells respond to
LH
what do theca cells release in response to LH
androgens and progesterone
what does the corpus luteum secrete
progesterone + estradiol + inhibin
what is the corpus hemorrhagicum
a temporary structure filled with clotted blood
when does the corupus hemorrhagicum form
immediately after ovulation and before the corpus luteum develops
what happens to the corpus luteum if no pregancy occurs after 10-12 days
it regresses and becomes corpus albicans (scar tissue)
what happens to the corpus luteum if pregancy occurs
it is supported by HCG (human chorionic gonadotrophin)
what happens to gonadotrophins LH and FSH during the ovarian cycle
they both spike right before ovulation (LH spikes much more) and come back down
what happens to estrogen during the ovarian cycle
gradually rises and sharp peak right before ovulation, then another moderate rise due to corpus luteum
what happens to progesterone during the ovarian cycle
dramatic rise after ovulation and falls sharply if no pregnancy
what happens to inhibin during the ovarian cycle
small rise before ovulation and a larger rise due to corpus luteum
what is oogenesis
production of female gametes (oocytes/ova) in the ovaries
when does oogenesis begin
begins during fetal development
how many new ova are formed after birth
none
how many primordial follicules does the ovary contain at birth
around 2 million
how many of these follicules actually mature
only about 400-500 oocytes
when does female meiosis begin and end
begins at fetal stage
ends at time of fertilisation
what are primordial germ cells
diploid stem cell precursors of oocytes
what is an oogonium
when the primordial germ cell arrives in the ovary, it is called an oogonium
how many oocytes does each oogonium form via mitosis
2
what happens to primary oocytes in meiosis
they start meiosis and arrest in prophase 1 of meiosis 1
what happens to primordial follicules each month after puberty
5-20 primordial follicules grow into primary follicules
what is the difference between these primordial and primary folllicles
primary follicles have an extra layer of granulosa cells
extra outer layer of theca cells
what happens when primary follicles become secondary follicles
granulosa cells multiply and produce fluid, which creates the antrum
what is the zona pellucida
surrounds the primary oocyte
what is the corona radiata
the innermost layer of granulosa cells
what does the secondary follicle mature into
graafian follicle
what happens to the graafian follicle if fertilisation occurs
it becomes a mature ovum and degnerates its 2nd polar body
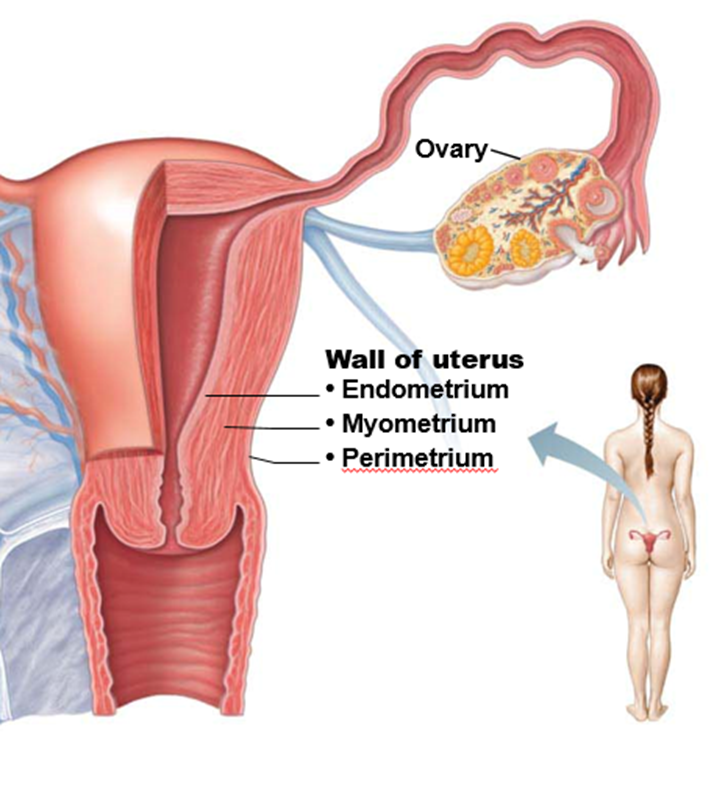
what does estrogen do
builds up endometrial lining
makes mucus fluid so sperm can pass to reach oocyte
what does progesterone do
maintains endometrial lining
what is menses/menustration due to
progesterone withdrawal due to corpus luteum dying
what are the phases of the menstrual cycle
menstrual phase (days 1-4)
proliferative phase (days 5-14)
secretory phase (days 15-26)
premenstrual phase (days 27-28)
what triggers the start of menstrual phase
lack of progesterone
what is the loss of blood due to
breakdown of superficial layers of uterine endometrium
how much blood is lost during menstruation
30-50ml of mainly arterial blood
how long does menstruation occur
3-6 days and often heavier on the 2nd day
what happens in the proliferative phase
FSH grows follicles and oocytes which produce estrogen
how does estrogen thicken the endometrium
it travels through blood to get to the uterus
what is the size of the uterine glands during the proliferative phase
small and round
what triggers corpus luteum formation
LH
what does the corpus luteum do in the secretory phase
produces progesterone and estrogen
what does progesterone and estrogen do in the secretory phase
maintains endometrial lining and enlarges glands
what do uterine glands do
secrete uterine milk
what is the size of the uterine glands in the secretory phase
elongated and coiled
what happens in the premenstrual phase
breakdown of glands
blood vessels leak
tissue death
what causes these outcomes of the premenstrual phase
lack of progesterone
what type of tissue is present on the luminal surface of the cervix
mucus secreting simple columnar epithelium
what type of tissue is present on the external surface of the cervix
moist non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what is the transformation/transitional zone
area between columnar and squamous cells
how big is a cervix during ovulation
22m in length
6mm in diameter
where is cervical mucus released from
the cervix
why does cervical mucus change composition
in response to hormonal changes
what are the 2 major fractions of cervical mucus
insoluble gel/mucin
aqueous phase containing the soluble components
what are the soluble components
lipids, fatty acids, prostaglandins, proteins, enzyme inhibitors, and immunoglobulins
what type of barrier is cervical mucus
physical or immune barrier to pathogens
what is the cervical mucus composition during early follicular phase
mucus is thick and sticky
what is the cervical mucus composition during late follicular phase
copious, watery, thin & alkaline
has a fern-like pattern when dried on a slide
sperm can penetrate mucus
what is the dominant influence on cervical mucus composition during late follicular phase
estrogens
what is the cervical mucus composition during ovulatory period
mucus is thinnest and wet and clear at time of ovulation
has a arborizing fernlike pattern when dried on a slide
sperm can easily penetrate mucus
what is the cervical mucus composition during luteal phase
mucus is thick, viscous and cellular
mucus is scanty
no ferning pattern when dried
what is the dominant influence on cervical mucus composition during luteal phase
progesterone
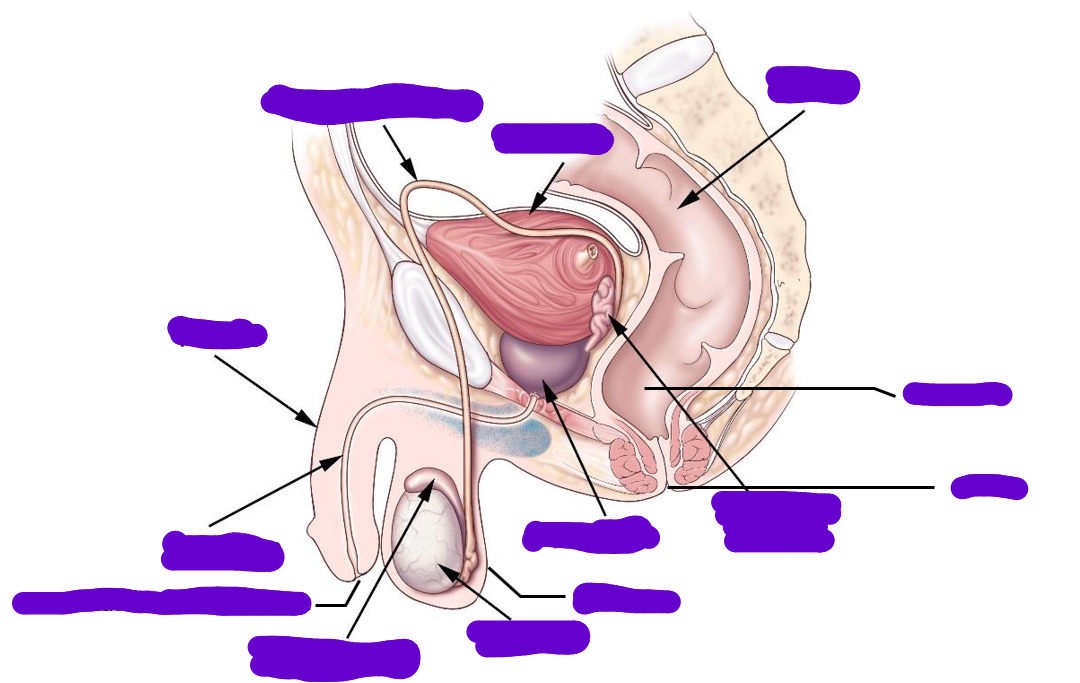
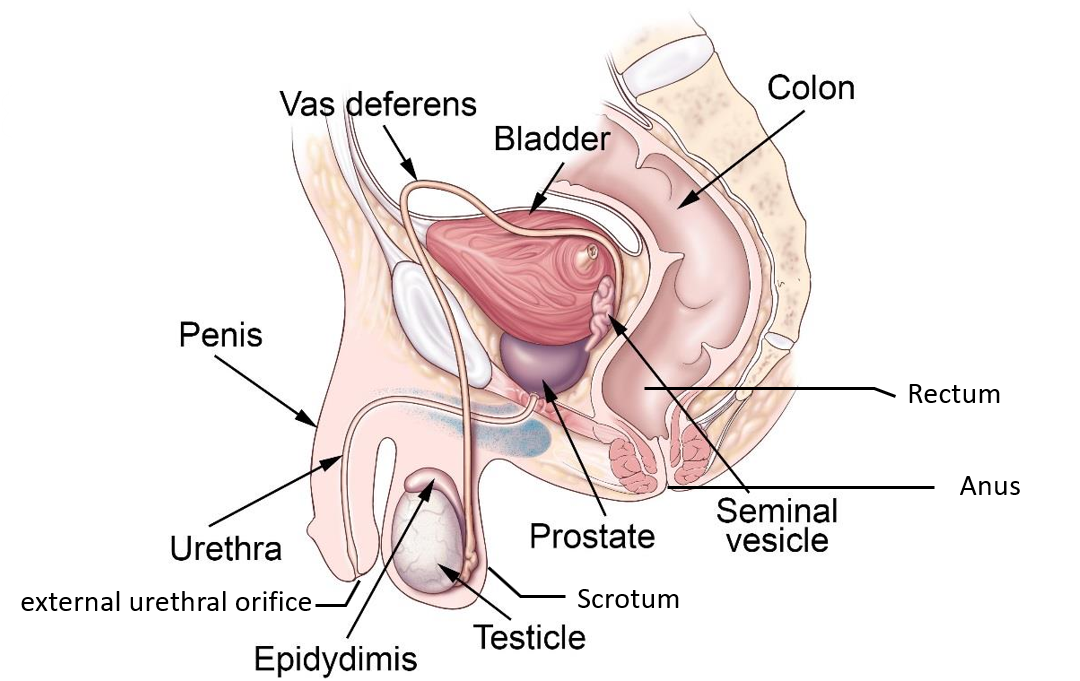
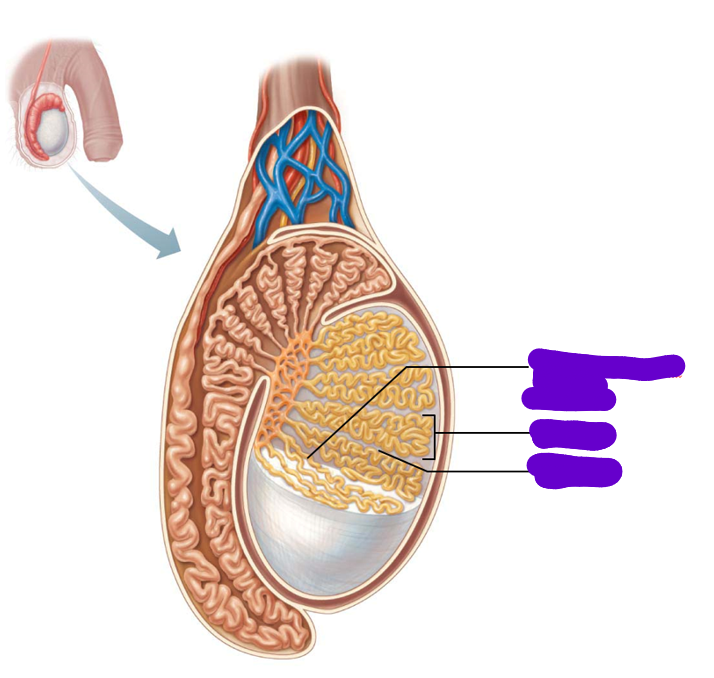
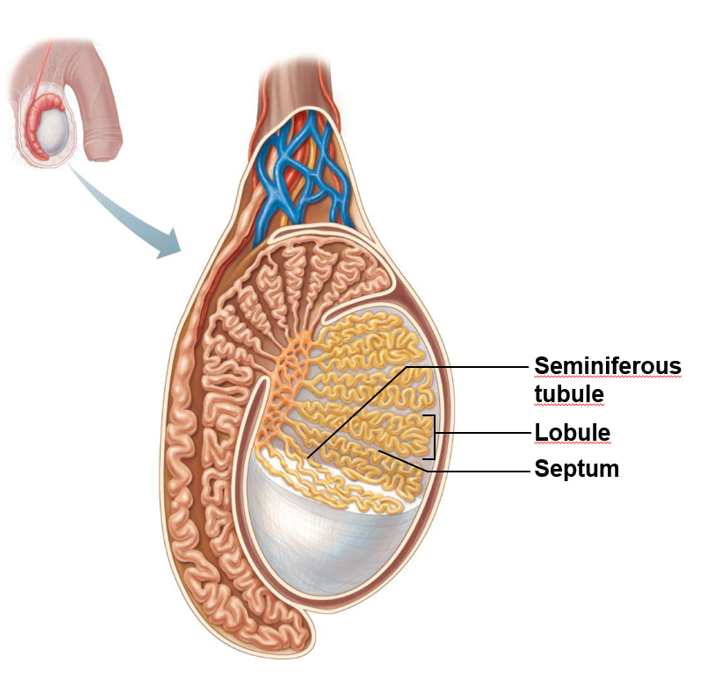
where are the testes located
in the scrotum
what do septa (septum plural) do
divide testis into around 250 lobules
what does each lobule contain
1-4 seminiferous tubules
where do male gametes develop
in the seminiferous tubules
what does spermatogonia mature into
spermatozoa
how is sperm delivered to exterior
through a system of ducts
what is the path of sperm
Seminiferous tubules
Straight tubules
Rete testis
Efferent ductules
Epididymis
Vas deferens
ejaculatory duct
urethra
how long is the duct of the epididymis
around 6m in length
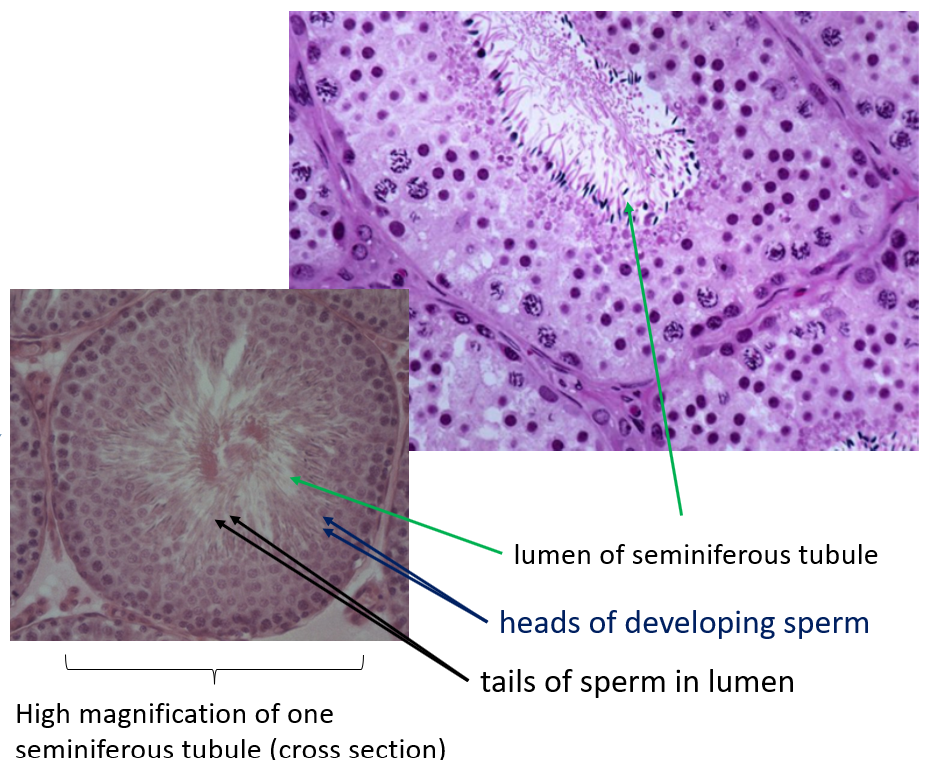
what happens in the seminiferous tubules
sperm production
what tissue lines the seminiferous tubules
complex stratified epithelium