PHPOrgChem (Lecture) | Module 7: (Part 3: REACTIONS OF ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS,THIOLS , ETHERS AND THIOETHERS)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Oxidation Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: It is a reaction where a molecule loses electrons/hydrogen and gains oxygen
Oxidation Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL:
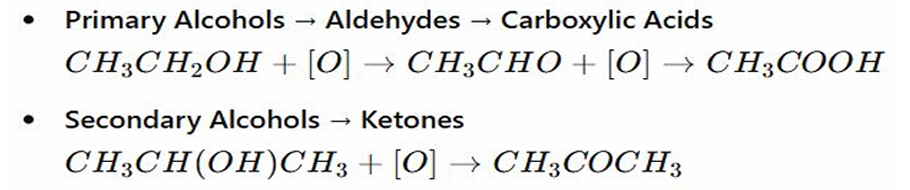
HYDROXYL GROUP
OXIDATION OF ALCOHOL: The _________________ is replaced by a CARBONYL GROUP
Oxidizing Agents
OXIDATION OF ALCOHOL: The presence of _____________ removes hydrogen from the (-OH) group and from the adjacent carbons.
Primary Alcohols
OXIDATION OF ALCOHOL: They are oxidized further further to CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Methanol
OXIDATION OF ALCOHOL:
Example: _________ (Primary Alcohols)
They first turn to ALDEHYDES (which has the carbonyl group: C=O), when oxidation continues they became CARBOXYLIC ACIDS like vinegars
Secondary Alcohols
OXIDATION OF ALCOHOL: Stops at KETONE
Isopropanol
OXIDATION OF ALCOHOL:
Example: __________ (Secondary Alcohols)
Stops at the KETONE STAGE (which also has the C=O group) and DOES NOT OXIDIZED FURTHER
Oxidation Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: When alcohols reacts they can lose hydrogen or gain oxygen in a process called?
Oxidation Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: This happens when special chemicals or oxidizing agents like potassium dichromate in acid removes hydrogen from the alcohol molecule
Oxidation Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: In short, this reaction changes alcohols by replacing their hydroxyl group (-OH) with a carbonyl group (C=O) and how far they change depends on the type of alcohol present.
Dehydration Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: It is a reaction where a molecule loses water to form a double bond
Double Bond
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: Dehydration is a reaction where a molecule loses water to form a?
Dehydration Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL:
The acid (sulfuric acid) protonates (add proton) the (-OH) group making it a good leaving group
The beta hydrogen from the adjacent carbon (neighboring carbon) is removed forming a double bond (alkene C=C)
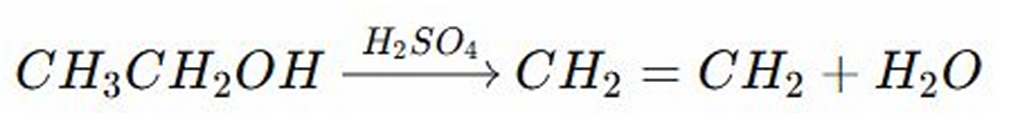
Esterification Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: It is a reaction between alcohol and carboxylic acid to form ester and water
Esterification Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL:
The hydroxyl group (-OH) of the carboxylic acid and Hydrogen from the alcohol combined to form water
The remaining parts forms an ester bond, connecting the alcohol and the acid
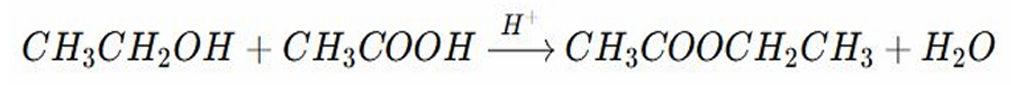
Esterification Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: In simple terms, it is a reaction where alcohol and an acid join together, losing water and forming esters.
Halogenation Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL:
In the given (specific substitution reaction), an alcohol (-OH) is replaced by a halogen molecule. Then the (-OH) forms water)
The hydrochloride protonates the (-OH) converting it into a better leaving group which is the water (nawawala).
The chloride ion from the hydrochloride attacks the carbon replacing the (-OH).
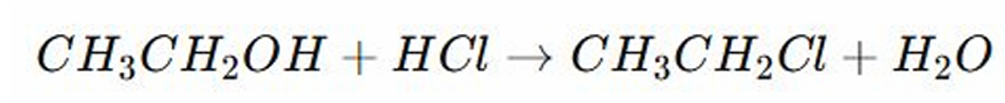
Substitution Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL: a reaction where one atom or a group in a molecule is replaced by another molecule.
Oxidation Reaction, Dehydration Reaction, and Halogenation Reaction
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOL
Acid-Base Reaction
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS: It is a reaction where an acid donates a proton or Hydrogen ion to a base.
Acid-Base Reaction
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS:
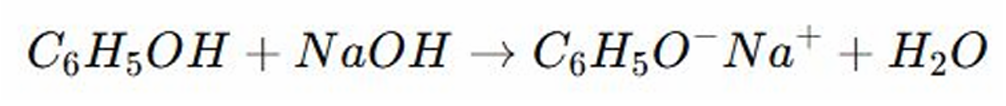
Slightly Acidic
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS: Phenol is ________ due to the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion.
Phenoxide Ion
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS:Phenol is slightly acidic due to the resonance stabilization of the?
Weak Acids
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS: PHENOLS AND THIOLS ARE _______ AND CAN REACT WITH BASES TO FORM SALTS
Losing
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS: Phenol reacts with bases like NaOH by _____ a proton to form a phenoxide ion
Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS: This is a reaction when an electrophile replaces a hydrogen in an aromatic ring
Bromination
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS: This reaction is also called as?
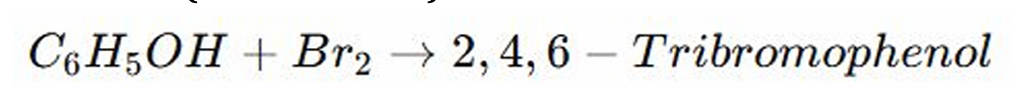
Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS:
The (-OH) group activates the benzene ring, making it highly reactive at the ortho and para positions.
Bromide adds (replaces the Hydrogen) to these positions by?
Ortho, and Para Positions
ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION OF PHENOLS: The (-OH) group activates the benzene ring, making it highly reactive at what positions?
Acid-Base Reaction, and Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
REACTIONS OF PHENOLS
Oxidation to Disulfides
REACTIONS OF THIOLS: A reaction where thioethers (R-S-R) are oxidized to sulfoxides, or sulfones
Sulfoxides, or Sulfones
REACTIONS OF THIOLS: Oxidation to Disulfides is a reaction where thioethers (R-S-R) are oxidized to?
Disulfide Bonds
REACTIONS OF THIOLS: Thiols are oxidized by losing hydrogen to form a sulfur atom. This forms _________, which are common in proteins.
Proteins
OXIDATION TO DISULFIDES OF THIOLS: This forms disulfide bonds, which are common in?
Oxidation to Disulfides
REACTIONS OF THIOLS: SH can be oxidized to thioethers which can be further oxidized to sulfoxides and sulfones.
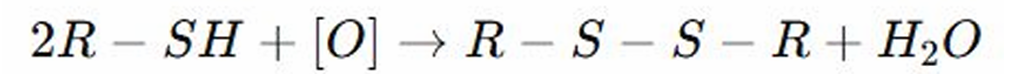
Thioethers
OXIDATION TO DISULFIDES OF THIOLS: SH can be oxidized to __________ which can be further oxidized to sulfoxides and sulfones.
Oxidation to Disulfides
REACTIONS OF THIOLS: Thiols loses hydrogen to form a sulfur atom during oxidation, as a result two thiol molecules can linked together to form a disulfide bonds
Sulfhydryl Group
REACTION WITH METALS OF THIOLS: Thiols are organosulfur compounds that contain _________
Strong Affinity
REACTION WITH METALS OF THIOLS: They are known for their higher reactivity especially with metals → The reaction of thiols with metals is primary due to the _________ between sulfur and metal ions
Reaction with Metals
REACTIONS OF THIOLS:
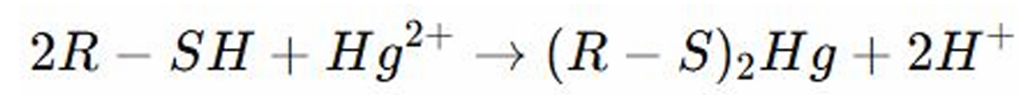
Acidic
REACTION WITH METALS OF THIOLS: Thiols are _____ and react with heavy metals ions (Mercury)
Reaction with Metals
REACTIONS OF THIOLS: Sulfur attaches to mercury/metal forming metal sulfide complexes (stable complexes)
Metal Sulfide Complexes
REACTION WITH METALS OF THIOLS: Sulfur attaches to mercury/metal forming? (stable complexes)
Oxidation to Disulfides, and Reaction with Metals
REACTIONS OF THIOLS
Acidic Cleavage Reaction
REACTIONS OF ETHERS: It is a reaction where a bond is broken, splitting of molecule into two parts
Acidic Cleavage by Hydrogen Iodide or Hydrogen Bromide
REACTIONS OF ETHERS: First Carbon (R1) in ether is attack by iodine, then the second carbon (R2) forms alcohol (ethanol)
Acidic Cleavage by Hydrogen Iodide or Hydrogen Bromide
REACTIONS OF ETHERS:
Hydroiodic acid (HI) protenates the ether, making the oxygen a better leaving group
Hydroiodic acid (HI) donates proton (H+) to another molecule
The iodide ion attacks, breaking the Carbon-Oxygen bond, the ether is protonated making it susceptible to nucleophilic attack
First Carbon (R1) in ether is attack by iodine, then the second carbon (R2) forms alcohol (ethanol)
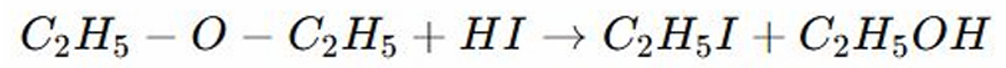
Autooxidation to Peroxides
REACTIONS OF ETHERS: it is a slow oxidation reaction of organic compounds with oxygen from the air.
Slow Oxidation
AUTOOXIDATION TO PEROXIDES: It is a ______________ reaction of organic compounds with oxygen from the air.
Peroxides
AUTOOXIDATION TO PEROXIDES: Ethers react with oxygen in the air to form ________, which are unstable and explosive
Autooxidation to Peroxides
REACTIONS OF ETHERS:
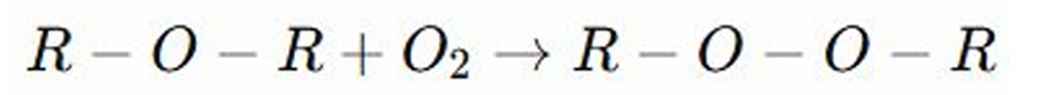
Acidic Cleavage by Hydrogen Iodide or Hydrogen Bromide, and Autooxidation to Peroxides
REACTIONS OF ETHERS
Oxidation to Sulfoxides and Sulfones
REACTION OF THIOETHERS: sulfur undergoes oxidation, forming first sulfoxides (SO) then sulfones (SO2).
Oxidation to Sulfoxides and Sulfones
REACTION OF THIOETHERS:
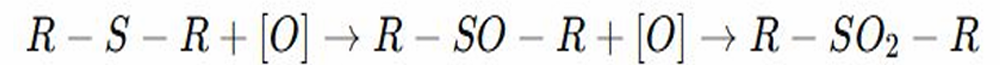
Sulfoxides
REACTION OF THIOETHERS: What is R-SO-R
Sulfones
REACTION OF THIOETHERS: What is R-SO2-R
Methylation Reaction
REACTION OF THIOETHERS: this is a reaction where a methyl group (CH3) is added to the molecule.
Methylation Reaction
REACTION OF THIOETHERS:
Sulfur donates electrons to the alkyl halide (iodomethyl), forming a sulfonium salt.
The sulfur atom in the thioether reacts with iodomethyl, adding a methyl group to the sulfur, and forming a sulfonium salt.
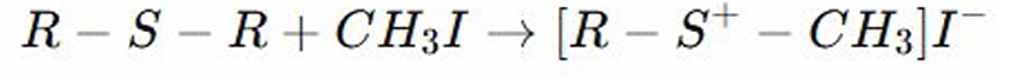
Sulfonium Salt
METHYLATION OF THIOETHERS: The sulfur atom in the thioether reacts with iodomethyl, adding a methyl group to the sulfur, and forming a __________
Oxidation to Sulfoxides and Sulfones, and Methylation
REACTION OF THIOETHERS