ID Lecture 31: Pathophysiology & Therapeutics of Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Adults | Quizlet
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
How much use of antibiotics for upper respiratory tract infections is inappropriate?
50%
What medications are the 2nd leading cause of ED visits due to adverse events?
Antibiotics
What antibiotic is no longer recommended for URTIs but is still commonly prescribed?
Azithromycin
Tier 1 diagnosis
antibiotics are sometimes indicated
Tier 2 diagnosis
antibiotics are sometimes indicated
Tier 3 diagnosis
antibiotics are rarely inficated
What type of diagnosis are URTIs?
Tier 2 or 3 (antibiotics are sometimes or rarely indicated)
Acute Rhinosinusitis
symptomatic inflammation of the mucousa, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses lasing LESS THAN than 4 weeks
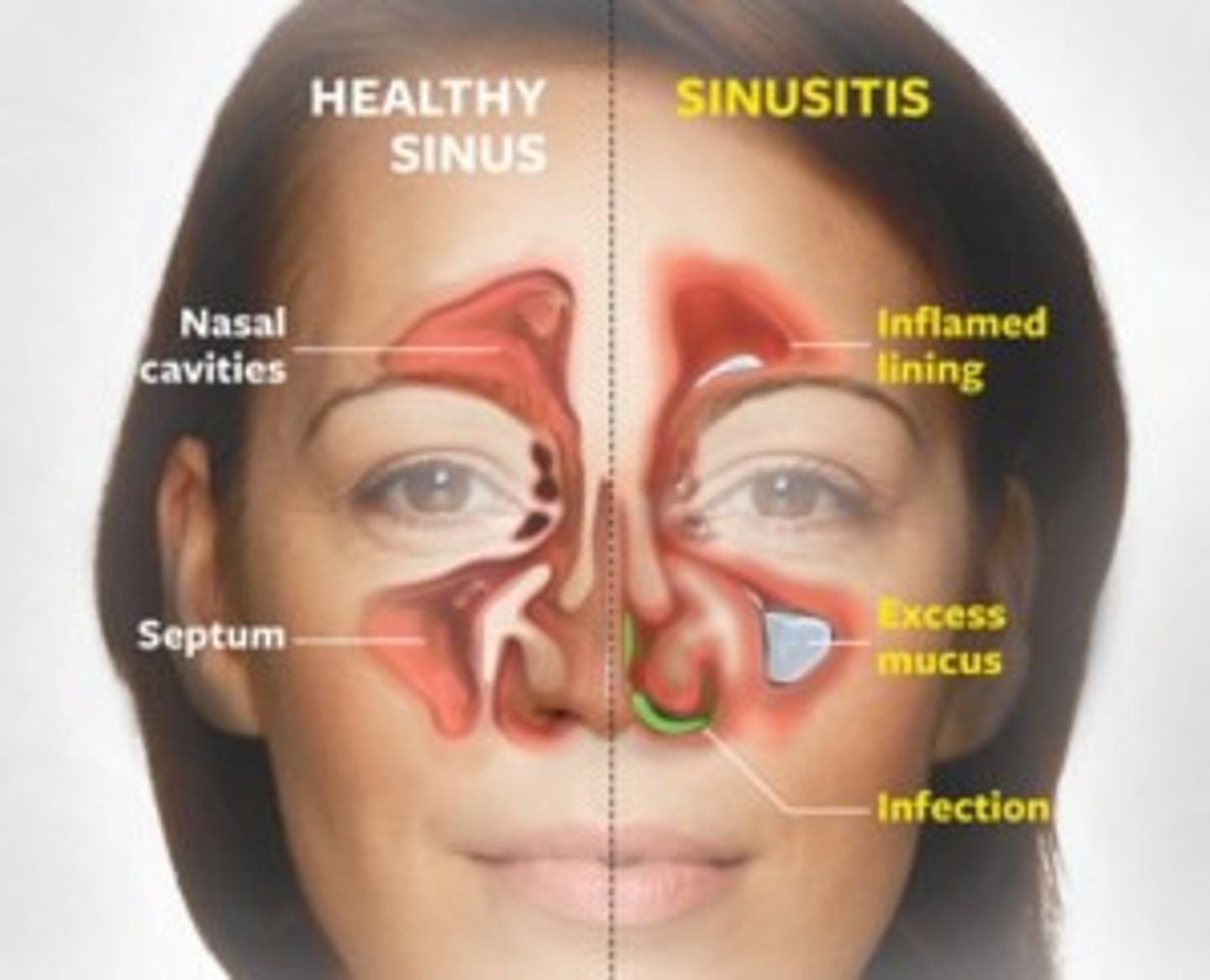
What are the s/sx of acute rhinosinusitis?
Purulent rhinorrhea
Facial pressure
HA
Fever
Maxillary dental pain
Cough
What bacteria cause acute bacterial rhinosinusitis?
S. pneumoniae
H. influenzae
+/- Moraxella catarrhalis
*typical flora for the region
What are the diagnostic criteria for bacterial acute rhinosinusitis?
Presence of at least ONE of the following:
- Persistence nasal discharge or daytime cough without improvement (>10 days)
- Worsening fever, daytime cough or nasal discharge after initial improvement
- Severe: fever, purulent nasal discharge for at least 3 consecutive days
What is the preferred treatment for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in adults?
Amoxicillin
OR
Augmentin
Plus symptom management
What is the treatment option for adult patients with severe acute rhinosinusitis?
High dose amoxicillin +/- clavulanate
Why are macrolides NOT preferred for acute bacterial rhinosinutitis?
risk of drug-resistant strep pneumo (DRSP)
Chronic rhinosinusitis
inflammatory condition involving the paranasal sinuses that lasts 12 weeks or LONGER
What are the 3 types of chronic rhinosinusitis?
w/o polyps
Allergic fungal
Nasal polyps
Chronic sinusitis is frequently _____________.
polymicrobial
When are antibiotics recommended in chronic rhinosinusitis?
in patients without nasal polyps or allergic fungal rhinosinusitis
What antibiotics are recommended in chronic rhinosinusitis?
Augmentin
Clindamycin
Moxifloxacin
Acute pharyngitis
infection of tonsils or posterior pharynx by microorganisms
What are some of the causes of acute pharyngitis?
Viral
Group A strep
Other bacteria
What is the main cause of acute pharyngitis?
Group A strep
When are antibiotics recommended in acute pharyngitis?
confirmed group A strep
(reduces chances of rheumatic fever)
What determines if a patient should be tested with a strep test?
Modified Centor Criteria:
Presence of TWO of the following:
- Temp >100.9F
- Swollen cervical nodes
- Tonsillar exudate
- Lack of cough/viral ARI symptoms
OR
Modified McIsaac Criteria:
- +1 point for ages 3-14 y/o
- -1 point for >45 y/o
- Temp >100.9F
- Swollen cervical nodes
- Tonsillar exudate
- Lack of cough/viral ARI symptoms
What are the Modified Centor Criteria?
Presence of TWO of the following:
- Temp >100.9F
- Swollen cervical nodes
- Tonsillar exudate
- Lack of cough/viral ARI symptoms
*used to determine if someone should be tested for Group A strep*
What are the Modified McIsaac Criteria?
Presence of at least TWO of the following:
- +1 point for ages 3-14 y/o
- -1 point for >45 y/o
- Temp >100.9F
- Swollen cervical nodes
- Tonsillar exudate
- Lack of cough/viral ARI symptoms
What treatment is recommended if the rapid strep test is negative?
no antibiotic therapy, only symptomatic tx
What treatment is recommended for a positive strep test?
Penicillin VK (DOC)
Amoxicillin
Benzathaine Penicillin
If allergy:
Keflex
Clindamycin
What is acute Rheumatic fever?
autoimmune reaction to infection with Group A strep
What are the s/sx of Rheumatic fever?
Polyarthritis
Myocarditis
Skin manifestations
Chorea
Long term heart damage --> CHF
When should antibiotic therapy be started for group A strep to prevent Rheumatic fever?
within 9 days of onset
What are some rare complications that can be mistaken for uncomplicated ARI?
Peritonsillar abcess
Epiglottitis
Ludwig's angina
Acute Bronchitis
infection and inflammation of bronchial airways
What is considered to the the only legitimate pathogen treated with antibiotics in acute bronchitis?
Pertussis
What is important to rule out before diagnosing for bronchitis?
pneumonia (CDC recommended)
What is the recommendation for antibiotic use in bronchitis?
Antibiotics are NOT routinely recommended for uncomplicated bronchitis
Azithromycin or Bactrim can be used if Pertussis confirmed or possible exposure
What are the criteria for using antibiotics in COPD exacerbations?
Increase in dyspnea
Increased sputum volume
Increased sputum purulence
Patient requires NIV or MV
What antibiotics are recommended for COPD exacerbations?
Augmentin
Macrolide
Doxycycline
What bacteria are we targeting in COPD exacerbations?
S. pneumoniae
H. influenzae
M. cattarhalis
Which COPD exacerbation patients recieve Quinolones?
patients that are hospitalized with respiratory failure/MV
What are the s/sx of the common cold (URI-NOS)?
Nasal congestion
Post nasal drip
Throat irritation
Sneezing
Coughing
HA
What is the recommendation of antibiotic use in URI-NOS?
antibiotics are NOT recommended, use symptomatic therapy
Patients with what ARIs should recieve antibiotics?
Pharyngitis
Bacterial Sinusitis
What antibiotics are the cornerstone of ARI therapy?
Penicillins
Penicillin-like abx
What are the reasons that antibiotics are overprescribed for ARIs?
Lack of knowledge
Diagnositc uncertainty
Patient pressure/satisfaction
Workload/habit
What are the 4 steps to managing expectations when it comes to prescribing antibiotics?
1. Communicate results of physical exam
2. Deliver a clear diagnosis
3. Negative followed by positive treatment recommendation
4. Contingency plan
What are the risks of overprescribing antibiotics?
ADEs
Abx resistance
Increased C. diff infections
Unnecessary HC resources