Class 2 - Secondary Data Analysis and Qualitative Research
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
pros and cons of secondary data
pros:
accessible
inexpensive
quick
cons:
relevancy
accuracy
methods - important questions
how was the data collected (context of where participant was), was there an adequate response rate (how many were asked vs how many responded), data quality, sampling technique, sufficient sample size?
how was the questionnaire designed (leading questions?), are the analyses appropriate for the questions, when was the data collected?
triangulation
using different methods to assess the same problem
there’s no perfect method, using multiple helps with accuracy
purpose and content
why was the data collected
how were the variables defined (ie. how was the construct measured?)
whenever possible, use original source
secondary data sources
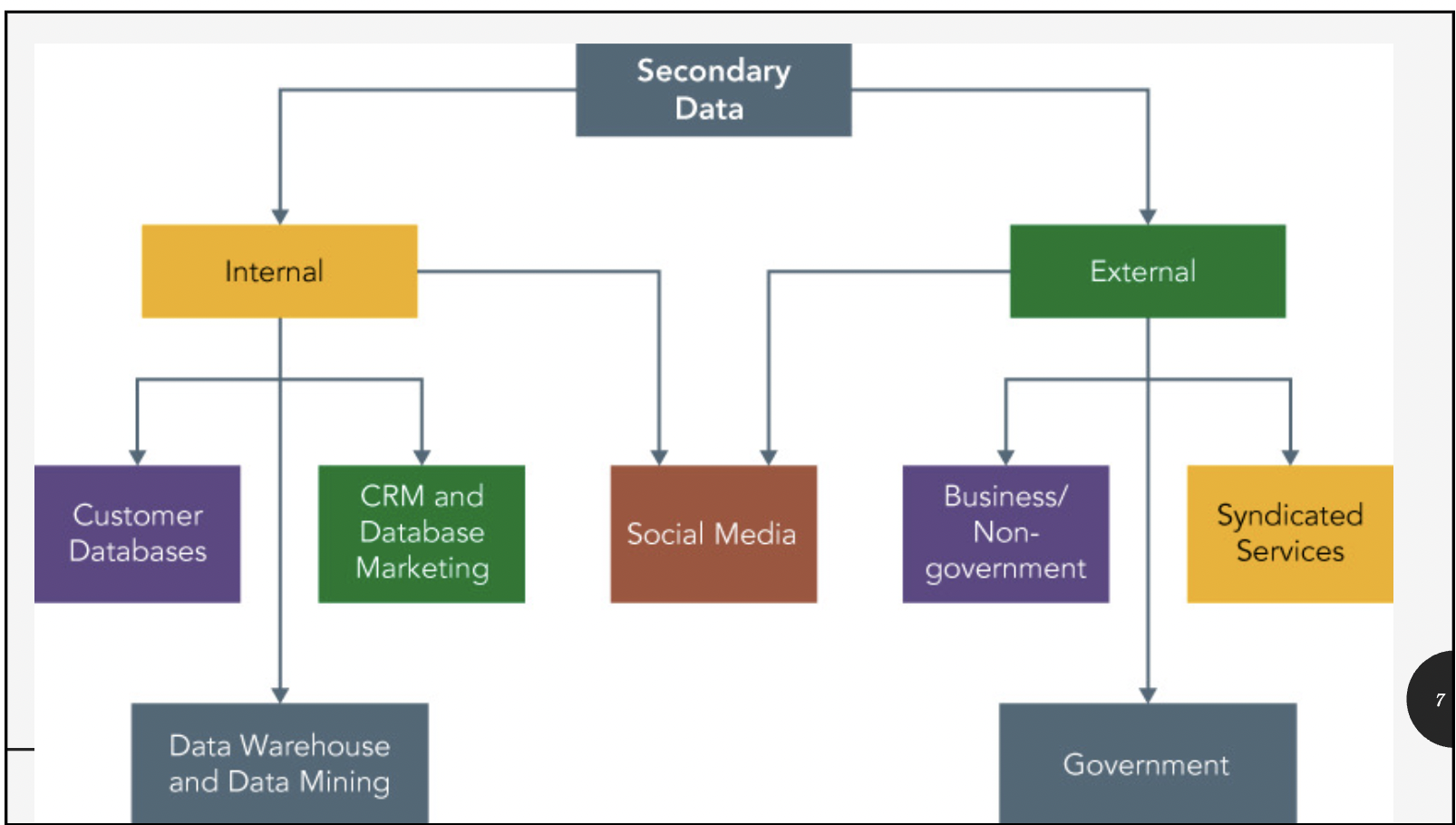
internal secondary data
customer databases
sales calls, invoices, warranty activations, loyalty programs
data warehouse and mining
company wide, operational, CRM, help discover patterns of data and inform marketing strategy
external secondary data
business sources
company info (S&Ps, Moodys), AMA publications, EBSCO database, SSCI (social science citation index)
government sources
census data (eg. household info., age, marital status etc.), categorized geographically
world FactBook, FedWorld, Bureau of Labour Statistics, etc.
syndicated services
data collected by market research firms that serve the information needs of many companies
syndicated sources
units of measurement:
households/ consumers
panels - purchase, media
surveys - psychographic and lifestyle, advertising evaluation, general
electronic scanner services - volume data tracking, scanner panels, scanner panels with cable tv
institutions
retailers, wholesalers - audits
industrial firms - direct inquiries, clipping services, corporate services
panel surveys
regularly conducted surveys
predesigned questionnaire
comprehensive
representative or targeted
participant has info about the survey, what’s going to be asked, purpose, etc.
syndicated panel surveys (or omnibus panels)
don’t measure the same variable
cross-sectional
arious survey techniques
targeted examples
pyschographics
psychological variables
attitudes, values, beliefs, motivation, goals, physical needs
psychological measures of lifestyle (AIOs)
varies in term of state or trait, traits are more stable
advertising evaluation
assess ad effectiveness
standardized measures
recall
persuasion
ad reactions
general surveys
general purchase and consumer behaviour
politics, sports, business, health
survey pros and cons
pros:
flexible, specific segment, predictive
cons:
drawbacks of self report (gaps between what people report and what they actually do, why triangulation is important)
biased questions?
media panels
used to select appropriate ads. track consumer behaviour after ad
passively measures TV viewing
Tv ratings and audience estimates
Purchase / Media Panels pros and cons
pros:
higher quality data (panel vs sample survey)
can be longitudinal
cons:
not always representative
biased behaviour due to involvement
scanner data
volume tracking scanner panel data
occurs at point of sale, can be coupled with media panel
qualitative research
largely unstructured and exploratory
best when you don’t have a theory or hypothesis
smaller samples, data is text (like a transcript of interview)
qualitative research procedures
direct (non disguised) (participants know general idea of study)
focus groups
depth interviews
indirect (disguised)
projective techniques
association techniques
completion techniques
construction techniques
expressive techniques
focus groups
trained moderator, minimally structured, unexpected findings
groups of 8-12, respondents should have something in common, 1-3 hours, video recroded
meant to facilitate conversation, want participants to be as similar as possible, prior experiences with product, don’t want people who have participated in a lot of focus groups
moderator must be kind, sensitive, involved, encourage conversation, get specifics
practical applications of focus groups
perceptions / preference
impressions of new product
generating new ideas
creative concepts
price impressions
depth interviews
semi structured
one on one
want to uncover lived experiences
build rapport and have a real conversation
encourage elaboration, ask open ended questions
depth interviews pros and cons
pros:
direct to respondent
large exchange of information
no conformity
cons:
expensive and difficult to source
quality depends on interview skills
qualitative analysis - coding
assigning meaning to passages of text, first analytic step of data analysis process
segment emerging themes into categories
make categories represent abstract (theoretical) ideas
meaningful analysis or themes that emerge out of the data
two steps of qualitative coding
initial coding
focused coding
initial coding
large quantities of raw qualitative data, reading through and finding themes
remain open to explore possibilities
guides core conceptual categories
what is this data a study of?
what does the data suggest?
from whose point of view?
what theoretical category does this indicate?
focus coding
category development, try to abstract and turn into broader themes / categories
direct, selective, conceptual
identify most significant /frequent codes
merge similar codes to form higher-level, more abstract codes (ie. broader overall themes that fit the data)
stop this process at saturation (when you consistantly see the same results)
ethnography
a qualitative method involving the immersion of researchers into consumers' natural environments—homes, workplaces, or stores—to observe actual behaviors, routines, and pain points
recording the life of a particular group, entials sustained participation and observation of their community or social world
often includes supplementary data from documents, diagrams, maps, photographs, and sometimes formal interviews)
netnography
an interpretive, qualitative methodology that adapts ethnographic research techniques to study consumer behavior, online cultures, and social interactions within digital communities
an ethnogrpahy conducted among online communities