Mark scheme flashcards
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Describe how you could obtain a pure, dry sample of the insoluble solid from the final reaction mixture. (3)
M1 filter (off the precipitate)
M2 wash (with distilled/deionised/pure water)
M3 dry in a warm oven / leave to dry / dry with filter paper
State what is meant by the term ionic bonding (2)
M1 electrostatic attraction/forces between ions
M2 of opposite charge
(metals and non-metals)
Explain why magnesium chloride has a high melting point. (3)
M1 attraction (between ions) is strong
M2 lots of ions (in structure) / giant structure / lattice / lots of/many bonds
M3 (therefore) lot of (thermal/heat) energy required to overcome attraction / to break down the lattice
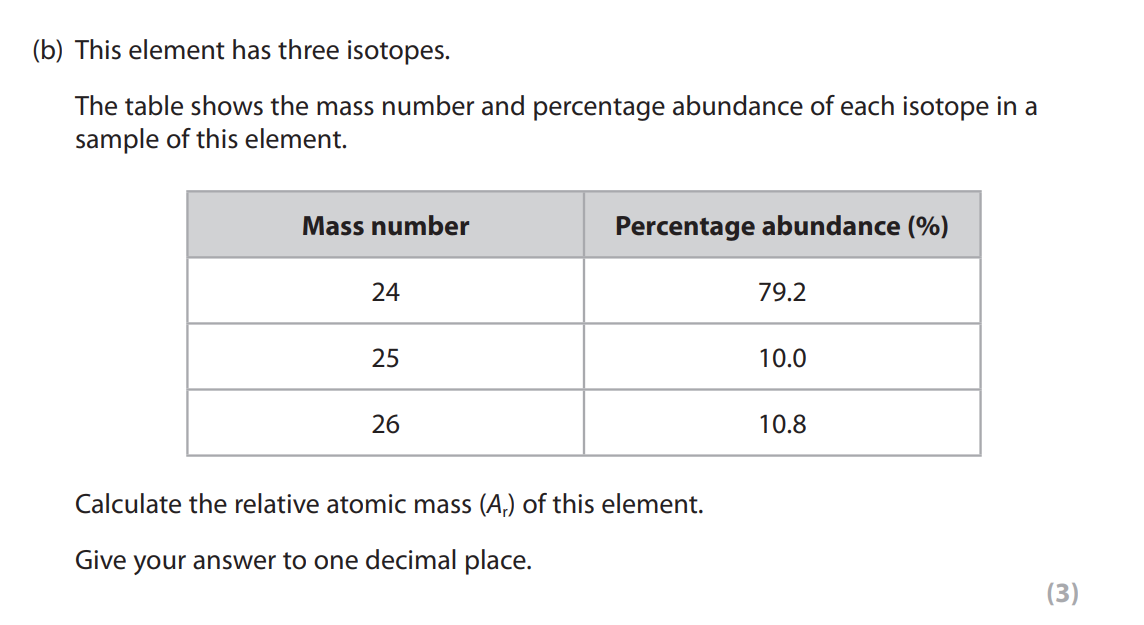

Give two characteristics of a homologous series. (2)
M1 (can be represented by a) general formula
M2 each member differs from the next by a CH2 group OWTTE
M3 (each member has) same functional group
M4 (each member has) similar/same chemical properties / similar/same (chemical) reactions
M5 trend in physical properties (between successive members)

Test for cation
M1 add sodium hydroxide (solution)
M2 if blue precipitate forms solution contains copper(II) ion(s) / contains Cu2+ / is a copper compound
M3 if green precipitate forms solution contains iron(II) ion(s) / contains Fe2+ / is an iron compound
Test for anion
M4 add silver nitrate (solution)
M5 if white precipitate forms solution contains chloride ion(s) / contains Cl- / is a chloride
M6 if cream precipitate forms solution contains bromide ion(s) / contains Br- / is a bromide

Any explanation that links any three of the following points for diamond
M1 each (carbon) atom is (covalently) bonded to four other (carbon) atoms
M2 in a (giant) tetrahedral lattice /network / structure
M3 the (covalent) bonds are (very) strong
M4 (therefore) diamond is (very) hard (and so good for cutting tools)
Any explanation that links any three of the following points for graphite
M5 each (carbon) atom is (covalently) bonded to three other (carbon) atoms
M6 (the structure is) in layers
M7 weak forces (between layers)
M8 (the layers can) slide over each other/ rub off
M9 this makes graphite soft (so it can make marks on paper)
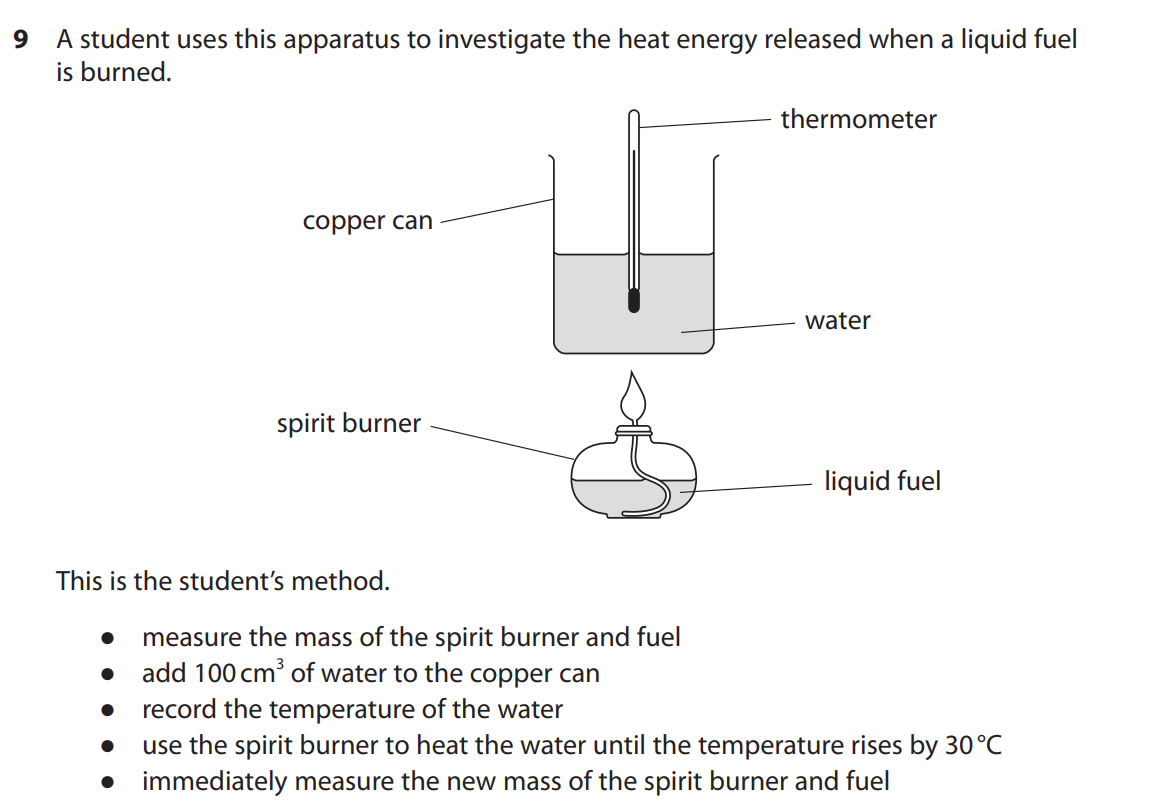
(b) When the fuel is burned, the student notices that a black solid forms on the bottom of the copper can.
(i) Identify the black solid.(1)
(ii) Explain why the black solid forms. (2)
(i) soot/carbon
(ii) M1 incomplete combustion (occurs)
M2 (because) the air/oxygen supply is limited OWTTE