4.3 Exchange rates
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
currency
system of money used in a country or group of countries
exchange rate
the price of one country’s currency in terms of another
appreciation
value of currency increasing in an exchange rate
depreciation
value of currency decreasing in an exchange rate
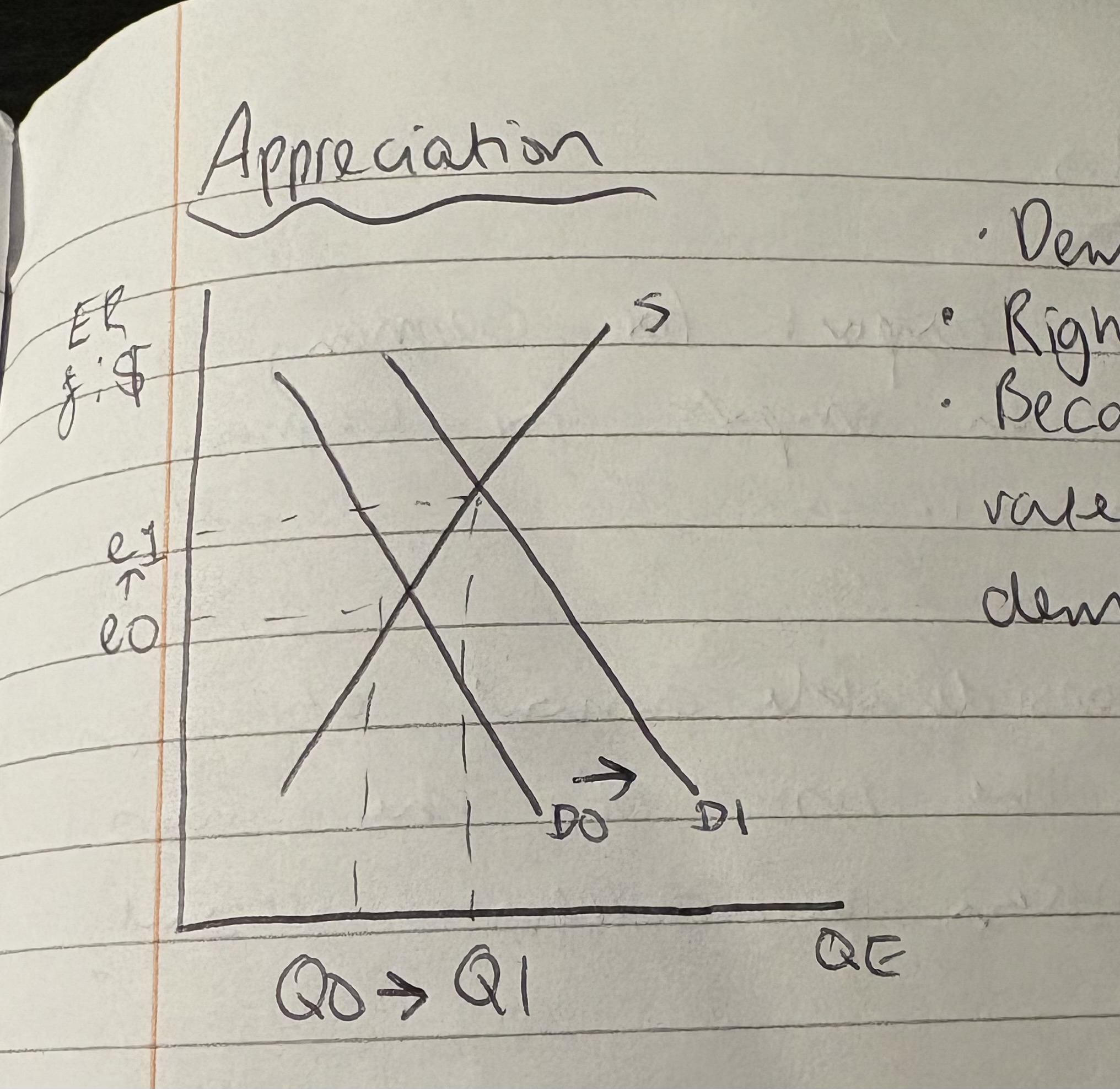
What is the graph for appreciation?
Demand for £ increases
Rightward shift in demand
Exchange rate increases as its higher in demand
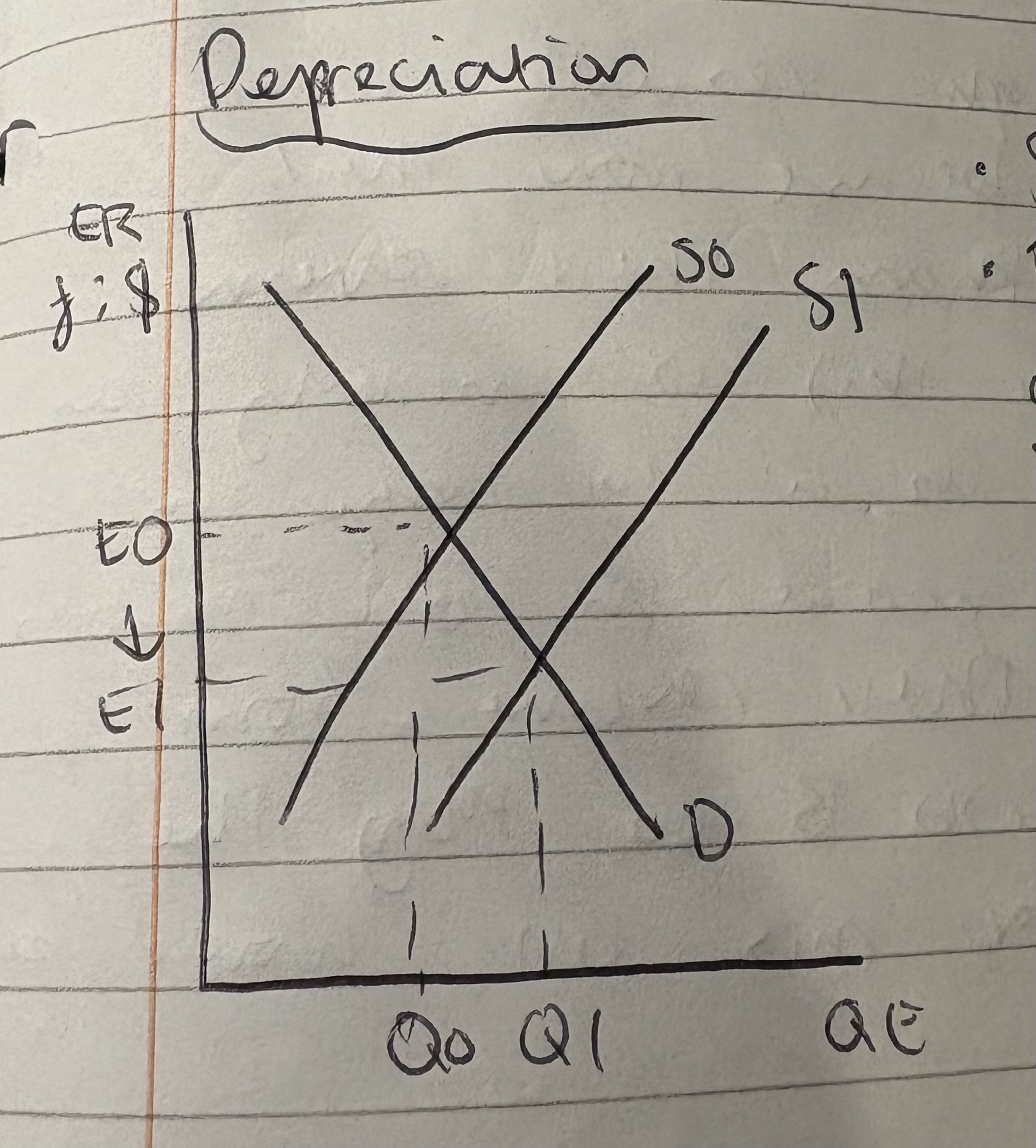
What is the graph for depreciation?
Supply for £ increases
Exchange rate value now decreases as there is a higher supply of it
What causes demand for pound?
If there is an increase in demand for UK exports there will also be an increase in demand for pounds to buy that with
S
P
I
C
E
D
Strong
Pound
Imports
Cheaper
Exports
Dearer
Effect of rise in exchange rate for consumers
import prices fall - domestic consumers may be more willing to buy imported goods
improved standard of living as domestic customers’ income can buy more goods
makes imports cheaper reducing inflation
Effect of rise in exchange rate for producers
fall in import prices - benefits producers that import raw materials
rise in export prices for foreign investors
fall in inflation rate due to total demand falling