Chapter 42 - Circulation and Gas Exchange
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:58 AM on 7/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
How do small molecules move between cells and surroundings?
Diffusion
2
New cards
What is the drawback for diffusion?
It is only efficient over small distances
3
New cards
What do animals who lack a circulatory system have?
Gastrovascular cavities
4
New cards
What functions in both digestion and distribution of substances throughout the body?
Gastrovascular cavities
5
New cards
What 3 things do a circulatory system have?
1. circulatory fluid
2. set of interconnecting vessels
3. muscular pump, the heart
6
New cards
What connects the fluid that surrounds cells with organs that exchange gases, absorb nutrients, and dispose of wastes?
Circulatory system
7
New cards
What 2 ways can the circulatory system be?
1. Open
2. Closed
8
New cards
What is the circulatory fluid that bathes organs in an open circulatory system in some animals?
Hemolymph
9
New cards
What 3 animals have hemolymph fluid?
Insects, arthropods, molluscs
10
New cards
Blood is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial fluid in what kind of circulatory system?
Closed
11
New cards
Humans and other vertebrates have a closed circulatory system called the what?
Cardiovascular system
12
New cards
What does the cardiovascular system include?
1. heart
2. blood vessels
13
New cards
What are the 3 types of blood vessels?
1. arteries
2. veins
3. capillaries
14
New cards
What do arteries branch into?
Arterioles
15
New cards
Where do arteries carry blood to?
Away from the heart to capillaries
16
New cards
What is a network of capillaries called?
Capillary beds
17
New cards
What do venules converge into?
Veins
18
New cards
What do veins take blood?
From the capillaries to the heart
19
New cards
Where does blood enter?
Atria
20
New cards
Where is blood pumped out through?
Ventricles
21
New cards
What form of circulation has blood leave the heart and pass through 2 capillary beds before returning?
Single circulation
22
New cards
What animals have single circulation with a two-chambered heart?
Sharks, rays, and bony fish
23
New cards
What form of circulation has no separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood?
Single circulation
24
New cards
What animals have double circulation?
Amphibians, reptiles, and mammals
25
New cards
What form of blood circulation maintains higher blood pressure in the organs?
Double circulation
26
New cards
Why does double circulation maintain higher blood pressure in the organs?
It passes through only one capillary bed
27
New cards
What side of the heart if oxygen-poor blood pumped from?
Right
28
New cards
What side of the heart is oxygen-rich blood pumped from?
Left
29
New cards
In amphibians, what circuit does oxygen-poor blood flow through to pick up oxygen via the lungs and skin?
Pulmocutaneous circuit
30
New cards
In reptiles and mammals, oxygen poor blood flows through what circuit to pick up oxygen from the lungs?
Pulmonary circuit
31
New cards
How are some vertebrates intermittent breathers?
It can breathe through the skin
32
New cards
How many chambers do amphibians have?
3
33
New cards
What are the 3 chambers of the amphibian heart?
Two atria and one ventricle
34
New cards
How many chambers does a mammal and bird heart have?
4
35
New cards
What do coordinated cycles of heart contraction drive in mammals?
Double circulation
36
New cards
What is the cycle in which the heart contracts and relaxes in a rhythmic cycle?
Cardiac cycle
37
New cards
What is the contraction or pumping phase called?
Systole
38
New cards
What is the relaxation or filling phase called?
Diastole
39
New cards
How is blood pressure measured?
Systolic/Diastolic
40
New cards
What is the volume of blood pumped into the systemic circulation per minute and depends on both the heart rate and stroke volume?
Cardiac output
41
New cards
What is the number of beats per minute?
Heart rate
42
New cards
What is the amount of blood pumped in a single contraction?
Stroke volume
43
New cards
What prevents backflow of blood into the hearts?
Valves
44
New cards
What valves separate each atrium and ventricle?
Atrioventricular valves
45
New cards
What controls the blood flow to the aorrta and pulmonary artery?
Semilunar valves
46
New cards
What sound does the recoil of blood against the Atrioventricular valves cause?
Lub
47
New cards
What sound does the recoil of blood against the semilunar valves?
Dup
48
New cards
What does the backflow of blood through a defective valve cause?
Heart murmur
49
New cards
What does it mean when a cardiac muscle contracts without any signal from the nervous system?
Autorhythmic
50
New cards
What sets the rate and timing at which cardiac muscle cells contract?
Pacemaker
51
New cards
What is another name for a pacemaker?
Sinoatrial node
52
New cards
What are the impulses that travel during the cardiac cycle recorded as?
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
53
New cards
Where do impulses from the sinoatrial node (pacemaker) travel to?
Atrioventricular node
54
New cards
Where are the impulses located?
Atrioventricular node
55
New cards
Where do impulses travel to from the atrioventricular node?
Purkinje fibers
56
New cards
What makes the ventricles contract?
Purkinje fibers
57
New cards
What do patterns of blood pressure and flow reflect in the blood vessels?
Structure and arrangement
58
New cards
What is the epithelial layer that lines blood vessels called?
Endothelium
59
New cards
How does endothelium minimize resistance?
By being smooth
60
New cards
What is only slightly wider than a red blood cell?
Capillaries
61
New cards
Why do capillaries have thin walls?
To facilitate the exchange of materials
62
New cards
What blood vessel has valves?
Veins
63
New cards
Why do veins have thinner walls?
They take blood back to the heart at a lower pressure
64
New cards
Why do arteries have thicker, elastic walls?
To accommodate the higher pressure it takes to pump blood away from the heart
65
New cards
What happens to the speed as it moves from larger vessels to smaller vessels?
Slows down
66
New cards
Blood flows in what direction of pressure?
High to low
67
New cards
What is the pressure in the arteries during ventricular systole called?
Systolic pressure
68
New cards
What is the rhythmic bulging of artery walls within each heartbeat?
Pulse
69
New cards
What is the pressure in the arteries during diastole (when the ventricles are relaxed)?
Diastolic pressure
70
New cards
What is the narrowing of arteriole walls?
Vasoconstriction
71
New cards
What is the widening of arterioles?
Vasodilation
72
New cards
What is a major inducer of vasodilation?
Nitric oxide
73
New cards
What is a potent inducer of vasodilation?
Peptide endothelin
74
New cards
What is caused by an inadequate blood flow to the head?
Fainting
75
New cards
What system returns fluids that leaked out from the capillary beds?
Lymphatic system
76
New cards
What is the fluid lost by capillaries called?
Lymph
77
New cards
What are organs that filter lymph and play an important role in the body’s defense?
Lymph nodes
78
New cards
What is swelling caused by disruptions in the flow of lymph?
Edema
79
New cards
What do blood components function in? (3)
1. Exchange
2. Transport
3. Defense
80
New cards
What is the liquid matrix that cells are suspended in within the blood in vertbrates?
Plasma
81
New cards
What percentage of blood does plasma make?
45
82
New cards
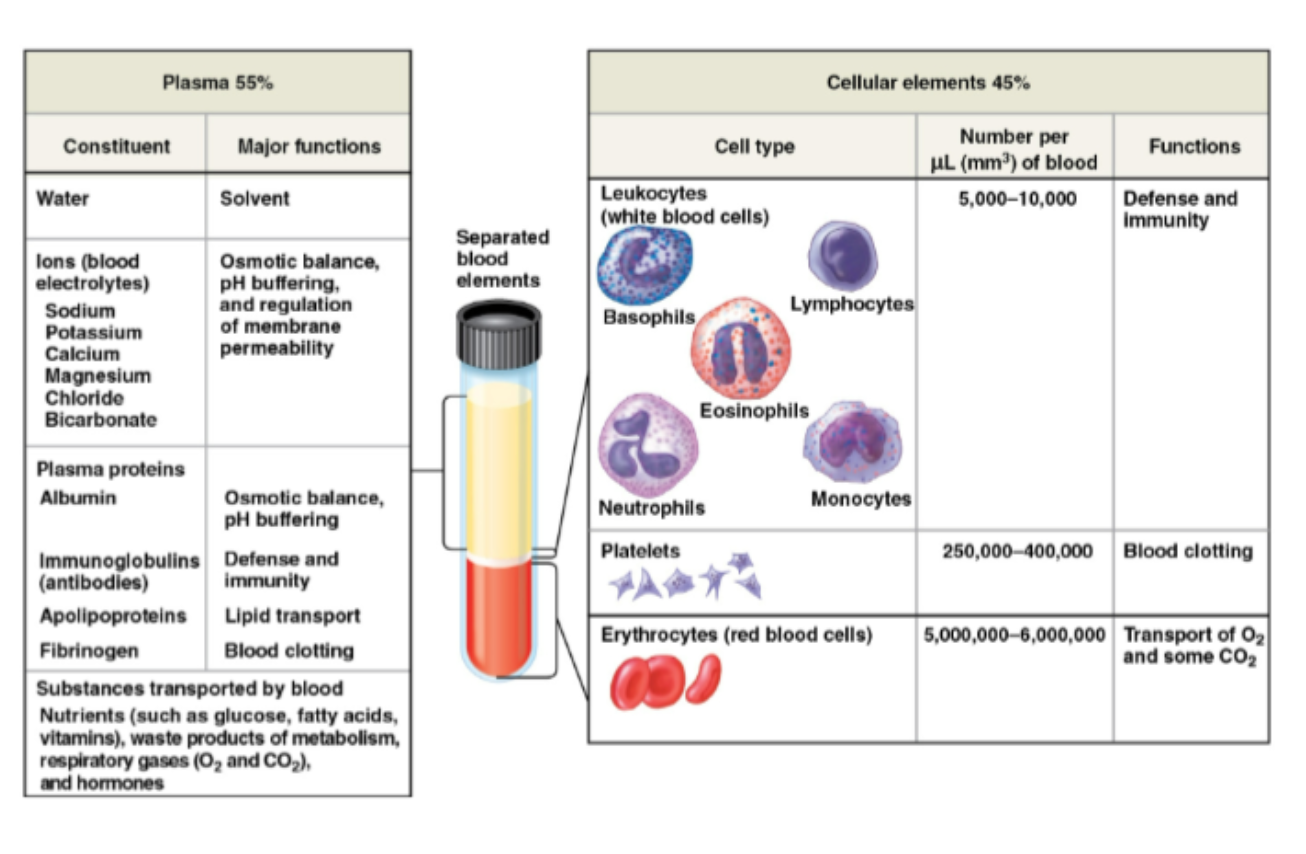
Chart
83
New cards
What are the fragments of cells involved in clotting?
Platelets
84
New cards
What is another name for red blood cells?
Erythrocytes
85
New cards
What is the iron-containing protein that transports oxygen?
Hemoglobin
86
New cards
What is caused by abnormal hemoglobin proteins that form aggregates?
Sickle-cell disease
87
New cards
Why is it called sickle cell disease?
The aggregates deform RBC into a sickle shape
88
New cards
What can occur to sickled cells?
They can rupture or block blood vessels
89
New cards
What happens to the RBC supply in individuals with sickle cell disease?
Reduces it
90
New cards
What is another name for white blood cells?
Leukocytes
91
New cards
What are the 2 ways WBC function in defense?
1. Phagocytosis
2. Mounting immune responses
92
New cards
Where are stem cells located?
Bone marrow
93
New cards
What hormone stimulates erythrocyte production when oxygen delivery is low?
Erythropoietin
94
New cards
What cells make up lymphocytes?
B cells and T cells
95
New cards
What is a blood clot formed in a blood vessel called?
Thrombus
96
New cards
What is the hardening of the arteries, caused by the buildup of fatty deposits within the arteries?
Atherosclerosis
97
New cards
What is the damage or death of cardia muscle tissue resulting in blockage of one or more coronary arteries?
Heart attack
98
New cards
What is the death of nervous tissue in the brain, usually resulting from rupture or blockage of arteries in the head?
Stroke
99
New cards
What delivers cholesterol to cells for membrane production?
Low-density lipoprotein
100
New cards
What scavenges excess cholesterol for return to the liver?
High-density lipoprotein