Chapter 4: Genes and Cellular Function
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merged flashcards from Chapter 4, McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Heredity
The transmission of genetic characteristics from parent to offspring
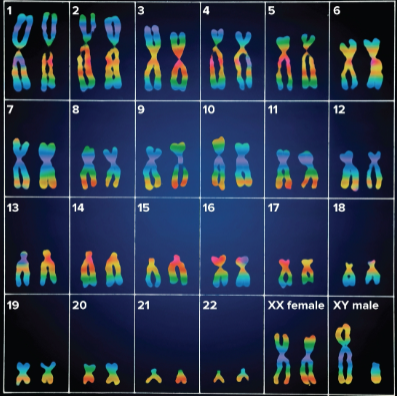
Karyotype
The chart of all 46 chromosomes by sides; shows 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes
1 chromosome from each pair inherited from each parent
Autosomes
Chromosomes that look alike and carry the same genes
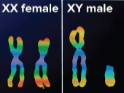
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine gender; men have one X and one Y chromosomes while women have homologous X chromosomes
Diploid
Any cell with 23 pairs of chromosomes; somatic (non-reproductive) cells are an example
Haploid
Cells with half as many chromosomes as somatic cells; human haploid cells contain 23 unpaired chromosomes such as sperm and egg cells to restore regular pairing
Locus
The location of a particular gene on a chromosome
Allele
Different form of a particular gene; the same alleles are found at the same locus on homologous chromosomes
Dominant allele
An allele that expresses a protein in an individual
Recessive allele
An allele that does not express in an individual if it is paired with a dominant allele; only appears when recessive on both homologous chromosomes
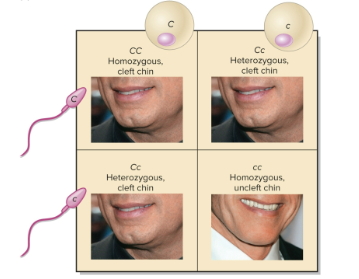
Genotype
The allele an individual possesses for a particular gene; visualized using Punnet square
Phenotype
An observable trait
Genetic counselors
Perform genetic testing and advise couples on genetic diseases
Gene pool
The genetic makeup of the whole population
Multiple alleles
More than two allelic forms of a gene; seen in A, B, and O blood types
Codominance
Both alleles equally dominant and phenotypically expressed; seen in AB blood types
Incomplete dominance
Heterozygous individual shows phenotype between traits each allele would have produced alone
Polygenic inheritance
Genes at two or more loci contribute to a single trait
Pleiotropy
One gene produces multiple phenotypic effects
Sex-linked traits
Traits carried on the X or Y chromosomes; men inherit more than the other due to having only one X chromosome
Penetrance of allele
Percentage of population exhibiting expected phenotype; allele may not fully express in population or can be modified by the environment
Epigenetics
Field examining nongenetic changes that alter gene expression and can be passed to offspring
Carcinogens
Environmental cancer-causing agents that can damage DNA; they can be found in radiation, chemicals, and viruses and cause uncontrolled cell growth
Law of Complementary Base Pairing
States that we can predict the base sequence of one DNA strand if we know the sequence of another
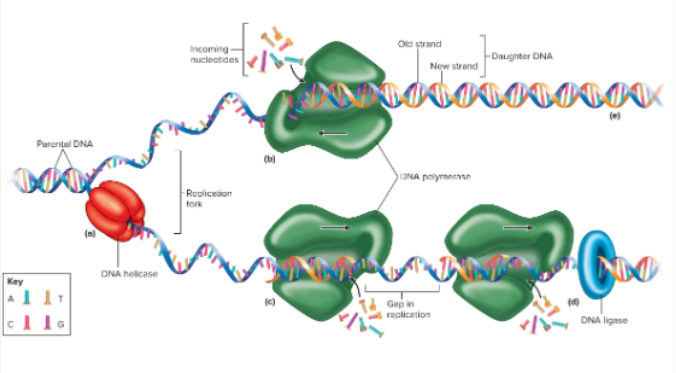
DNA replication steps
Unwinding
Unzipping
Building new strands
Repackaging
Replication fork
The point of DNA opening, this is made in step 1 after unwinding form histones
DNA helicase
The enzyme that unzips a segment of the DNA’s double helix structure in step 2
DNA polymerase
The enzyme that builds new DNA strands by matching free nucleotides to the unwinded DNA strand in step 3; the DNA is then repackaged and replicated for step 4
DNA Damage Response (DDR)
Mechanisms in place to correct replication errors by DNA polymerase; replaces unstable base pairs with correct pairs for a 1/1000000000 failure rate
Mutations
Changes in DNA structure due to replication errors or environmental factors; some may be harmless while others can cause defects or cancer later on
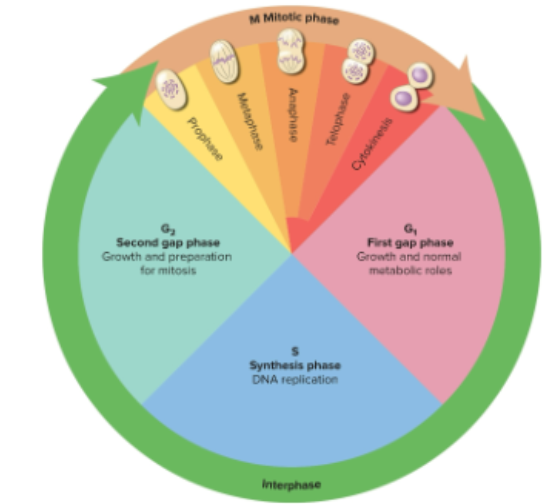
Cell cycle
The interphase and mitotic phases
Interphase
A part of the cell cycle that includes the first gap phase (G1), synthesis phase (S), and second gap phase (G2)
Mitotic phase
A part of the cell cycle that includes the prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis
First gap phase (G1)
Interval between cell birth and DNA replication; cell carries out normal tasks and accumulates materials for next phase
Synthesis phase (S)
Phase in interphase when the cell replicates all nuclear DNA and duplicates centrioles
Second gap phase (G2)
Interval between DNA replication and cell division; repairs errors and synthesizes enzymes
Mitotic phase
Phase where the cell replicates its nucleus
G zero phase (G0)
Cells that have left the cycle and ceased dividing for a long time
Mitosis
The cell division resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells; develops fertilized egg to 50 trillion cells and helps tissue growth
Phases of mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
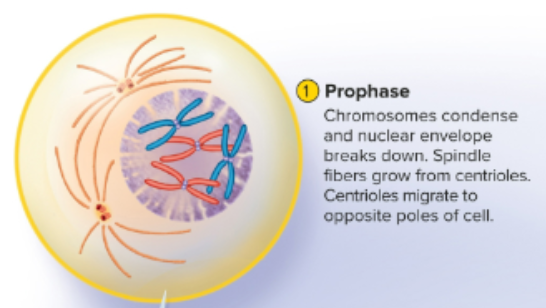
Prophase
First phase in mitosis where genetic material condenses into compact chromosomes; nuclear envelope disintegrates and centrioles sprout spindle fibers
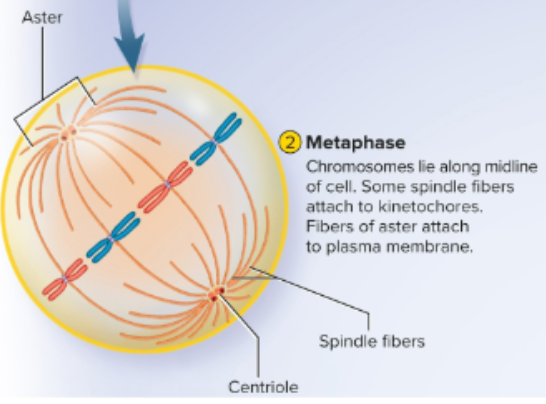
Metaphase
Second phase in mitosis where chromosomes align on the cell equator; microtubules extend from side to middle
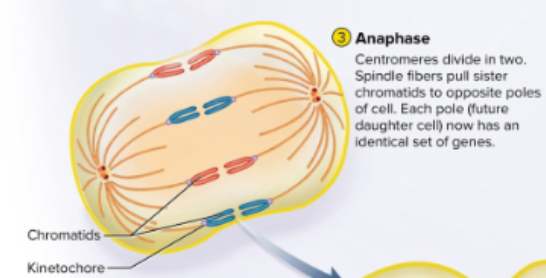
Anaphase
Third phase in mitosis where the spindle fibers cleave chromatids apart to opposite poles of cell
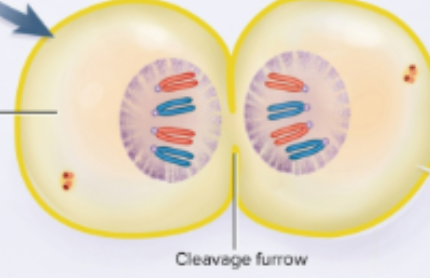
Telophase
Fourth phase where chromosomes cluster on each side of the cell; the rough ER makes a new nuclear envelope and the mitotic spindles disintegrate
Cytokinesis
Divison of the cytoplasm into two cells where the cell pinches in two; comes after telophase
Cell division factors
Starts when:
Adequate cytoplasm
DNA replicated
Nutrients supplied
Cell stimulated
May stop when:
Neighboring cells
Nutrients or growth factors withdrawn
Gene
An information-containing segment of DNA that codes for the production of RNA which in turn helps synthesize proteins
Genome
All the DNA in one 23 chromosome set
Genomics
The study of the whole genome
Genomic medicine
The application of knowledge of the genome to the prediction, diagnosis, and treatment of disease
Base triplet
Sequence of three DNA nucleotides that stand for one amino acid
Codon
A three base sequence in RNA
Start codon
Begins the amino acid sequence of the protein (AUG for methionine)
Stop codon
Ends the amino acid sequence like a period (UAG, UGA, and UAA)
Transcription
Copying the genetic instructions from DNA to mRNA
RNA polymerase
Binds to DNA and opens up the helix; reads bases from one strand of DNA to build a complementary strand of mRNA; then rebinds it
Pre-mRNA
Immature RNA produced by transcription
Exons
Segments of pre-mRNA exported from the nucleus and translated into protein which are spliced by enzymes
Introns
Segments of pre-mRNA that will be removed before translation
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Carries code from the nucleus to cytoplasm and ribosome
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Delivers a single amino acid to the ribosome; includes three nucleotides called an anti-codon to bind to mRNA and bring free amino acid using one ATP
Ribosome
Organelles that read mRNA and build peptide chains from amino acids; pulls mRNA through like a ribbon
Initation
Leader sequence in mRNA binds to a ribosomal subunit, joining the complex ribosome and allows for reading
Elongation
tRNA binds to the ribosome to pair with mRNA, brings amino acids to form a peptide bond
Termination
Releasing a protein and mRNA after reaching a stop codon; proteins may need to be packaged or exported
Chaperone proteins
Guides the folding of new proteins into secondary and tertiary structures; defends against heat or stress into correct shapes
Posttranslational modification
Proteins made on the ER are threaded into pores and enzymes to modify the protein through amino acid trimming, folding, and stabilization
Johann Miescher
A Swiss biochemist who lived from 1844 to 1895; he studied the nuclei of white blood cells and coined the term nuclein - what we now call genes
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
A long, thread-like molecule with uniform diameter and varied length; it’s a polymer of nucleotides
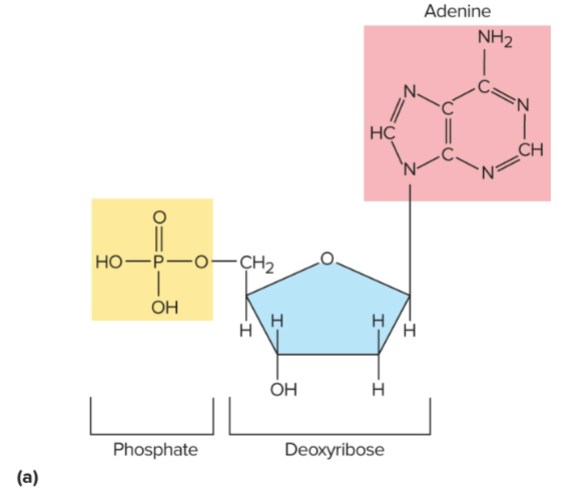
Nucleotide
A molecule made of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base
Ribose
The sugar in nucleotides
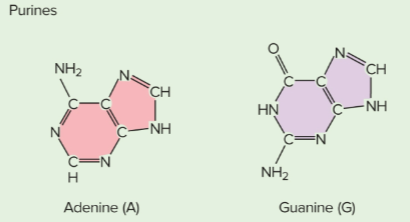
Purines
The adenine and guanine nitrogenous bases
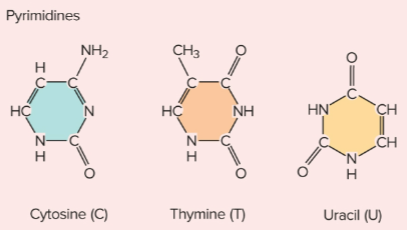
Pyrimidines
The cytosine, thymine, and uracil nitrogenous bases
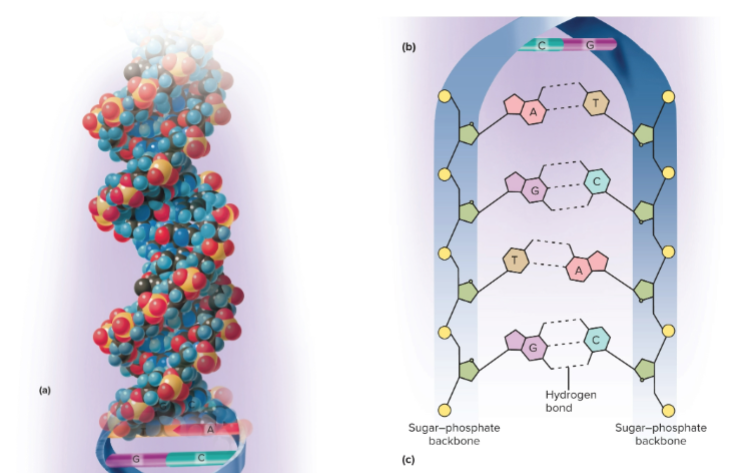
Double helix
The structure of a DNA molecule; resembles a spiral staircase with the ‘steps’ being the nitrogenous base pairs
Base pairing
How DNA is bonded using hydrogen bonds; A always pairs to T with 2 bonds and C always pairs to G with 3 bonds
Gene
Segment of DNA coding for the synthesis of a specific protein
Genome
All the genes of one person; humans have 20,000 but only 2% is human-specific while the other 98% is for chromosome structure and gene activity regulation
Chromatin
Fine filamentous DNA material complexed with proteins; may change movement in non-dividing cells according to genetic activity
Ribonucleic acids (RNAs)
Contain the sugar ribose; uracil takes the place of thymine in DNA and is smaller
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Sends the genetic code to ribosomes
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Carries out protein synthesis in enzymes
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Obtains amino acids for ribosomes according to mRNA