Genetics: Molecular, Transmission, and Population Genetics Review
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
What is genetics?
The study of DNA, RNAs, proteins, the genetic code, gene regulation, genotypes, phenotypes, genetic pathways, genomes, inheritance, variation, natural selection, and evolution.
What are the subdivisions of genetics?
Transmission genetics, molecular genetics, quantitative genetics, and population genetics.
What is transmission genetics?
The study of how traits are passed from one generation to the next and how alleles and genes interact to produce phenotypes.
What does molecular genetics focus on?
Gene sequences, genetic information, gene replication, mutation, and gene expression.
What does quantitative and population genetics study?
How genes and the environment contribute to complex traits and genetic variation within populations over time.
What are the characteristics of model organisms in genetics?
Short generation time, production of numerous progeny, ability to carry out controlled genetic crosses, laboratory rearing, isolation of isogenic individuals, and ability to cause mutations.
Name some major model organisms used in genetics.
E. coli, S. cerevisiae, C. elegans, Drosophila (D. melanogaster), Zebrafish (D. rario), Mice (M. musculus).
What is the importance of model organisms?
They help understand gene function within a defined context, although they have limitations in fully understanding gene functions in natural populations.
What is a gene?
The unit of inheritance in transmission genetics.
What is a monohybrid cross?
A genetic cross between two individuals with different alleles for a single gene.
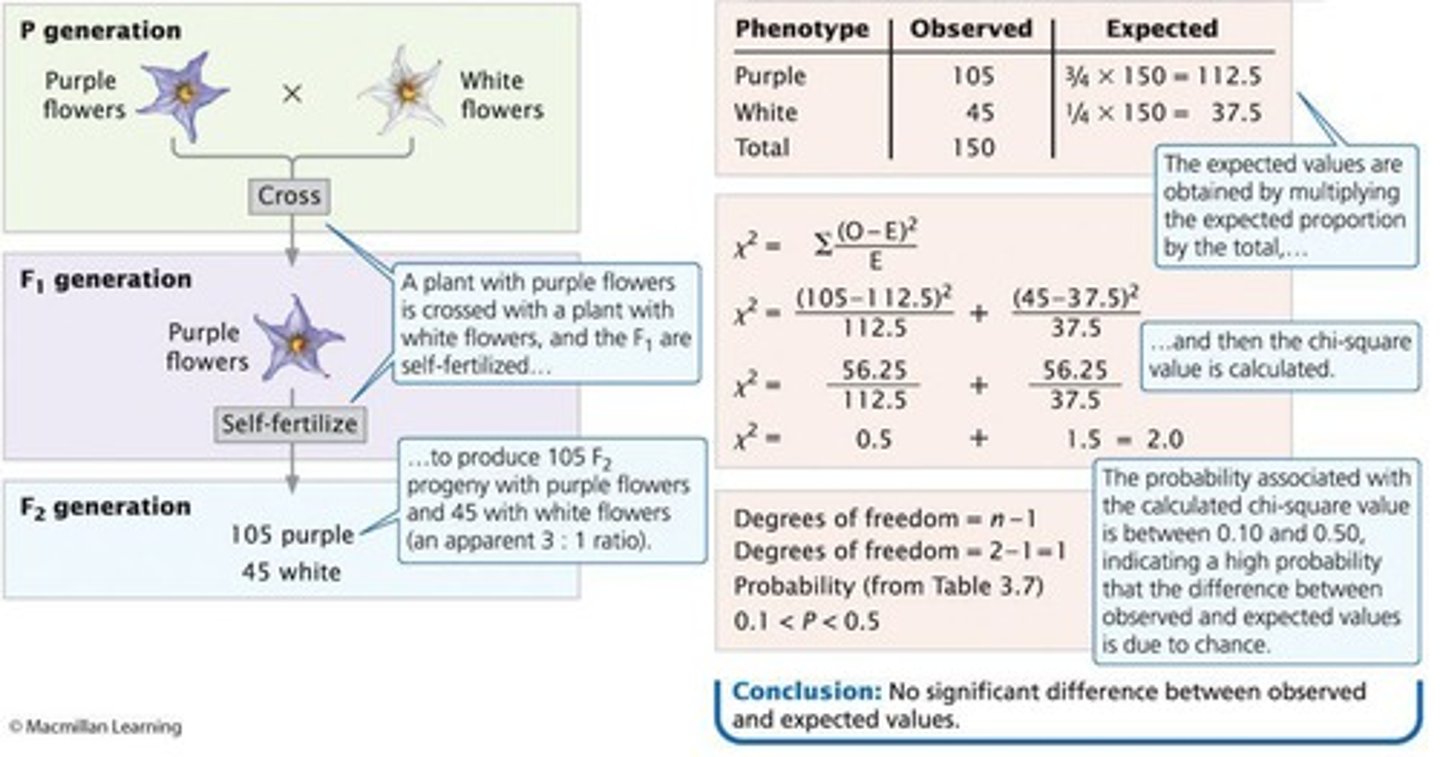
What is the genotype ratio in the F1 generation of a monohybrid cross (GG x gg)?
0:1:0 (GG:Gg:gg).
What is the phenotype ratio in the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross?
3:1 (yellow:green).
What is binomial expansion in genetics?
A mathematical way to predict outcomes in genetic crosses, calculating probabilities of various outcomes.
What does the equation p2 + 2pq + q2 represent?
The probabilities of genetic outcomes in a binomial expansion for two progeny.
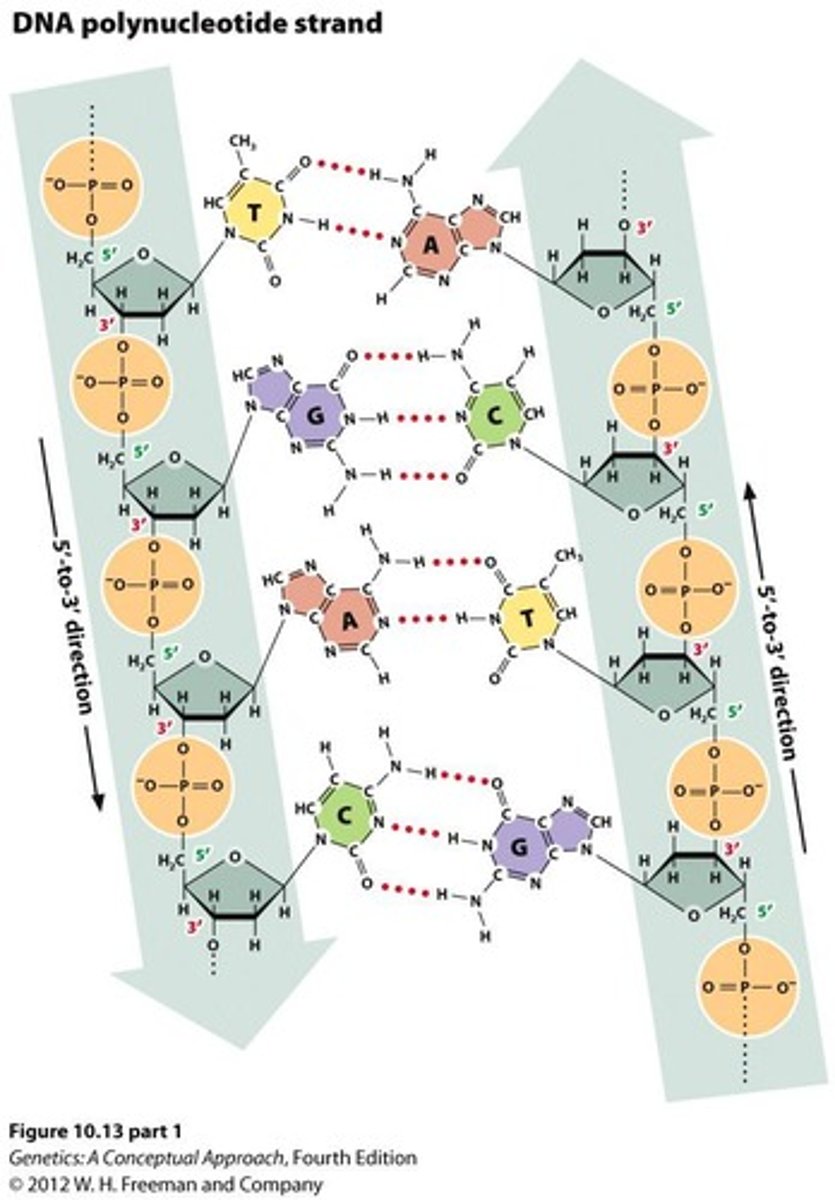
What is the role of DNA in genetics?
DNA is the genetic material that carries genetic information and is structured as antiparallel strands.
What are the base pairing rules in DNA?
Purines pair with pyrimidines: Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T), and Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C).
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genetics?
Prokaryotes are haploid and divide by binary fission, while eukaryotes can be haploid, diploid, or polyploid and divide by mitosis or meiosis.
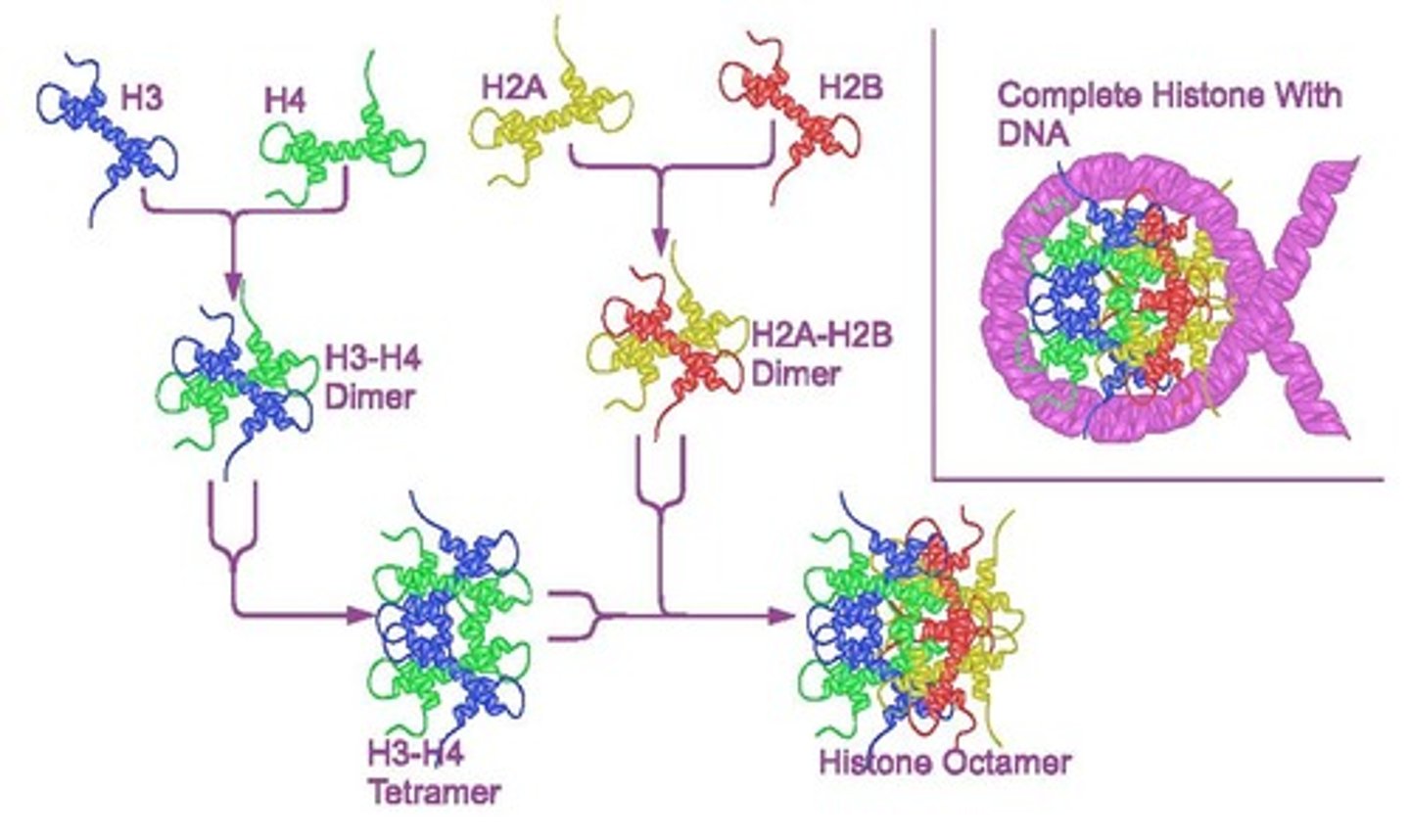
What is chromatin?
The complex of DNA and proteins that packages DNA in eukaryotic cells.
What is a nucleosome?
The primary level of chromatin packaging, consisting of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer.
What are the characteristics of euchromatin?
Less condensed, located on chromosome arms, contains many genes, and is often transcribed.
What are the characteristics of heterochromatin?
More condensed, located at centromeres and telomeres, contains few genes, and is infrequently transcribed.
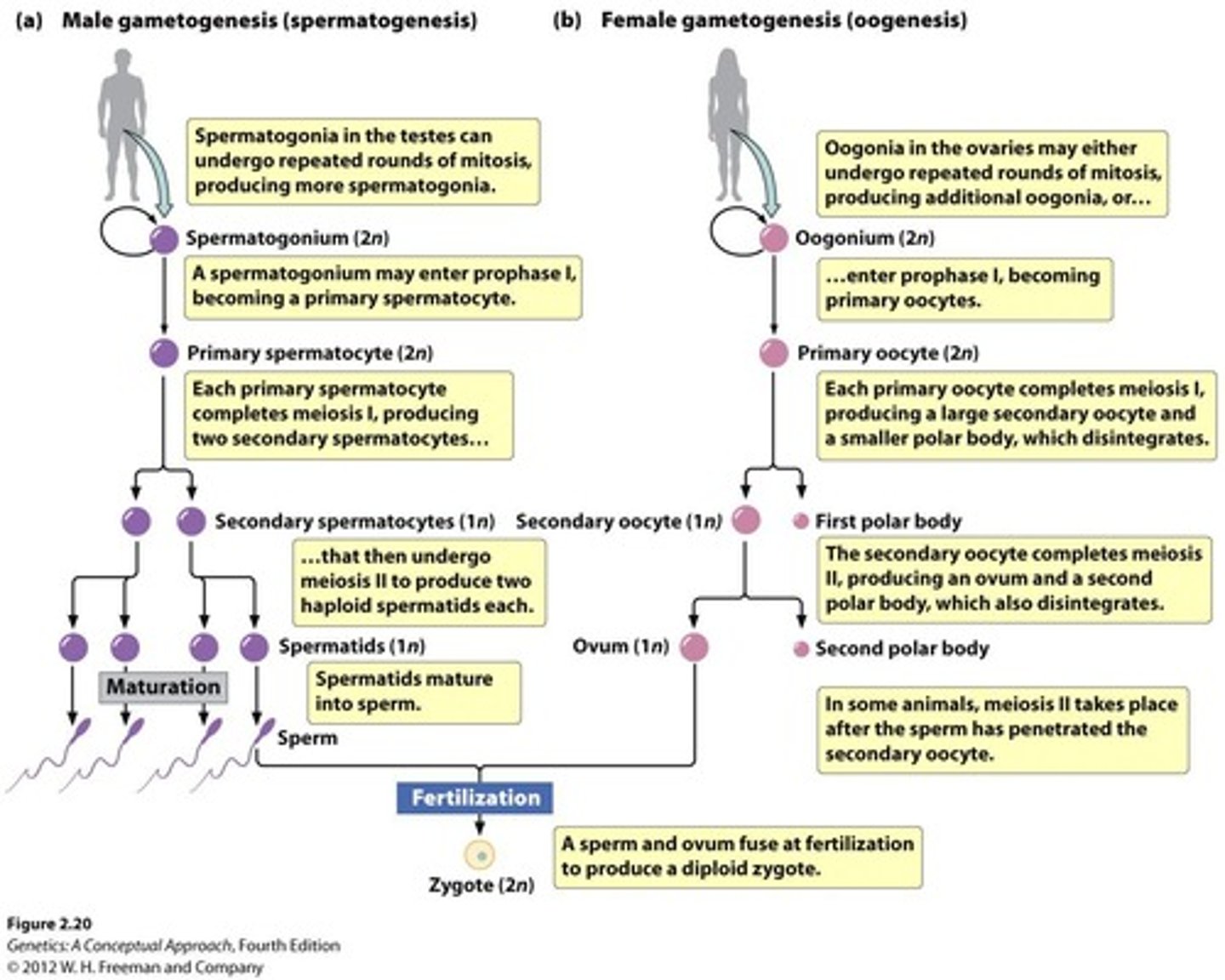
What is gametogenesis?
The process that generates gametes (egg and sperm) through meiosis.
What happens during prophase I of meiosis?
Chromosomes condense, homologous chromosomes synapse, crossing over occurs, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
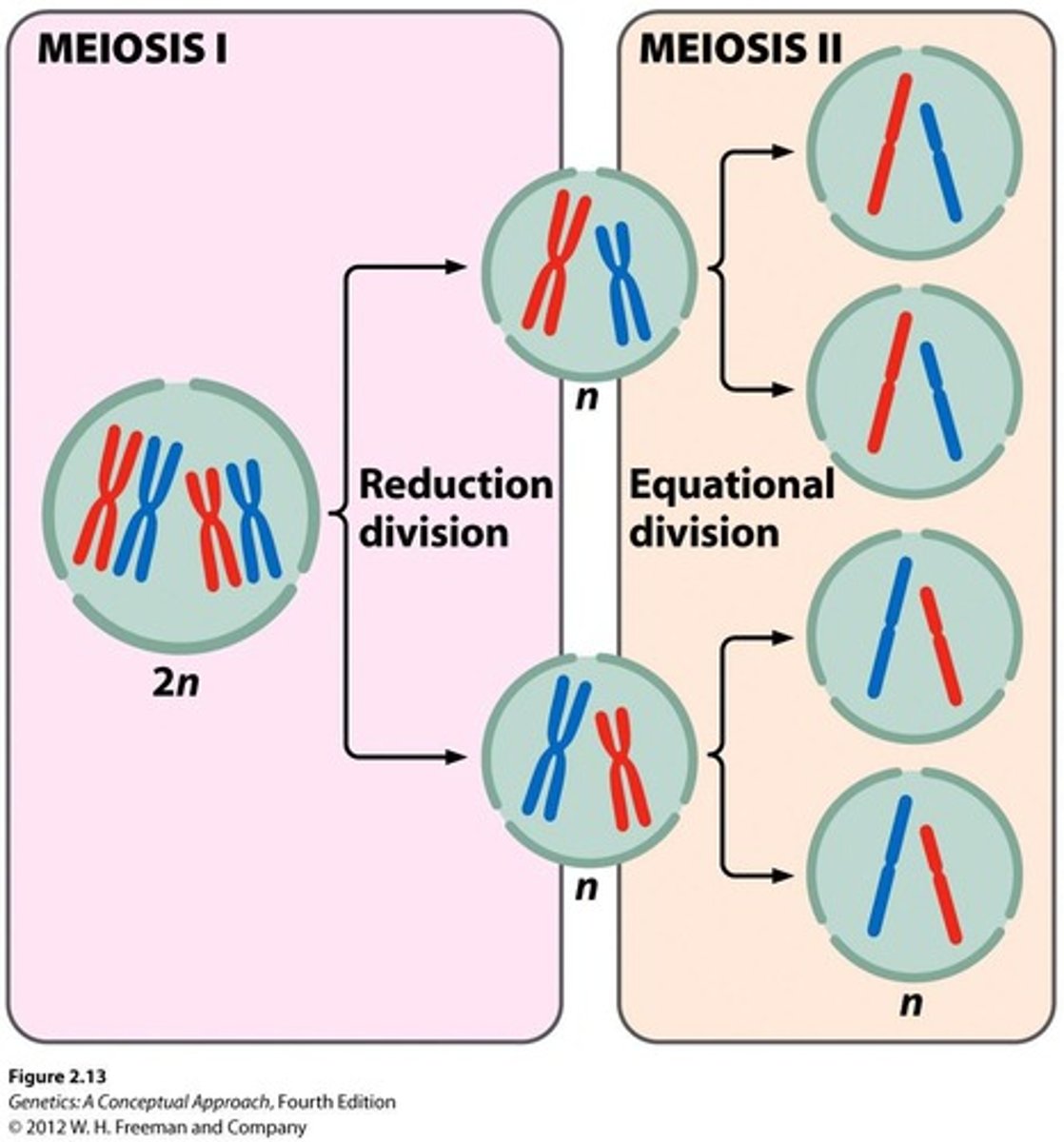
What is crossing over?
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis.
What is the significance of the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
It describes the genetic variation in a population that is not evolving.
What is the formula for calculating heritability (H2)?
H2 = VG / VP, where VG is genetic variance and VP is phenotypic variance.
What does the term 'standing genetic variability' refer to?
The genetic variation present in a population at a given time.
What occurs during Metaphase I of meiosis?
Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate.
What happens during Anaphase I of meiosis?
The two chromosomes of a homologous pair separate and move toward opposite poles.
What is the outcome of Telophase I in meiosis?
Chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles.
What is Cytokinesis?
The cytoplasm divides to produce two cells, each having half the original number of chromosomes.
What occurs during Interkinesis?
The spindle breaks down, chromosomes relax, and a nuclear envelope re-forms, but no DNA synthesis takes place.
What is the first stage of Meiosis II?
Prophase II, where chromosomes condense, the spindle forms, and the nuclear membrane disintegrates.
What happens during Metaphase II?
Individual chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate.
What occurs during Anaphase II?
Sister chromatids separate and move as individual chromosomes toward the spindle poles.
What is the result of Telophase II?
Chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles; the spindle breaks down and a nuclear envelope re-forms.
What is the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
Growth and development of the cell; G1/S checkpoint.
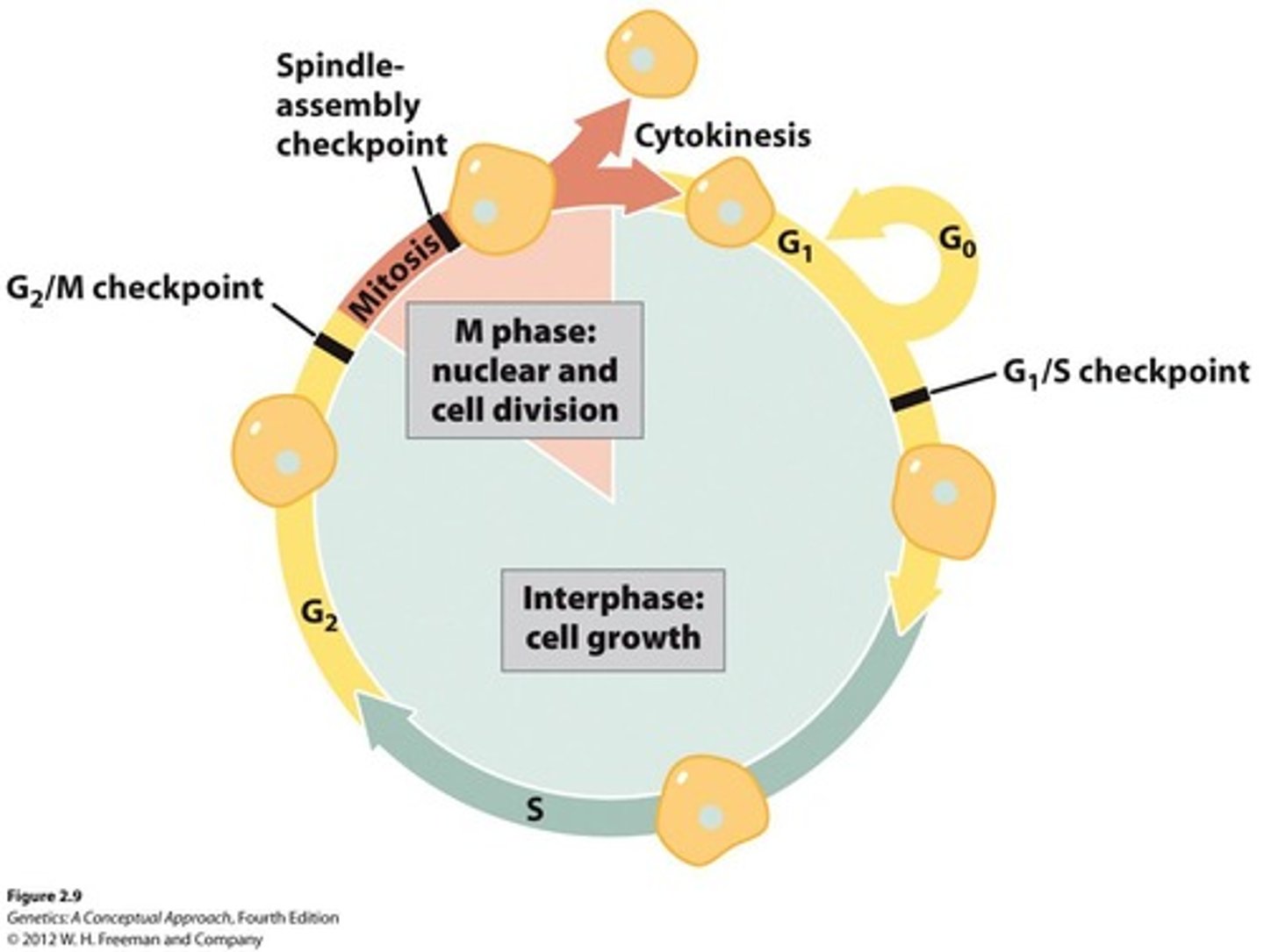
What occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle?
Synthesis of DNA.
What is the purpose of the G2 phase?
Preparation for division; G2/M checkpoint.
What is the role of checkpoints in the cell cycle?
To ensure conditions are suitable for cell division.
What is the difference between biological sex and gender?
Biological sex involves gamete formation, while gender is a social construct.
What are male gametes and their characteristics?
Sperm, which are smaller, motile, and primarily contribute DNA.
What do female gametes contribute?
Oocytes contribute DNA, mitochondria, cytoplasm, and mRNAs.
What is a hermaphroditic organism?
An organism that has both male and female reproductive organs.
What are sex-influenced characteristics?
Traits that have higher penetrance in one sex than another, acting like dominant traits in one sex and recessive in the other.
What is genetic maternal effect?
The phenotype is determined by the mother's genotype before the embryo begins transcribing its DNA.
What is cytoplasmic inheritance?
Traits passed from the mother through mitochondrial DNA.
What is genomic imprinting?
Genes whose expression is affected by the sex of the transmitting parent.
What is the role of DNA Polymerase?
It is the enzyme that copies DNA, adding nucleotides to the 3' end.
What is the speed of E. coli DNA Polymerase III?
1 kb/s (1,000 base pairs per second).
What is the fidelity of E. coli DNA Polymerase III?
1 error in every 10 million base pairs.
What is the processivity of E. coli DNA Polymerase III?
100 kb (100,000 base pairs).
What is the significance of the G0 phase?
It is a stable, non-dividing state of variable length.
What happens during cytokinesis in plant cells?
The cell wall forms as the cytoplasm divides.
What is the direction of DNA polymerase activity?
5' to 3'
What type of activity does DNA polymerase I have?
Removes and replaces primers
What is the function of DNA helicase?
Unwinds DNA at the replication fork
What do single-strand-binding proteins do?
Attach to single-stranded DNA and prevent secondary structures from forming
What is the role of DNA primase?
Synthesizes a short RNA primer to provide a 3'-OH group for DNA nucleotides
What is the function of DNA ligase?
Joins Okazaki fragments by sealing breaks in the sugar-phosphate backbone of newly synthesized DNA
What are the three modes of DNA replication?
Rolling-circle, Theta, and Linear
What is aneuploidy?
A change in the number of individual chromosomes
What is the definition of nullisomy?
Loss of both members of a homologous pair of chromosomes (2n-2)
What is trisomy?
Gain of a single chromosome (2n+1)
What is the difference between autopolyploidy and allopolyploidy?
Autopolyploidy is due to accidents of meiosis or mitosis from the same species; allopolyploidy consists of chromosome sets from 2+ species.
What is a point mutation?
A change in a single nucleotide base pair
What is the function of DNA gyrase?
Moves ahead of the replication fork, making and resealing breaks in DNA to relieve torque
What are the types of chromosome mutations?
Rearrangements, aneuploidy, and polyploidy
What is a phenocopy?
An environmental condition that causes a similar defect as a mutation
What is penetrance?
The percentage of individuals with a genotype that express the trait
What are the termination codons in the genetic code?
UAA, UAG, and UGA
What is the significance of the AUG codon?
It is the initiation codon for protein synthesis
What is the difference between transitions and transversions?
Transitions are substitutions between purines or pyrimidines; transversions are substitutions between a purine and a pyrimidine.
What is the role of transposons?
Segments of DNA that can move around to different positions within the genome
What is a missense mutation?
A mutation that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into a protein
What is a nonsense mutation?
A mutation that creates a premature stop codon in the protein sequence
What is the genetic code composed of?
64 codons that specify amino acids
What is the function of the DNA sliding clamp?
Helps DNA polymerase with processivity during DNA replication
What is the result of a reciprocal translocation?
Exchange between segments of nonhomologous chromosomes
What is the significance of telomeres?
They protect the ends of chromosomes from deterioration
What is the definition of dominance in genetics?
Dominance refers to the relationship between alleles where one allele masks the expression of another in a heterozygote.
What does expressivity refer to?
Expressivity is the degree to which a phenotype is expressed among individuals with the same genotype.
What is the expected genotypic ratio from a dihybrid cross (AaBb x AaBb)?
1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1 for AABB:AABb:AAbb:AaBB:AaBb:Aabb:aaBB:aaBb:aabb.
What is the expected phenotypic ratio from a dihybrid cross (AaBb x AaBb)?
9:3:3:1 for AB:Ab:aB:ab.
What is genetic linkage?
Genetic linkage occurs when genes are located close together on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together.
What is the significance of crossing over in prophase I of meiosis?
Crossing over creates recombinant chromosomes, increasing genetic variation.
What is a testcross?
A testcross is a breeding experiment used to determine the genotype of an individual with a dominant phenotype by crossing it with a homozygous recessive individual.
What does recombination frequency indicate?
Recombination frequency represents the genetic distance between alleles, usually expressed in map units (mu) or centiMorgans (cM).
What are SNPs?
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are variations at a single nucleotide position in the genome that occur in more than 1% of the population.
What is the role of GWAS in genetics?
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are used to identify genetic variants associated with phenotypes or diseases.
What is the effect of epistasis in genetic interactions?
Epistasis occurs when the expression of one gene is affected by one or more other genes, leading to novel phenotypes.
What is the phenotypic ratio for recessive epistasis?
9:3:4, where one gene's recessive allele masks the expression of another gene.
What is the phenotypic ratio for dominant epistasis?
12:3:1, where a dominant allele of one gene masks the expression of another gene.
What is the significance of gene interactions in phenotypic expression?
Gene interactions can lead to variations in phenotypes beyond simple Mendelian inheritance patterns.
What happens when genes assort independently?
When genes assort independently, all allele combinations occur in roughly equal proportions in the progeny.
What is the role of Gal4 in yeast galactose utilization?
Gal4 is a transcriptional activator that initiates the expression of galactose utilization genes in the presence of galactose.
How does Gal80 function in the regulation of Gal4?
Gal80 inhibits Gal4 by blocking its activation domain, preventing transcription of galactose utilization genes.
What is the role of Gal3 in the galactose utilization pathway?
Gal3 binds to Gal80 in the presence of galactose, allowing Gal4 to activate transcription of galactose utilization genes.
What is the expected outcome of a testcross with complete linkage?
All offspring will display the parental phenotypes, with no recombinant types.
What is the expected outcome of a testcross with independent assortment?
Offspring will show a 1:1:1:1 ratio of phenotypes if two genes assort independently.