Mendelian Genetics Assessment
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Gregor Mendel
Austrian monk, father of genetics
Molecular Genetics
Study of DNA
Genetics
Study of how information is passed down
What did Gregor Mendel study?
Pea Plants
Why did Mendel think peas are a good organism to study genetics?
Fast Generation
Easy to obtain and cheap
Small/Take up little space
Have lots of offspring
Very distinct/clear
Peas can reproduce sexually and asexually
What was the purpose of Mendel’s pea plant experiments?
To study how traits are inherited and discover inheritance patterns.
What are true-breeding plants?
Plants that always produce the same trait when self-pollinated (homozygous).
What is the P generation?
The original parental true-breeding plants in Mendel’s crosses.
What is the F1 generation?
The first offspring generation, produced by crossing P plants.
What is the F2 generation?
The offspring of F1 plants (from self-pollination or F1 × F1 cross).
In Mendel’s monohybrid cross, what ratio did he observe in the F2 generation?
About 3 dominant : 1 recessive phenotype.
Mendel’s Conclusion
Traits are inherited as distinct units (genes)/Traits are passed from parents to offspring as individual units (genes)
Organisms have 2 alleles for each gene that they inherit from their parent
Some factors/alleles are dominant over others (recessive)
Law of Segregation: During gamete function only 1 factor/allele for each gene will be carried in the sperm or egg
Law of Independent Assortment: Alleles for different genes will be inherited separately or independently
Gene
A unit of heredity that codes for a trait
Allele
An alternative form of a gene that determine how a trait is expressed, such as tall vs short
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism (the allele combination)
Phenotype
The observable physical traits of an organism, determined by genotype
Homozygous
When two alleles are the same for a given trait (ex: TT or tt)
Heterozygous
Two different alleles for a gene/trait
Gamete
A sex cell (sperm or egg) that carries only one set of chromosomes
Dominant Allele
The allele that is expressed when present, masking the other allele
Recessive Allele
The allele that is masked when the dominant allele is present
Punnet Square
A chart used to predict the probability of genetic outcomes in offspring
Law of Segregation
Principle stating that allele pairs separate during gamete formation, so each gamete carries only one allele
Law of Independent Assortment
Principle stating that genes for different traits separate independently during gamete formation (if genes are unlinked)
Hybrid
Another term for a heterozygous individual
Incomplete Dominance
When the heterozygous trait is mixed instead of either color. One allele is not completely dominant of the other.
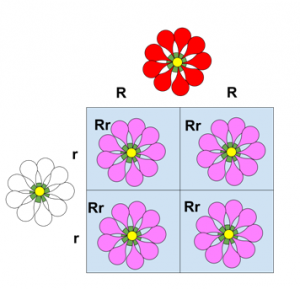
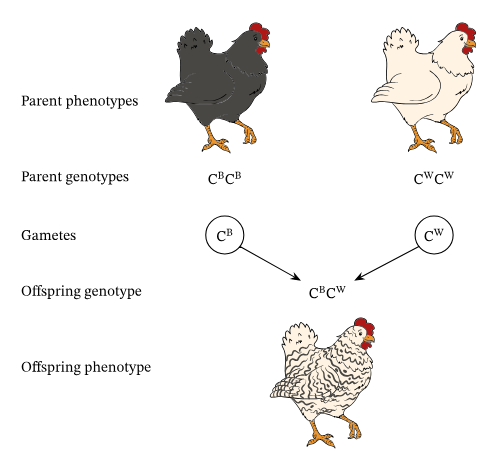
Co Dominance
When both alleles are fully expressed in the offspring.
Ex: vitiligo
Multiple Alleles
When a gene has more than two allele forms in a population

Test Cross
Crossing a dominant phenotype with a homozygous recessive to find the genotype