Chapter 25, Lesson 3: The Stomach
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 25, Lesson 3 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
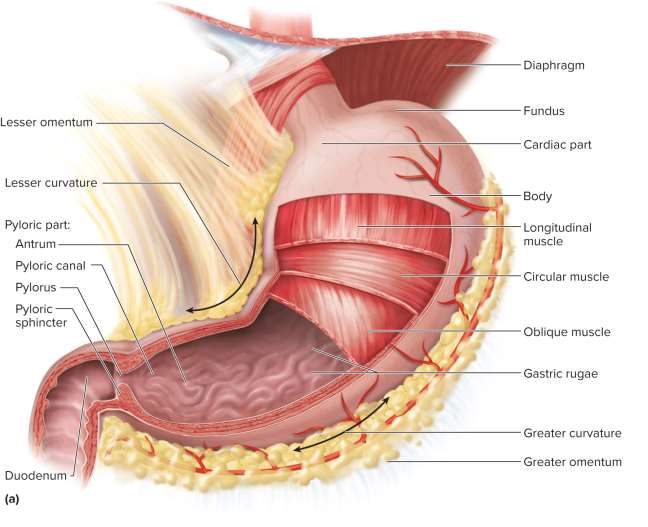
Stomach
A J-shaped, muscular sac in the upper left abdominal cavity that functions as a food storage organ for mechanical and chemical digestion
Chyme
The acidic, soupy mixture of semidigested food that passes on to the small intestine
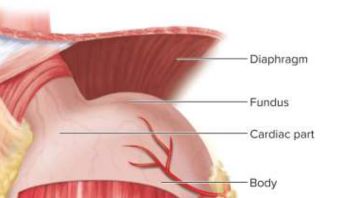
Cardiac part
A small area within about 3 cm of the cardiac orifice; connects esophagus to stomach
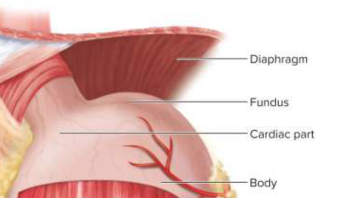
Fundic region (fundus)
Dome superior to the esophageal attachment
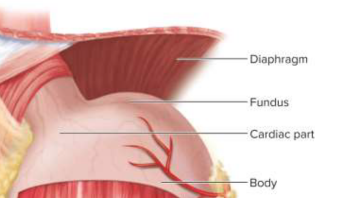
Body
The greatest part of the stomach distal to the cardiac orifice
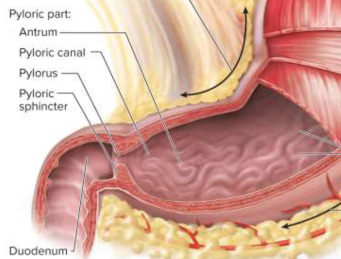
Pylorus
The narrow passage from the stomach to the duodenum
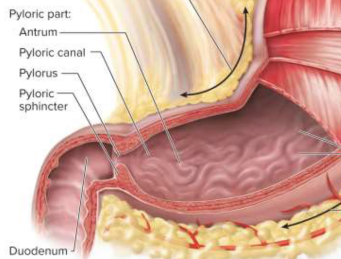
Pyloric sphincter
A ring of smooth muscle around the pylorus that regulates the passage of chyme into the duodenum
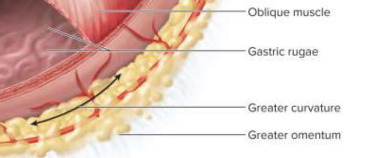
Greater curvature
40 cm curvature from which the greater omentum hangs
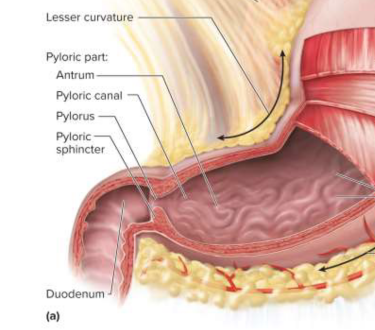
Lesser curvature
10 cm curvature from which the lesser omentum hangs
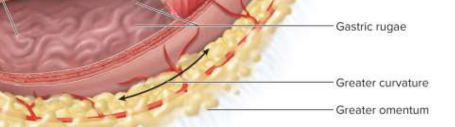
Gastric rugae
Longitudinal wrinkles that allow for expansion when full and contraction when empty
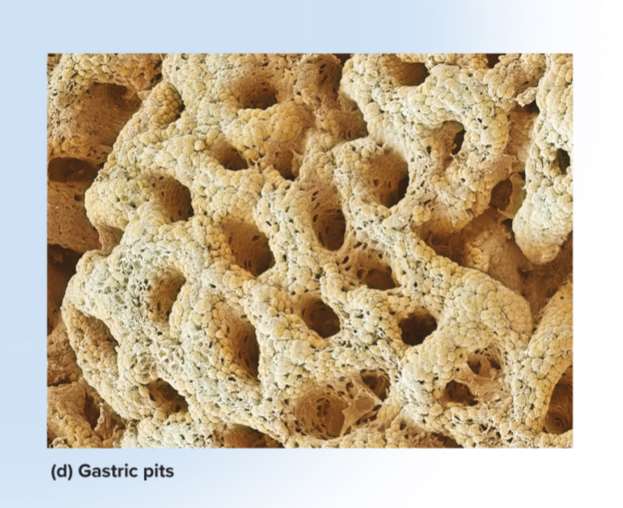
Gastric pits
Depressions in the gastric mucosa with two or three tubular glands at the bottom; secretes substances
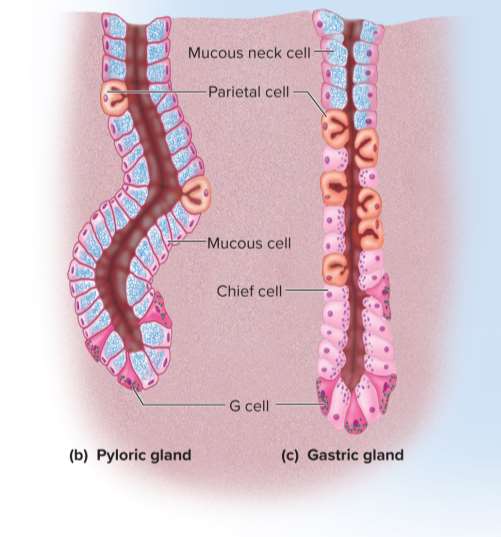
Mucous cells
Cells that secrete mucus in the cardiac and pyloric glands (called mucous neck cells in gastric glands due to their position)
Regenerative cells (stem cells)
Cells found in the base of the gastric pit and neck of the glands; divides rapidly and produces a continual supply of new cells for replenishment
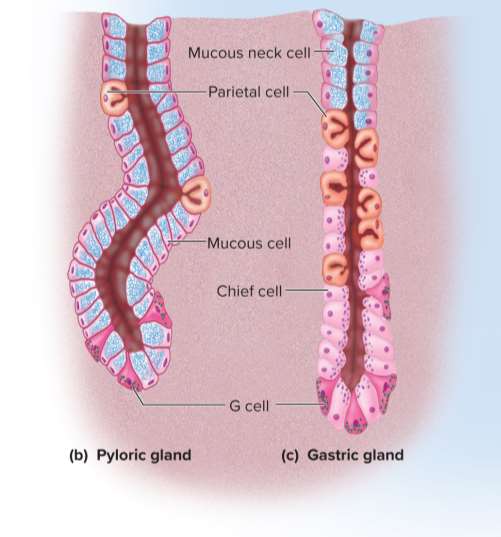
Parietal cells
Cells found mostly in the upper half of the glands; secretes hydrochloric acid, intrinsic factor, and a hunger hormone called ghrelin

Chief cells
The most numerous cell type in the stomach; secretes gastric lipase and pepsinogen in the gastric glands to dissolve lipids and proteins
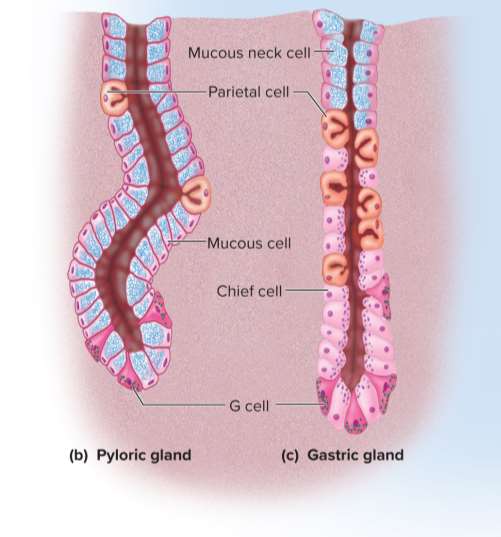
Enteroendocrine cells
Cells concentrated in the lower end of the glands that secrete hormones and messengers to regulate digestion
Gastric juice
The 2 to 3 liters of juice produced by the gastric glands per day; mainly a mixture of water, hydrochloric acid, and pepsin
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Acid that breaks up connective tissues and plant cell walls for liquification and chyme formation; also destroys pathogens
Pepsinogen
Enzyme that is secreted by chief cells to digest proteins
Gastric lipase
Enzyme that digests about 10 to 15% of dietary fats in the stomach (the rest is digested in the small intestine)
Intrinsic factor
Helps absorb vitamin B12 in the small intestine to later synthesize hemoglobin — secretion of this is the only indispensable function of the stomach
Swallowing center
Part of the medulla oblongata that signals the stomach to relax during swallowing; controls chyme flow to 3 mL for digestion and neutralization
4 to 6 hours
The typical time needed for the stomach to empty after a meal (higher fat contents extend time)
Vomiting
The forceful ejection of stomach and intestinal contents (chyme) from the mouth; can be caused by overstretching the stomach, alcohol or other irritants, trauma, or pain or sensory stimuli
Retching
Spasms of the chest and abdomen that dilate the esophagus before vomiting, often accompanied by tachycardia, salivation, and sweating, with chyme sometimes moving into the esophagus
Projectile vomiting
Sudden vomiting with no prior nausea or retching; common in feeding infants
Bulimia
An eating disorder with sometimes chronic, intentional vomiting; hydrochloric acid in vomit can cause tooth enamel erosion and respiratory tract destruction
Digestion
The chemical and mechanical breakdown of food; partially done by salivary and gastric enzymes but primarily done in the small intestine
Absorption
Obtaining nutrients or substances from food; not done by the stomach (except for some drugs like aspirin) and can be affected by capacity (as is with alcohol being more intoxicating with food)
Mucous coat
The thick, highly alkaline mucus in the stomach that resists the action of acid and enzymes
Tight junctions
Junctions between the stomach’s epithelial cells that prevent gastric juice leakage and cell digestion
3 to 6 days
The lifespan of the stomach’s epithelial cells; replaced rapidly as they are digested over time
Gastritis
The inflammation of the stomach; can lead to peptic ulcers
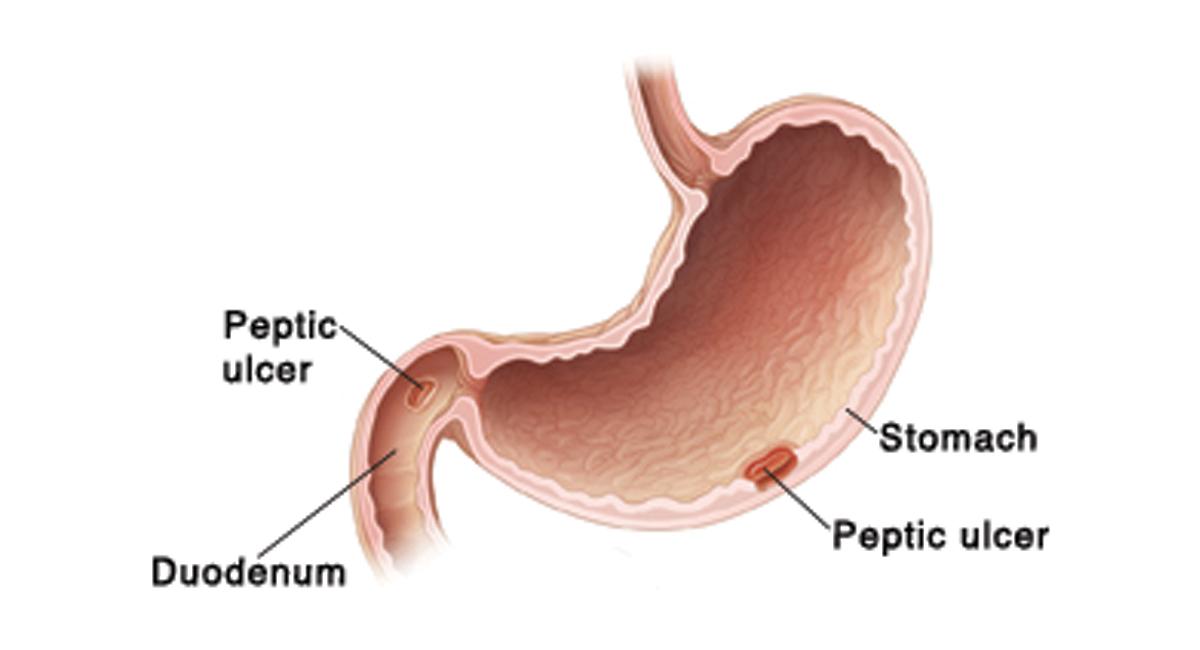
Peptic ulcer
The deterioration of the stomach wall; risk factors include stress, higher acid levels, smoking, and drugs like aspirin and NSAIDs
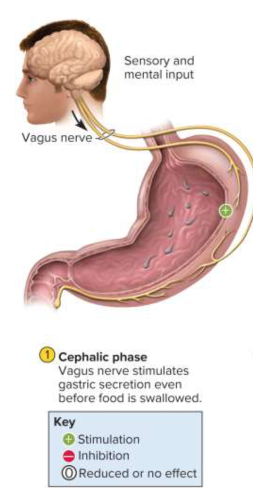
Cephalic phase
The phase of the stomach controlled by the brain as it responds to stimuli of food; controls 40% of all acid secretion
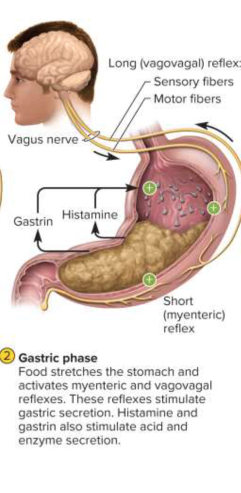
Gastric phase
The phase of the stomach controlling itself after swallowing food and semidigested protein; \frac{2}{3} of gastric secretion and \frac{1}{2} of acid secretion occur in this phase as the stomach is stretched and pH rises
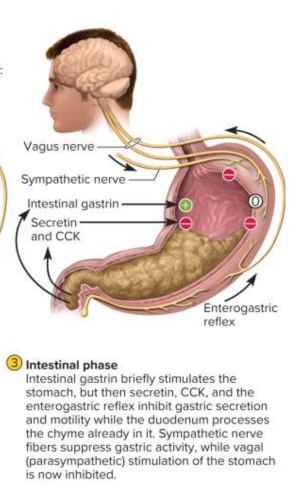
Intestinal phase
The phase of the stomach controlled by the small intestine as more chyme arrives to moderate gastric activity
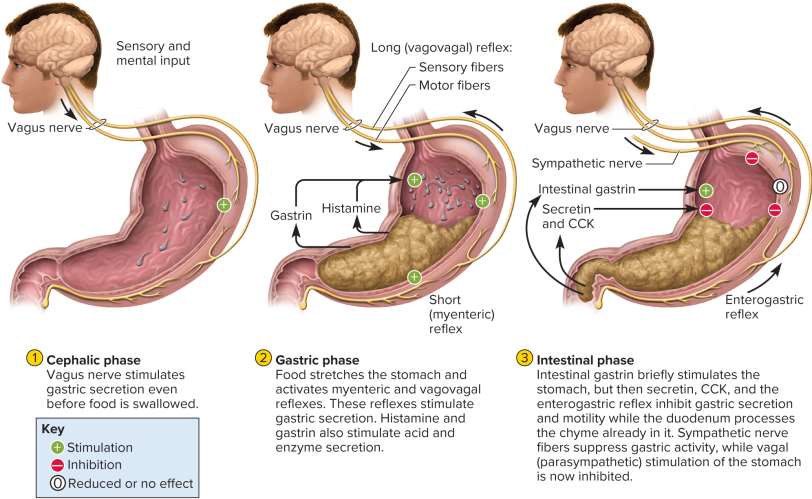
Gastric phases
Phases to regulate gastric secretion, control, and motility that can occur simultaneously:
Cephalic phase (brain)
Gastric phase (stomach itself)
Intestinal phase (small intestine)
Enterogastric reflex
Reflex where the duodenum sends inhibitory signals to the stomach with more digestion