Bio Exam Mats 2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nerds (im updating this as i go). When i ask for an example, it can be any example of the sort. It does not have to be identical to the written example
Last updated 6:52 PM on 3/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
What type of plant is Angiosperm?
Flowering Plants
2
New cards
What are the 3 stages of an angiosperm plant life cycle? (the 3 Fs)
Flowering
Fertilization
Fruits
Fertilization
Fruits
3
New cards
What is a Sporophyte and define its life cycle
Definition
* Diploid phase of the plant
Life cycle
* Multicellular diploid form from union of gametes (fertilization)
* Sporophyte produces haploid spores (which eventually turn into female gametophyte) via meiosis
\
* Diploid phase of the plant
Life cycle
* Multicellular diploid form from union of gametes (fertilization)
* Sporophyte produces haploid spores (which eventually turn into female gametophyte) via meiosis
\
4
New cards
Why does sporophyte undergo meiosis?
To produce spores
5
New cards
What do plants do with the spores that they make from meiosis?
It divides the spores via mitosis and make gametes
6
New cards
Define Fertilization
When diploid zygote form new sporophyte
7
New cards
Name and define 2 parts of the flower
* Reproductive shoot
* Reproductive part of flower
* Determinate shoot
* Stops the flower from growing after a certain length
* Reproductive part of flower
* Determinate shoot
* Stops the flower from growing after a certain length
8
New cards
What are the 4 organs of a flower?
1. Sepals
2. Pedals
3. Stamens
4. Carpels
9
New cards
What is the function of the stamen and carpel?
Reproduction
10
New cards
What is the function of Sepals?
It hovers over and protects the floral bud before it opens
11
New cards
What is the function of Petal?
Gives flower its unique color
12
New cards
Define Stamen
Reproductive organ that contains stalk and anther
13
New cards
What is an anther?
Top part of stamen that contains male gametophyte
* this is where pollen is produced
* this is where pollen is produced
14
New cards
Define carpel
Reproductive organ that contains ovary, stigma, and style.
15
New cards
Define Style
Neck of the carpel
16
New cards
Where is the ovary located?
At the base of the carpel
17
New cards
Define Stigma
Sticky structure at the top of the style
18
New cards
True or False: It is still a complete flower regardless if it has all 4 organs
False: A complete flower __**requires**__ the presence of all 4 organs
(Carpel, Pedal, Sepal, and Stamen)
(Carpel, Pedal, Sepal, and Stamen)
19
New cards
True or False: The flower is still incomplete even when one of its organ is missing
True
20
New cards
How many pollen sac does each anther have?
4
21
New cards
True or False: A pollen sac contains 4 microspores
True
22
New cards
Each microspore undergoes _______ to produce pollen grain (sperm)
Each microspore undergoes __**mitosis**__ to produce pollen grain (sperm)
23
New cards
What does pollen grain contain? (2 things)
A generative cell and a tube cell
24
New cards
True or False: The pollen grain was made from the carpel and move to the stamen to be fertilized
False: The pollen grain was made from the __**stamen**__ and move to the __**carpel**__ to be fertilized
25
New cards
What do pollen grain do after they reached the stigma?
Tube cell within the pollen grain produces pollen tube that deliver the sperm to the carpel (where the female gametophyte is located)
26
New cards
How many sperms are delivered to the carpel?
2
27
New cards
Describe the process of the development of the male gametophyte
1. Each anther has 4 pollen sacs
2. Each sac produces 4 microspores via meiosis
3. Each microspores undergo mitosis and produce generative cell and tube cell (pollen grain)
28
New cards
True or false: The male gametophyte was transferred to the __**sepal**__ after it produces the pollen grain
False: The male gametophyte was transferred to the __**carpel**__ after it produces the pollen grain
29
New cards
Describe the process of female gametophyte
* One megasporocyte the ovule undergoes meiosis and produces 4 haploid megaspores
* Megaspores undergoes mitosis and form 8 haploid nuclei (the embryonic sac)
* The ovule becomes the seed
* Megaspores undergoes mitosis and form 8 haploid nuclei (the embryonic sac)
* The ovule becomes the seed
30
New cards
True or False: Ovary becomes the fruit and ovule becomes the seed
True
31
New cards
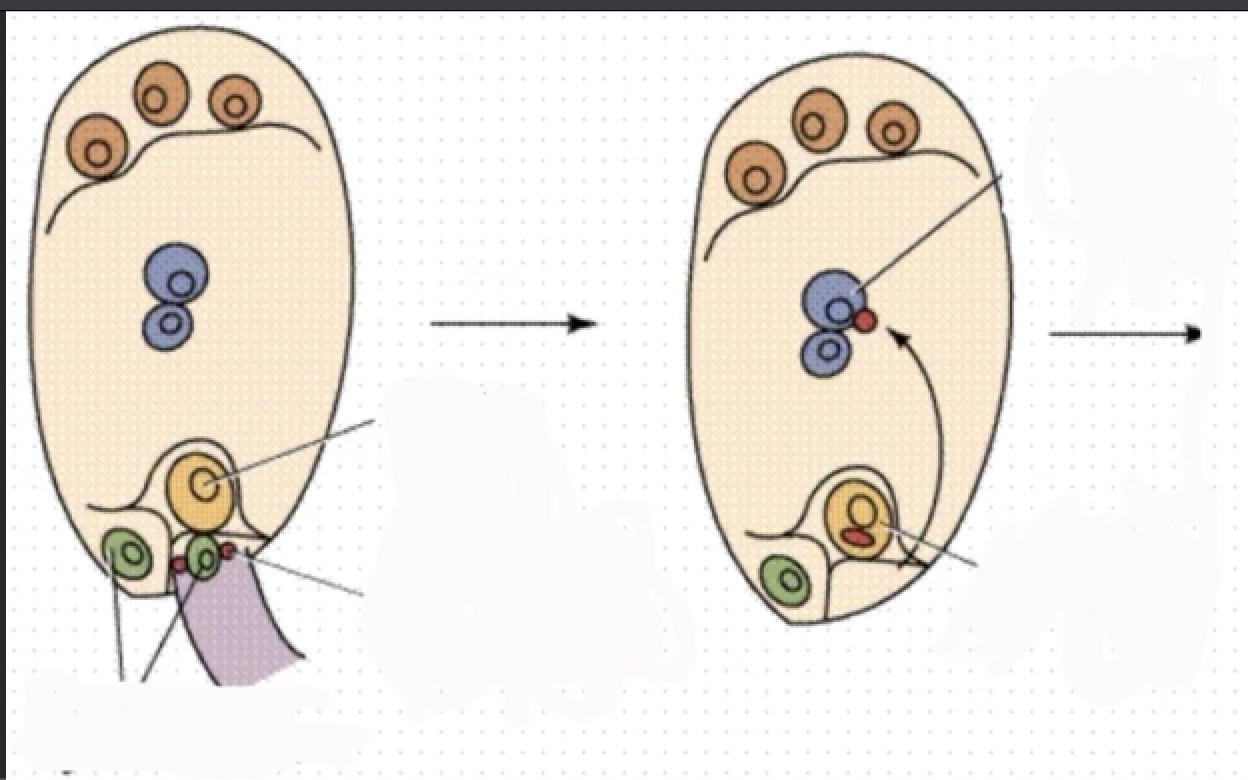
Fill in the Blank (Embryonic Sac structure edition): Click on the picture
\
\
Click on the picture to check your answer
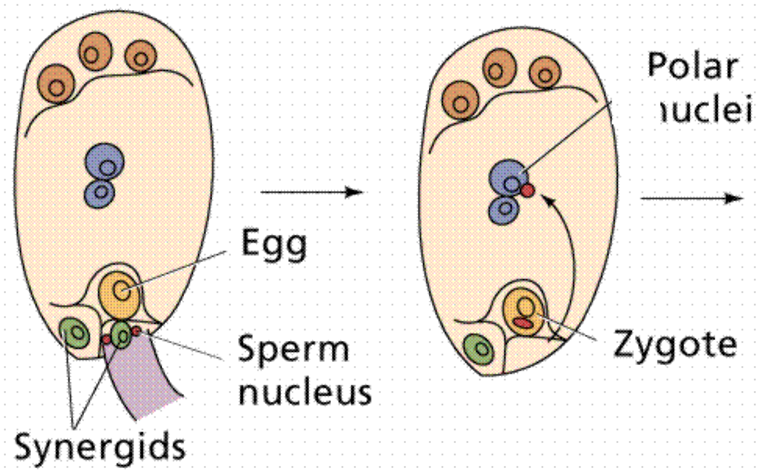
32
New cards
One end of the embryonic sac contains an egg cell and 2 cells. What are these 2 cells called?
Synergids
33
New cards
What is the function of synergids cells?
To attract and guide pollen tube
34
New cards
Define Polar nuclei
* The 2 nuclei located in the center of the embryonic sac
* Shared a cytoplasm
* Shared a cytoplasm
35
New cards
What locate at the opposite end of the synergids?
3 (antipodal cells) cells with unknown function
36
New cards
Define Pollination
Transfer of pollen from one anther to another stigma
37
New cards
How does plant compensate for the inefficiency of wind pollination?
By making a large amount of pollen
38
New cards
Aside from the wind, what other factors pollinate the plants? What attracts the pollinators to the flower?
Bees - They are attracted to bright color flowers
Moths, butterflies, flies, bats, and birds - Attracted by odor
\
Moths, butterflies, flies, bats, and birds - Attracted by odor
\
39
New cards
Describe the process of double fertilization
* 2 sperms are directed to the ovary through the pollen tube by GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
* 1 sperm fertilize the egg, form zygote, produce concetrated Ca2+ to prevent the another sperm from entering the zygote
* 1 combines with 2 polar nuclei and form endosperm (food storing tissues of the seed)
* 1 sperm fertilize the egg, form zygote, produce concetrated Ca2+ to prevent the another sperm from entering the zygote
* 1 combines with 2 polar nuclei and form endosperm (food storing tissues of the seed)
40
New cards
What is the function of the endosperm?
Provide nutrients for the seed
41
New cards
Where do monocot and dicot seed store their nutrient?
Monocot - they store their nutrient in the endosperm
Dicot - They transfer the nutrient from the endosperm into the cotyledon
Dicot - They transfer the nutrient from the endosperm into the cotyledon
42
New cards
What is cotyledon?
The first part of the dicot seed that is above the ground.
43
New cards
How many cotyledon does monocots and dicots have?
Monocot - 1
Dicot - 2
Dicot - 2
44
New cards
What does hypocotyl attach to in the seed?
It attaches to the root (the radicle)
45
New cards
What does the epicotyl attach to in the seed?
It attaches to the first leaves
46
New cards
Describe the maturation state of the seed
Seed dehydrate itself
Seed coat harden to trap the nutrient inside the seed
Seed coat harden to trap the nutrient inside the seed
47
New cards
Describe seed dormancy
Seed will not germinate until it meet its environmental requirement to germinate
Example:
* Some seed requires heavy rainfall to germinate
Example:
* Some seed requires heavy rainfall to germinate
48
New cards
What is imbibition and why does seed relies on it to germinate?
Imbibition is the hydration of the seed
* (Just know that the seed take in water because the inside has low water potential and water likes to go from high to low)
Seed relies on imbibition to expand and rupture the seed coat
* (Just know that the seed take in water because the inside has low water potential and water likes to go from high to low)
Seed relies on imbibition to expand and rupture the seed coat
49
New cards
Explain the germination stage of the seed
* Imbibition: Seed receives enough hydration, start to expand, and seed coat ruptures
* Enzymes began to digest the nutrient and transfers them to the embryo
* The embryonic root (the radicle) forms first and shoots the seed upward
* Hypocotyl straighten, and raises the cotyledon and the epicotyl, as it responds to light
* Epicotyl spread its first leaves and start to perform photosynthesis
* The cotyledon breaks off of the epicotyl after all the nutrient is used
* Enzymes began to digest the nutrient and transfers them to the embryo
* The embryonic root (the radicle) forms first and shoots the seed upward
* Hypocotyl straighten, and raises the cotyledon and the epicotyl, as it responds to light
* Epicotyl spread its first leaves and start to perform photosynthesis
* The cotyledon breaks off of the epicotyl after all the nutrient is used
50
New cards
True or false: Fruits are developed from the ovary
True
51
New cards
What is the requirement for the development of fruit?
Pollination
* Without pollination, fruit cannot be able to develop
* Without pollination, fruit cannot be able to develop
52
New cards
What is simple fruit?
Fruit that develop from 1 carpel
53
New cards
What is aggregate fruit?
Fruit develop from more than 1 carpel and forms fruitlets.
* An example is raspberry
* An example is raspberry
54
New cards
What are the two mechanisms for the asexual reproduction of plants? Describe the mechanism
Fragmentation
* Separation of a parent plant that develops into a whole plant
* An example: Severed stem develops root
Apomixis
* Asexual reproduction of seeds
* An example: Dandelions
\
* Separation of a parent plant that develops into a whole plant
* An example: Severed stem develops root
Apomixis
* Asexual reproduction of seeds
* An example: Dandelions
\
55
New cards
What are some of the advantages and disadvantages of asexual reproduction
Advantages
* Does not require pollinators
* Can clone itself if it is well adapted to its envrionment
Disadvantages
* Greater risk of extinction because they all have the same genes
* Does not require pollinators
* Can clone itself if it is well adapted to its envrionment
Disadvantages
* Greater risk of extinction because they all have the same genes
56
New cards
What are some advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction
Advantages
* Genetic variation (able to adjust environmental changes
Disadvantages
* Relies on pollinator
* Exposed to predators
* Genetic variation (able to adjust environmental changes
Disadvantages
* Relies on pollinator
* Exposed to predators
57
New cards
What is self-fertilization and why does plant prevent itself from doing it?
Self-fertilization - Plants fertilize itself
Plants prevent itself from fertilizing to ensure genetic diversity
Plants prevent itself from fertilizing to ensure genetic diversity
58
New cards
How do plants prevent self-feritilization?
* Some flower lacks either the carpels or the stamen
* The maturity rate of the stamen and carpel is different
* Self-incompatibility (Prevents the growth of pollen tube)
\
* The maturity rate of the stamen and carpel is different
* Self-incompatibility (Prevents the growth of pollen tube)
\
59
New cards
What is plant breeding
Humans cross-breeding plants to obtain the desired trait
60
New cards
Define the 2 meanings of plant bio tech and give an example for each
* Innovation in the use of plants
* Weaving monocots leaf into hat
* The use of genetically modified organism
* increase crop yield
\
* Weaving monocots leaf into hat
* The use of genetically modified organism
* increase crop yield
\
61
New cards
Define transgenic and give an example
GM organism that is genetically modified to express another species’ genes
* Corns can secrete BT that is lethal to insects
\
* Corns can secrete BT that is lethal to insects
\
62
New cards
What are the 3 pros of GM plants?
* GM plants can increase
* Food yields and reduces world hunger
* Improves nutritional value
* The use of GM can reduce the green house gases
* GM plants can absorbs more efficiently
* Food yields and reduces world hunger
* Improves nutritional value
* The use of GM can reduce the green house gases
* GM plants can absorbs more efficiently
63
New cards
What are the 2 cons of GM plants?
* Unknown risk to humans such as decreaseallergens exposure to insecticides
* Transgenic genes can cause herbicide resistant
* Transgenic genes can cause herbicide resistant
64
New cards
What is Etiolation?
Plant sprout regardless of the presence of light
65
New cards
What is De-etiolation?
Formation of shoots and leafes due to the presence of light
66
New cards
Name at least 1 example of de-etiolation
* Stem elongation slows
* Root elongation
* Leaf expands
* Shoot produces chlorophyll
* Root elongation
* Leaf expands
* Shoot produces chlorophyll
67
New cards
What is the process of the signal transduction pathway?
1. Reception
1. Receptor receives stimulus (a signal)
2. Transduction
1. Second messenger activated and amplifies the signal within the cell
3. Response (2 types of response)
1. In transcriptional regulation
1. Protein binds to a part of DNA and control the production of certain genes
2. In post-translational modification
1. Alters the proteins and changes its activity
68
New cards
What is the light receptor that involve in de-etiolation called?
Phytochrome
69
New cards
Describe the process of the transduction pathway in de-etiolation
1. Light hits the phytochrome (light receptor)
2. Phytochrome changes its shape
3. The shape change causes cyclic GMP (cGMP) and Ca2+ level to increase
4. cGMP activates protein kinases which phosphorylates proteins and other enzymes
70
New cards
Define phototropism
Growth of shoots towards or away from the light
71
New cards
What did Darwin and his son observe regarding phototropism?
* Grass tends to bend towards the light only if the tip of the grass is present.
* If the tip is cut off, the grass does not curve towards the light
* Darwin concluded that the tip of the grass is responsible for sensing light
* If the tip is cut off, the grass does not curve towards the light
* Darwin concluded that the tip of the grass is responsible for sensing light
72
New cards
Describe a hypothesis that was made after Darwin’s grass observation
Asymmetrical distribution of auxin causes the darker side of the grass to grow faster than the side that faces the light
73
New cards
Describe Auxin and identify its function and location
* Growth hormone
* Function
* Stimulates cell growth and cell elongation
* Inhibit axillary growth
* Location
* Apical meristem in both shoot and root
* Influence by phototropism and gravitropism
* Function
* Stimulates cell growth and cell elongation
* Inhibit axillary growth
* Location
* Apical meristem in both shoot and root
* Influence by phototropism and gravitropism
74
New cards
Name (at least) 1 consequence of having too much and too little of Auxin
* Too much
* No axillary growth
* Axillary buds on the shoot and root cannot grow
* Too little
* Apical meristems in shoot and root can’t elongate.
* 2 consequences
* Root can’t elongate to find water and mineral
* Shoot can’t elongate and result in being shaded by the surrounding plants
\
* No axillary growth
* Axillary buds on the shoot and root cannot grow
* Too little
* Apical meristems in shoot and root can’t elongate.
* 2 consequences
* Root can’t elongate to find water and mineral
* Shoot can’t elongate and result in being shaded by the surrounding plants
\
75
New cards
Describe cytokinins and identify its function and location
* Axillary growth hormone
* Function
* Signals the growth of axillary buds
* Slows the deterioration of the leaves
* Location
* Produced in actively growing tissues such as fruits, roots, and embryos
* Function
* Signals the growth of axillary buds
* Slows the deterioration of the leaves
* Location
* Produced in actively growing tissues such as fruits, roots, and embryos
76
New cards
Name (at least) 1 consequence of having too much and too little of Cytokinins
* Too much
* There will be more of photosynthesis and less of glucose production because there will be a lot of chlorophyll in the leaf
* Too little of
* There will be less chlorophyl pigment and reduces photosynthesis efficiency
* There will be more of photosynthesis and less of glucose production because there will be a lot of chlorophyll in the leaf
* Too little of
* There will be less chlorophyl pigment and reduces photosynthesis efficiency
77
New cards
Describe gibberellins and identify its function and location
* Growth hormone
* Function
* Stimulate stem and leaf growth
* Work with auxin to stimulate stem elongation and formation of fruits
* Break seed dormancy
* Location
* Apical buds
* Apical roots
* Young leaves
* Seeds
\
* Function
* Stimulate stem and leaf growth
* Work with auxin to stimulate stem elongation and formation of fruits
* Break seed dormancy
* Location
* Apical buds
* Apical roots
* Young leaves
* Seeds
\
78
New cards
Name (at least) 1 consequence of having too much and too little of gibberellins
* Too much
* Over-sized fruit production
* Too little
* Stem don’t elongate much
* Fruit infertility
\
* Over-sized fruit production
* Too little
* Stem don’t elongate much
* Fruit infertility
\
79
New cards
Describe ABA (abscisic acid) and identify its function and location
* Hormone that regulate growth
* Function
* Slows down growth (growth control)
* Inhibit seed germination
* Gives seeds the ability to withstand dehydration
* Location
* ABA can be found in all plant cells
\
* Function
* Slows down growth (growth control)
* Inhibit seed germination
* Gives seeds the ability to withstand dehydration
* Location
* ABA can be found in all plant cells
\
80
New cards
Name (at least) 1 consequence of having too much and too little of ABA
* Too much
* Plant will die because over accumulation of ABA in the leaf can cause the stomata too close
* Seed will not germinate
* Too little
* No growth control; plant will grow uncontrollably
* Seed will suffer hydration
* Plant will die because over accumulation of ABA in the leaf can cause the stomata too close
* Seed will not germinate
* Too little
* No growth control; plant will grow uncontrollably
* Seed will suffer hydration
81
New cards
Describe ethylene and identify its function and location
* Ripening hormones
* Function
* Ripen fruits
* Thickens stem
* Cell destruction
* Example: leaf during the fall
* Less auxin makes ethylene more effective
* Breaking down the green chlorophyll and exposes the red pigment in the leaf
* Leaf abscissions
* Aging of the leaf
* Location
* Made by most plant cells
* Function
* Ripen fruits
* Thickens stem
* Cell destruction
* Example: leaf during the fall
* Less auxin makes ethylene more effective
* Breaking down the green chlorophyll and exposes the red pigment in the leaf
* Leaf abscissions
* Aging of the leaf
* Location
* Made by most plant cells
82
New cards
Name (at least) 1 consequence of having too much and too little of Ethylene
* Too much
* Kills the plant internally
* Premature ripening in fruits
* Too less
* Plants die under stress condition
* Kills the plant internally
* Premature ripening in fruits
* Too less
* Plants die under stress condition
83
New cards
True or False: Ripening of the fruit caused by ethylene is a form of negative feedback
False: Ripening of the fruit caused by ethylene is a form of __**positive feedback**__
84
New cards
Define Circadian rhythm
Cycle that is controlled by environmental variable such as light
85
New cards
What enable plants to measure the passage of day and night?
Phytochrome
86
New cards
Give an example of short day plant
Poinstattias
87
New cards
Give an example of long day plant
Radishes
88
New cards
Define Gravitropism and which hormone participate in this
Plant growth in response to gravity
* Shoot moves upward
* Root moves downward
* Shoot moves upward
* Root moves downward
89
New cards
How does statoliths, auxin, and gravity play a role in root growth
* Statolith aggregate at the bottom of the cells in the root cap (due to gravity) and stimulates auxin
* Auxin stimulates the elongation of root cell and helps it move downward
* Auxin stimulates the elongation of root cell and helps it move downward
90
New cards
Define thigmomorphogenesis and give an example.
Definition
* Changes in plant occur due to mechanical influence
Example
* Rubbing young plants will cause them to be shorter
* Changes in plant occur due to mechanical influence
Example
* Rubbing young plants will cause them to be shorter
91
New cards
Define thigmotropism and provide an example
Plant growth in response to touch
* Example: Vine will grow straight until it found something to latch onto
* Example: Vine will grow straight until it found something to latch onto
92
New cards
How do plant respond to drought?
ABA clogged up in the stomata preventing it from open
* Plant can slow down transpiration and conserve water this way
* The downside is photosynthesis is reduce
* Plant can slow down transpiration and conserve water this way
* The downside is photosynthesis is reduce
93
New cards
How dos\\ plants respond to flooding?
They secrete ethylene into the cortex of the root, killing the cell there to create air space for O2 to diffuse
\
\
94
New cards
How do plants respond to cold stress
Plants produces sugar to
* Help prevent water loss
* Slows down the freezing of the cell
* Help prevent water loss
* Slows down the freezing of the cell
95
New cards
What is Metabolic Rate and how do we measure them?
Definition:
* The amount of energy required for chemical reaction to occur
We can measure the metabolic rate by measuring:
* Rate of heat loss
* Rate of O2 consumed
* Rate of CO2 produced
* The amount of energy required for chemical reaction to occur
We can measure the metabolic rate by measuring:
* Rate of heat loss
* Rate of O2 consumed
* Rate of CO2 produced
96
New cards
Define the 2 bioenergetic strategies
Endothermic
* Body temperature s regulated within organism
* The heat is generated by metabolism
Ectothermic
* Has to regulate heat via external source
* Ex:
* Snake warm its body by sunbathing on top of a rock
* Snake cool its body by hiding in the shade
* Body temperature s regulated within organism
* The heat is generated by metabolism
Ectothermic
* Has to regulate heat via external source
* Ex:
* Snake warm its body by sunbathing on top of a rock
* Snake cool its body by hiding in the shade
97
New cards
What is the relationship between body size and metabolic rate?
They have an inverse relationship
* The smaller the animal, the more calories requirement (and vice versa)
* The smaller the animal, the more calories requirement (and vice versa)
98
New cards
Why does a rat burn more calories than an elephant?
The rat has more surface to volume ratio that generate a great amount of heat
99
New cards
What is the consequence of burning more calories
Higher heart rate
Higher breathing rate
Higher breathing rate
100
New cards
Define Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Amount of calories you need to maintain function
* Can measure when an adult endotherm is at rest
* Can measure when an adult endotherm is at rest