PSY220 Final Exam
1/162
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Maya's quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Social Cognition (social thinking)
- social attitudes towards ourselves and others
- impressions of ourselves and others
- beliefs of ourselves and others
Self-concept
who am i?
Self-knowledge
how can i explain and predict myself?
Self-esteem
my sense of self-worth
Social self
my roles, my group identity
Self-schema
beliefs about self that organize and guide the processing of self-relevant info
- "mental templates"
Social comparisons
- we compare ourselves to others
- we are conscious of those differences
- may have either positive or negative effects on the self
Social comparisons study: Lockwood and Kunda (1997)
- participants were either 1st or 4th year students
- had them read an article about a "super-star" 4th year student
- 1st years: felt inspired
- 4th years: felt pathetic, self-doubt
Spotlight effect
- assume everything we do is gonna be highlighted and paid attention to
- see ourselves as if on centre stage
Illusion of Transparency
worry about being evaluated negatively, especially when feeling self-conscious
Illusion of Transparency study: Savitsky and Gilovich (2003)
- asked participants to give speech
- reassured condition: being reassured doesn't really do anything for confidence
- informed condition: inform participants about illusion of transparency, had positive impact on speech
Individualism
- culture's main focus is the individual person, self achievement and fulfillment
- independence, autonomy
- independent self: stable self-concept, personal self-esteem
Collectivism
- culture's main focus is the collective group, group happiness and fulfillment
- relationships, environment
- interdependent self: malleable self-concept, relational self-esteem
Culture and Cognition study: Masuda and Nisbet (2001)
- gave East Asians and Americans a photo of a marine scene
- East Asian individuals describe environment and the relationship among the fish
- Americans attend more to the single big fish in the photo
Culture and Cognition study: Kim and Marcus (1999)
- offered some pens, all the same colour but one
- different cultural preferences for uniqueness and conformity were displayed in pen choice
Self-Knowledge - predicting behaviour
- planning fallacy: always gonna underestimate time needed to complete a task
- makes us not great at predicting our own behaviours
Self-Knowledge - predicting feelings
- affective forecasting: predicting how we'll feel in the future
- impact bias: assuming something has more impact than it actually will, tend to overestimate emotional impact of certain events
Self-Knowledge Accuracy
self-reports are often untrustworthy because we're not good at predicting own behaviour or feelings
Dual attitudes - Implicit Attitudes
- automatic
- change slowly, with practice that forms new habits
Dual attitudes - Explicit Attitudes
- consciously controlled
- may change with education or persuasion
Low/High Self-Esteem outcomes
- low associated with: anxiety, loneliness, eating disorders
- Narcissism: not exactly self-esteem, but when there is too much self-esteem
Self-Efficacy
- a belief in one's own competence
- high: lots of belief in one's abilities
- low: little belief in one's abilities
- different from self-esteem, not "i am great" but "i can be great if i try"
Self-Serving Bias
tendency to attribute positive outcomes to yourself and negative outcomes to other factors
Attribution styles
- Stable vs Instable
- Global vs Local
- Internal vs External
Comparison to Others
- most people consider themselves better than average (on a variety of dimensions)
- subjective behaviour dimensions more susceptible to this
Unrealistic Optimism
- predisposed to optimism
- tend to have unrealistic optimism towards future events, which is supported by pessimism about other's futures
BUT
- illusory optimism increases vulnerability
- defensive pessimism helps people prepare for problems
False Consensus Effect
overestimating commonality of one's opinions and one's undesirable or unsuccessful behaviours
False Uniqueness Effect
underestimating the commonality of one's abilities and one's desirable or successful behaviours
Self-Presentation - self
- different ways we present ourselves
- personal style, social media, language use
- all trying to present DESIRED IMAGE for both external and internal audience
- external: how others see you
- internal: reinforcing how you see yourself
Self-Handicapping
protecting one's self-image with behaviours that create an excuse for later behaviour
Impression Management
- want to present desired image to the world
- familiar vs unfamiliar situations
- in unfamiliar situations: try harder to make good impression and present oneself in positive light
Self-Monitoring
- being attuned to the way one presents oneself in social situations and adjusting performance to create desired impression
- High: change behaviour based on social environment, very perceptive
- Low: stable personality and behaviour regardless of environment
Self-Presentation Theory
- suggests we are eager to present ourselves in ways that make us look good
- motivated to impress others, but we have self-doubts
- thus, we feel social anxiety
Overpersonalizing Situations
- concerning for people who are shy, anxious, or self-conscious
- views incidental events as related to themselves
- tendency breeds anxious concern and maybe paranoia
- especially prone to spotlight effect
Perceived Self-Control
- learned helplessness: individuals become passive when feel like they have no control over negative events
- too much freedom and self-determination can have negative effects such as decreased life satisfaction, depression, and regret
- low self-efficacy
Attitudes
- a favourable or unfavourable evaluative reaction toward something/someone
- Exhibited in one's BELIEFS, FEELINGS, or INTENDED BEHAVIOURS
Tripartite Model of Attitude
- attitude made up of: AFFECT, BEHAVIOUR, COGNITION
- typically all three align with each other
- cognitive dissonance when they aren't all positive or negative
- attitudes susceptible to social context or outside influences
Measurement of Attitude
- attitudes cannot be observed directly
- measures of attitude either explicit or implicit
Explicit Attitudes Measures
self-reports, measures, etc
Implicit Attitudes Measures
- implicit association test (IAT)
- facial muscle responses, physiological measures, etc
- researchers hold that implicit attitudes show more about true beliefs - not as impacted by environmental influences
Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- uses reaction times to measure how quickly people associate concepts
- given choice between two different pictures/words/concepts
- react quicker with something you have connections with in brain
- assumptions: unbiased, uncovers unconscious attitudes
- example: Race IAT
Principle of Aggregation
effects of an attitude or behaviour become more apparent when looking at person's aggregate or average behaviour
Theory of Reasoned Action (Fishebin & Ajzen, 1973)
Attitude + Norm -> Intention -> Behaviour
- attitudes can predict planned deliberate behaviour
- an individual's intention is determinant of their behaviour
- intention as the motivation to act - influenced by ATTITUDE and NORM
- use of explicit measurement
Theory of Reasoned Action - REVISED (Ajzen 1988)
- revised theory to add factor of control (self-efficacy)
Attitude + Norm + Control -> Intention -> Behaviour
- control can also directly impact behaviour
- not all factors always equally strong impact - depends on situational context
- only applies to PLANNED behaviour
When Attitudes are Potent
- many behaviours are automatic, driven by routines and habits
- attitudes predict behaviour better when:
- opportunity to review past actions
- highlighted self-awareness
- attitude formed through experience
Impact of Role on Attitudes
- actions expected of those who occupy particular social positions
- our roles shape our attitudes
- impact of social situtation
Impact of Roles: Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo, 1972)
- prison simulation study with guards and prisoners
- planned two-week study but forced to stop after 6 days
- guards became too cruel and began abusing power
Foot in the Door Phenomenon
- tendency for people who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request
- low-ball technique
Door in the Face Phenomenon
- tendency for people who have declined large request to agree with smaller one
- request then moderation procedure
Three Ways Behaviours Influence Attitudes
1. Self-presentation
2. Self-justification
3. Self-perception
Self-Presentation - attitudes
- impression management
- concerned with making good impression to gain social and material rewards, to feel better about selves, to become more secure in social identities
- wanting to appear consistent
Self-Justification
- selective exposure: prefer to expose ourselves with info that agrees with pov
- cognitive dissonance: feel tension when aware that we have two thoughts that are inconsistent/incompatible
- dissonance also when behaviour inconsistent with attitude
Self-Justification: Cognitive Dissonance Process
1. choose between two equally (un)attractive alternatives
2. undesirable features of the chosen alternative and desirable features of the rejected alternative remain
3. dissonance is created
4. "manage" dissonance by upgrading the chosen alternative and downgrading rejected alternative
Self-Perception
- self-perception theory (Bem, 1972)
- suggests we make similar inferences when we observe our own behaviour
- when attitudes weak, in position of someone who observes us from outside
- come to conclusions about own actions based on behaviour and ignore our intentions/feelings
Self-Perception: Overjustification Effect
- when individuals do something they enjoy without reward or coercion, they attribute behaviour to their love of activity
- external rewards undermine intrinsic motivation by leading people to attribute their behaviour to the incentive
Three Theories of Self Overview Example: Coffee
Self-presentation
- drinking coffee cause it makes me seem put together
Self-justification
- know coffee is bad for me, but its not that bad cause keeps me awake
Self-perception
- i'm drinking coffee, i must like coffee
A Group
two or more people who, for longer than a few moments, interact with, influence, and perceive one another as "us"
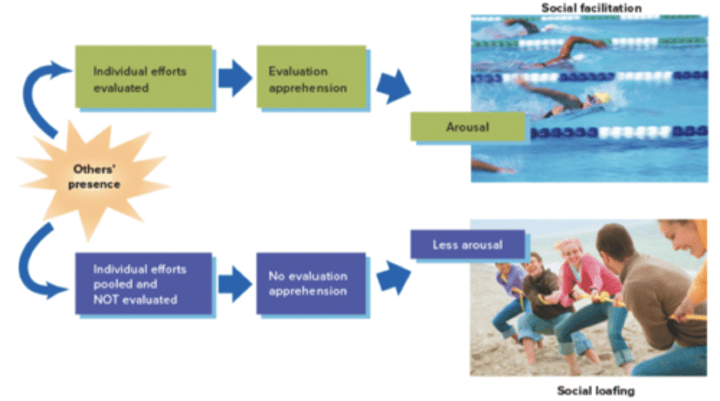
Social Facilitation Study: Triplett (1898)
- mere presence of others has an impact on our behaviour
- others may be passive or co-actors
- children winding fishing reels
- when in presence of others, wound reels faster
Social Facilitation Effect
- tendency of people to perform simple or well-learned tasks better when others are present
- strengthening of the dominant responses owing to the presence of others
Effects of Social Arousal
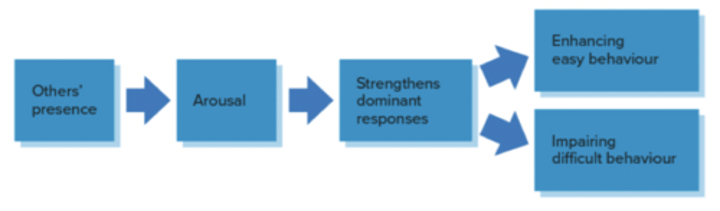
Crowding
- intensifies positive or negative reactions
- enhances arousal, large number of people
Reasons for Arousal
1. evaluation apprehension
2. driven by distraction
3. mere presence
Collective Effort Effects: Rope Pulling
- rope-pulling apparatus
- collective effort of tug-of-war teams only about half of sum of individual efforts
- people try less in groups
Social Loafing
- tendency for people to exert less effort when they pool their efforts toward a common goal than when they are individually accountable
- free riders: people who benefit from group but give little in return
less likely to occur when:
- task is challenging, appealing, or involving
- when group members are friends
Social Loafing vs Facilitation
Deindividuation
- loss of self-awareness and evaluation apprehension
- occurs in group situations that foster anonymity and draw attention away from the individual
- group experiences that diminish self-consciousness tend to disconnect behaviour from attitudes
Deindividuation Facilitators
- group size
- physical anonymity
- arousing and distracting activities
Group Polarization
group-produced enhancement of member's pre-existing tendencies
- strengthening of the members average tendencies, not a split within the group
- impact of group discussion on individual opinions: the "risky shift"
Group Polarization: Normative Influence
most persuaded by our "reference groups"
Group Polarization: Information Influence
combining of ideas which likely favour the dominant viewpoint
Groupthink
- tendency for groups (while in decision making process) to suppress dissenting cognitions in the interest of ensuring group harmony
- "mode of thinking" that individuals engage in when concurrence-seeking becomes dominant in a cohesive ingroup
- overrides realistic appraisals of alternative courses of action
Groupthink Symptoms: Overestimating the group's might and right
1. an illusion of invulnerability
2. unquestioned belief in the group's morality
Groupthink Symptoms: Group members becoming close-minded
3. rationalization
4. stereotyped view of opponent
Groupthink Symptoms: Pressure to conform and be uniform
5. conformity pressure
6. self-censorship
7. illusion of unanimity
8. mindguards
Preventing Groupthink
- be impartial
- assign a devil's advocate
- subdivide the group
- invite critiques from outside experts
- have a "second chance" meeting as opportunity to discuss lingering doubts
Group Problem Solving Methods
- combine group and solitary brainstorming
- have group members interact by writing
- incorporate electronic brainstorming
4 Types of Leadership
1. Task leadership
2. Social leadership
3. Transactional leadership
4. Transformational leadership
Task Leadership
- directive style
- goal-oriented
- motivates high achievement
Social Leadership
- democratic style
- delegate authority
- welcome input from team members
- good for morale
Transactional Leadership
- focus on getting to know subordinates
- listen carefully
- fulfill others' needs
Transformational Leadership
- consistently stick to goals
- self-confident and charismatic that makes them influential
- motivates others to identify and commit themselves to goal
Individuals Influencing Group
- influence of the minority
- consistency: minority slowness effect
- self-confidence
- defections from majority penetrate unanimity
Aggression
physical or verbal behaviour intended to hurt someone
- can be physical, social, or emotional
Hostile Aggression
- directing aggressive behaviour to person who directly wronged you
- driven by anger and performed as an end in itself
- ex: most murders, bullying
Instrumental Aggression
- aggression that is a means to some other end
- aggressive behaviour for a greater cause
- ex: most acts of war or terrorism
3 Theories of Aggression
1. aggression as a biological phenomenon
2. aggression as a response to frustration
3. aggression as learned social behaviour
Biological Theory
- aggression as instinct
- aggression as biologically adaptive
- helps us be more competitive
Biological Theory: Instinct Theory
- from Freud
- humans have some self-destructive impulses
- then expanded
Biological Theory: Neural Influences
- no center of aggression in the brain, but involves amygdala and hypothalamus
- more aggressive men have smaller amygdala
Biological Theory: Genetic Influences
- sensitivity to aggression cues: things in environment that trigger aggression
- ex: facial expressions, tone of voice, weapons
- temperament
Biological Theory: Biochemical Influences
- Alcohol
- Low serotonin
- Testosterone
- Poor diet
- Biology and behaviour interact
Frustration Theory
- frustration-aggression theory: frustration triggers a readiness to anger
- displacement: redirection of aggression to a target other than the source
Frustration Theory: Simplified Frustration-Aggression Theory
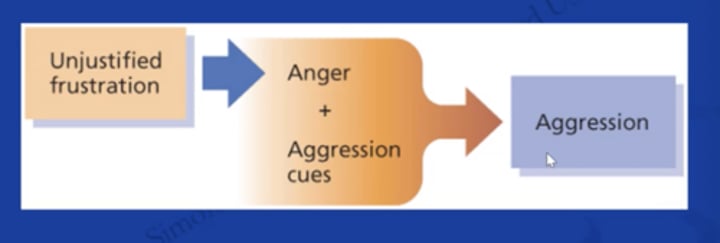
Frustration Theory: Relative Deprivation
- perception that one is less well off than others to whom one compares onself
- RELATIVE- what is perceived
Learned Behaviour Theory
- the rewards of aggression
- social learning theory
- learn social behaviour by observing and imitating, by being rewarded and punished
Learned Behaviour Theory: Observational Learning
- Bandura (1977): Bobo doll experiments
- Family: violence produces violence
- Culture: certain cultures support aggression more
Learned Behaviour Theory: Social Learning Theory
- we learn aggression from models: media, culture, family etc.
aversive experiences -> emotional arousal
rewards and costs -> anticipated consequences
arousal + consequences -> dependency, achievement, withdrawal and resignation, aggression, bodily symptoms, constructive problem solving, coping with drugs
Influences on Aggression: Aversive Incidents
pain
- rat experiments: delivering shocks, the greater the shock the more violent they got
heat
- intense heat as an environmental factor
- students felt more tired and aggressive in hot conditions
attacks
- if insulted or attacked, we are more likely to retaliate
Influences on Aggression: Arousal
- given state of bodily arousal feeds one emotion or another
- dependent on how person interprets and labels arousal
Influences on Aggression: Arousal Study (1962)
- made men physiologically aroused by injecting them with adrenaline
- some were told drug effects
- some were not told
- shown picture of either a hostile or happy person
- those informed had no reaction
- those not informed felt aggressively to hostile person and attracted to happy person