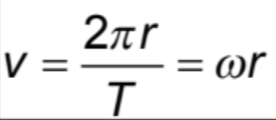A2: Forces and momentum
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Translational equilibrium
the sum of the resolved components of all the forces in any direction is equal to zero (no resultant force)
Newton’s first law
A body continues to move at uniform velocity or stays at rest unless a resultant external force acts on it.
Newton’s second law
The resultant force exerted on a body is directly proportional to the rate of change of linear momentum of the body in the direction of the force.
Newton’s third law
Forces never arise singly but always in pairs that are equal and opposite
Static Friction
acts between surfaces at rest, parallel to the surfaces, when a force is applied to make them slide past one another.
Dynamic Friction
acts between surfaces (parallel to the surfaces) as they slide over one another
Hooke’s Law
the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the load attached to it as long as the elastic limit is not reached or exceeded.
Momentum
product of mass and velocity
Law of conservation of momentum:
if the total external force acting on a system is zero the momentum of the system is constant OR In any collision, the momentum before collision must equal the momentum after the collision, provided no external force acts.
Elastic Collision
An interaction in which total energy and kinetic energy is conserved
Time Period (T)
time taken to complete one circle, measured in seconds.
Centripetal force
causes an object to move in a circle, always acts at a right angle to the motion of an object.
Impulse
change of momentum/product of force and time taken
Frequency (f)
the number of revolutions completed per unit time, Hz. f = 1/T.
Angular displacement (θ)
the angle swept out by a line joining the body to the centre, radians.
Angular velocity (ω)
the angle swept out by a line joining the body to the centre per unit time, rad s^−1
Frictional Force (with coefficient of static friction)
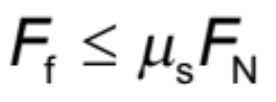
Frictional Force (with coefficient of dynamic friction)
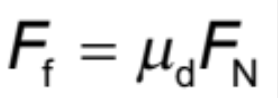
elastic force from helical spring (Hooke’s Law)
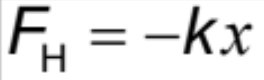
Drag force (resistive force from fluids)
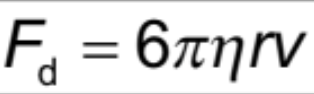
Buoyant force (upthrust)
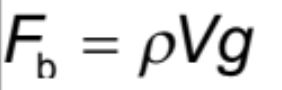
Gravitational Force (weight close to Earth’s surface)
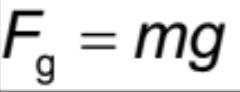
Momentum
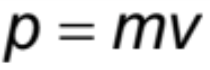
Impulse
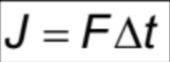
Resultant/Net Force
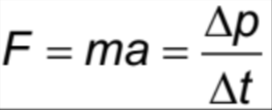
Centripetal Acceleration
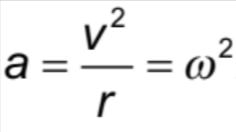
Radius
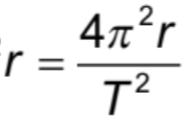
Linear Velocity