Lecture 4: Shortcomings of Our Measures & Measuring Inflation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
How important is GDP? What is it missing (according to the article) ?
inequality
happiness (inability to measure non- material well being.)
environment
unpaid work
Does not account for income distribution (In GDP per capita it is assumed that everyone has an even cut of resources but in reality this is not the case- Bill Gates.)
Solutions to GDP’s flaws
1) Gini Coefficient- applied to deflate GDP based on innequality.
2) Circular economy- Reuse/ recycle (overfishing created GDP, destroying forests creates GDP)
3) Measuring Happiness
The World Happiness Report
The Happy Planet Index
From GDP to…? Circular economy
Circular economy: An economic system that is based on the reuse and repair of materials to extend the life cycle of products for as long as possible.
Why is this better: It prioritizes value-retention. This means "old" production—like a high-quality engine—is treated as an asset. Instead of smelting it down to make a new one, companies use remanufacturing or refurbishment to bring it back to "as-new" condition for 80-90% less energy and material cost.
From GDP to…? World Happiness Report (WHR)
Survey of global happiness- ranks 143 countries based on how happy citizens appear to be.
“Cantril ladder question” that invites survey participants to imagine their current position on a ladder with steps numbered from 0 to 10, where the top represents the best possible and the bottom the worst possible life for themselves.
The worlds happiest nations are Finland, Sweden, and Denmark.
US 24th from top
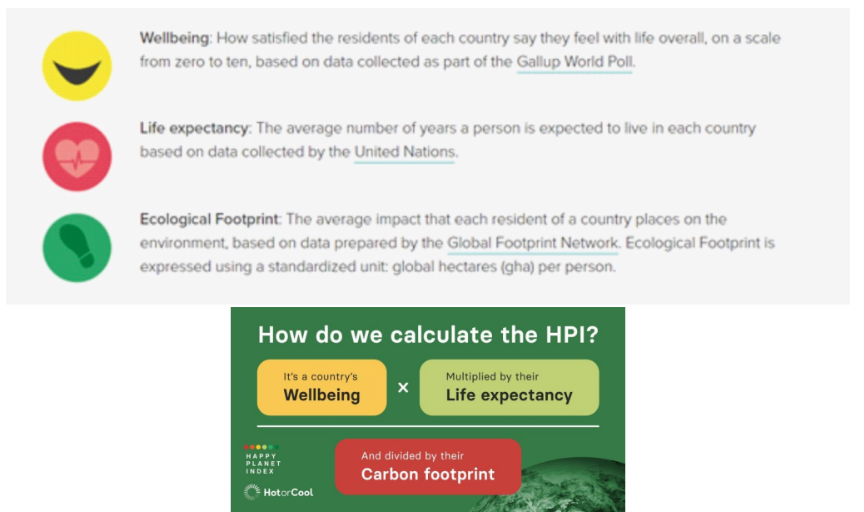
From GDP to…? The Happy Planet Index
Vanuato #1
US # 102
Why do we use GDP and not happiness?
product of things outside the Bureau of Economic Analysis’s purview.
it is subjective
The Producer Price Index (PPI)
average price level of all goods & services purchased by producers (firms).
Formula for PPI
cost of producer basketcurrent year/ cost of producer basketbase year
Why is the PPI Useful?
a limitation of CPI is that is examines price levels faced by a representative consumer (remember when a person buys something its consumption, but when a firm buys something it is investment)
PPi computes the relative price of raw materials and other inputs for firms.
PPI helps predict changes in the CPI and GDP deflator. Increase in the price of raw materials would imply that producers have to incorporate the higher prices in the goof that they produce thus raising CPI and GDP deflator.
Issue with using CPI and PPI
1) CPI/PPI fixes quantities base year “fixed basket of goods” (inaccurate compared to GDP deflator): There is no effect on Qd when price rises (no substitution towards cheaper goods). This leads to overestimating inflation because substitution is not considered.
2) Price Exclusions: Prices of government purchases & producers purchases are in PGDP not in PCPI.
Issues with using GDP deflator
1) CPI/PPI includes imports but GDP does not (accurate compared to GDP deflator): GDP deflator may exaggerate decreases in purchasing power because the cost of imports may be getting lower, and imports are a major component of American consumption, so even if the price of domestically produced goods is rising, it could be offset by goods purchased abroad (this is because imports are not counted in GDP.)
2) Prices of used goods are in CPI and PPI (but not GDP deflator). Common “used” prices faced by consumers are cars and trucks.
Problems with GDP Deflator, CPI, & PPI
1) Changes in Quality:
CPI and GDP deflator do not account for how changes in quality imporce purchasing power
EX: computers have been around the price range of 2500 for a while, yet the quality of their computing technology has rapidly improved. This causes both measures to overestimate inflation. Consumer could be getting twice as much computing power at same price level.
2) New Goods:
Old goods remain in the CPI until it is updated again. People could be buying cheaper new good bur expensive old good remains in the basket. Same issue with RGDP.
problem solved with chain weighted GDP.
Define Inflation Rate
percent change in the price index (typically CPI or GDP deflator) from the preceding period.
Inflation Formula
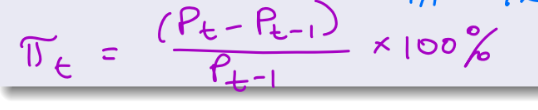
“inflation”
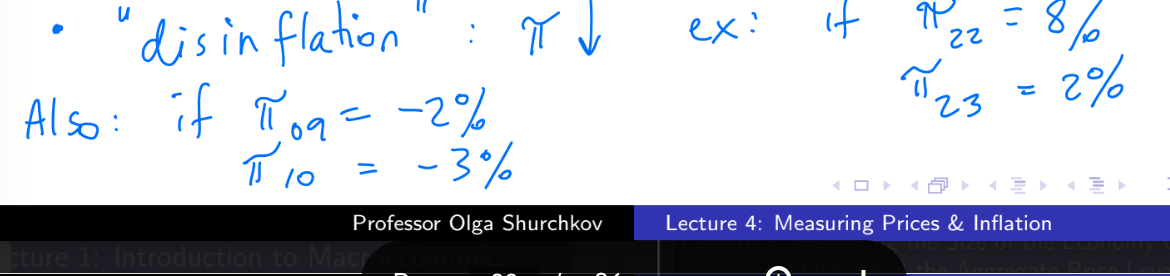
positive rate of inflation πt > 0
“deflation”
πt < 0
Note: if πt = 0, P are constant
“disinflation”
inflation itself decreases
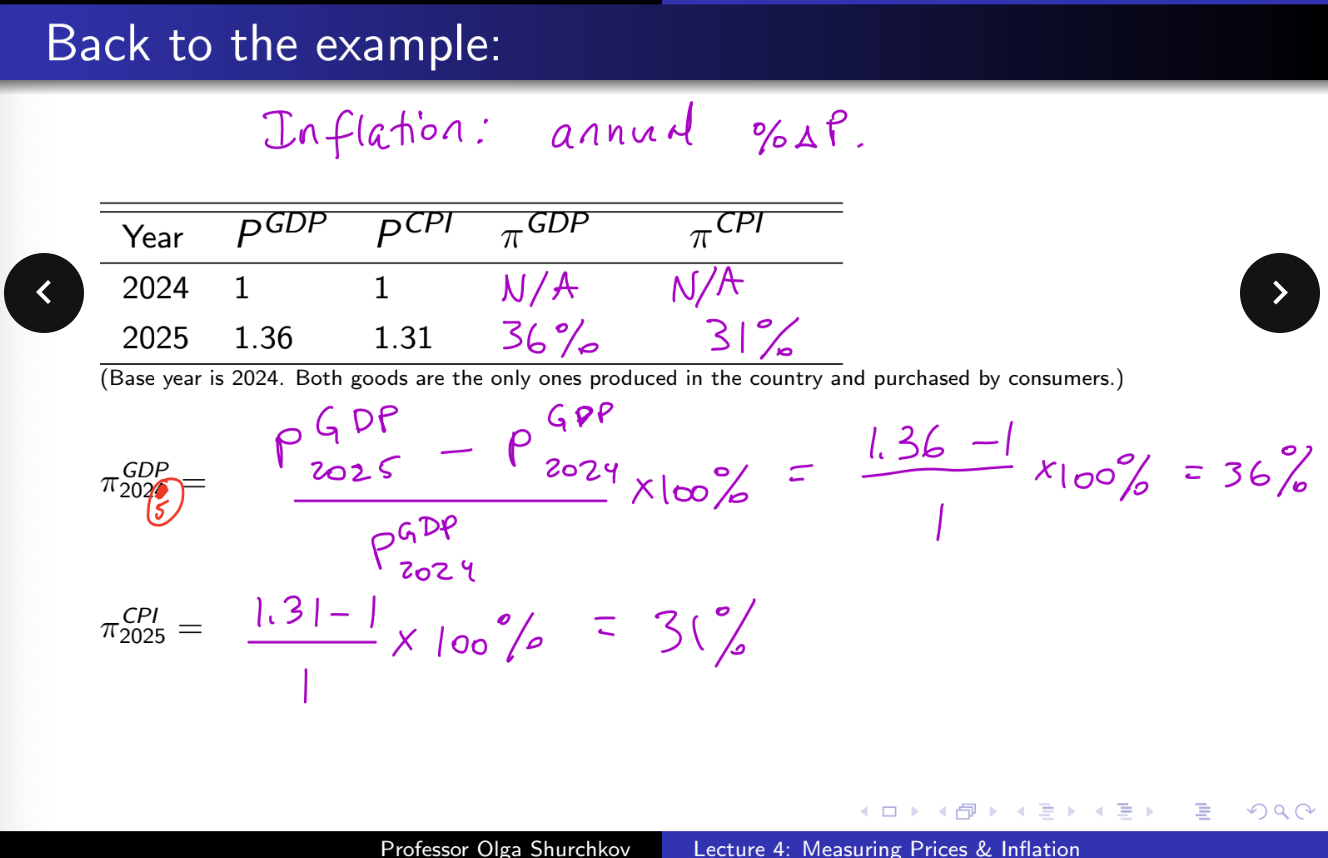
inflation problem practice 1
inflation practice 2

inflation practice 3

How do you know if a given inflation rate is high or low?
it is all relative- each country has a benchmark of normal inflation- in the United states it is 2%.
In 2025 inflation was at 2.5%
World inflation has been decreasing (disinflation)
trends in inflation over time
inflation increased between 1960-80.
inflation declined 1980 onward.
Why might inflation have spiked up around the 1970s?
The Oil Shocks.
recessions relation to inflation rates
spikes in inflation precede recessions
Drops in inflation appear during and after recessions.
recessions usually cause inflation to drop because people spend less, which lowers demand and cools off prices