PHRM 82500: Estrogens & Tamoxifene Actions | Lecture 12-13
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
what are the characteristics of estrogens?
- development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues (ovaries, uterus, breast, vagina)
- regulation in CNS (temperature, mood)
- effects in peripheral tissues (bone, cardiovascular, liver)
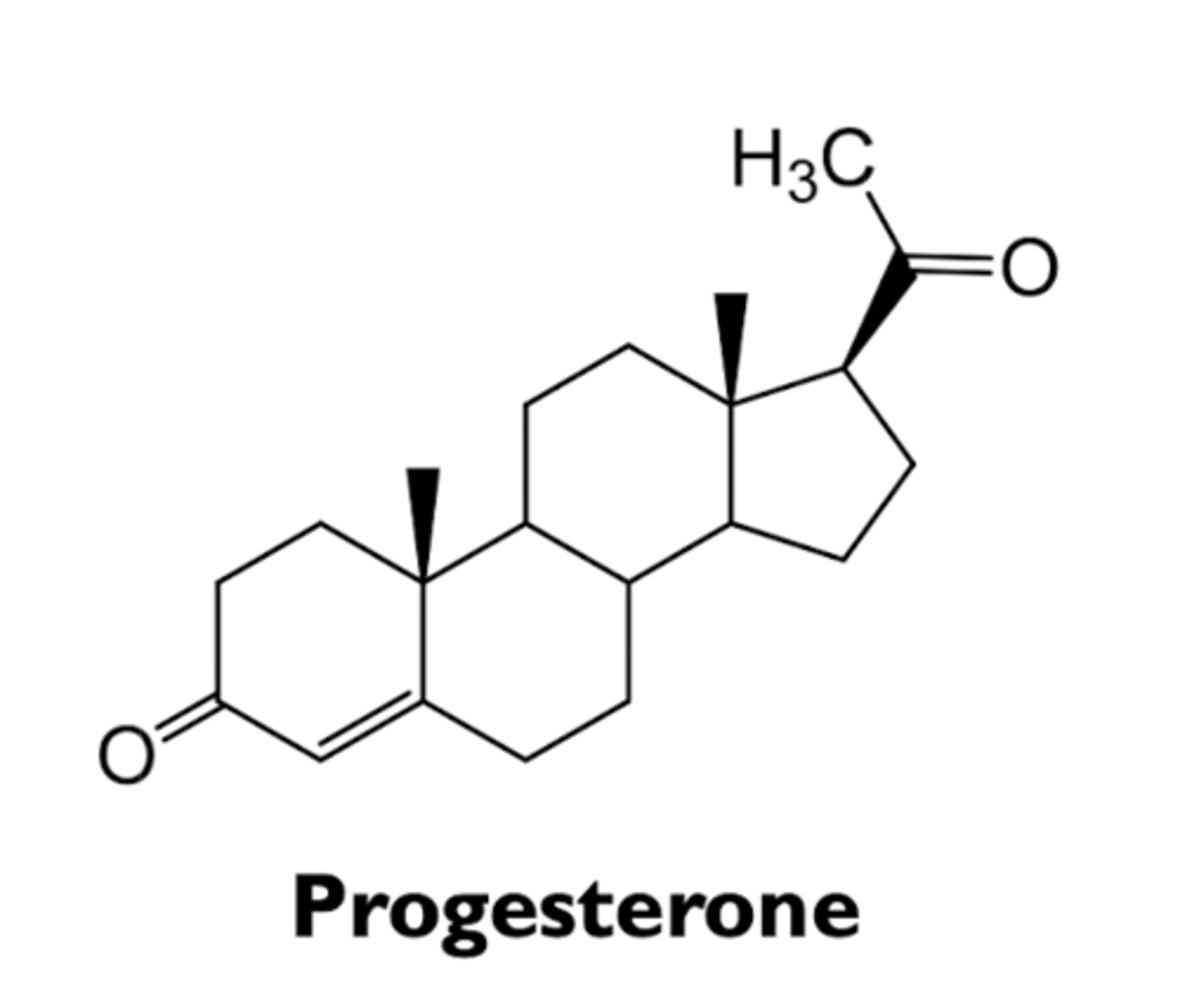
what are the characteristics of progesterone?
- development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues (uterus and breast)
- maintenance of pregnancy
- effects in other tissues (brain)
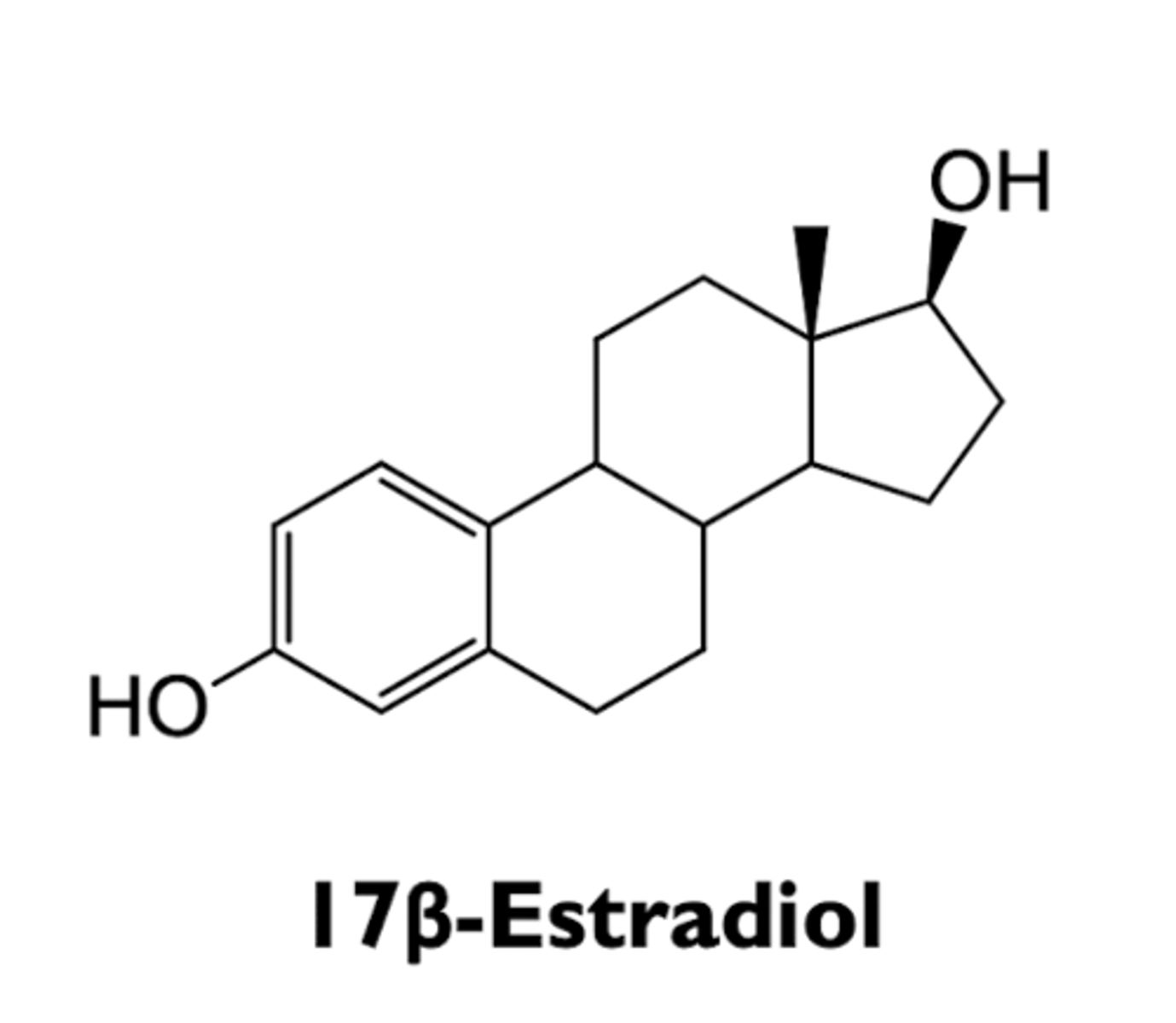
what is 17B-estradiol?
most potent estrogen in human
where does 17B-estradiol bind?
estrogen receptor and alters rate of transcription
where is 17B-estradiol produced?
mostly in ovaries in premenopausal women
- synthesized most in placenta during pregnancy
what are the plasma levels of 17B-estradiol?
5-85ng/dL
- cyclically varies during the menstrual cycle
what is 17B-estradiol mostly bound to?
sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin and only 2% free in circulation
how is the synthesis of estrogen regulated?
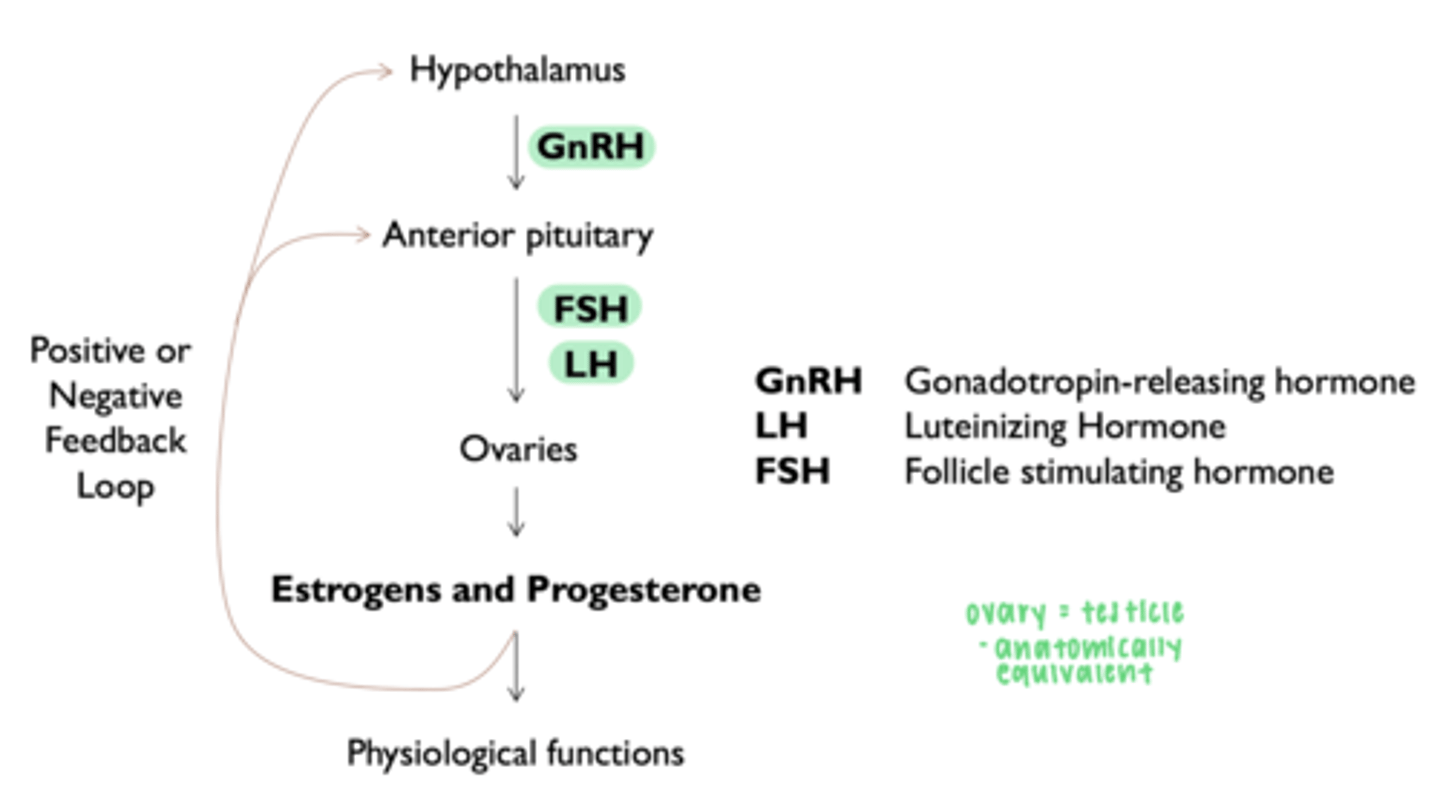
__________ produces estrogen
granulosa cells
__________ produces both estrogen and progesterone
corpus luteum
what are the phases of the menstrual cycle?
- early follicular phase
- late follicular phase
- luteal phase
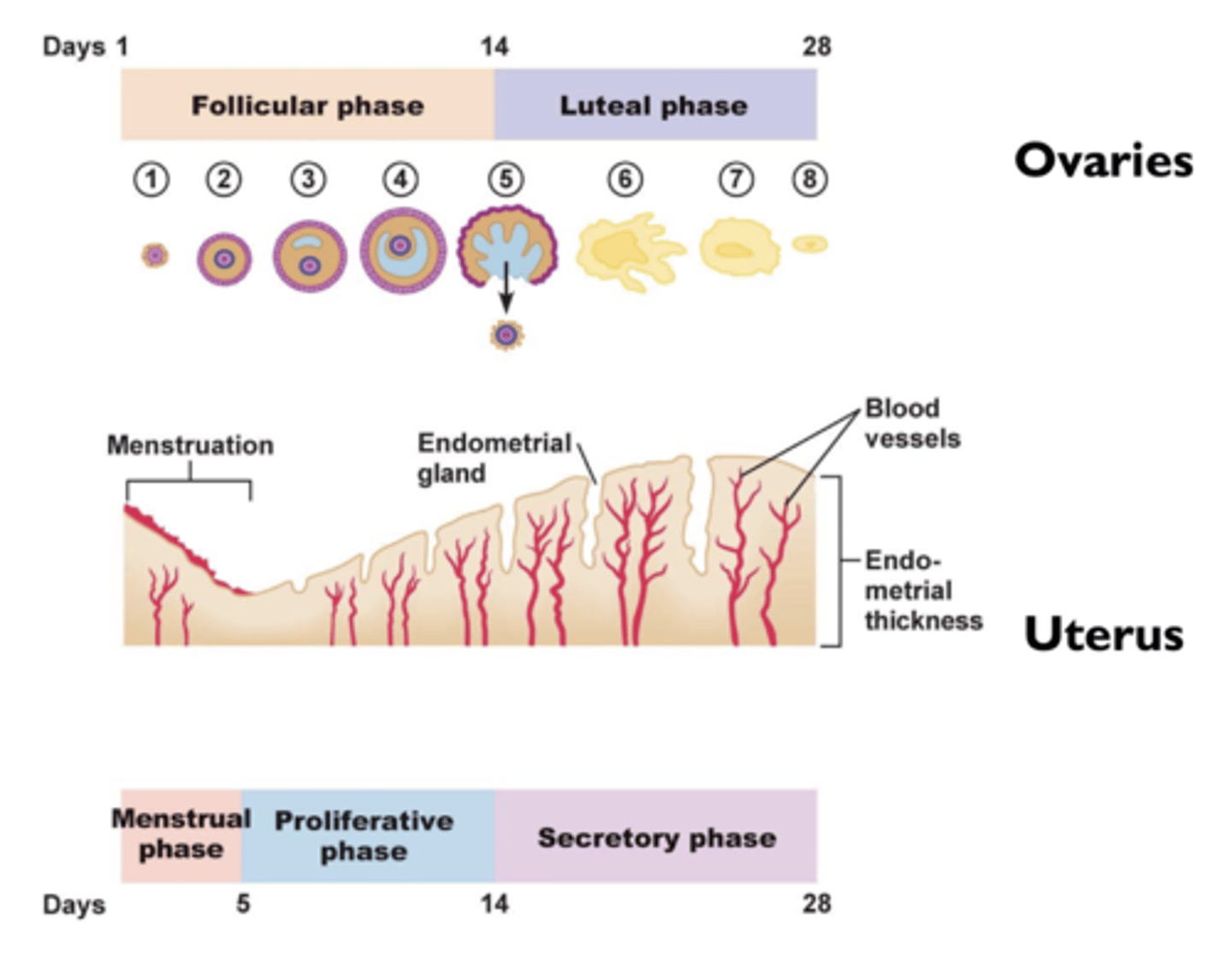
what is the early follicular phase?
estrogen suppresses production of FSH
what is the late follicular phase?
estrogen stimulates surge of LH and FSH
- ovulation and formation of corpus luteum
what is the luteal phase?
estrogen and progesterone suppresses production of LH and FSH
how does the menstrual cycle affect plasma levels?
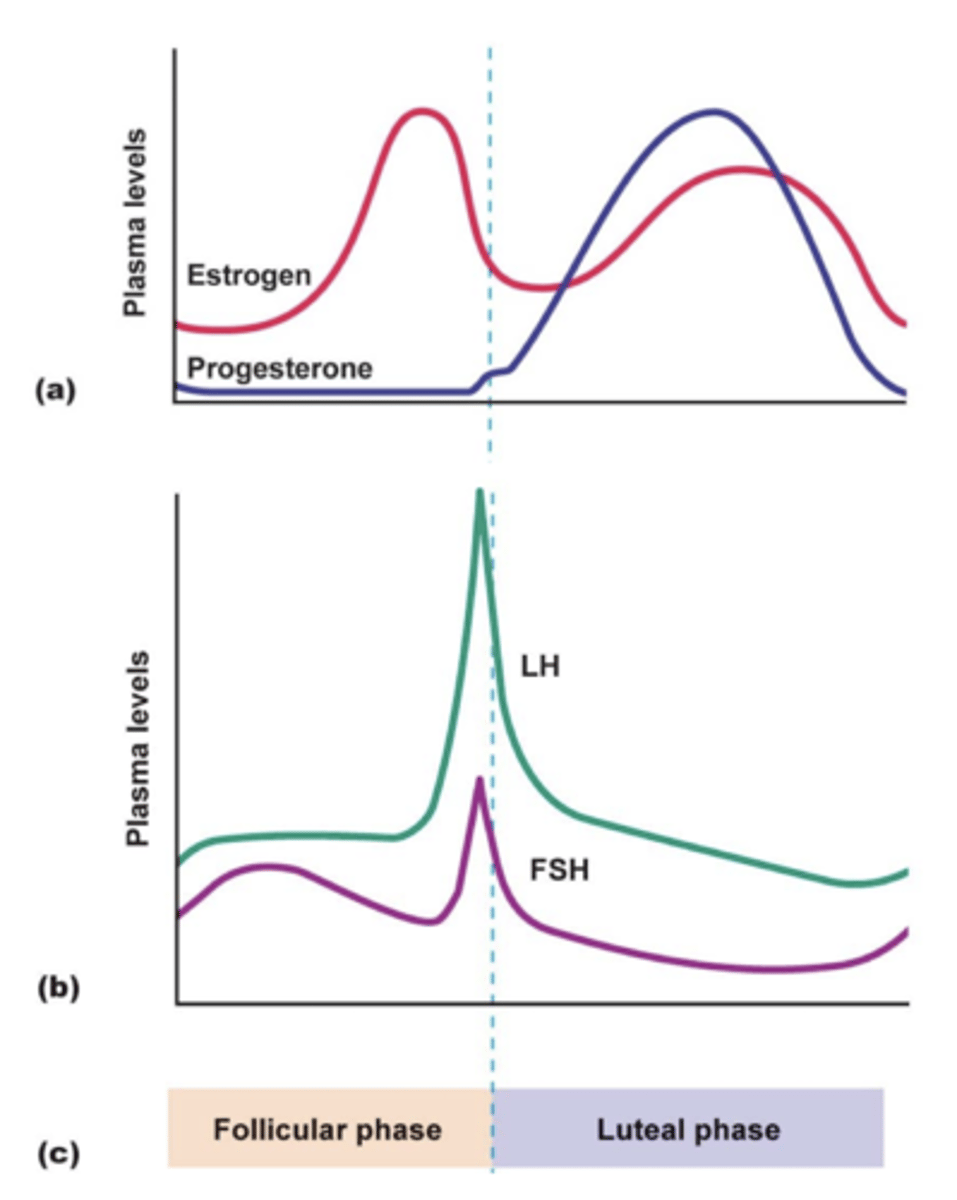
what is the effect of the menstrual cycle if pregnancy does not occur?
- corpus luteum degenerates
- production of estrogen and progesterone by corpus luteum declines (menstruation)
what is the effect of the menstrual cycle if pregnancy does occur?
- fertilized egg/embryo secretes human chorionic gonadotropic (hCG)
- hCG acts like LH to stimulate corpus luteum to produce progesterone during the first trimester
- higher progesterone levels support maintenance of endometrium
- chromatopraphic immunoassays of hCG in urine are used as pregnancy tests
what are the types of estrogens?
estrogenic activity is shared by a large number of chemical substances
- natural estrogens
- synthetic estrogens
- phytoestrogens
- environmental estrogens
what are natural estrogens?
- 17B-estradiol (most potent)
- estrone (less potent)
- estriol (less potent)
what is the most dominant form of natural estrogens during pregnancy?
estriol
- synthesized in placenta
what are synthetic estrogens?
drugs with estrogenic activities
(steroidal and non-steroidal)
what are phytoestrogens?
estrogen-mimetic compounds in plants
- flavonoids
what are environmental estrogens?
compounds used in the manufacture of plastics
- bisphenols, alkylphenols, phthalate phenols
where is estrogen metabolized?
liver
where is estrogen excreted?
bile and urine
what is the metabolism and excretion of estrogen?
- conjugated estrogens in bile can be hydrolyzed in intestine and reabsorbed (enterohepatic circulation)
- orally administered estrogens have a high ratio of hepatic to peripheral effects; can be avoided by using routes that avoid first-pass liver exposure
what are the physiologic effects of estrogen on female maturation?
- development of vagina, uterus, and uterine tubes
- stromal development and ductal growth in breast
- accelerated growth phase and epiphyseal closure
- growth of axillary and pubic hair
- alteration in distribution of body fat to produce female body contours
- pigmentation in the skin (nipples, areolae, genital region)
what are the physiologic effects of estrogen on endometrial effects?
- development of endometrial lining during menstrual cycles
- prolonged exposure leads to hyperplasia of endometrium and abnormal bleeding
what are the physiologic effects of estrogen on metabolic and cardiovascular effects?
- decrease in rate of resorption of bone
- stimulation of synthesis of transcortin and SHBG
- alteration in composition of plasma lipids
how does the decrease in rate of resorption of bone affect physiologic effects of estrogen?
estrogen deficiency can lead to osteoporosis
how does estrogen alter composition of plasma lipids?
- increase in HDL
- decrease in LDL
what are the physiologic effects of estrogen on blood coagulation?
enhancement of coagulability of blood
what are the physiologic effects of estrogen on CNS?
mood
what are the clinical uses of estrogens?
- hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women
- osteoporosis
- hormonal contraception
how do estrogens contribute to hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women?
- relief of CNS disturbances (hot flashes, sweating flushing)
- relief of symptoms resulting from urogenital atrophy (vaginal dryness, increased risk of infections)
- relief of psychological effects (mood swings, insomnia, depression, nervousness)
- replacement therapy in patients with primary hypogonadism
how do estrogens contribute to osteoporosis?
- for post-menopausal osteoporosis only
- estrogens decrease rate of bond resorption
how do estrogens contribute to replacement therapy in patients with primary hypogonadism?
- failure of development of ovaries
- chromosomal disorders (turner syndrome)
- castration (oophorectomy)
what are the adverse effects of estrogen?
- uterine bleeding
- endometrial carcinoma
- breast cancer
- nausea, headache, fluid retention, weight gain
how do estrogens contribute to uterine bleeding?
- estrogen therapy is a major cause of post-menopausal uterine bleeding
- endometrial hyperplasia
- estrogen should be given cyclically
- can be prevented by administration of a progestin in each cycle
how do estrogens contribute to endometrial carcinoma?
concomitant use of a progestin reduces the risk
how do estrogens contribute to breast cancer?
- particularly for long-term use
- addition of a progestin does not have a protective effect
what is the structure-activity relationship of estrogen?
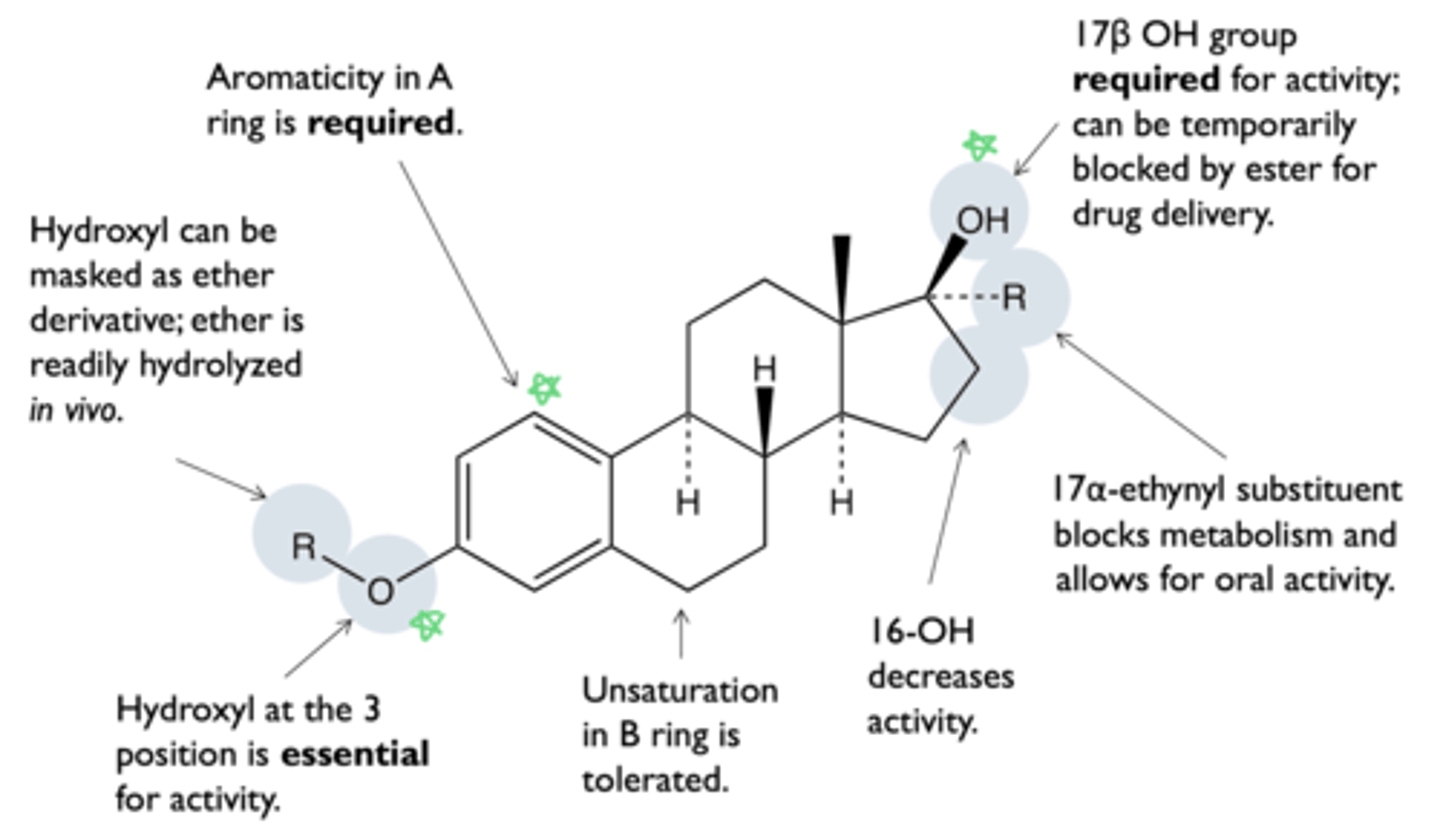
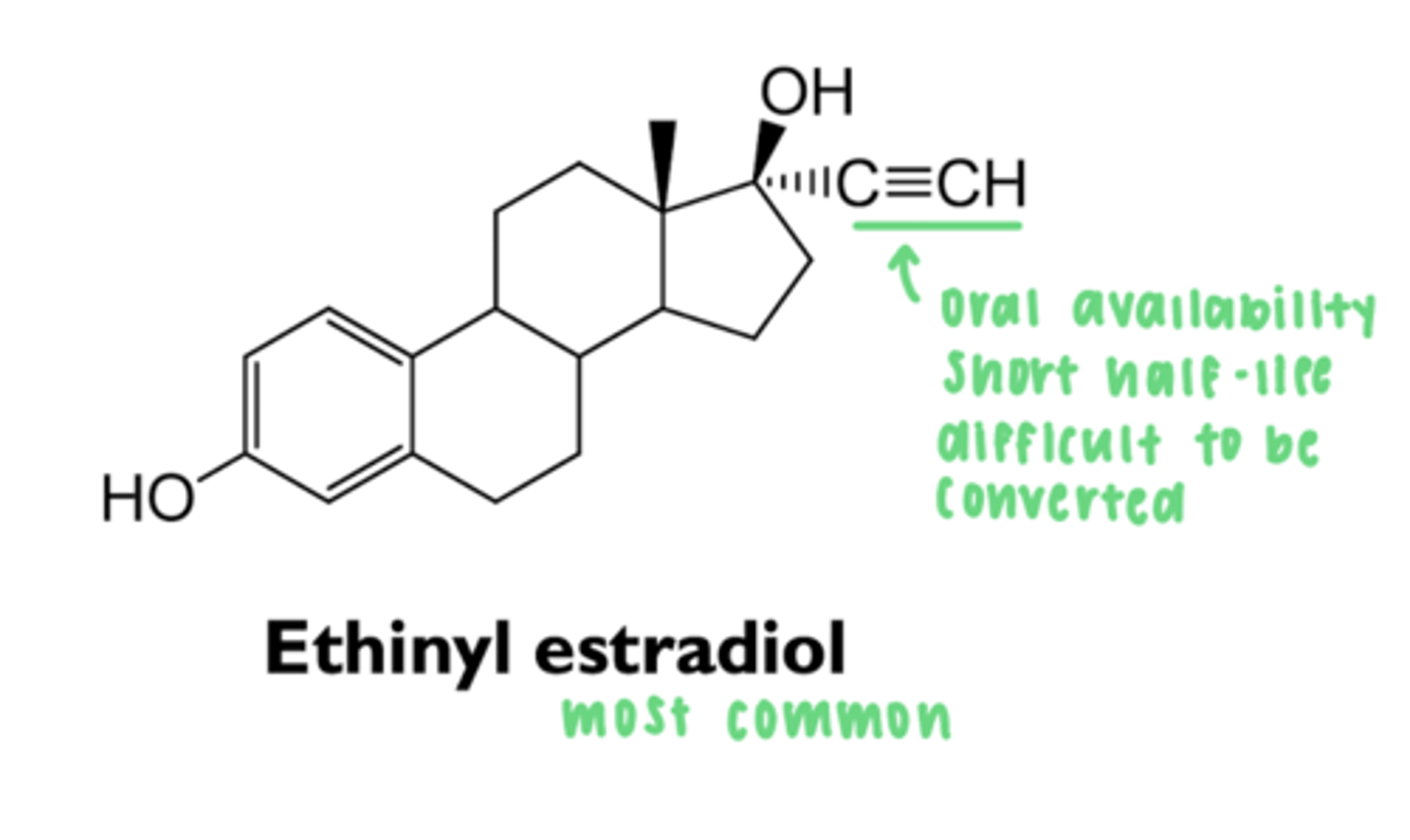
what are types of 17a-alkylated estrogens?
- ethinyl estradiol
- mestranol
- quinestrol
what is the effect of 17a-alkylation on estrogen?
prevents conversion to estrone
- enhances oral bioavailability and increases half life
- 3-alkylated ether is quickly dealkylated in vivo
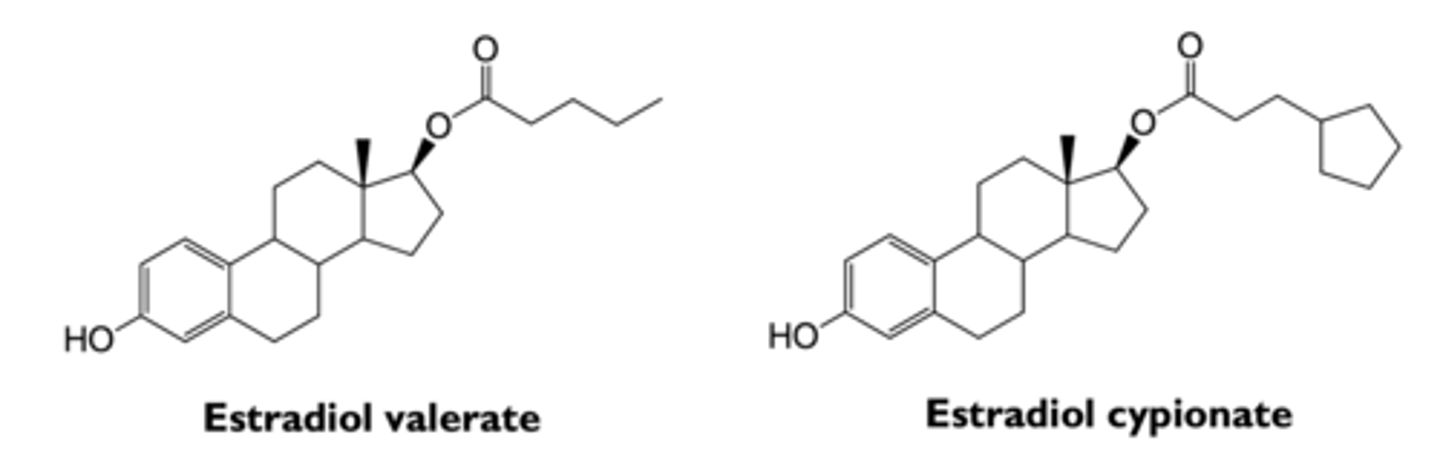
what are types of estrogenic esters?
- estradiol valerate
- estradiol cypionate
what is the effect of esterification on estrogen?
decreases solubility and slows absorption
- prolongs action
- less frequent injections
where are conjugated estrogens derived from?
usually collected from pregnant mares' urine
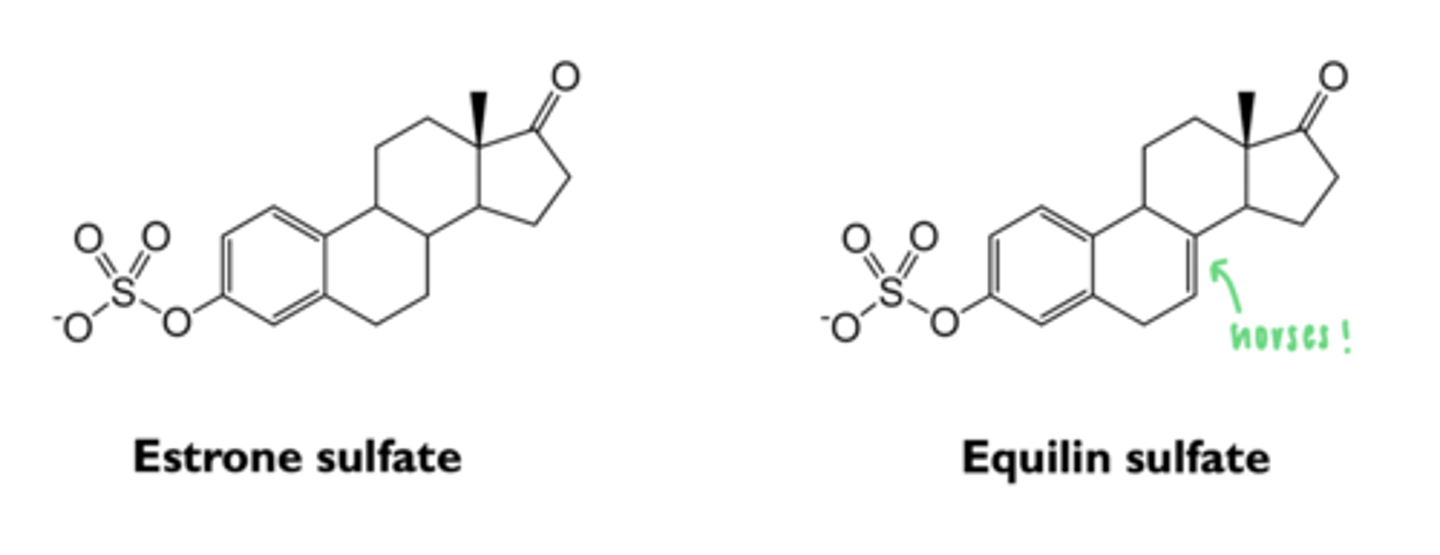
what are the types of conjugated esters?
- 50-60% estrone sulfate
- 20-30% equilin sulfate
- other estrogenic substances
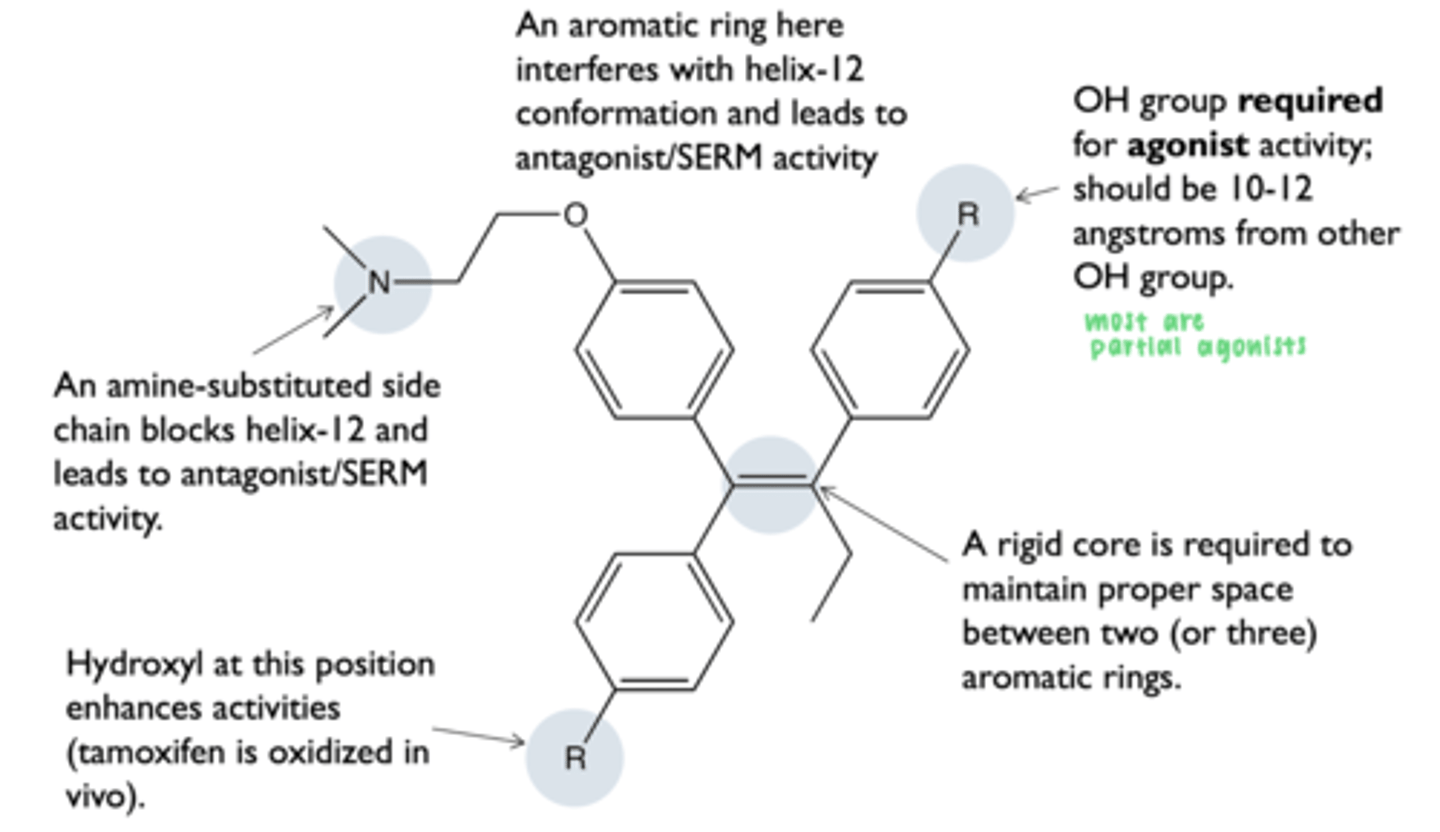
what is the structure-activity relationship in non-steroidal estrogens?
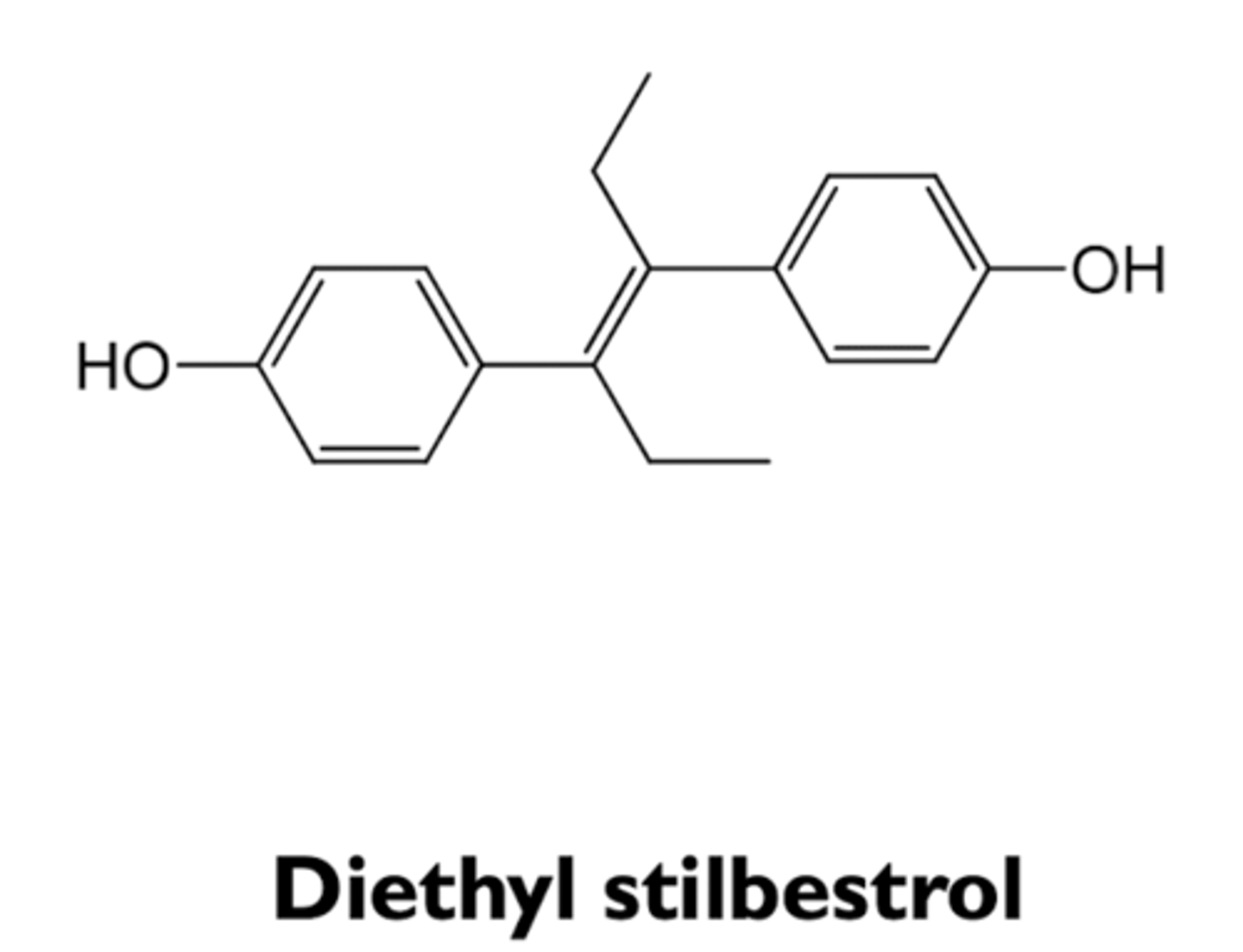
what are the types of non-steroidal estrogens?
- diethylstilbestrol
- chlorotrianisene
what are the characteristics of diethylstilbestrol?
- used in 1940-1970 to prevent miscarriage
- increased risk of vaginal adenocarcinoma in women exposed in utero
- used in advanced prostate cancer
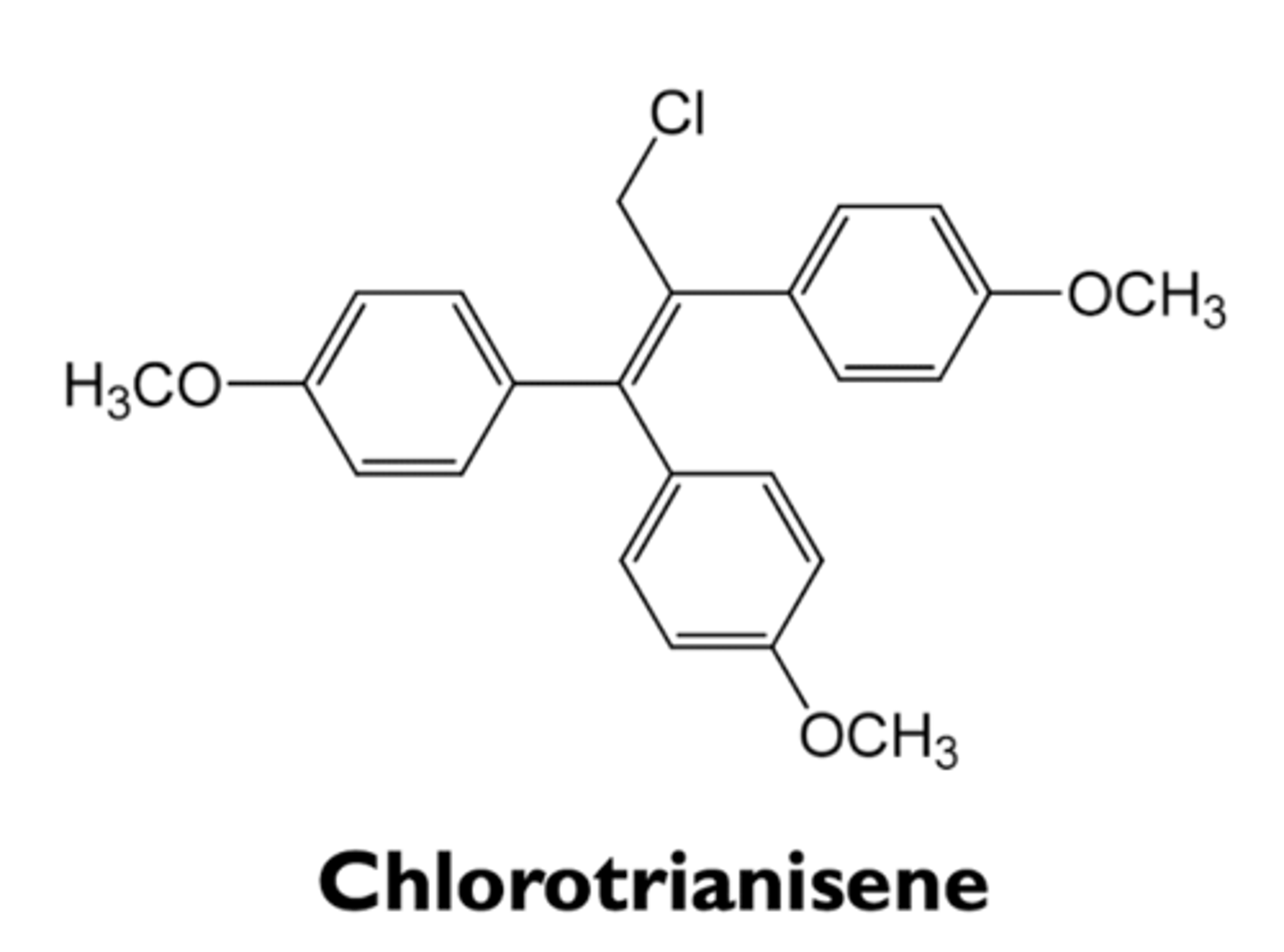
what are the characteristics of chlorotrianisene?
- postpartum breast enlargement
- menopause symptoms
- prostate cancer
what are the characteristics of selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERM)?
- "designer estrogens"
- partial estrogen agonists
- estrogenic in some tissues and antiestrogenic in others
- mostly non-steroidal estrogens
- hold promise as the alternative for estrogen replacement therapy
how does SERMs act as partial estrogen agonists?
block action of stronger estrogens
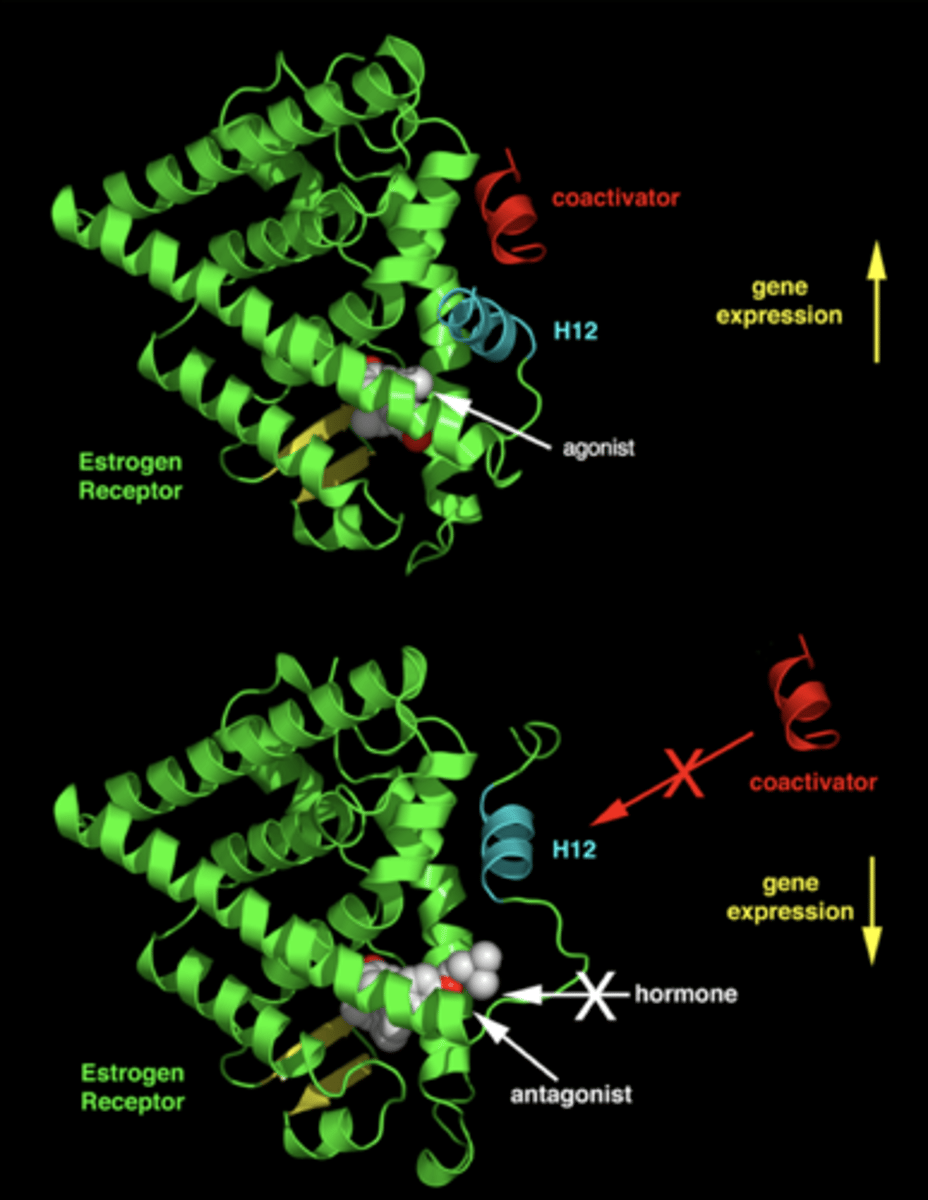
what is the structural basis of SERM activity?
ligand binding domain with an agonist (diethyl stilbestrol) bound
- helix 12 conformation allows for coactivator binding
ligand binding with a SERM bound
- helix 12 conformation blocks coactivator binding
what are the types of SERMs?
- tamoxifen
- toremifene
- ospemifene
- raloxifene
- bazedoxifene
- clomiphene
what are the characteristics of tamoxifen?
- prodrug (oxidized in vivo)
- partial estrogen agonist
- antiestrogen actions
- estrogenic actions
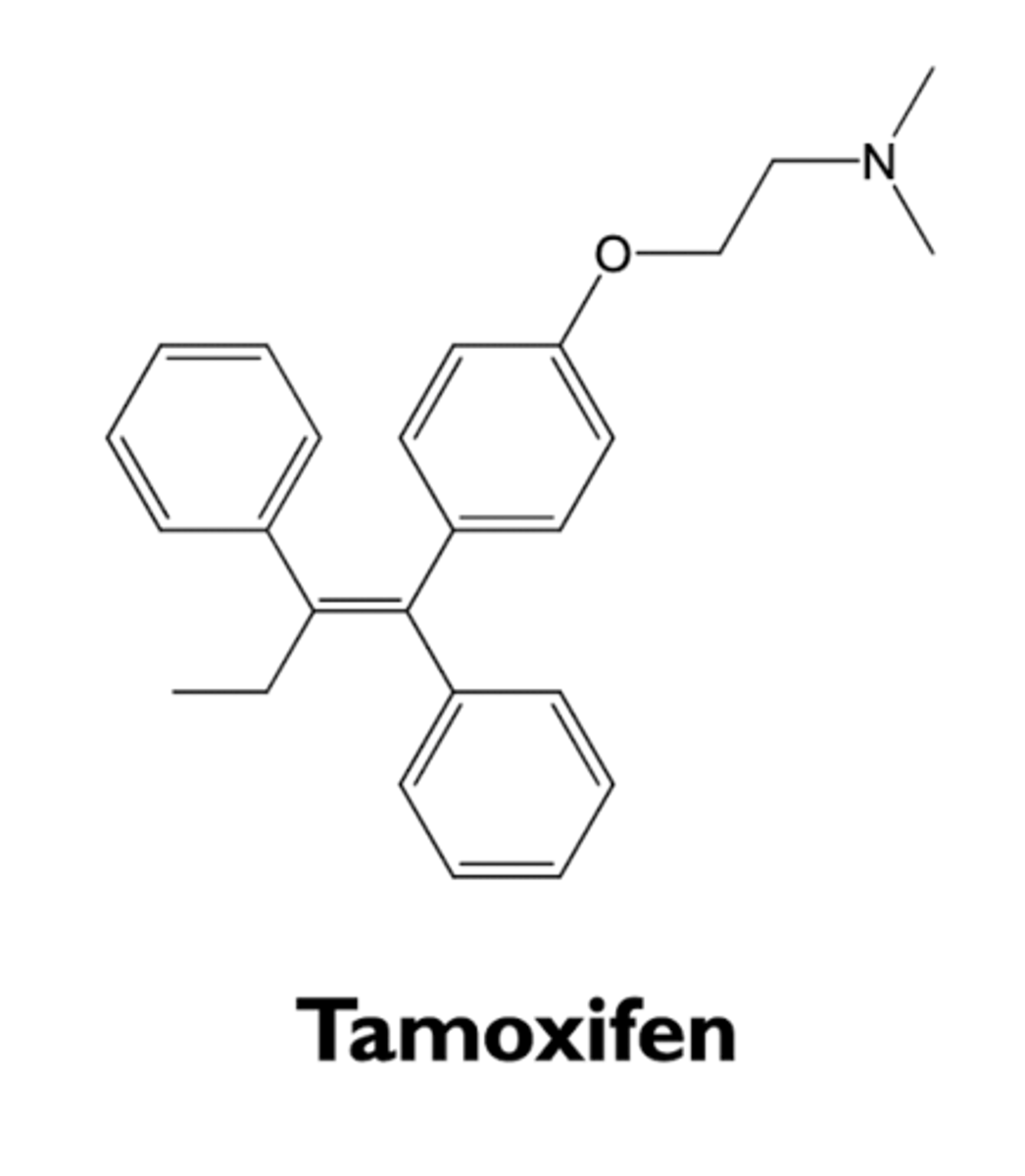
what are the antiestrogenic actions of tamoxifene?
- treatment of breast cancer
- prevents breast cancer in high risk women
what are the estrogenic actions of tamoxifene?
- weak estrogen agonist at endometrial actions
- increases risk for thromboembolic events
- prevents osteoporosis
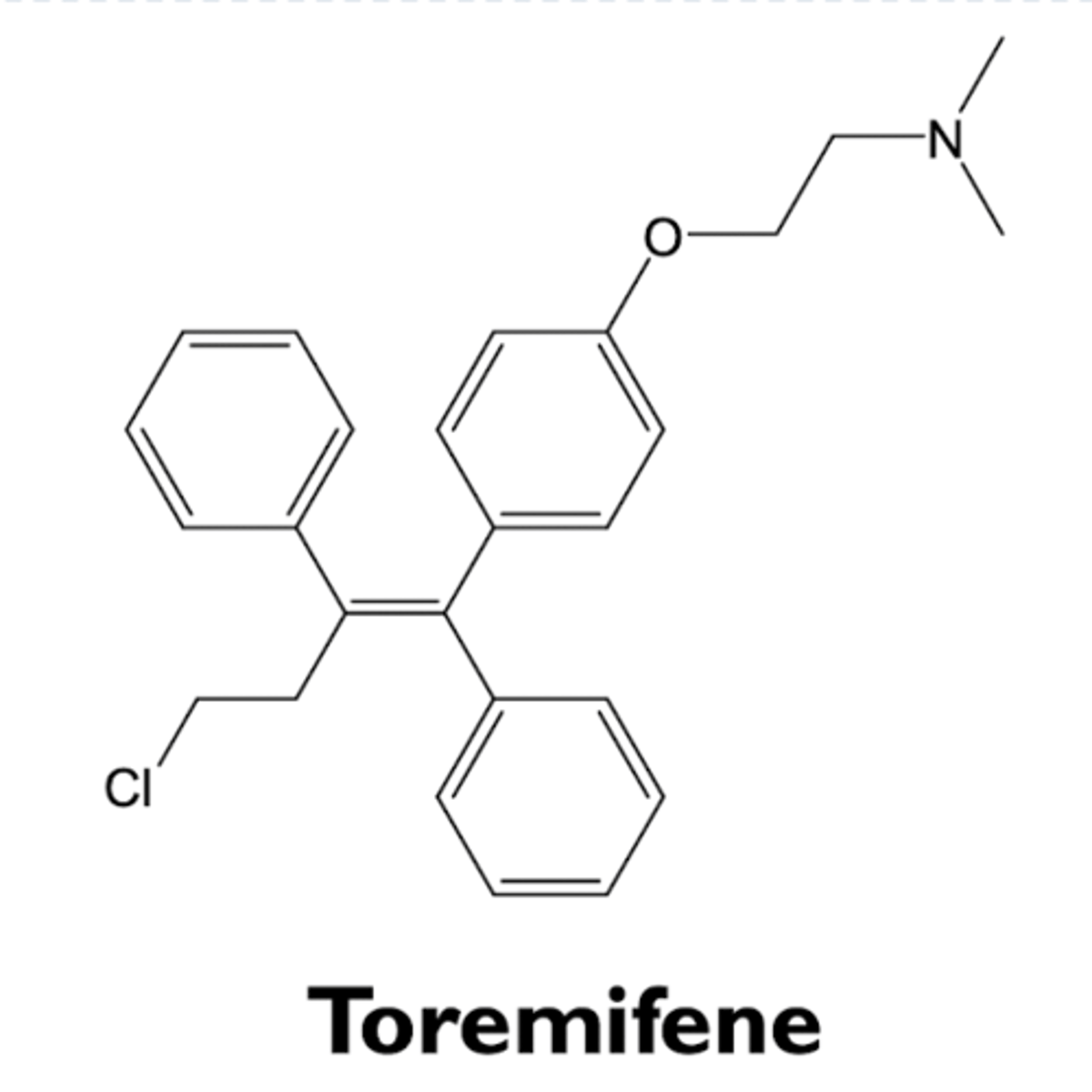
what are the characteristics of toremifene?
- structurally similar to tamoxifen
- SERM
- used to treat advanced breast cancer
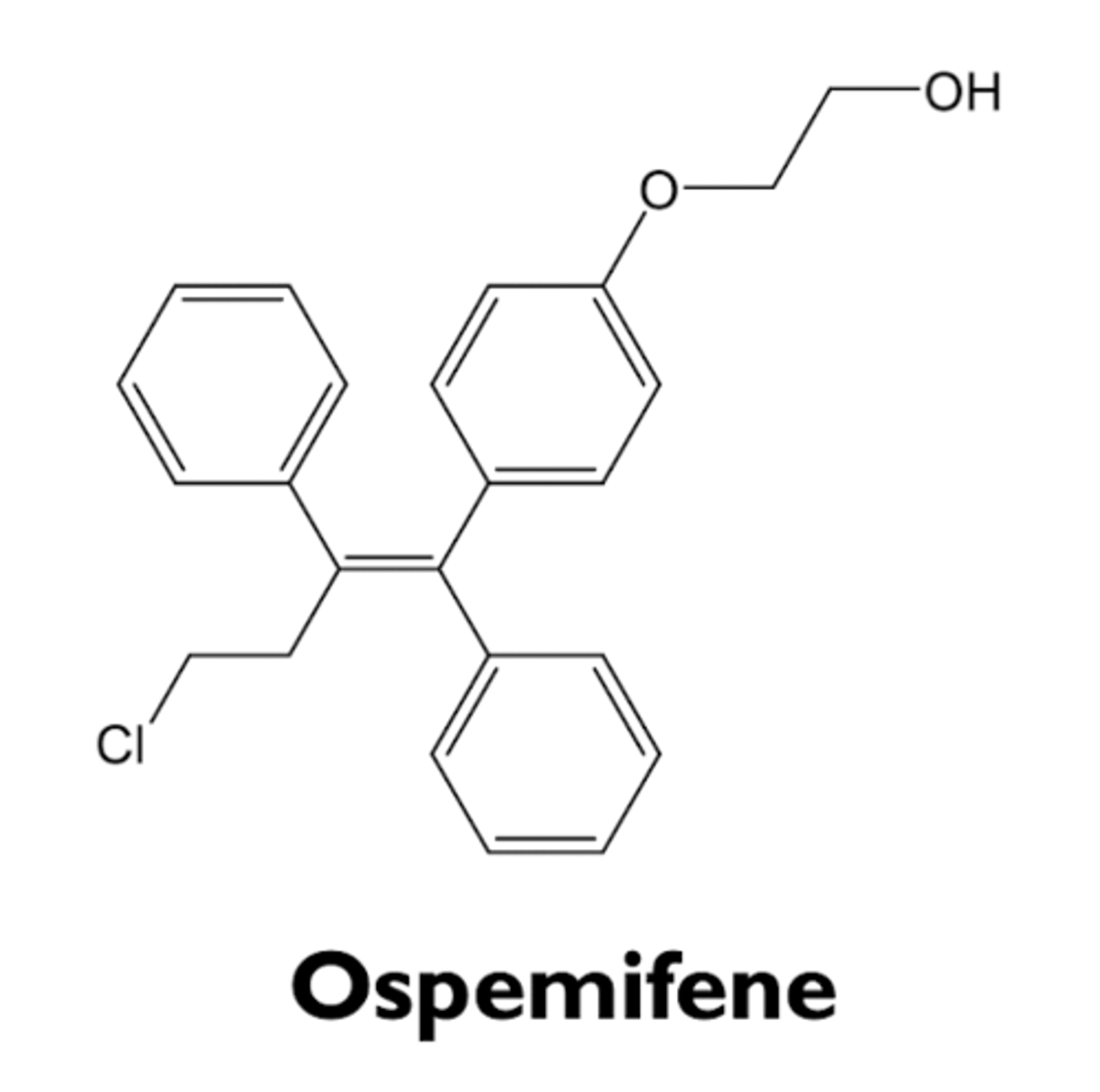
what are the characteristics of ospemifene?
- structurally similar to toremifene
- SERM
- estrogenic effects on vaginal epithelium
- used to treat dyspareunia in post-menopausal women
what are the characteristics of raloxifene?
- SERM; partial estrogen agonist
- tissue-specific activities
- estrogen actions
- antiestrogen actions
- bazedoxifene is a recently approved analog with similar activities
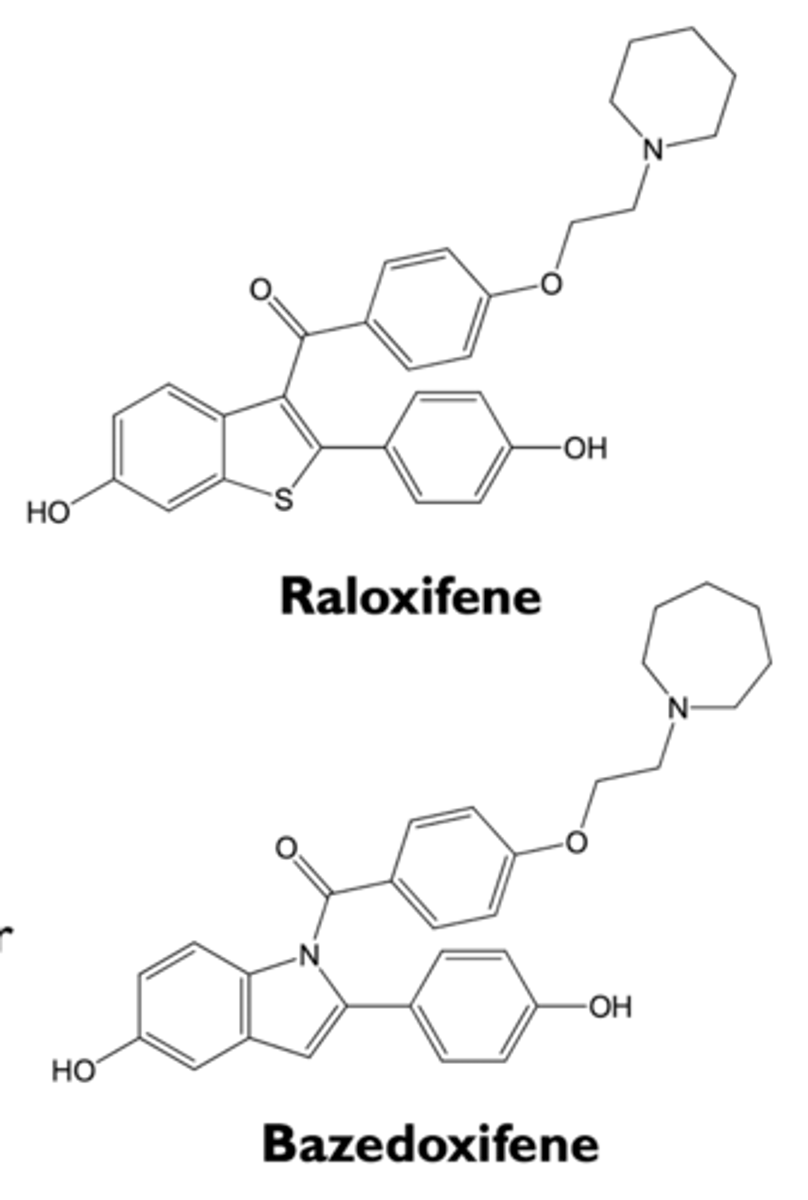
what are the estrogenic effects of raloxifene?
- prevents osteoporosis in postmenopausal women (approved)
- decreases LDL levels in blood
- increases risk for blood clots
what are the antiestrogenic actions of raloxifene?
- decreases risk for breast cancer (approved)
- does not stimulate endometrial cells
- may cause hot flashes
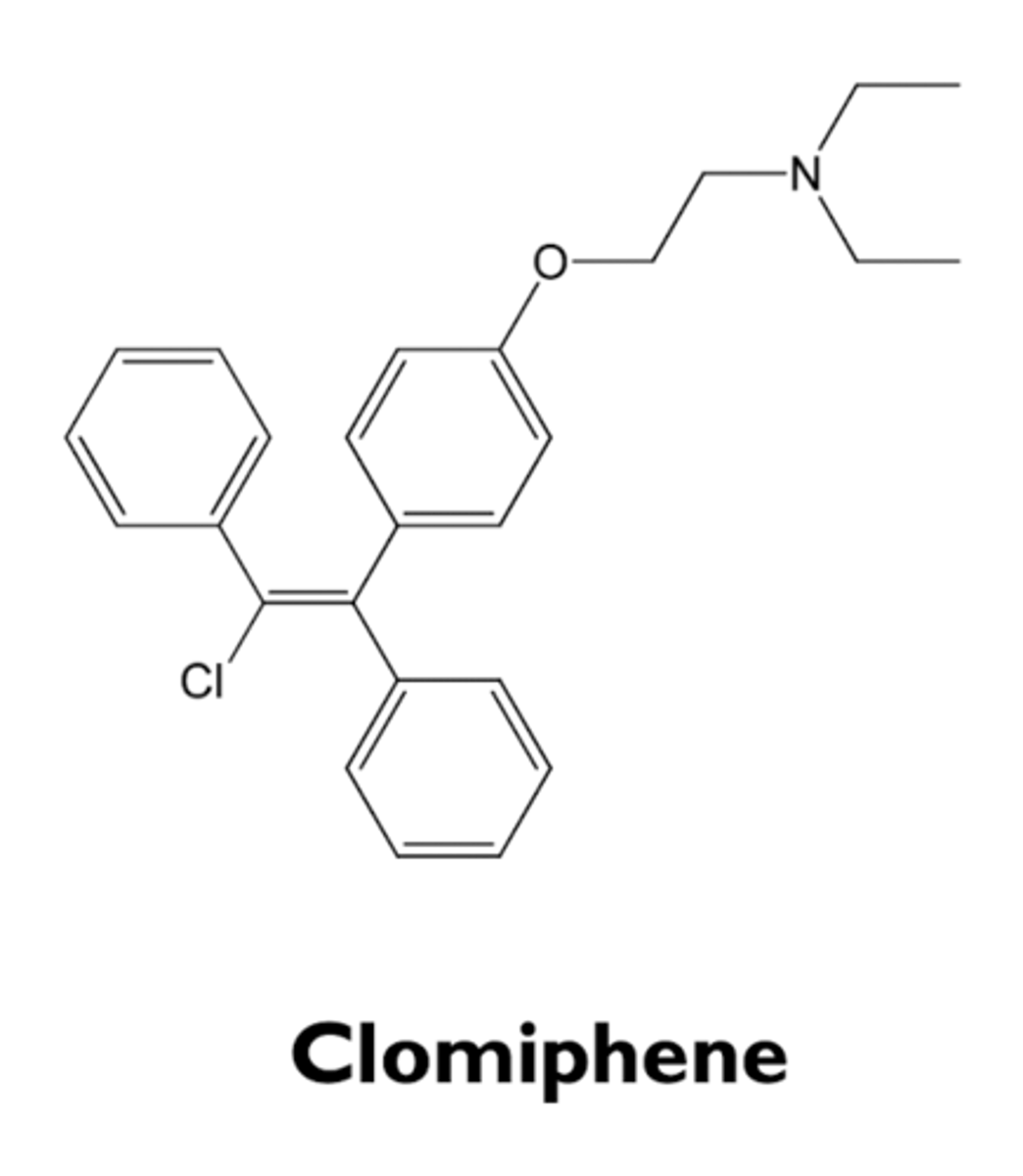
what are the characteristics of clomiphene?
- SERM; partial estrogen agonist
- increases secretion of FSH and LH by inhibiting negative estradiol feedback
- used to stimulate ovulation in women with oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea and ovulatory dysfunction (frequently from polycystic ovary syndrome)
- polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
what is polycystic ovary syndrome?
- 7% of women of reproductive age
- gonadotropin-dependent ovarian hyperandrogenism
- anovulation and infertility
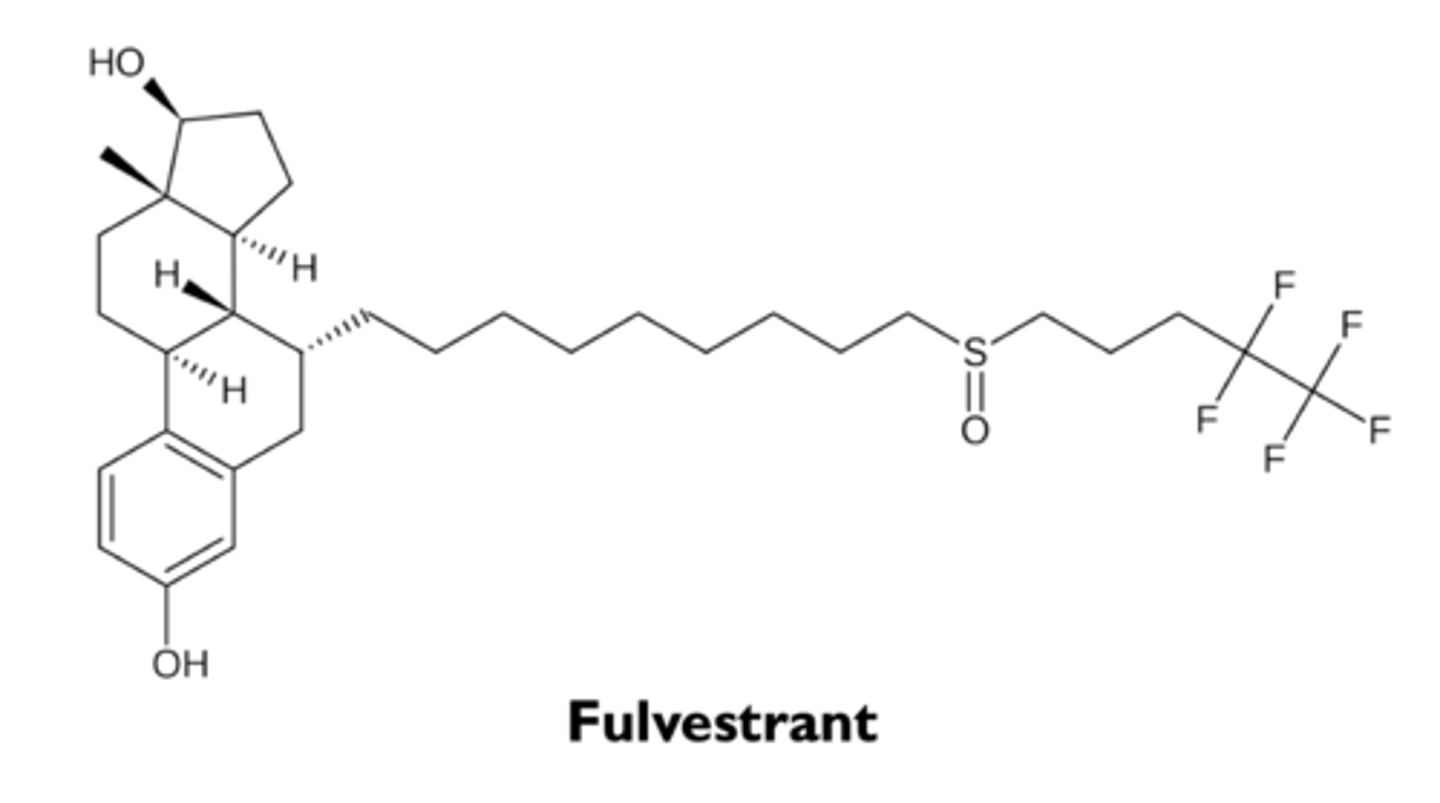
what are the types of selective estrogen receptor downregulators (SERD)?
fulvestrant
what are the characteristics of fulvestrant?
- SERD
- pure estrogen receptor antagonist for the treatment of breast cancer
- somewhat more effective than SERM in patients who have become resistant to tamoxifen
what are the types of aromatase inhibitors?
- anastrozole
- letrozole
- exemestane
what are the characteristics of aromatase inhibitors?
- block biosynthesis of estrogens
- effective in some patients whose breast cancer has become resistant to tamoxifen
- ovulation induction (off-label use)
- gynecomastia