Lesson 1 : Introduction to Research
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Research
a systematic process of gathering information, interpreting information, and analyzing information to resolve a specific problem
Inquiry
a learning process that motivates you to obtain knowledge or information about people, things, places, or events. You look for information by asking various questions about the thing you are curious about
Systematic
having, showing, or involving a system, method, or plan.
Process
a series of actions or steps taken in order to achieve a particular end.
Accuracy
Research must provide correct or accurate data which should be honestly and appropriately documented or acknowledged in the footnotes, notes and bibliographical entries.
Objectiveness
Research must present the evidence, not mere assumptions resulting from theories, generalizations, projections or conclusions.
Timeliness
Research has to work on a topic that is original, modern and important to society today.
Relevance
The topic of research must be instrumental in improving society or in solving problems affecting the lives of people in a community.
Clarity
Research must succeed in expressing its central point or discoveries by using simple, direct, concise, and correct language.
Systematic
Research must take place in an organized or orderly manner
Ethics
generally is considered to deal with beliefs about what is right or wrong, proper or improper, good or bad.
is important in research because it is for the researcher to avoid from committing errors while seeking knowledge and truth
it promotes essential values that help researchers working on a topic to have a common understanding of how things should go about
Honesty
Strive for honesty in all scientific communications. Rightfully report data, results, methods and procedures, and publication status. Do not fabricate, falsify, or misrepresent data.
Objectivity
Strive to avoid bias in experimental design, data analysis, data interpretation, peer review, personnel decisions, grant writing, expert testimony, and other aspects of research where objectivity is expected or required.
Integrity
Keep your promises and agreements; act with sincerity; strive for consistency of thought and action.
Carefulness
Avoid careless errors and negligence; carefully and critically examine your own work and the work of your peers. Keep good records of research activities, such as data collection, research design, and correspondence with agencies or journals.
Openness
Share data, results, ideas, tools, resources. Be open to criticism and new ideas.
Respect for Intellectual Property
Honor patents, copyrights, and other forms of intellectual property. Do not use unpublished data, methods, or results without permission.
Confidentiality
Protect confidential communications, such as papers or grants submitted for publication, personnel records, trade or military secrets, and patient records.
Responsible Publication
Publish in order to advance research and scholarship, not to advance just your own career. Avoid wasteful and duplicative publication.
Responsible Mentoring
Help to educate, mentor, and advise students. Promote their welfare and allow them to make their own decisions.
Respect for Colleagues
Respect your colleagues and treat them fairly.
Competence
Maintain and improve your own professional competence and expertise through lifelong education and learning; take steps to promote competence in science as a whole.
Legality
Know and obey relevant laws and institutional and governmental policies.
Animal Care
Show proper respect and care for animals when using them in research. Do not conduct unnecessary or poorly designed animal experiments.
Human Subject Protection
When conducting research on human subjects, minimize harms and risks and maximize benefits; respect human dignity, privacy, and autonomy; take special precautions with vulnerable populations; and strive to distribute the benefits and burdens of research fairly.
IMRad Research Paper
Refers to a paper that is structured by four main sections: Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. This format is often used for lab reports as well as for reporting any planned, systematic research in the social sciences, natural sciences, or engineering and computer sciences.
Traditional Research Paper
A systematic process thatdemands a standard scientific method
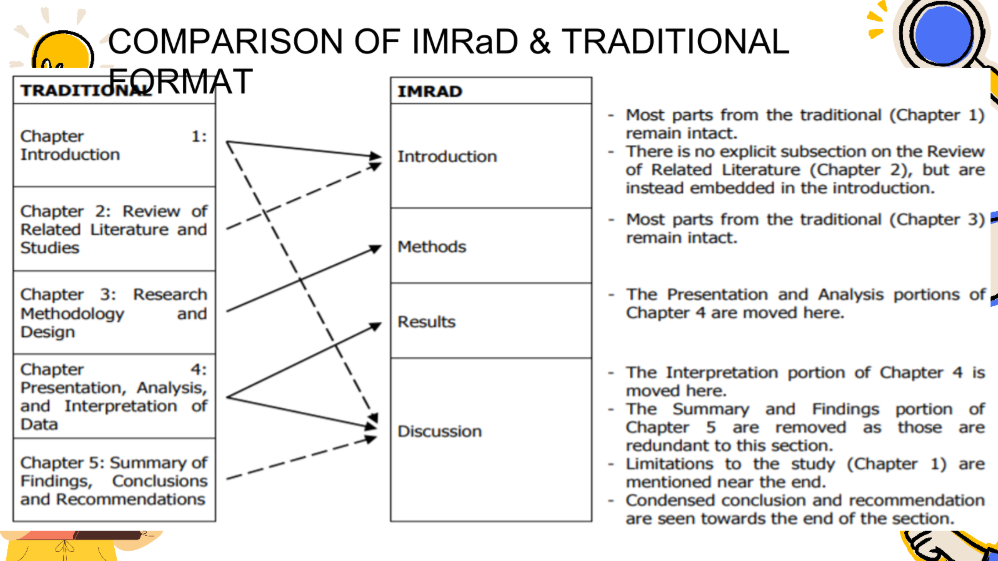
Comparison of IMRad vs. Traditional Research Paper