Payment and Coverage in O&P
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Where does money in an O&P clinic come from?
customer
payer
Customer
customers have the ability to negotiate services/fees with partners such as O&P businesses
entity that orders care for a patient and pays for the services/device provided
terms of payment agreed upon in negotiated contract between O&P practice and customer
Who is the Customer?
hospital, SNF, worker’s compensation, VA
Payer
entity with a set code/fee schedule for services/products
entity who pays for patient services but is not the ordering provider
reimbursement is determined by a fixed fee schedule and compliance with coverage policies
Who is the Payer?
Medicare, Medicaid, TRICARE, Commercial insurance, and other healthcare insurances
Public Payers
government programs like: Medicare, Medicaid, or Veterans Health Administration
Private Payers
Commercial like: United Healthcare, Anthem, Aetna, Cigna, Humana, BCBS, etc.
What are the key differences between public and private insurance?
funding
eligibility
provider choice
cost-sharing
Medicare Facts
Federal health insurance program for people age 65+ OR with certain disabilities.
added to the Social Security Program in 1965
consists of several different parts
complex and controversial program
funded by payroll taxes
beneficiaries pay for some basic coverage, deductibles and gaps in coverage but generally low cost
Medicare Eligibility
US citizen or 5 year permanent resident
65 yrs or older
under 65 with disabilities or people of any age with End-Stage Renal Disease
Medicare Enrollment
3 months before your birth month (when you turn 65) to 3 months after it
Medicare Part A
Hospital Insurance
original Medicare through the federal government
Medicare Part B
Medical Insurance
original Medicare through the federal government
Medicare Part C
Medicare Advantage/Replacement
bundled plans that include part A, part B, and usually part D from a private insurance company
Medicare Part D
Prescription Drug Coverage
from a private insurance company
Medicare Supplement Plan/ Medigap
Medigap
will help fill some of the gaps that Original Medicare doesn’t cover
additional insurance that you can buy from a private company
helps pay your share of (out of pocket) costs
O&P services are billed under Medicare Part ____.
B
Medicare Part A: Hospital Insurance
Medicare pays the facility
often single bundled payment using a Prospective Payment System (PPS)
most O&P services are often considered part of the bundled payment
SNF/hospital becomes the customer with payment and coverage dictated by contract negotiated between parties (i.e. O&P business and facility)
Three parts of Medicare Part A: Hospital Insurance
Inpatient Hospital Care
inpatient stay classified into diagnosis related groups (DRGs)
DRG determines how much hospital is paid for entire stay
all O&P devices consolidated into payment, no carve out
Skilled Nursing Facility Care
only “Step Down Care” (Sub Acute Hospital Care)
specific eligibility
requires 3 day hospital stay prior to SNF care and subject to 100 days of coverage
per day payments
PPS called the Patient Driven Payment Model (PDPM) based on clinical presentation
custom prostheses are not subject to SNF consolidated billing
Hospice
Medicaid
joint federal and state public program
Medicaid Eligibility
people with significant needs including pregnant women; children, especially those with special needs; disabled people; and elderly people, including those who need long term care services and support
income below the federal poverty level
$15,060 for individual (2024)
Private or Commercial Insurance
Offered in both individual and group plans
individual plans purchased directly from insurance company or through the Health Insurance Marketplace
group plans provided through employer
Higher patient cost sharing, broader access to service and providers.
deductible
co-insurance
annual out of pocket limits
Deductible
an amount an individual policyholder must pay before the insurance company will pay on their behalf
Co-insurance
percentage of costs of a covered health care service policyholder pays after the deductible is paid
Annual Out of Pocket Limits
highest amount an individual or family must pay in a plan year before the insurance plan pays 100% of the costs
Veterans Health Administration (VA)
All veterans enrolled in the VA health care system are eligible for O&P devices.
O&P provided directly by VA-employed CPOs OR indirectly through contracted O&P clinics.
Service members, active or retired, can have both VA benefits and TRICARE.
VA
healthcare system and payer for veterans
TRICARE
public health insurance for active or retired members of service and their families
Worker’s Compensation
state mandated insurance program providing benefits to employees who have suffered a job-related injury or illness
often managed by 3rd party organizations serving as intermediary (ex. One Call Care Management, CorVel)
SNF and Hospitals
facilities can become pay sources
patients are on Medicare Part A stay or when payers using similar bundled payment system
financial responsibility and billing can be complex and misunderstood
2 day rule
codes not subject to SNF consolidated billing
billing and reimbursement dictated by contract between facility and O&P business
What is the 2 day rule?
allows O&P to bill Medicare Part B while on a Part A stay as long as the pt is discharged in 2 days to HOME not a SNF
Individual patient
Non covered services
Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) required to collect money from Medicare beneficiary
common for other payer policies to mandate similar waivers prior to collecting money directly from a beneficiary
responsibility of provider (O&P business) not beneficiary (patient) to know the insurance policy and covered services
Deductibles or co-insurance
Coverage
How and when will an item or device be covered by a pay source?
It usually start with Medicare
many insurers follow Medicare policy to set own
recognized as benchmark for industry
highly regulated Federal program
evidence based policy
clinicians must be informed on policy to properly code
Social Security Act (SSA)
passed in 1935, establishing Social Security
Medicare added in 1965
sets the groundwork for coverage
coverage can be vague
National Coverage Determination (NCD)
policies created by CMS that grant, limit, or exclude coverage
more specific than the SSA
apply nationally
developed and published by CMS through evidence based processes
few NCDs relevant to O&P
Medicare Coverage Partners
DME MAC - Durable Medical Equipment Medicare Administrative Contract
private insurance company contracted by Medicare to process Durable Medical Equipment, Orthotics, and Prosthetics (DMEPOS) claims and develop policy
Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs): what is medically necessary? what is the coverage criteria?
difficult to change requiring public meetings and comments
Policy Articles: provides statutory limitations on coverage and coding guidelines
more readily updated and changed - do not require public comment
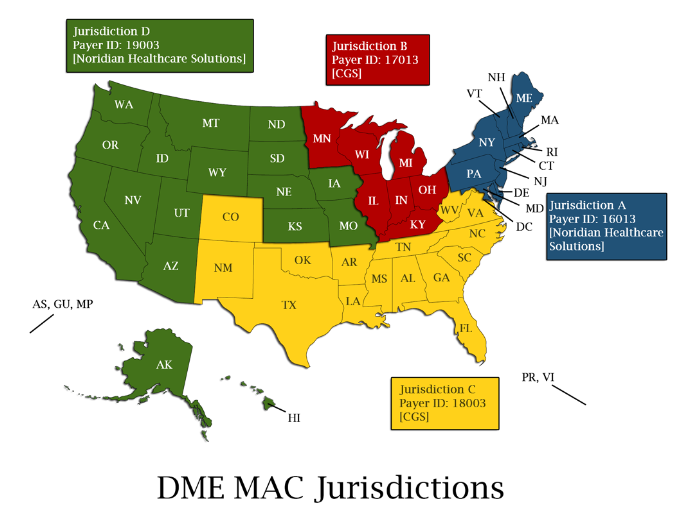
DME MACs
organized by geographic region (A, B, C, and D)
LCDs are effective only within the issuing region
Non-Medicare Coverage
policy documents exist for most payers
follow the guideline outlined in the specific pay source policy you are working with
when policy is non-specific or silent, follow Medicare rules