Pathology of uterus
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
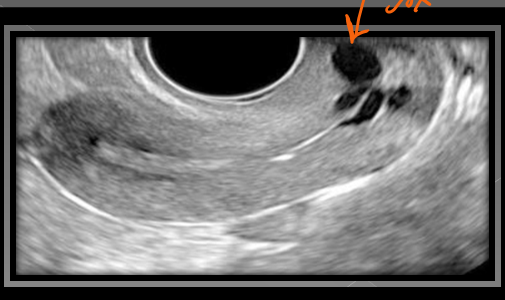
Nabothian cysts originate from the ______ and are considered ______
Cervix; benign
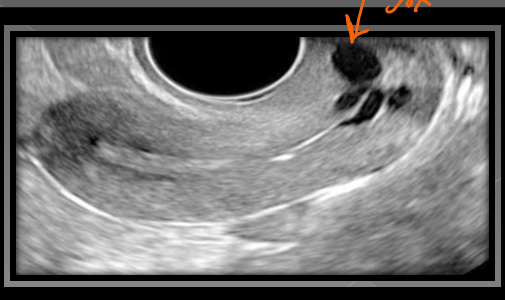
What do Nabothian cysts usually measure?
Less than 2 cm (<2cm)
What causes nabothian cysts?
Chronic cervicitis which is the inflammation of the cervix
What are nabothian cysts also called?
Epithelial inclusion cyst
What clinical symptoms do cervical polyps present with?
Irregular bleeding
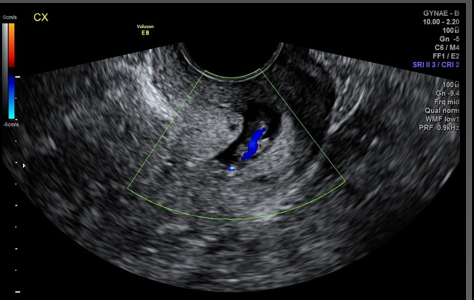
Cervical polyps may be _________ and are more common in ______ women
pedunculated; middle-aged
Large cervical leiomyomas may cause _____ or _____ obstruction
Bladder; Bowel
Large leiomyomas can ______ into the _______ ______
prolapse; vaginal canal
A myoma may be pedunculated and prolapse into the _____ _____
vaginal canal
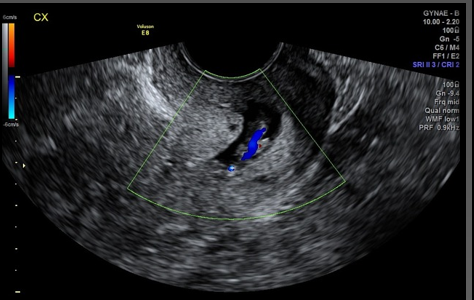
Leiomyomas and cervical polyps are best visualized with _________
Sonohysterography
What is cervical stenosis?
Obstruction of the cervical canal
What is an obstruction of the cervical canal?
Cervical stenosis
Cervical stenosis causes a ______, _____ uterus
distended; fluid-filled
Cervical stenosis is a result from prior _______, _______, ______, ______, ______, or _______
instrumentation, childbirth, surgery, atrophy, cancer, irradiation
Premenopausal patients with cervical stenosis may experience ________, _________, __________, _________
oligomenorrhea; amenorrhea; dysmenorrhea; cramping
What is the most common type of cervical cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma
What is a precursor of cervical carcinoma?
Cervical dysplasia on PAP exam
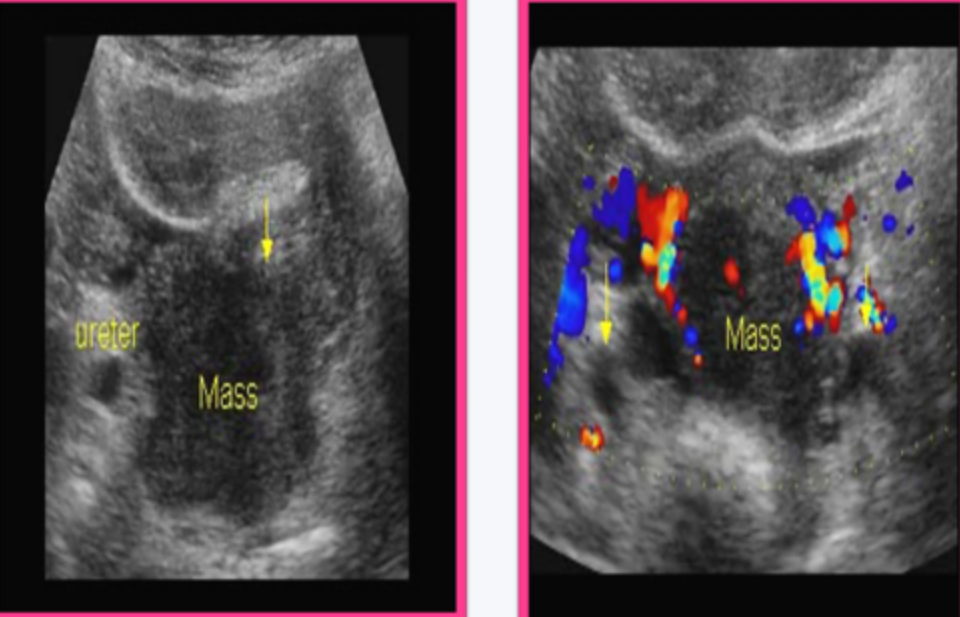
Cervical carcinoma appears on ultrasound as a _____, ________ mass and irregular ______ or _________ areas
solid; retrovesical; hyperechoic; hypoechoic
Cervical carcinoma typically appears in ________ women
menstruating
What is the optimal view for cervical carcinoma?
Translabial and transperineal
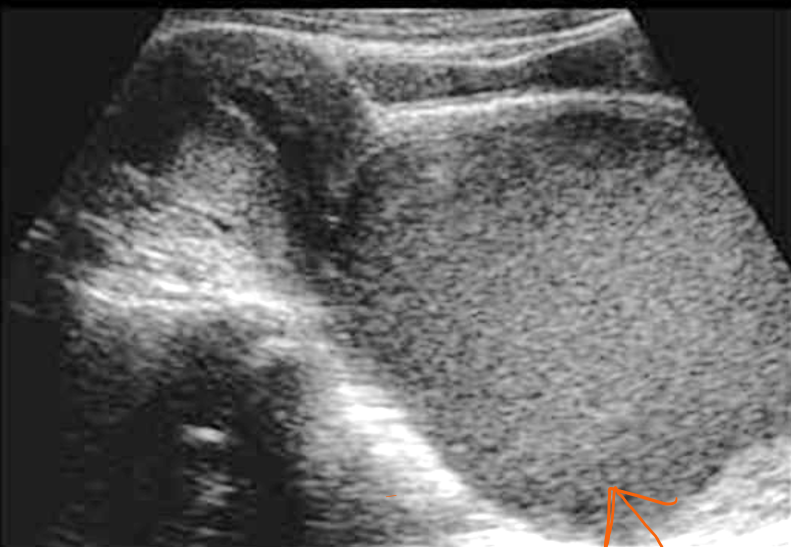
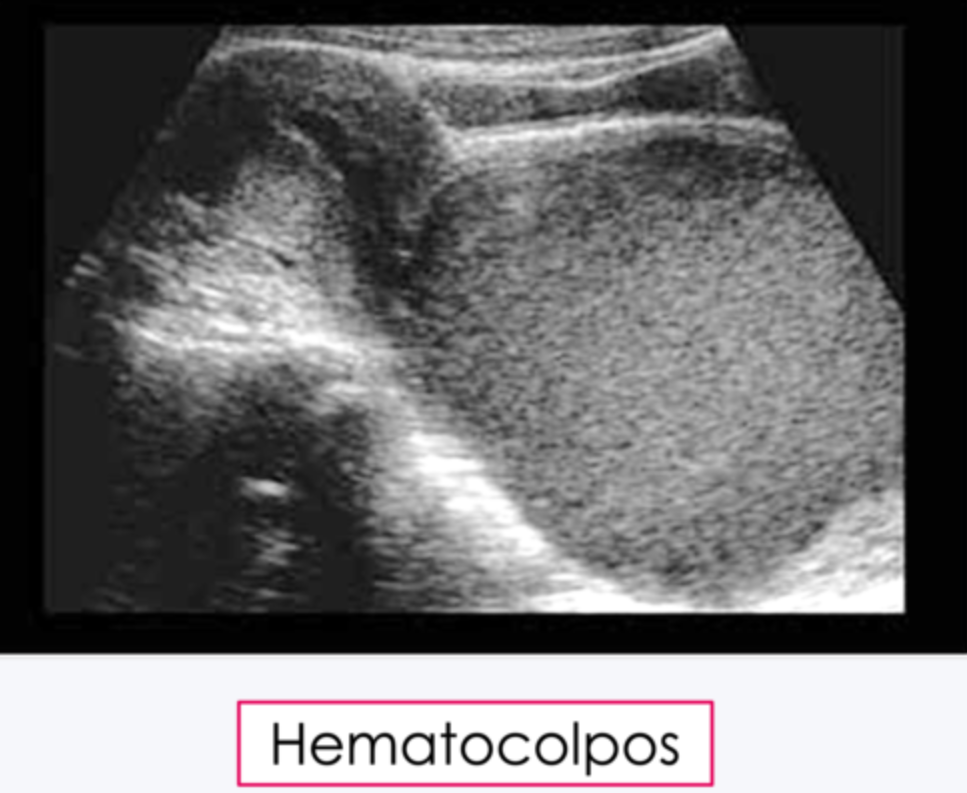
What is this condition called?
Hematocolpos
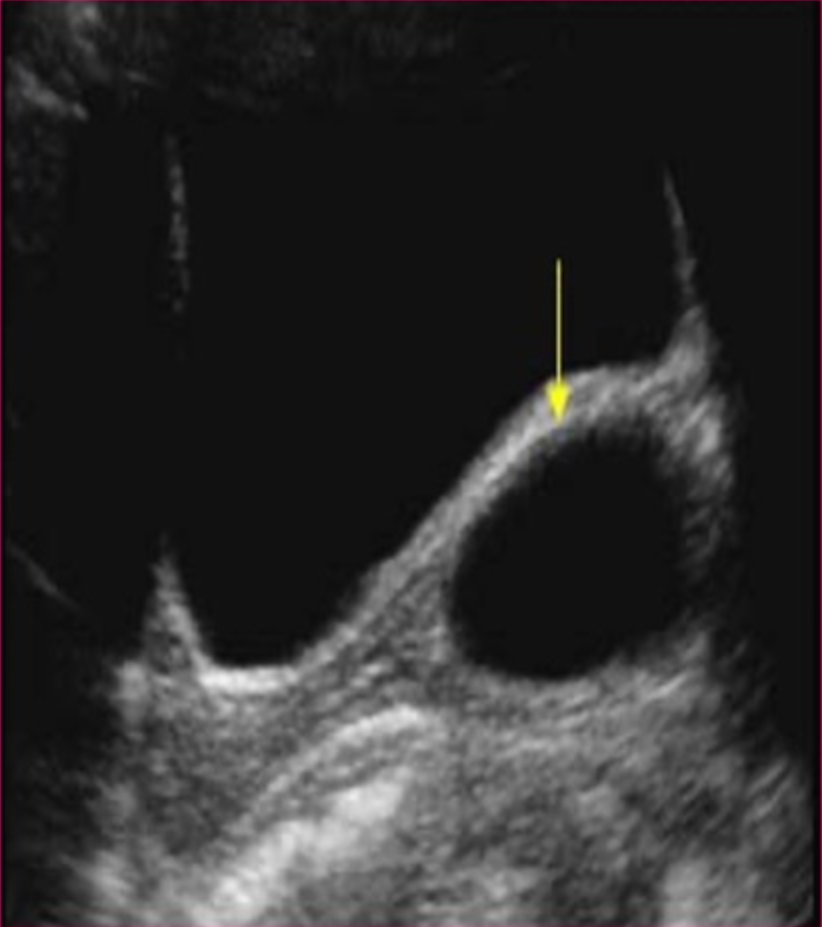
What is the most common cyst of the vagina?
Gartner’s duct cysts
What is the most common congenital abnormality of the female genital tract, resulting in obstruction?
Imperforate hymen
Obstruction of the uterus or the vagina may result in an accumulation of fluid such as, _______, _______, ________
hydrometra; hematometra; pyometra
What may result with an imperforate hymen?
- hydrocolpos / hydrometra
- hematocolpos / hematometra
- pyocolpos / pyometra
Solid masses of the vagina are _____. When found, the lesion is usually vaginal ________ or __________
rare; adenocarcinoma; rhabdomyosarcoma
What is seen post hysterectomy?
Vaginal cuff
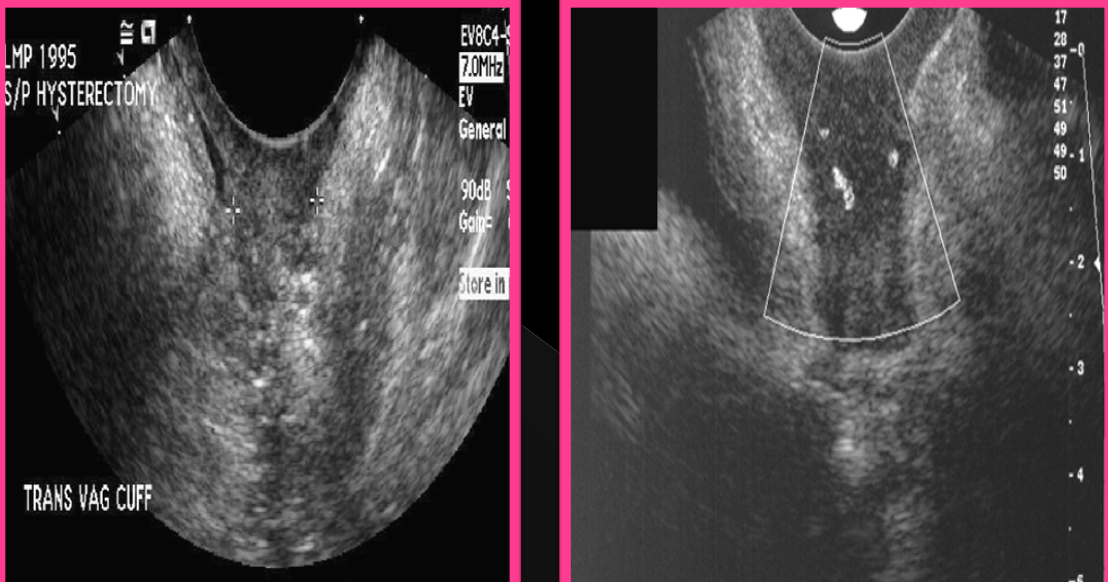
The normal measurement of a vaginal cuff is?
Less than 2.1 cm (<2.1 cm)
Suspicious for malignancy, if vaginal cuff is _______ or contains a _________ mass
enlarged; well-defined
Nodular areas in the vaginal cuff may be due to ________ _______
post-irradiation fibrosis
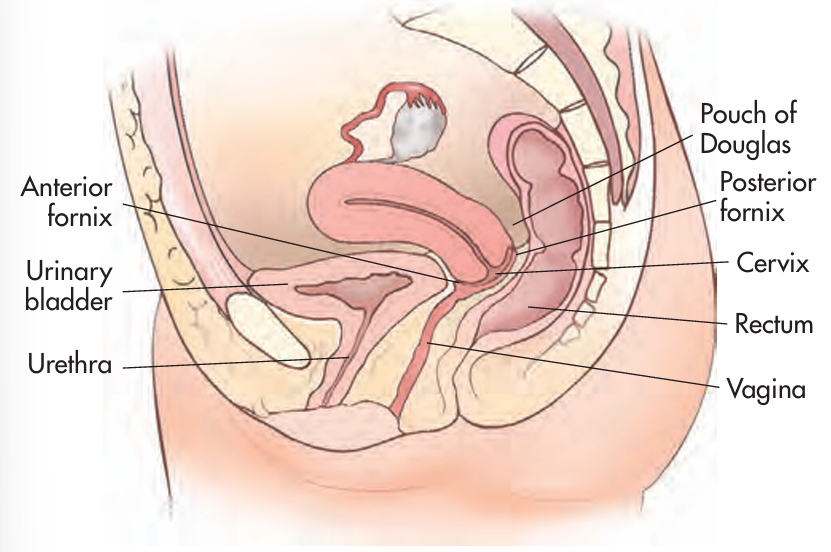
Rectouterine pouch is AKA?
Pouch of Douglas or posterior cul de sac
The rectouterine pouch is the most _________ reflection of intraperitoneal fluid collections located between the _____ and _____
posterior/inferior; rectum;vagina
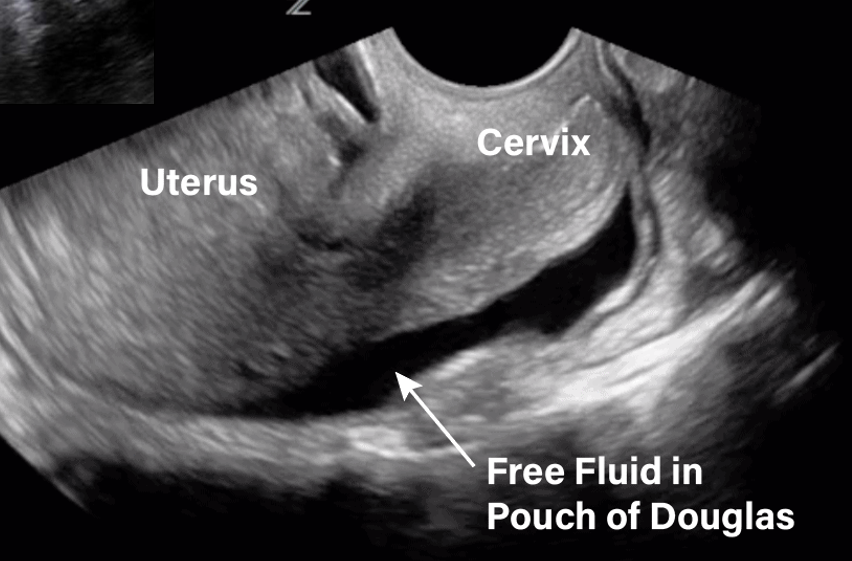
What amount of fluid can be seen in posterior cul de sac transvaginally?
5 mL or greater (>5 mL)
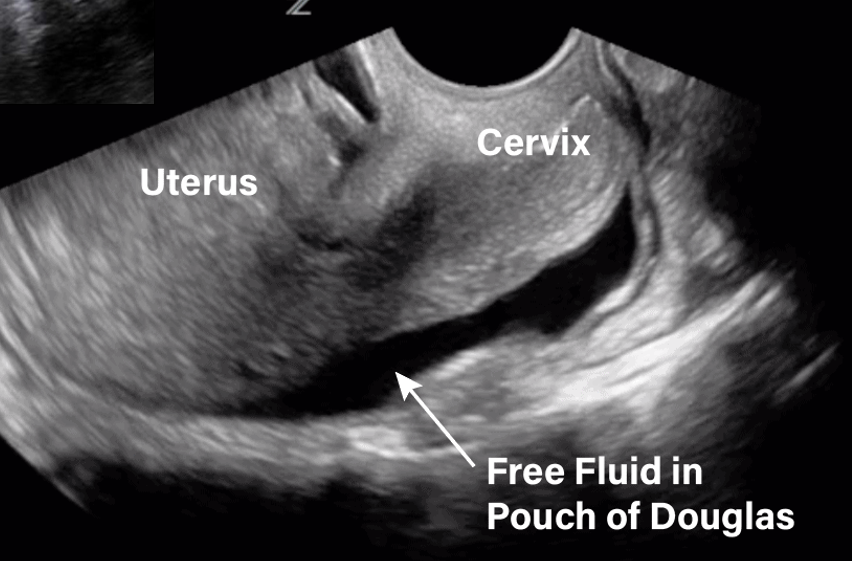
______ in the cul de sac is a _____ finding in _______ women and can be seen during all phases of the menstrual cycle
Fluid; normal; asymptomatic
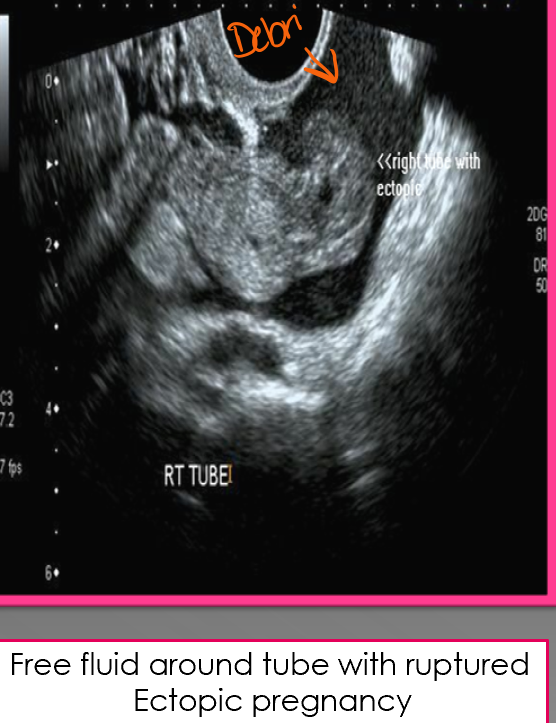
What are the primary causes for large amount of fluid collections?
Ascites
blood resulting from ruptured ectopic pregnancy
hemorrhagic cyst
pus
What is the most common benign reproductive tumor?
Leiomyomas
Leiomyomas occur to ___ to _____ of women over ____ years old
20-30%;30
Leiomyomas are more common in ______ ______ women
African American
Leiomyomas are _______ and separated from the ______ easily
encapsulated; myometrium
With _____ and _____ compromise as a result of outgrowing their blood supply, fibrotic changes and degeneration of the myomas can occur
Atrophy; vascular
Leiomyomas are ______ dependent
estrogen
Leiomyomas can be seen with ___, ___, ___, ___ and ___
atrophy; calcification; hemorrhage; liquefaction; necrosis
Leiomyomas may increase in size during ______ or -__________
pregnancy; post-hormone replacement therapy
Leiomyomas rarely develop in _________ women
postmenopausal
What are clinical symptoms of a leiomyoma?
Uterine irregularity; uterine enlargement; pelvic pressure; pain; menometrorrhagia; menorrhagia
Myomas contribute to _______ by distorting the fallopian tube or endometrial cavity.
infertility
Leiomyomas may be ______ and ______
pedunculated; migratory
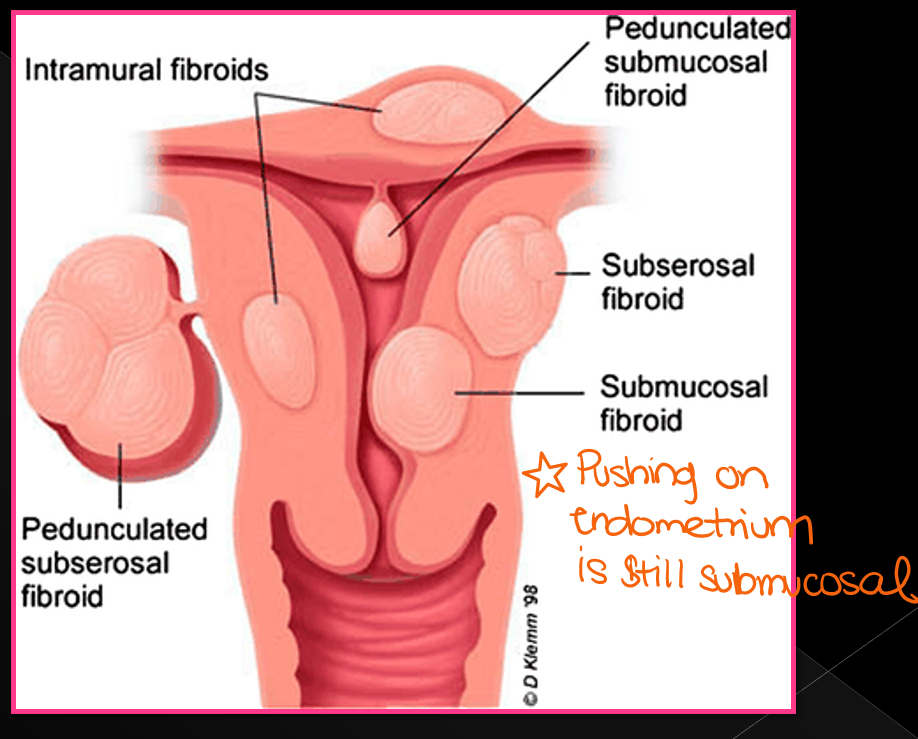
Leiomyomas can be located in ____ portion of the _________. Can be uncommonly found in the _______, _____, and ______
any; uterine; lower uterine segment; cervix; broad ligament
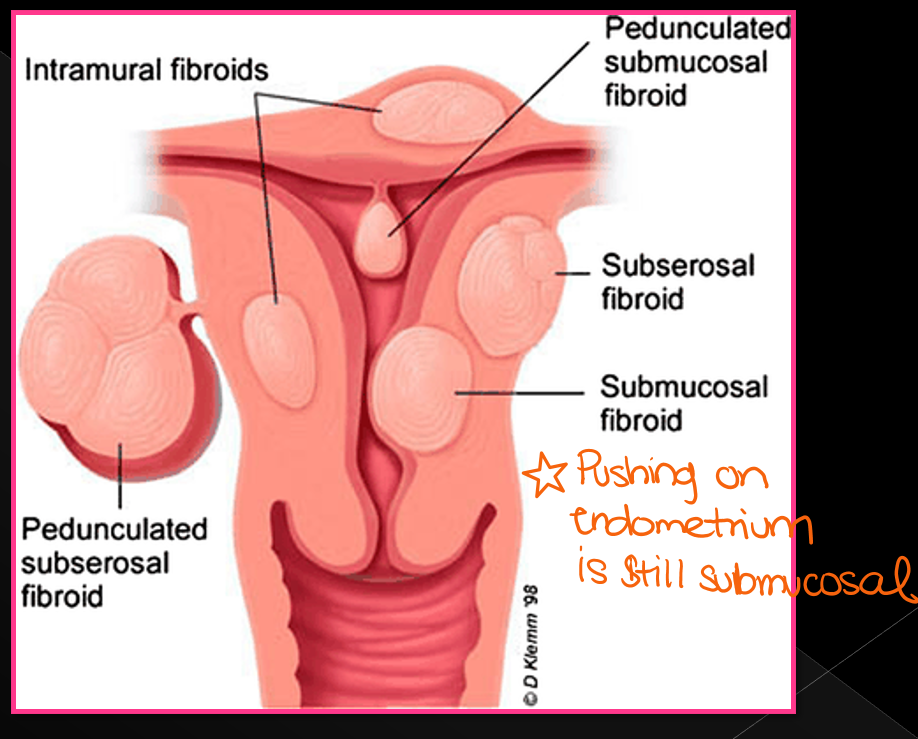
Leiomyomas can be described as three types, what are they?
Submucosal; Intramural; subserosal
Submucosal leiomyomas can disrupt the _______, causing ______, or ______ bleeding and _______
endometrium; irregular; heavy; infertility
Intramural leiomyomas are located within the ______, they are the most ______, cause _____ or recurrent _____
myometrium; common; infertility: miscarriages
Subserosal leiomyomas are located in the _______ or _______
Perimetrium; pedunculated
Sonographic findings of leiomyomas are:
Uterine enlargement
Heterogenous
Contour distortion
Hypoechoic normally, or hyperechoic
Calcifications
Difficult to image
What is the measurement of an abnormal endometrium in the follicular phase?
Greater than 6mm (>6mm)
What is the measurement of an abnormal endometrium with untreated menopause?
Greater than 5mm (>5mm)
What is the treatment of choice in cases of infertility and a submucosal myoma?
Surgery by myomectomy
What is the treatment of choice in cases of menorrhagia for myomas?
Hormonal suppression (hormonal suppression)
Endometrial ablation
Uterine artery embolization (UAE)
High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU)
What is the least invasive treatment for women with menorrhagia for myomas?
Hormonal suppression
Leiomyomas are the most common cause of uterine _________
calcifications
What is a less common uterine calcification?
Arcuate artery calcification
What is a benign disease with a collection of ectopic endometrial tissue infiltrating within the myometrium that may be diffuse or focal?
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis may be ___ or ___ and is more common on the ___ wall
diffuse; focal; posterior
Adenomyosis sonographically presents as a ___, ___ uterus without ___
bulky; enlarged; focal mass
Adenomyosis has a ___ or ___ pattern
Swiss cheese; honeycomb
With adenomyosis, the tissue penetration reaches a depth of ______ from the basal layer of the endometrium
Greater than 2.5 mm
Adenomyosis may be diffuse or focal, with ___ pattern being the most common
diffuse
Focal pattern appears as isolated _________ and creates an enlarged _______
adenomyoma; uterus
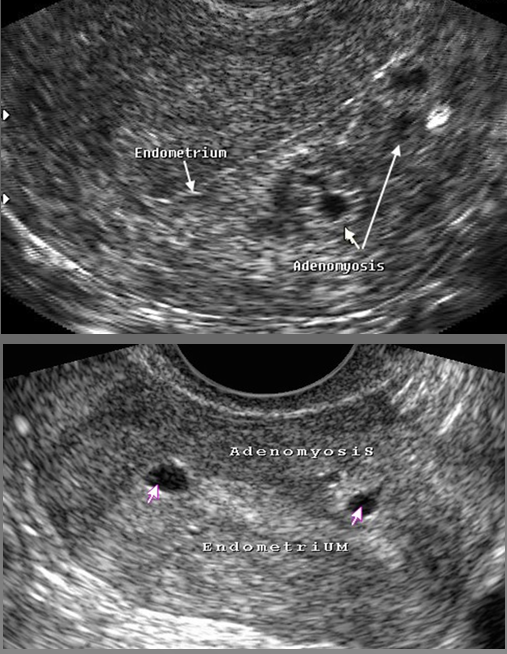
Focal adenomyosis appears as isolated _______
adenomyomas
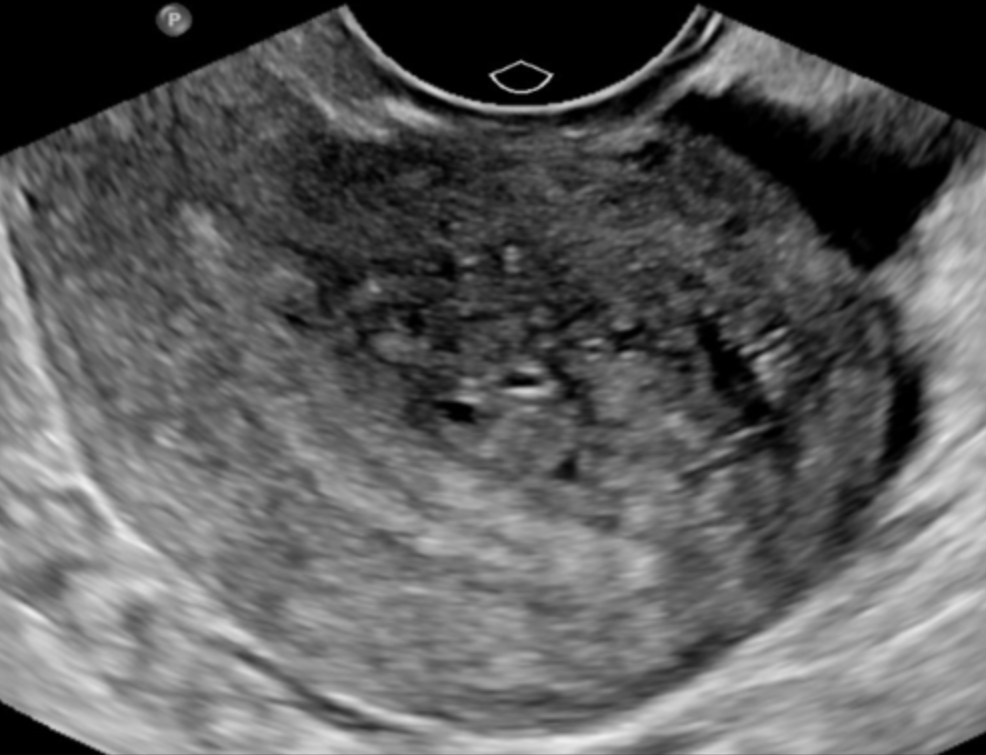
60% of women with adenomyosis experience:
Abnormal uterine bleeding (hypermenorrhea)
Prolonged/profuse uterine bleeding (menorrhagia)
Irregular, acyclic bleeding (metrorrhea)
25% of patients with adenomyosis also suffer from ______ during menstruation (_______)
pelvic pain; dysmenorrhea
Patients with adenomyosis are often _______ and ______ than patients with endometriosis
multiparous; older
Adenomyosis is managed with ________
hormone therapy
Clinical symptoms of adenomyosis cause patient to present with:
Painful, ____ _____
The uterus is found to range from normal to ______ times the normal size
Globular in _____, _____, and somewhat _____
abnormal menses;
3x
contour; boggy; tender
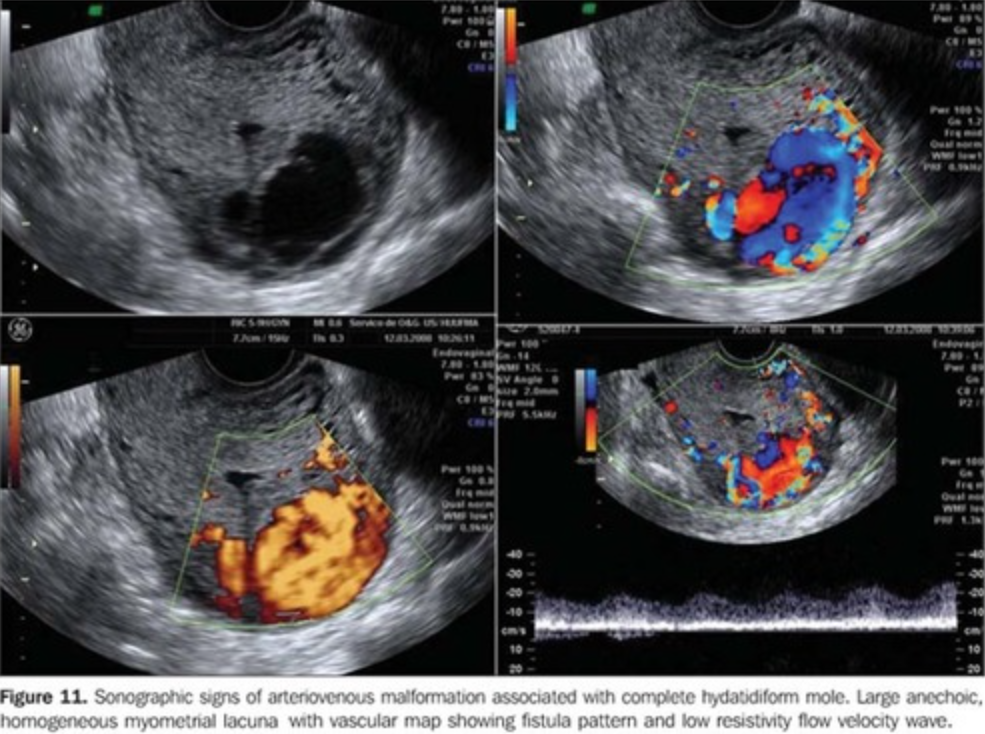
Uterine arteriovenous malformations consist of a ____ ____ of arteries and veins without an intervening ______ network
vascular plexus; capillary
Uterine arteriovenous malformations are _____ and usually involve the _______, rarely the ________
rare; myometrium; endometrium
Uterine arteriovenous malformations can be _____, but most are __________ (acquired) resulting from _______, _______, and ________
congenital; teratogenic; pelvic trauma; surgery; pregnancy
What is a clinical symptom of uterine AV malformation?
Metrorrhagia (heavy, extended bleeding)
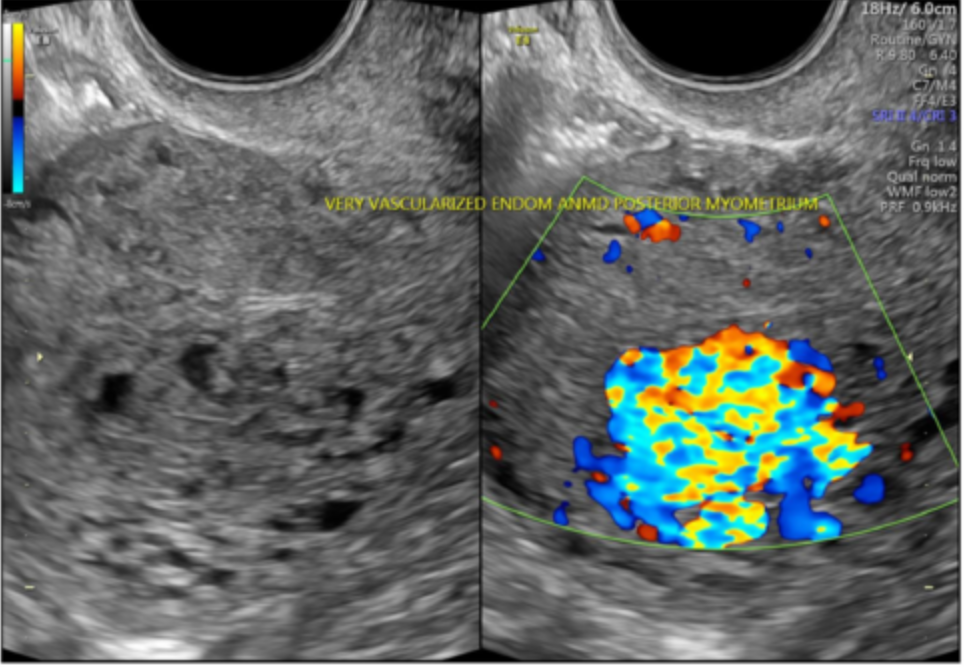
Sonographic findings of subtle myometrial inhomogeneity, tubular spaces within the myometrium, intramural uterine mass, endometrial or cervical mass, or prominent parametrial vessels are present with what?
Uterine AV malformations
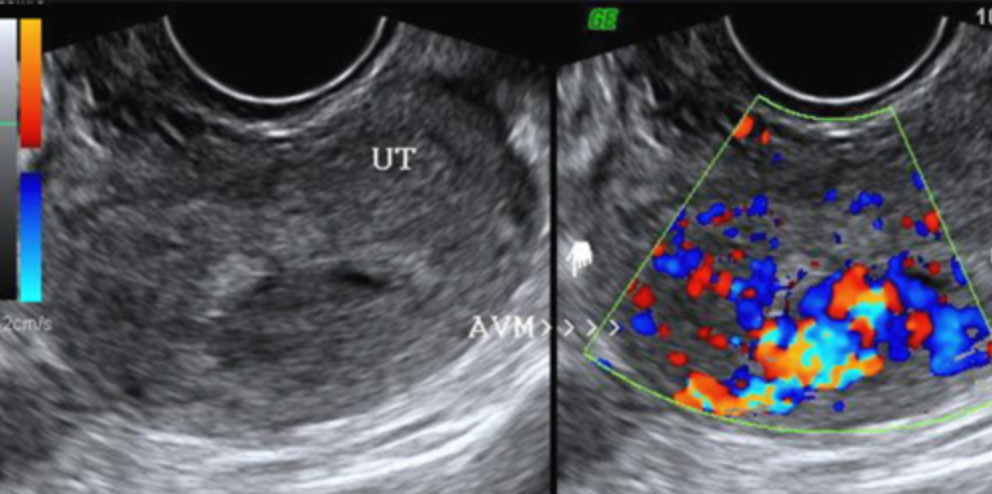
With uterine AV malformations, color doppler will show a ___-colored ___ pattern
Florid; mosaic
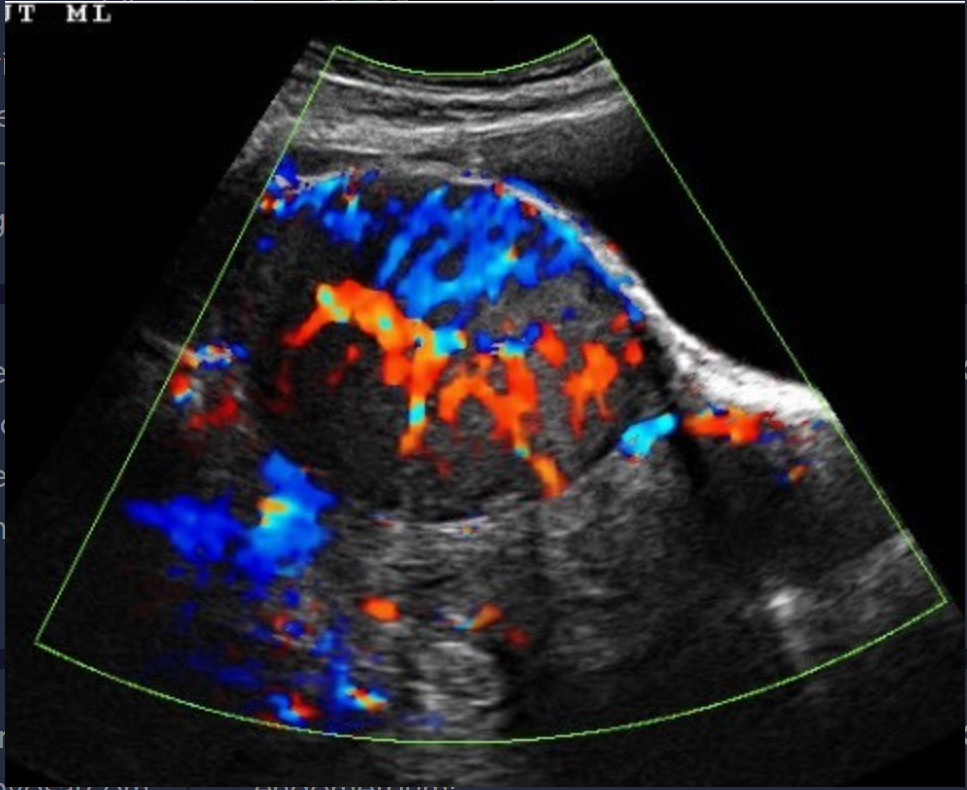
Uterine leiomyosarcoma is a ____, rapidly growing aggressive uterine malignancy that accounts for ___ of all uterine malignancies
rare; 1%
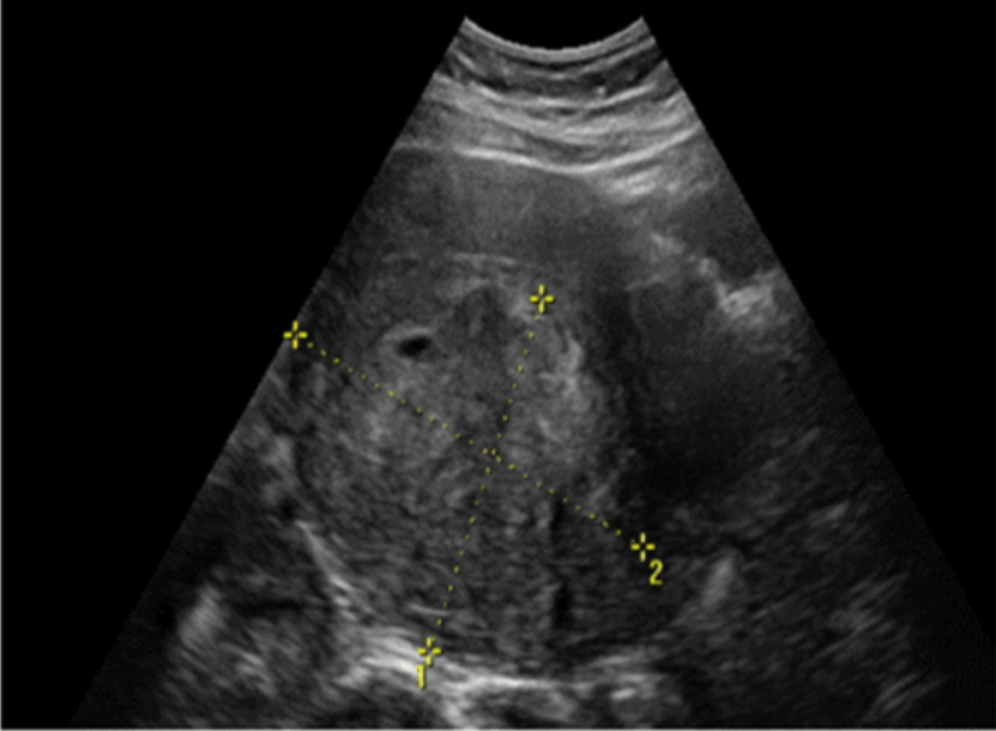
Pre-existing ______ are common in those with leiomyosarcoma
leiomyomas
Leiomyosarcoma arises from the ______ or _______ and is commonly found in the ______
myometrium; endometrium; myometrium
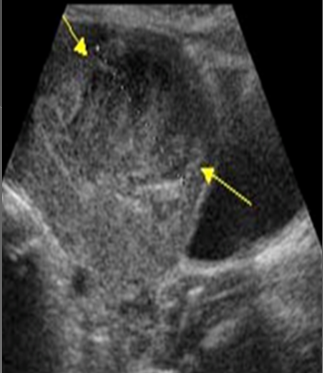
Leiomyosarcoma can affect any age group but most common in women ____-____ yrs of age
40-60
Normal endometrial thickness (mm)
Menstrual:
Early proliferative (3 line sign):
Preovulatory:
Secretory (thickest; about to menstruate):
2-3mm
4-6 mm
6-8 mm
8-15 mm
Reasons for an abnormally thick endometrium:
Early pregnancy
Gestation trophoblastic disease (molar pregnancy)
Endometrial hyperplasia (precursor of endometrial cancer)
Secretory phase
HRT (breast cancer patients taking tamoxifen)
Polyps
Endometrial carcinoma
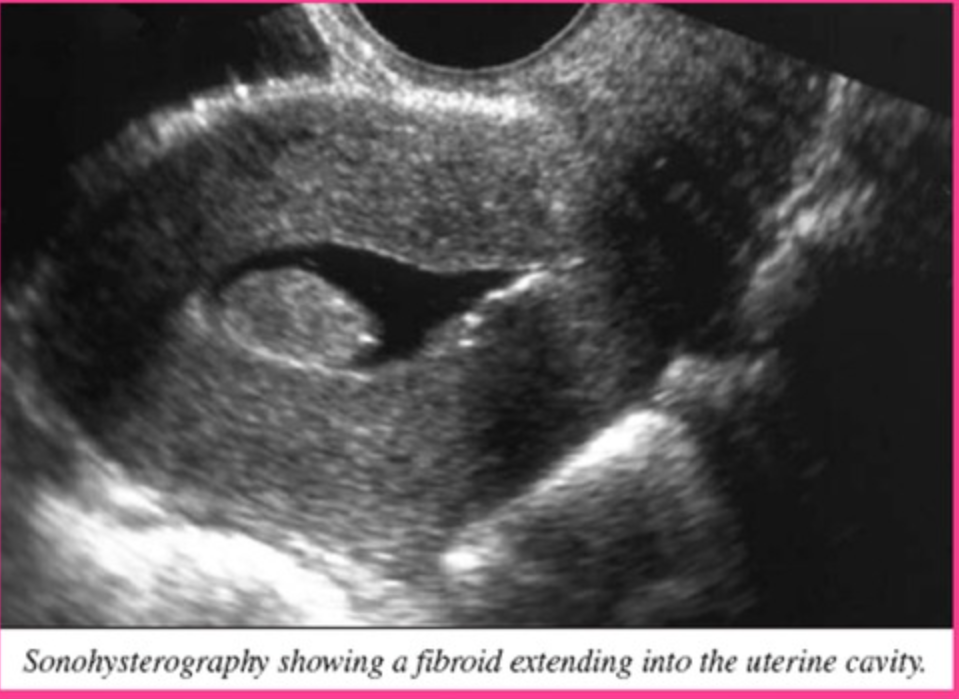
What is sonohysterography?
Evaluation of the endometrium using saline infusion
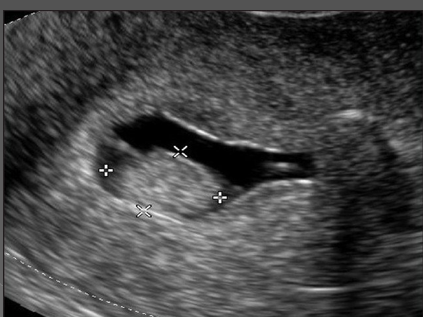
In premenopausal women, sonohysterography is performed in the _________ cycle, usually between days ___ and _____
midmenstrual; 6;10
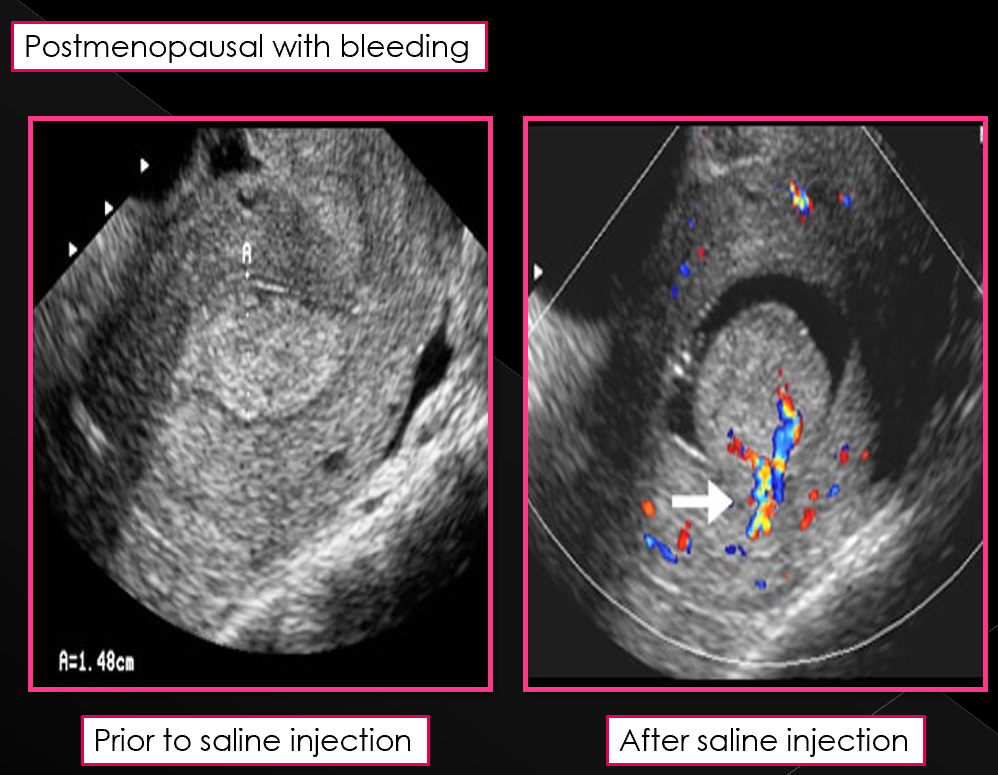
Sonohysterography is NOT performed in women with acute _____
PID (pelvic inflammatory disease)
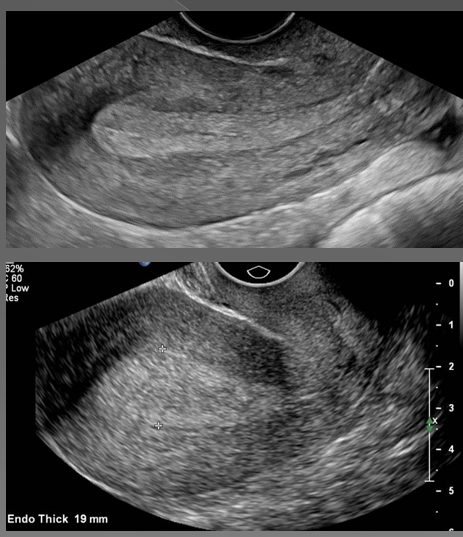
what is the most common cause of abnormal uterine bleeding?
Endometrial hyperplasia
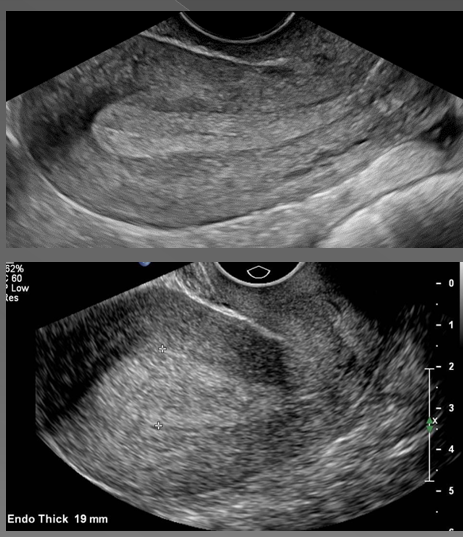
What is endometrial hyperplasia?
Thickening of the endometrium
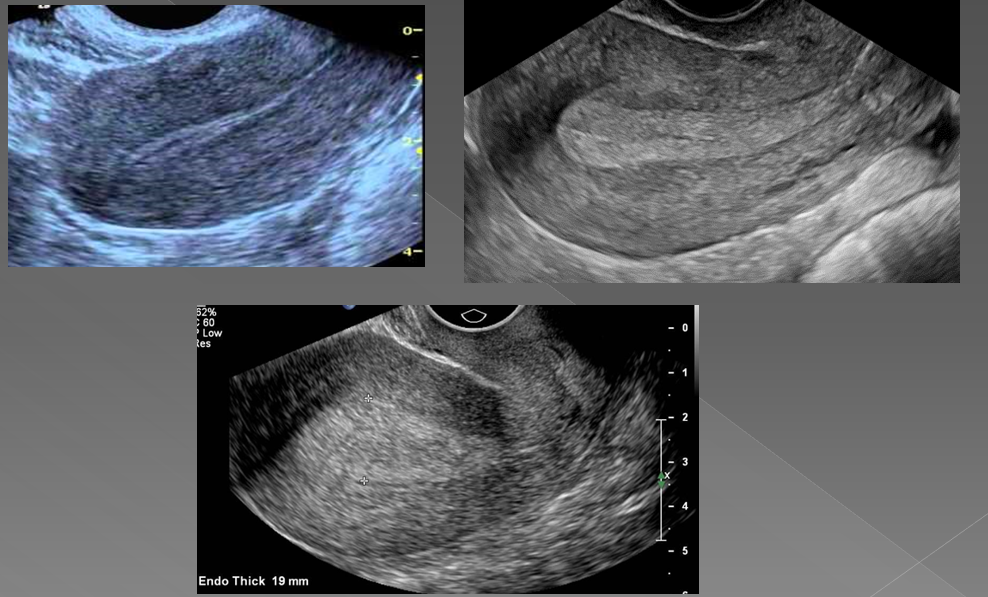
In premenopausal women, if the endometrium measures more than ____, hyperplasia is suggested
14 mm
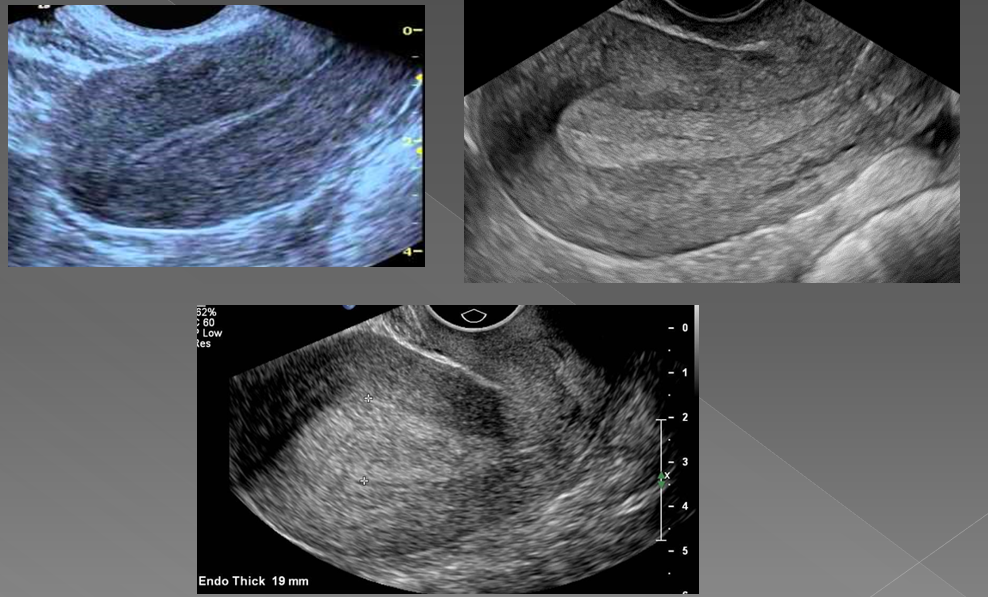
In asymptomatic postmenopausal women, if the endometrium measures more than _____, hyperplasia is suggested
8 mm
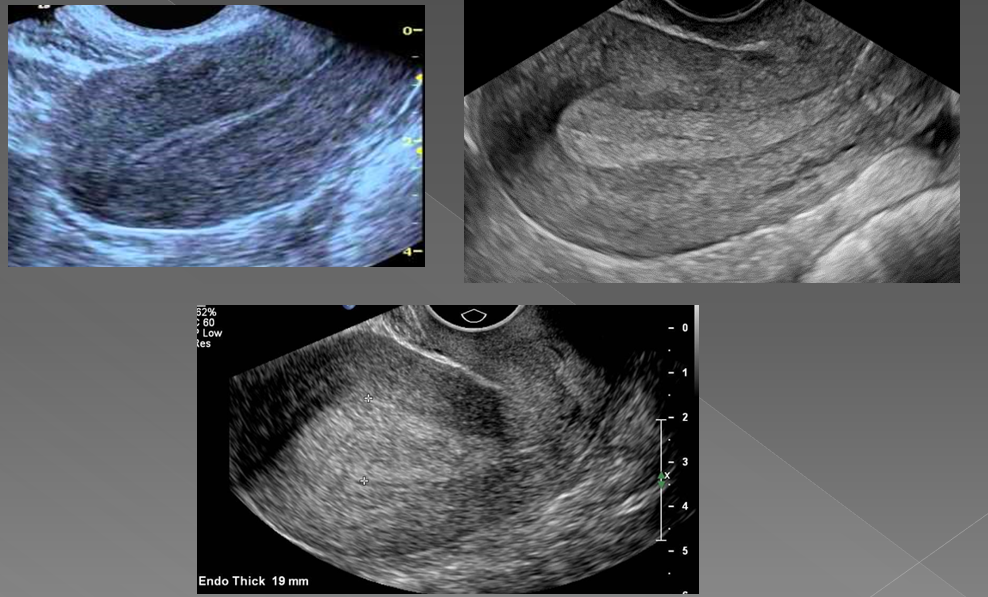
Endometrial hyperplasia is a _____ to endometrial cancer
precursor
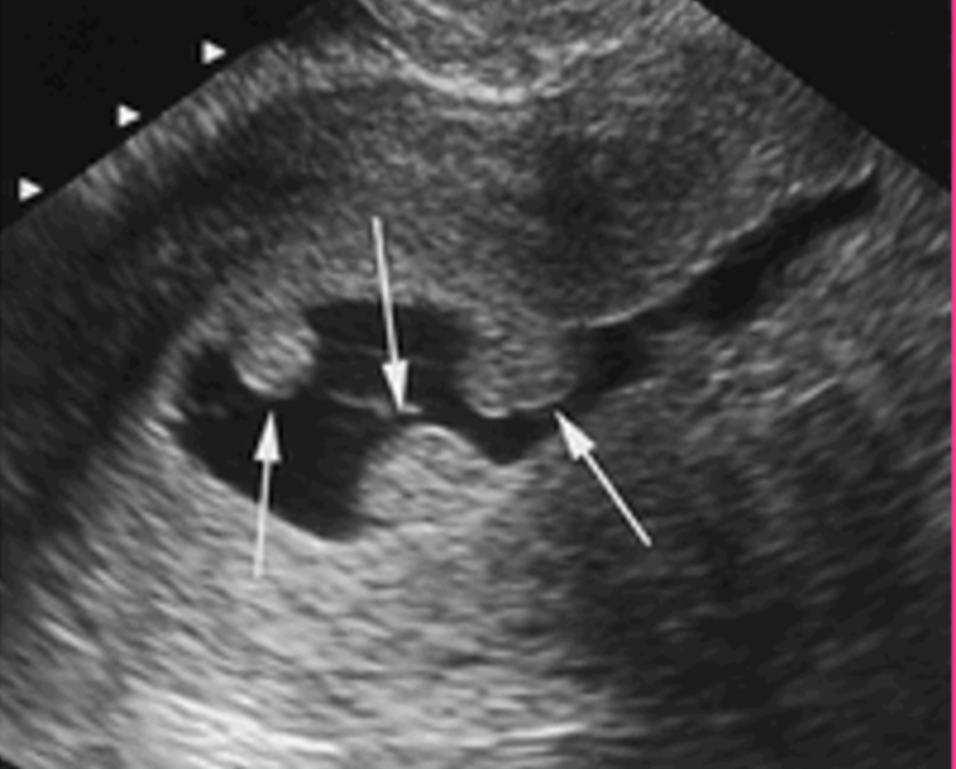
What is an endometrial polyp?
An overgrowth of endometrial tissue covered by epithelium
Patients with endometrial polyps can be _____
Asymptomatic
Endometrial polyps typically cause ____ or _____ endometrial thickening and are seen in ________ and _________ women
diffuse; focal; perimenopausal; postmenopausal
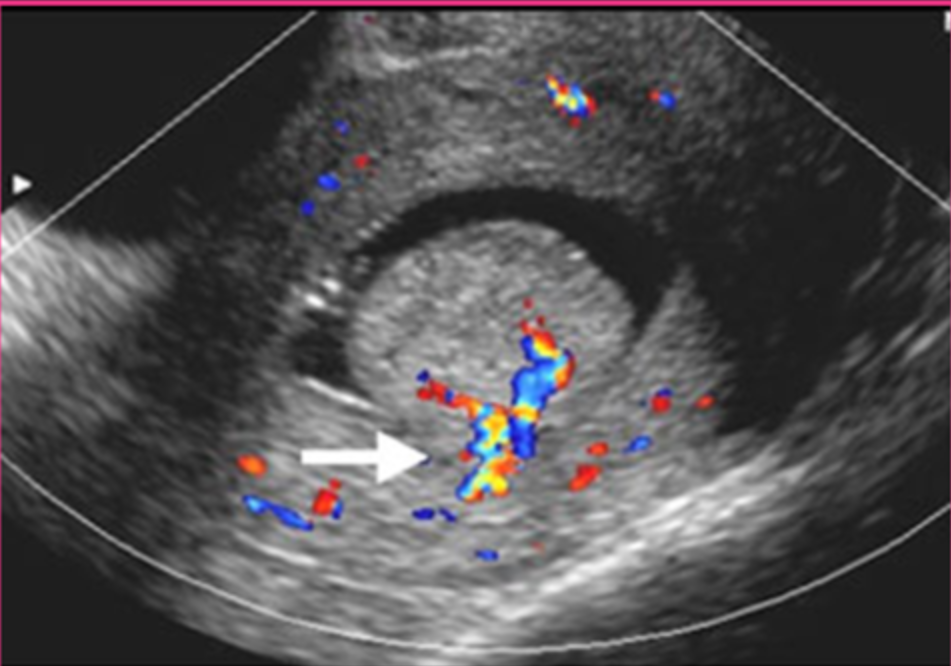
What is the sonographic appearance of endometrial polyps?
Isoechoic/hypoechoic to endometrium
Echogenic, round
Feeding artery