1: Amino acids and peptides
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is reaction thermodynamics?
Describes the energetic of chemical reactions
What is Gibbs free energy?
Energy of the reaction available to do work, also called ‘available energy’
How is ΔG calculated?
G(products) - G(reactants)
What is the difference between enthalpy and entropy?
enthalpy = heat
entropy = disorder
How is ΔG calculated?
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
change in Gibbs free energy = change in enthalpy - T x change in entropy
Is ΔG positive or negative for spontaneous reactions?
negative
Describe an exergonic reaction
ΔG = -ve
free energy released
favourable, spontaneous
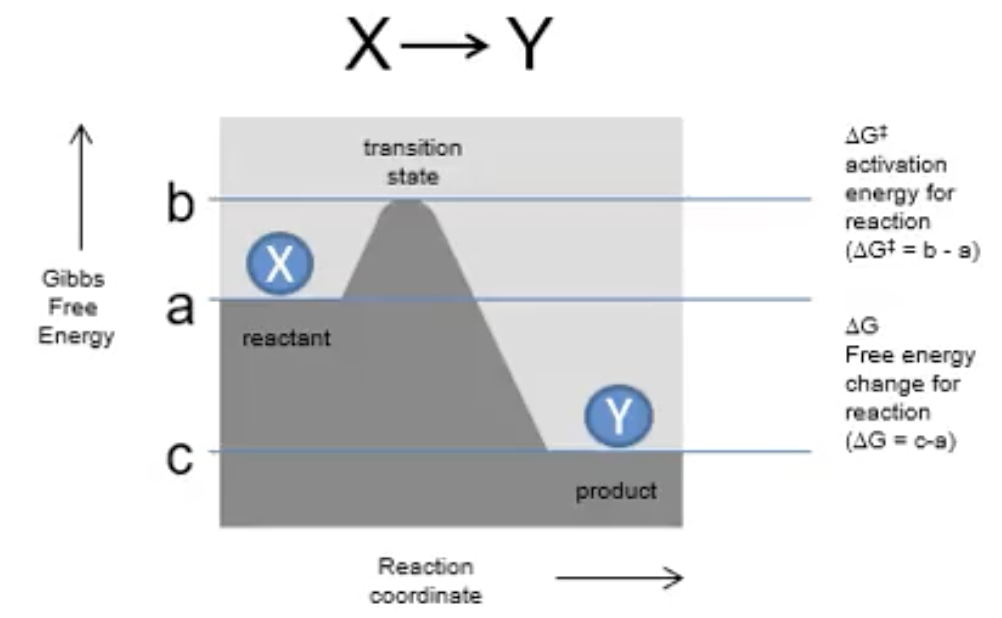
Describe an endergonic reaction
ΔG = +ve
free energy absorbed
unfavourable, not spontaneous
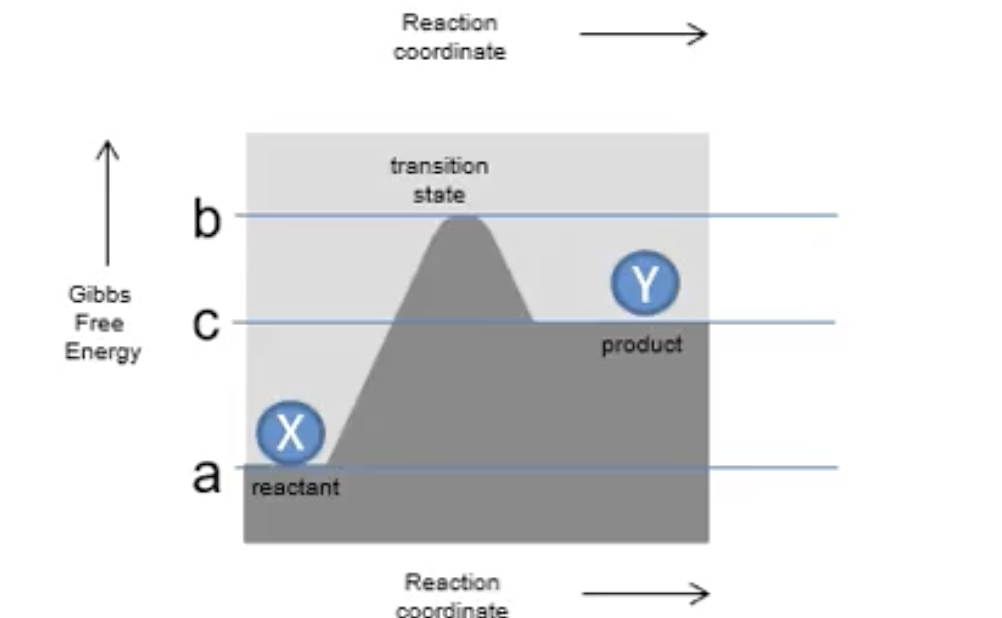
What is the difference between exergonic and endergonic reactions?
exergonic is spontaneous and free energy is -ve and released. endergonic is unfavourable and free energy is +ve and absorbed
What is the difference between exothermic and exergonic?
exothermic = heat released
exergonic = free energy released
What does +ΔS mean?
more disorder
What does -ΔS mean?
less disorder
What is Keqm?
equilibrium constant, describes the relative concentration of each components when reaction is at equilibrium
What is the expression for K?
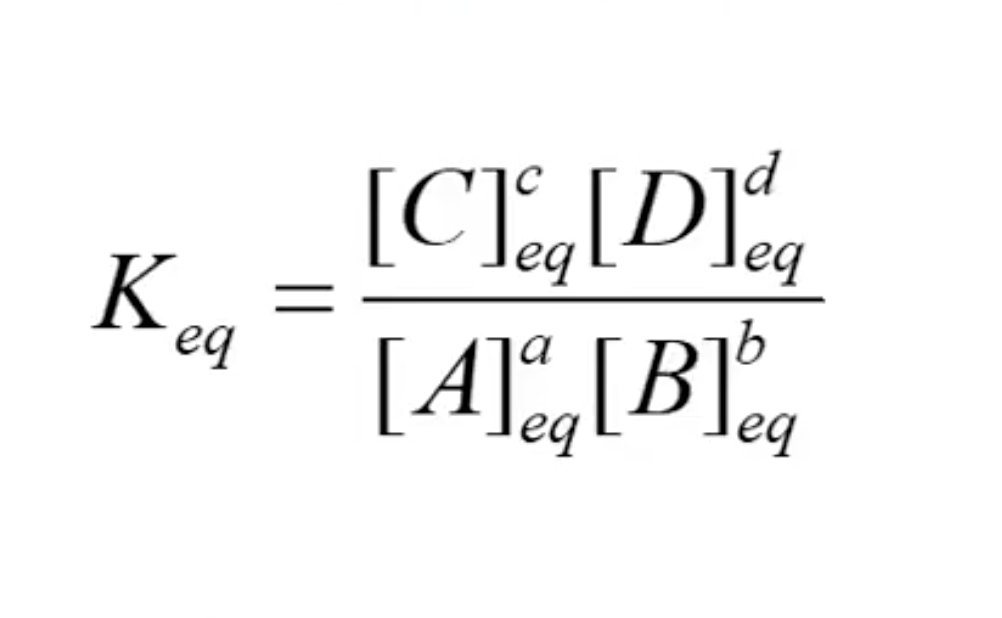
What is ΔGº?
the standard free energy change, a constant for the particular reaction which is measured upon standard conditions, measures how much work the reaction can do
How do ΔG and ΔGº differ?
ΔG is variable, ΔGº is a constant
How is ΔG calculated?
i for initial conditions
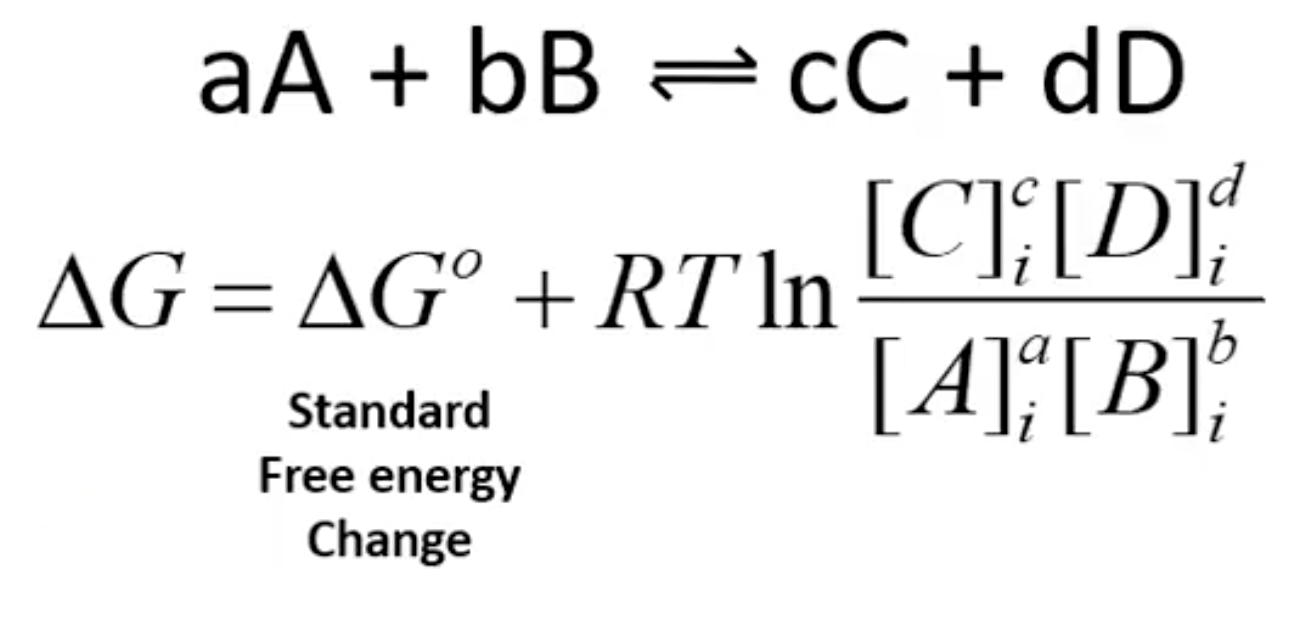
What is R?
universal gas constant
Why are standard conditions used?
to compare changed (like in free energy or pressure) easily
What is ΔG’º?
biochemistry standard conditions
298K (25ºC)
gases at partial pressure of 101.3 kPa (1 atm)
reactants and products at 1M
[H+] = 10-7
Mg2+ = 1mM
Why does ΔGº and ΔG’º differ?
ΔGº = standard conditions for chemists/physicists
use conditions that are suitable for chem/phys
ΔG’º = standard conditions for biochemists
use well buffered aqueous solutions at pH 7, like the body
When does ΔG = ΔGº?
when the concentration for products/reactants = 1
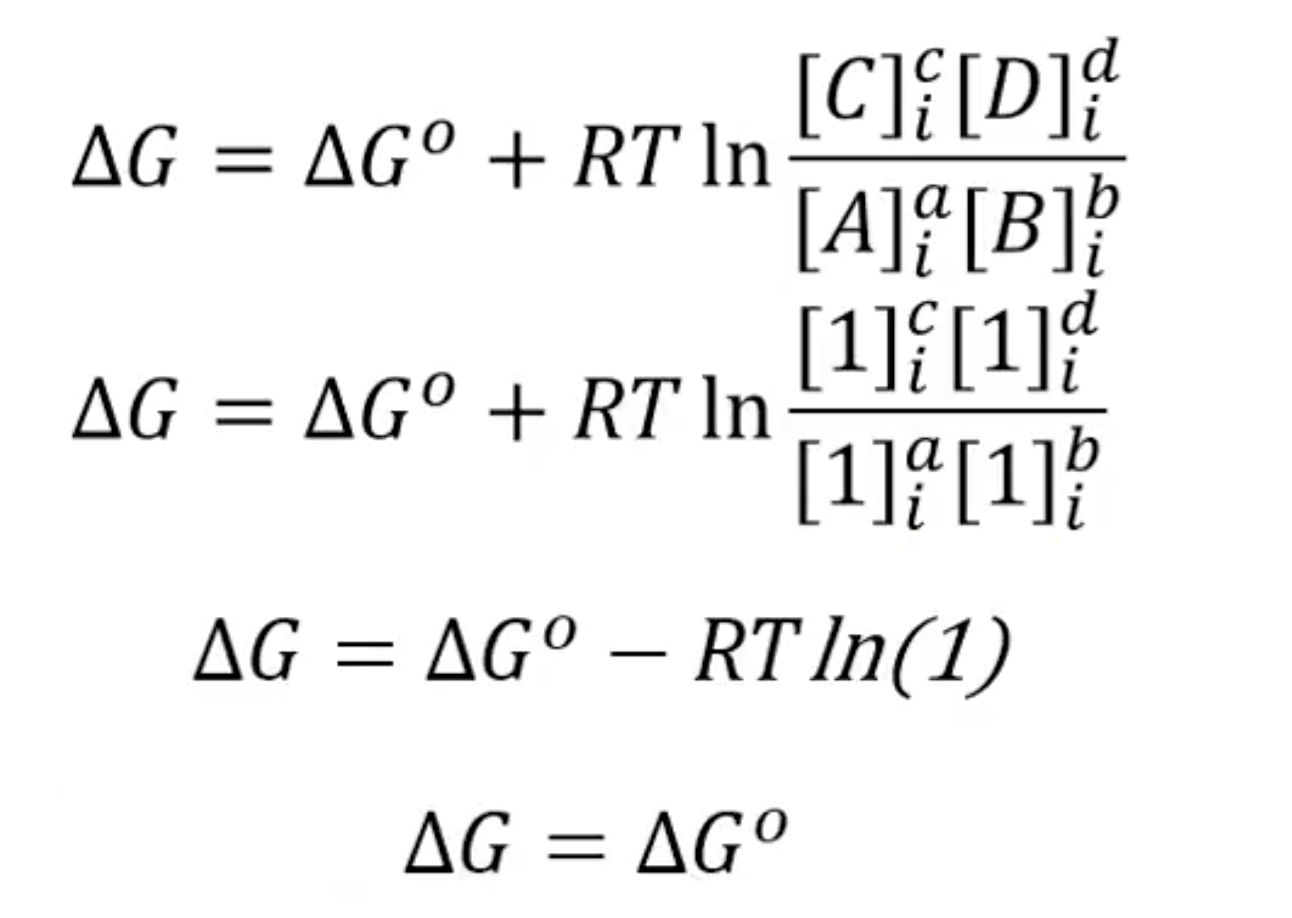
What is ΔG at eqm?
ΔG = 0
What are the three main equations for free energy?
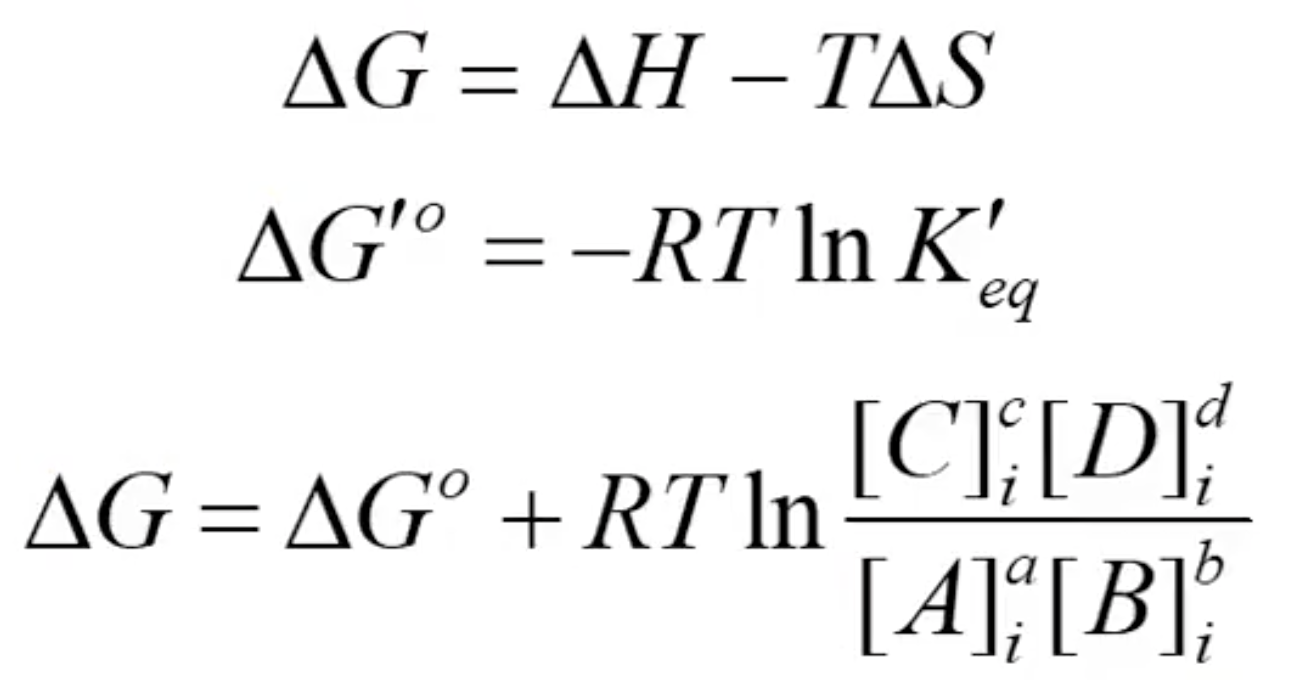
What term is most important to predict if a reactions is spontaneous?
ΔG
What is a kinetically driven reaction?
reaction where one or more of the products are being removed at a rate much faster than it is being produced OR
reaction where one or more reactants are being replenished at a faster rate than it is removed
How can you make an unfavourable reaction go?
replenish reactants (kinetic)
remove products (kinetic)
couple the unfavourable reaction with a highly favourable one (thermodynamic)
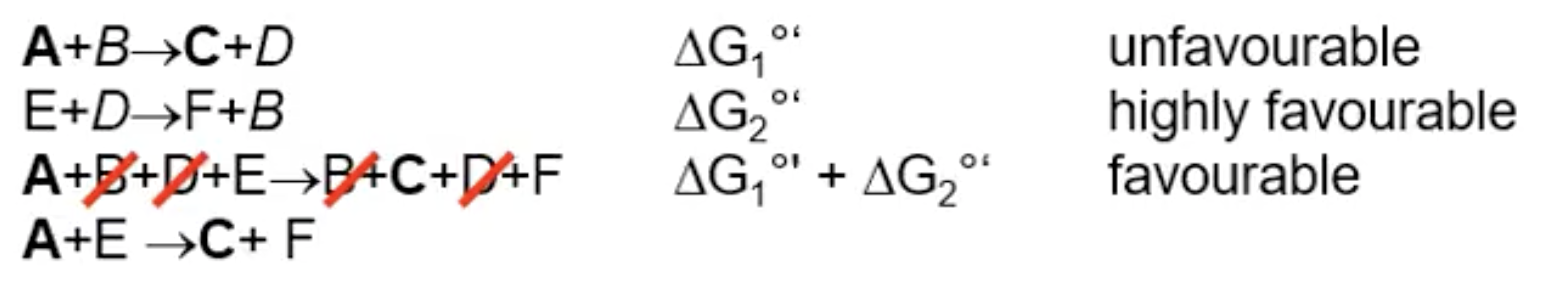
What do you need to keep in mind about coupling reactions together?
they are done under standard conditions, need to consider actual free energy/conditions in the cell
Does a positive change or a negative change in free energy indicate a favourable reaction?
negative
How is the free energy change of the reverse reaction related to that of the forward reaction?
If some spontaneous event is endothermic, what must have been the “driving force” behind that event, enthalpy or entropy?
enthalpy as thermic = heat, entropy = free energy
If a reaction has a positive DG′⁰ it is often described as ‘unfavourable’. What is wrong with this statement?
It can still occur, it just need extra energy added for it to occur
Explain why energy is released when ATP is hydrolysed and why energy is absorbed when ATP is formed from ADP and Pi.
What is a nucleotide?
base + sugar + phosphate
What is a nucleoside?
base + sugar like ADP
What is the difference between a nucleotide and nucleoside?
nucleoside is just base + sugar like ADP
nucleotide is base + sugar + phosphate like ATP
What is ATP?
adenosine triphosphate
a nucleotide (adenine + ribose + three phosphate)
Where bond released energy in ATP when broken?
phosphoanhydride bonds
Is energy required or released when bonds are broken and repaired?
breaking bonds = energy absorbed
forming bonds = energy released
What is the ATP → ADP reaction?
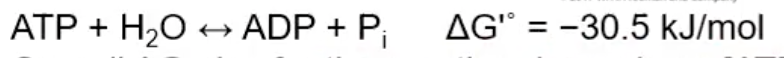
Is ATP → ADP exergonic or endogonic?
exergonic (release free energy)
Why is ATP → ADP exergonic?
ATP (-4) less stable because it has higher negative charge density than ADP (-3)
Pi is very stable; multiple resonance stated exist
ATP phosphoanhydride bonds are very weak
ADP phosphoanhydride and Pi bonds are very strong
What are proteins and what are they used for?
main agents of biological function
used in:
catalysis
transport
structure
motion
signalling (transduction)
What are proteins made of?
linear heteropolymers of α-amino acids
What are functions of amino acids?
capacity to polymerise
useful acid-case properties
varied physical propertirtes
varied chemical functionality
What is the structure of amino acids?
tetrahedral (Sp3 central carbon)
central carbon
acidic carboxyl group (COO-)
basic amino group (NH3+)
hydrogen
R group (unique)
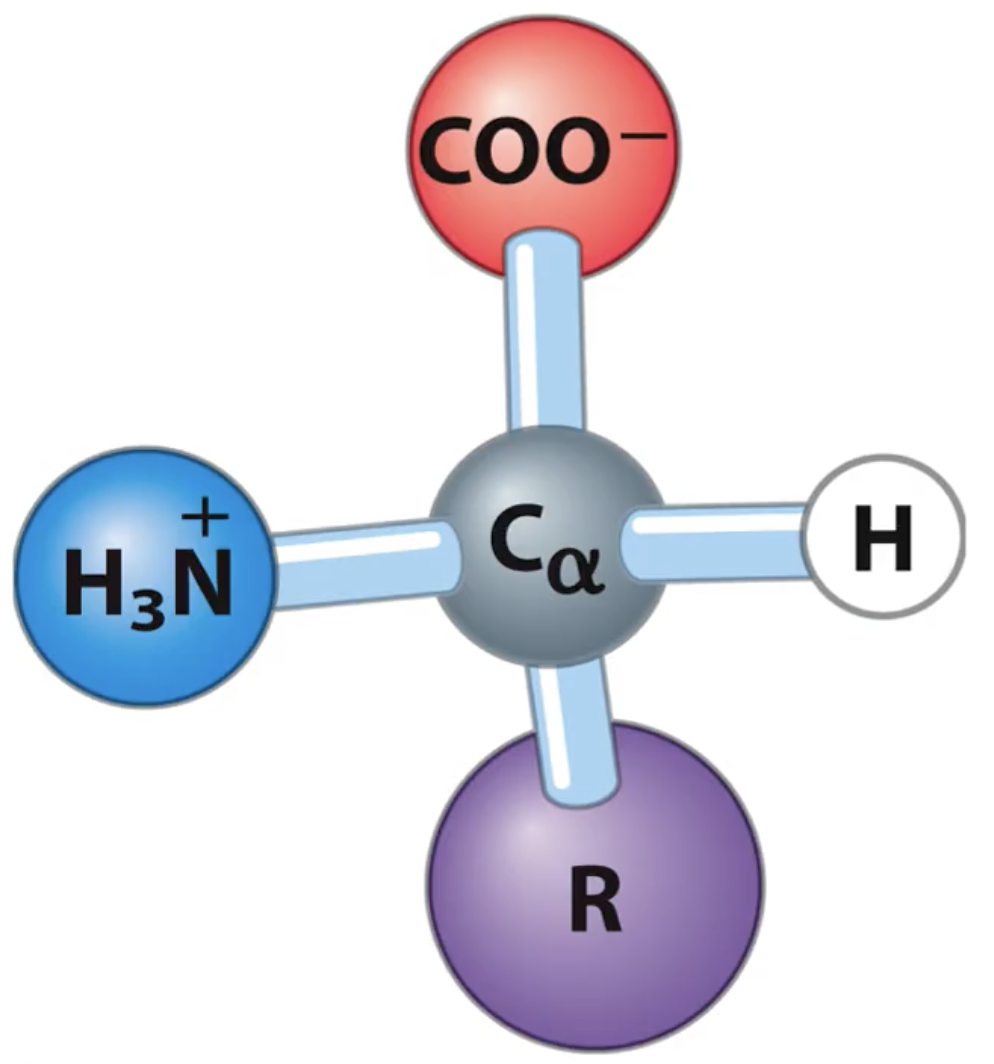
Are amino acids chiral?
Yes! Because they are tetrahedral and have different substituents bonded.
Are naturally occurring proteins L- or D- amino acids?
L
What are D- and L- amino acids?
stereoisomers, optical isomers
D = dextrorotatory (+), right, clockwise
L = levorotatory (-), left, anticlockwise
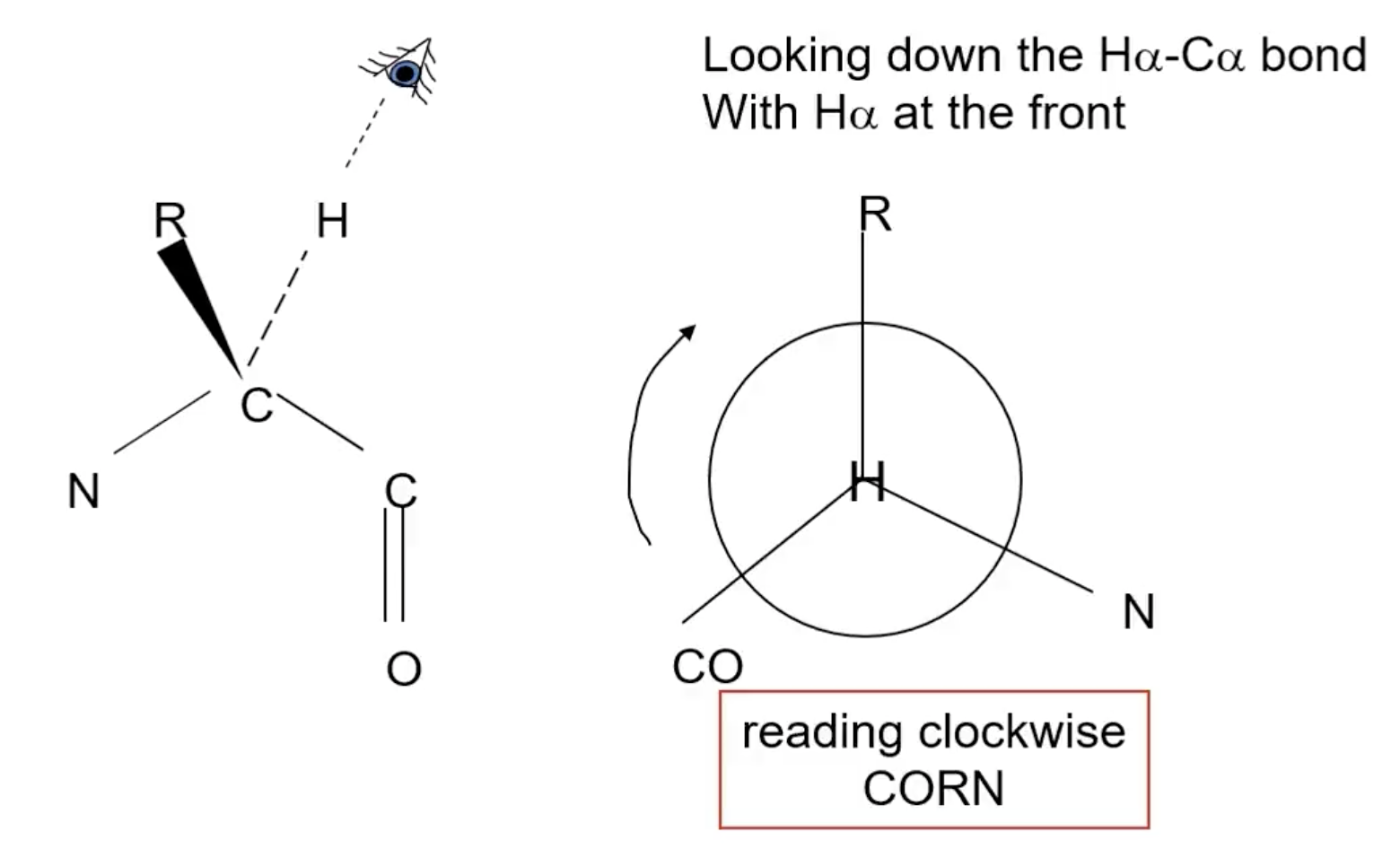
How to determine chirality rotation?
place H to the back, if CORN can be read clockwise = L
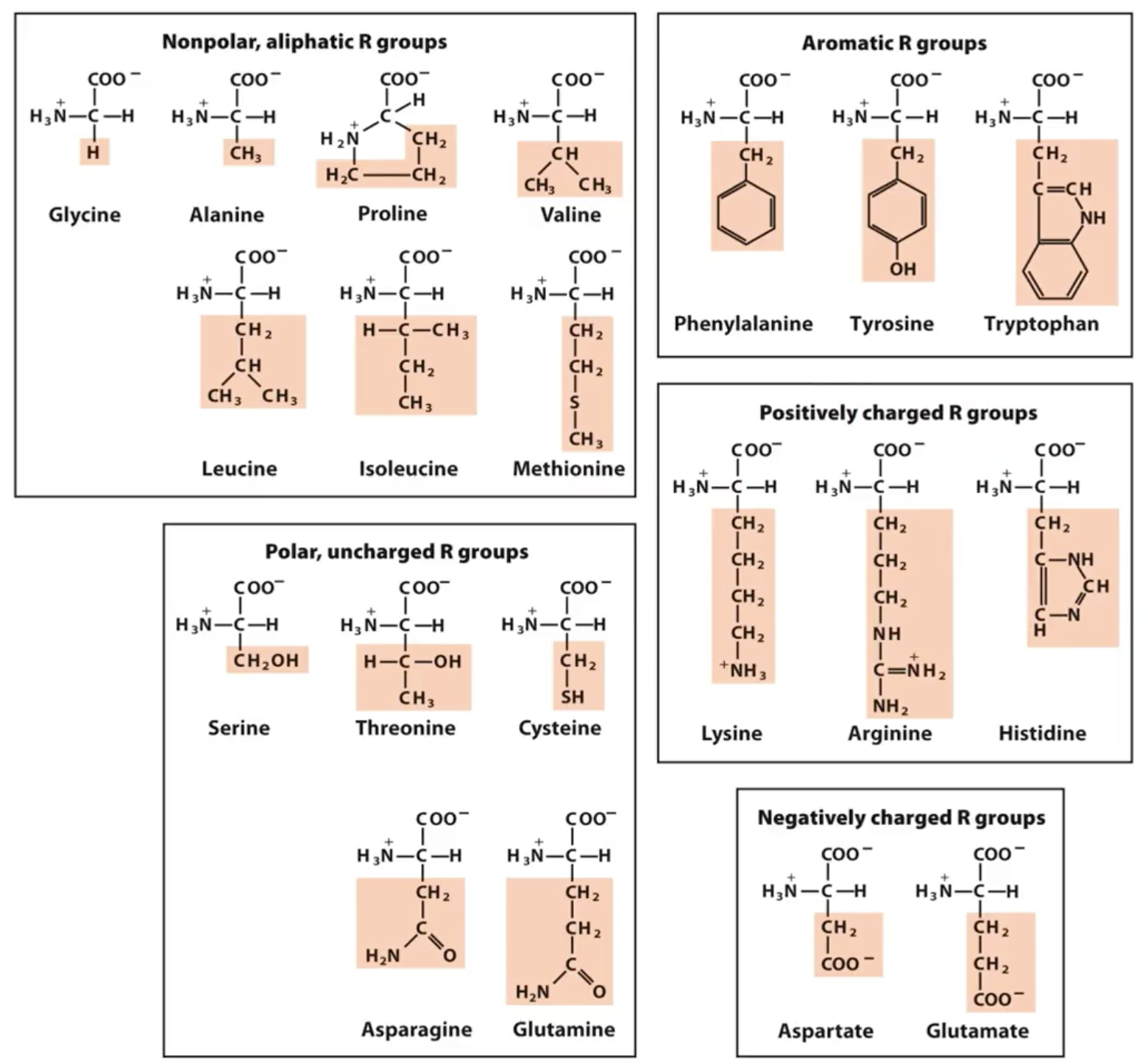
How can amino acids be categorised?
polar/non-polar
aliphatic/aromatic
charged/uncharged/negative/positive
What is pKa?
pH when an ionisable group is 50% protonated, 50% de-protonates
How are the side chain atoms lettered?
greek alphabet
backbone = alpha
beta
gamma
delta
epsilon
zeta
eta
what is a guanidino group?
trigonal planar of central C and three Ns surrounding it
What is the Beer-Lambert law?
A = εcl
absorbance = extinction coefficient/molar coefficient x concentration x path length
What are aromatic side chains responsible for?
most ultraviolet absorbance and fluorescence properties of proteins
What does aliphatic mean?
relating to oils and fats, alkanes, almost exclusively hydrogen and carbon
What is lysozyme and what does it do?
a protein/enzyme which cleaves the polysaccharide chains in the cell walls of bacteria
What is the native conformation of a protein?
fold with the lowest free energy, therefore it is favoured over mis-folded/semi-folded states.
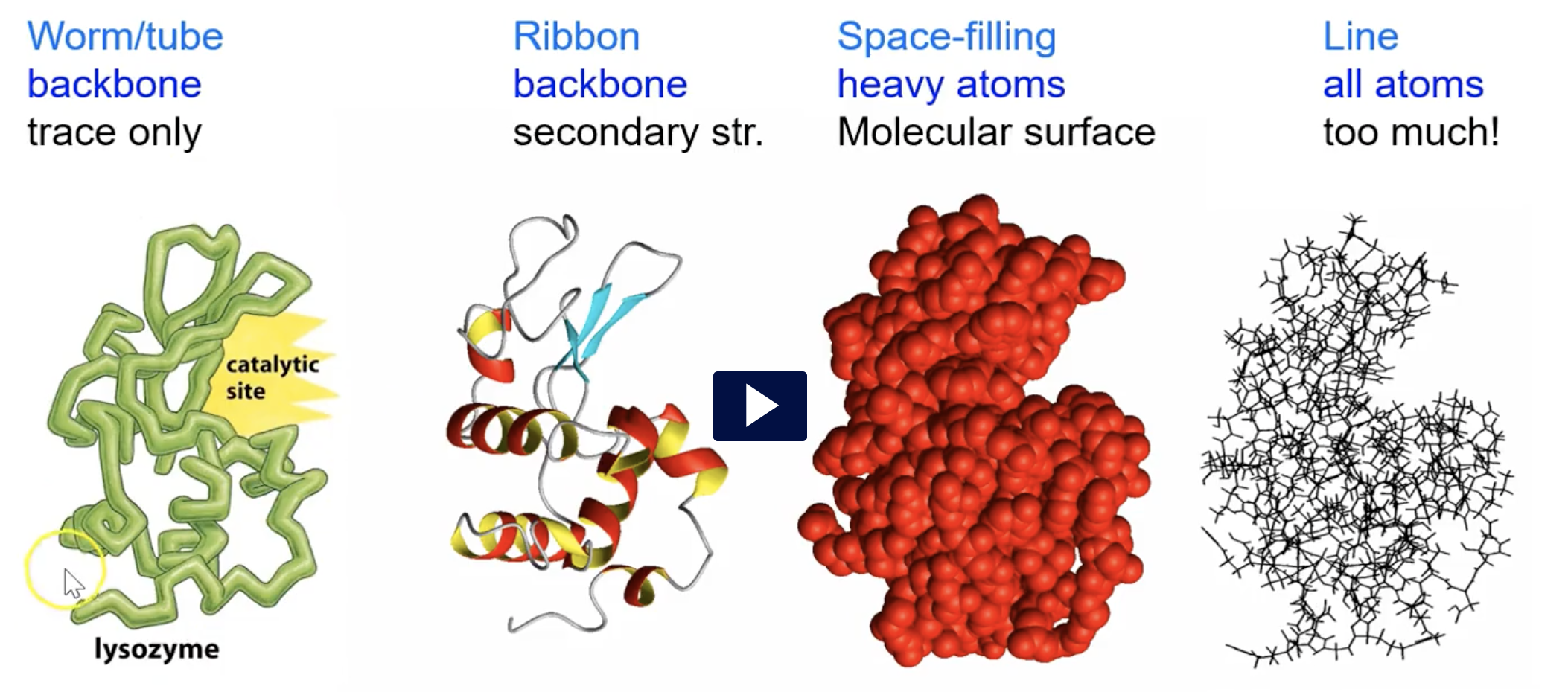
How are protein structures represented?
worm/tube - backbone - trace only
ribbon - backbone - secondary structure
space-filling - heavy atoms - molecular surface
line - all atoms
How are peptide bonds formed?
carboxylic acid group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of the next one to form a peptide bond through a dehydration reaction
What is the N- and C-terminus and how are they formed?
N- = +ve Nitrogen terminus
C- = -ve Carbon terminus
the order and structure of amino acids is fixed, so when they form a polypeptide chain, there will always be a positive and negative terminal
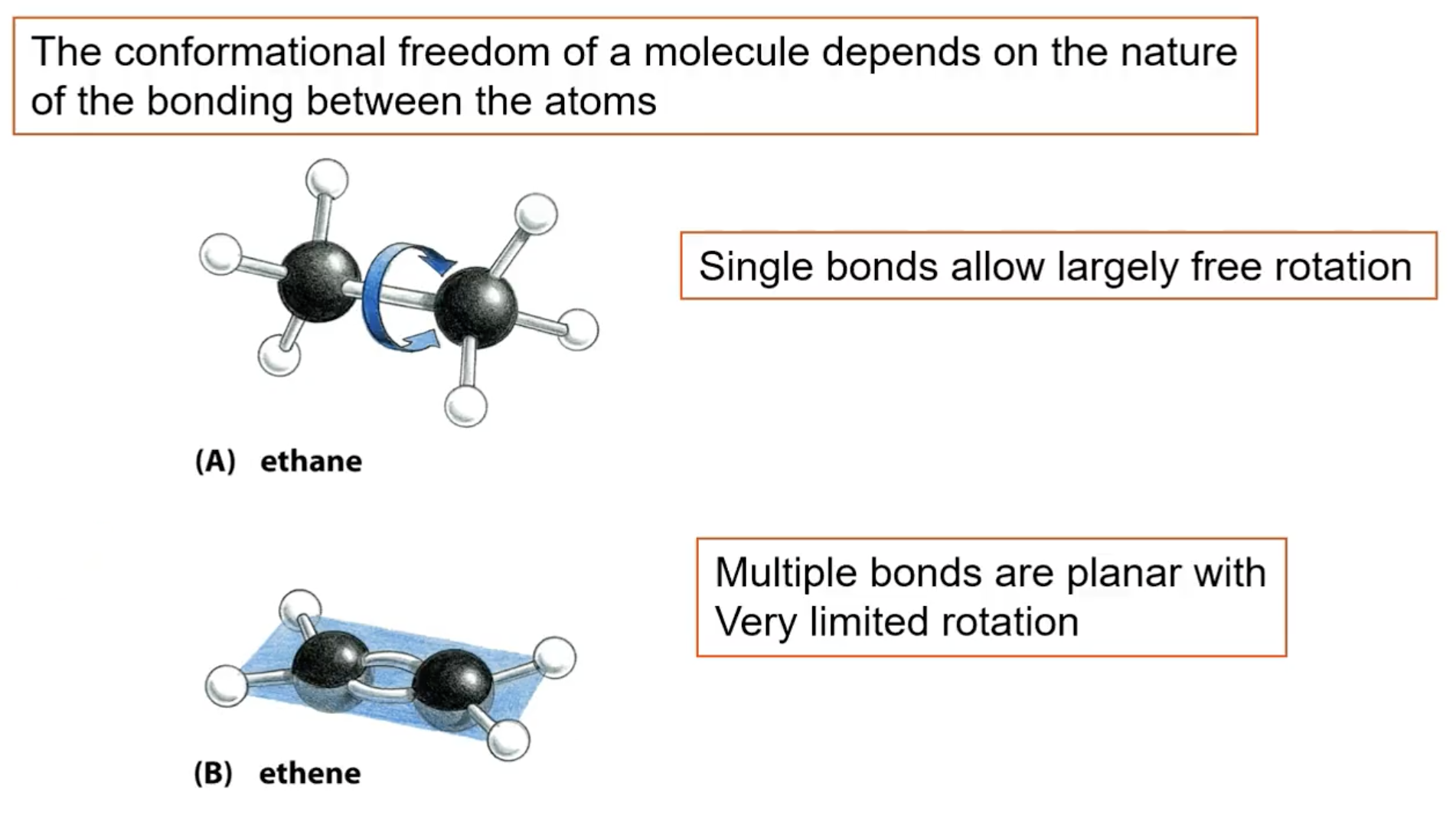
How do bonds affect rotation?
single bonds allow free rotation
multiple bonds are planar with very limited movement
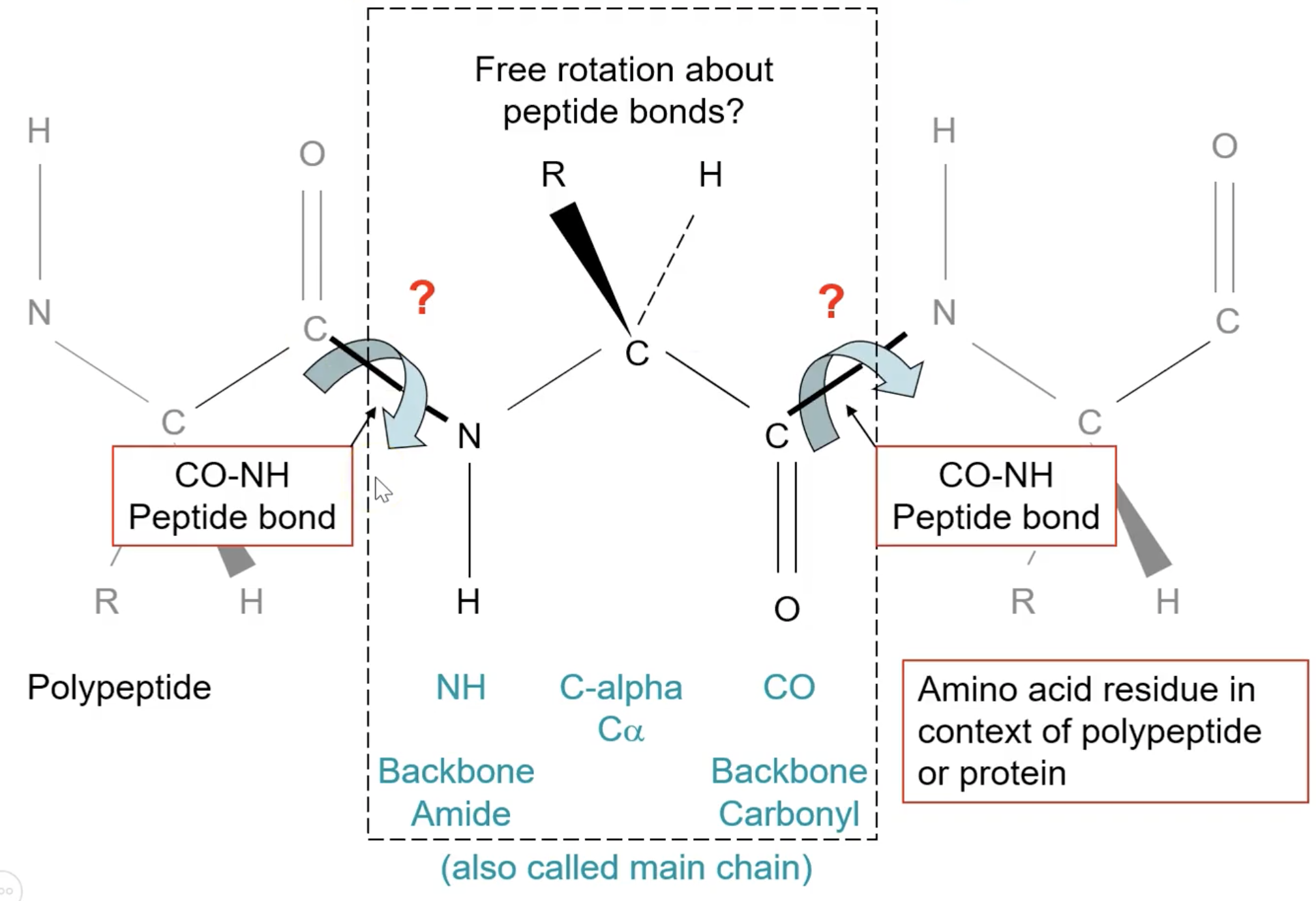
What is the peptide bond geometry? Where are the peptide bonds?
(-N-Cα-C)peptide(-N-Cα-C-)…
Can peptide bonds have isomers?
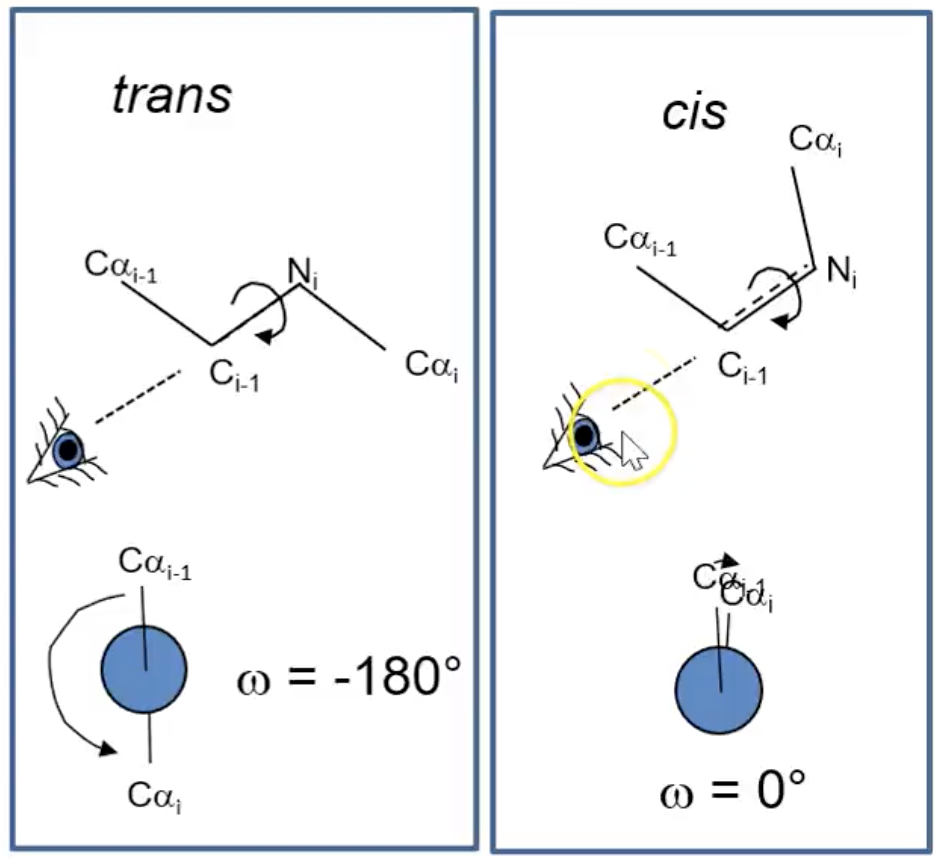
Yes! Due to partial double bonds, can have cis and trans isomers
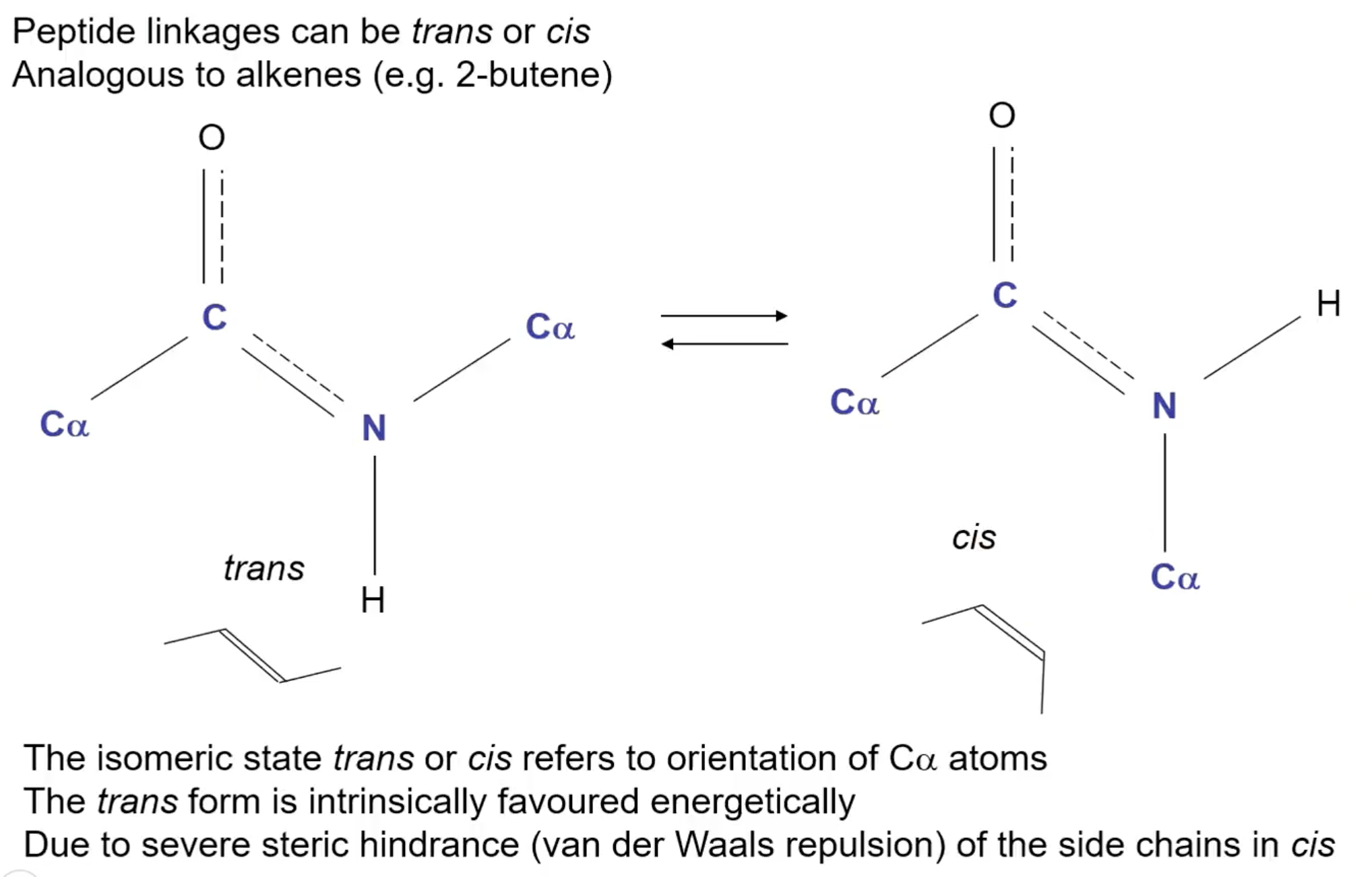
Are cis or trans conformations favoured in peptide bonds?
Trans due to steric hinderance of the CO - Cα on opposing amino acids - EXCEPT for proline where cis is favoured
What order are amino acids in a polypeptide labeled?
N → C terminus
i-2, i-2, i, i+1, i+2
True or False: peptides bonds are flat and planar
true
trans omega (ω) bonds
ω = -180º
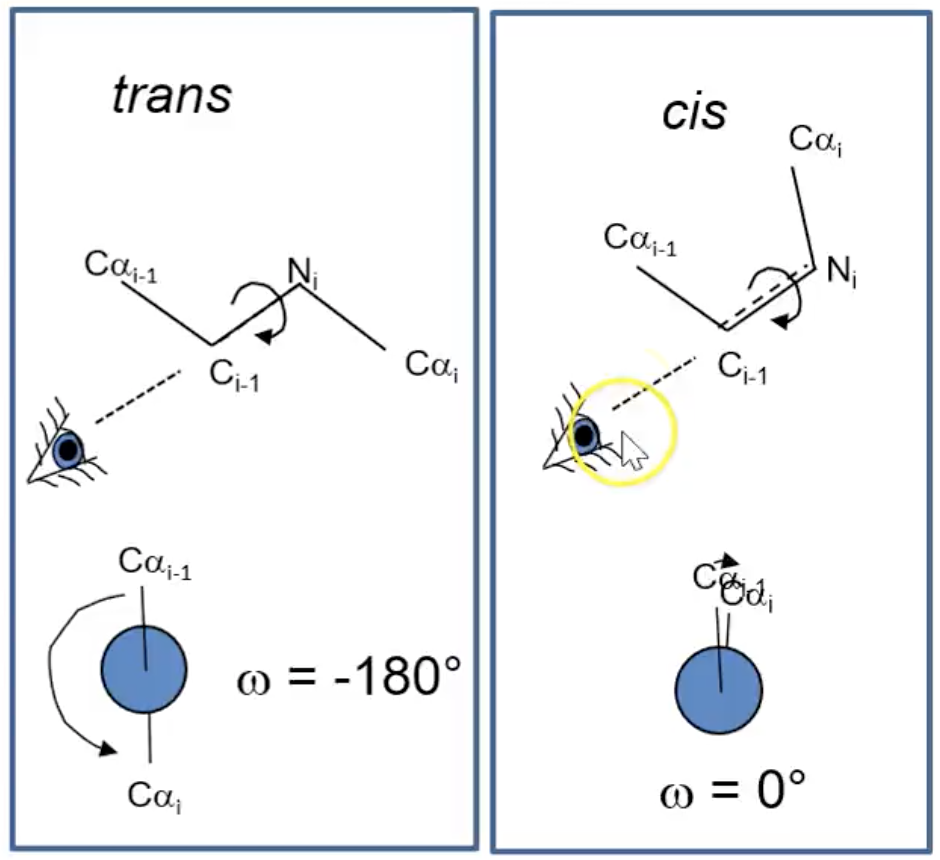
cis (ω) bond
ω = 0º
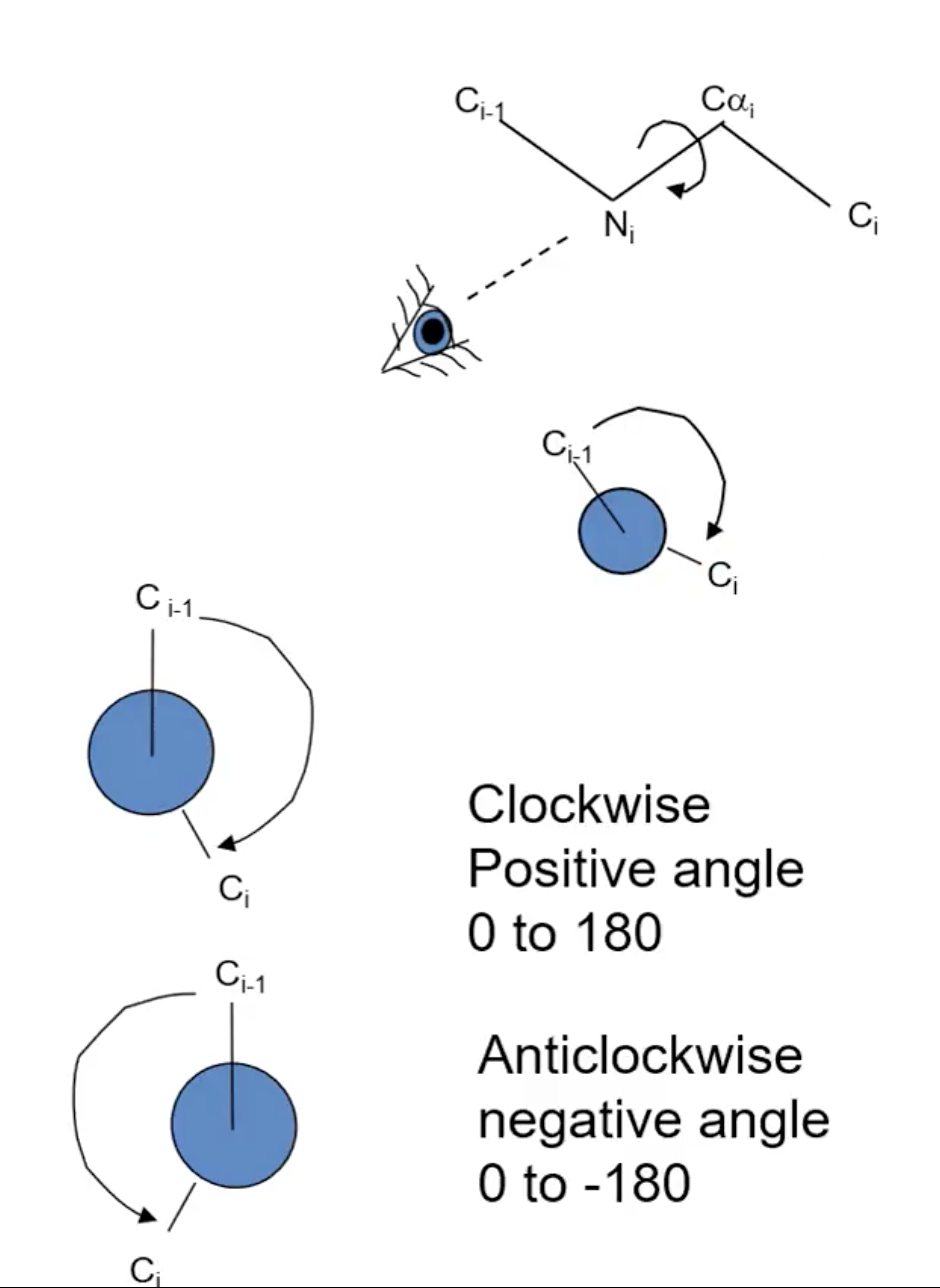
How do proteins fold if there is limited movement in the CO - NH backbone peptide bond?
via. the N - Cα - C single bonds within an amino acid = dihedral angles
What are dihedral angles?
the N - Cα - C single bonds within an amino acid
N - Cα = φ angle (phi)
Cα - C = Ψ angle (psi)
What is the φ angle (phi)?
N - Cα, comparing the C(O)s
What is the Ψ angle (psi)?
Cα - C, comparing the Ns
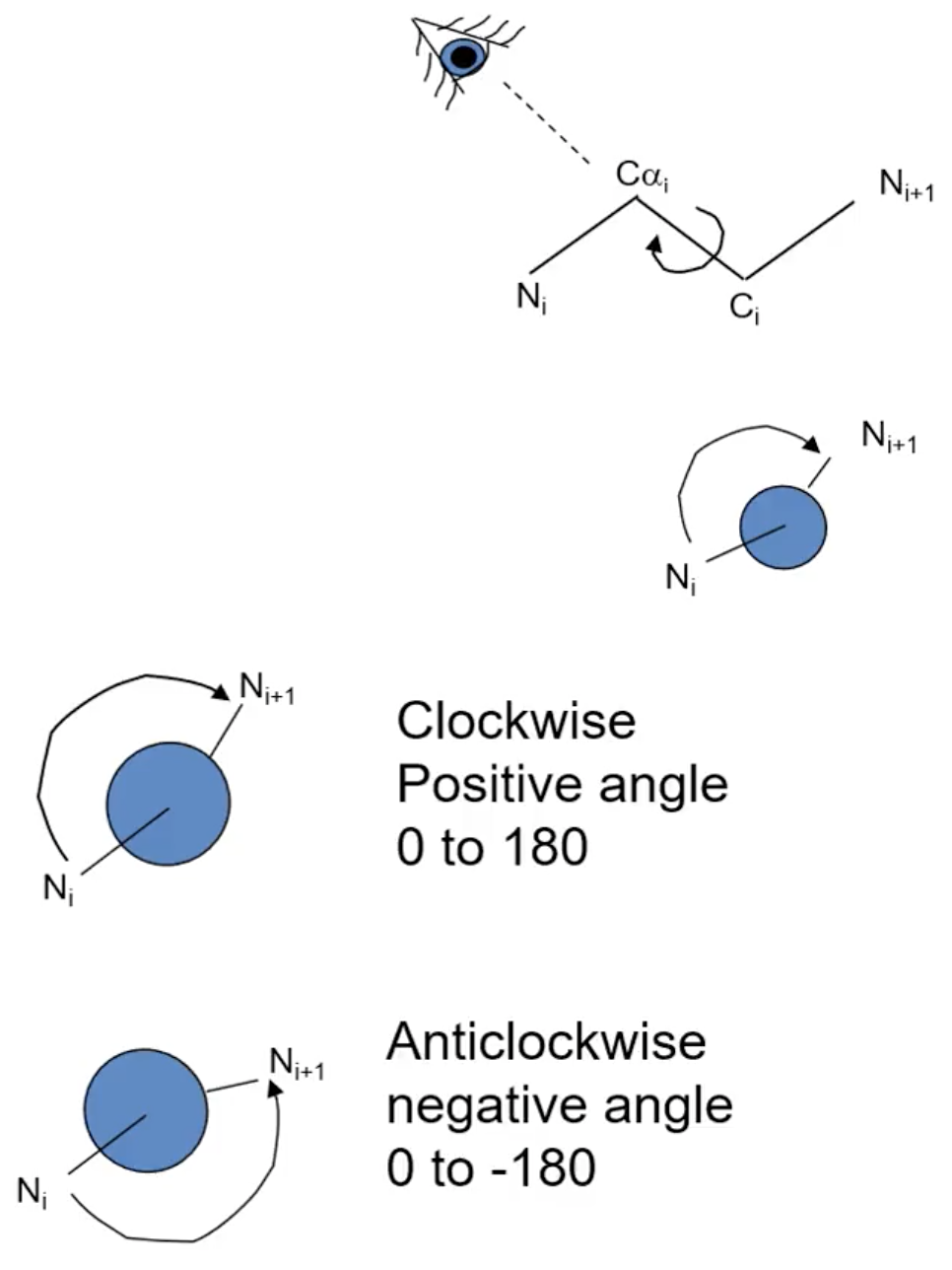
Why are φ and Ψ so important?
because, if assuming all the peptide bonds are trans, the only conformational freedom is between these dihedral bonds, everything else is fixed
What are side chain dihedral angles called?
χ (chi)
χ1 between Cα and Cbeta
χ2 between Cbeta and Cgamma
χ3 between Cgamma and Cdelta