Biol 300 Class 2.3: DNA Replication Diagram | Quizlet
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What are the two types of DNA Synthesis?
Synthesis involved in Replication and Synthesis involved in Repair
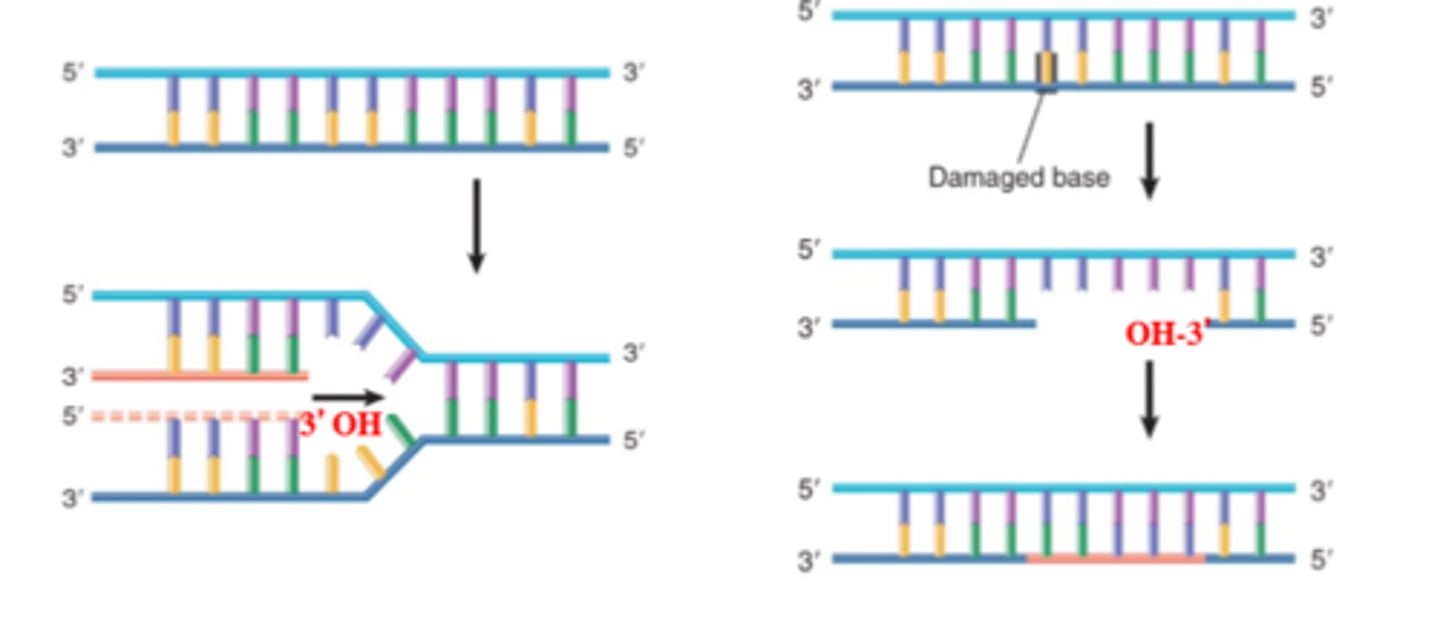
Is every Polymerase involved in replication?
Not all polymerase is involved in replication.
What is replicase?
DNA pol that can synthesize a new DNA strand on a template
What arethe DNA Polymerases found in E. Coli?
1. polA
2. polB
3. polC
4. dinB
5. umuD2C
TERM
What is the function of polA?
DEFINITION
It replaces primers in Okazaki Fragments, major repair enzyme
What is the function of polB?
Replication restart when forks stalls at damaged site
TERM
What is the function of polC?
DEFINITION
MAJOR replicase, part of large transient complex replisome
What is the function of dinB and umuD2C?
Translesion replication, Repair; synthesize DNA using template strand that contains the damaged bases
What is the error rate of DNA Replication?
~10^-3 per nucleotide replicated
What are the two types of errors that DNA Replication can make?
1. Frameshifts
2. Substitutions
What causes Frameshift mutations?
When an extra nucleotide is added or a nucleotide is removed; this is often prevented because the enzyme is processive. Most common in homopolymeric regions which can cause slippage
What causes Substitution Mutations?
A wrong nucleotide is incorporated; rate of error depends on proofreading. It is easily fixed on new strands
What is the function of Proofreading?
All DNA Polymerase has its own 3'-5' exonuclease activity
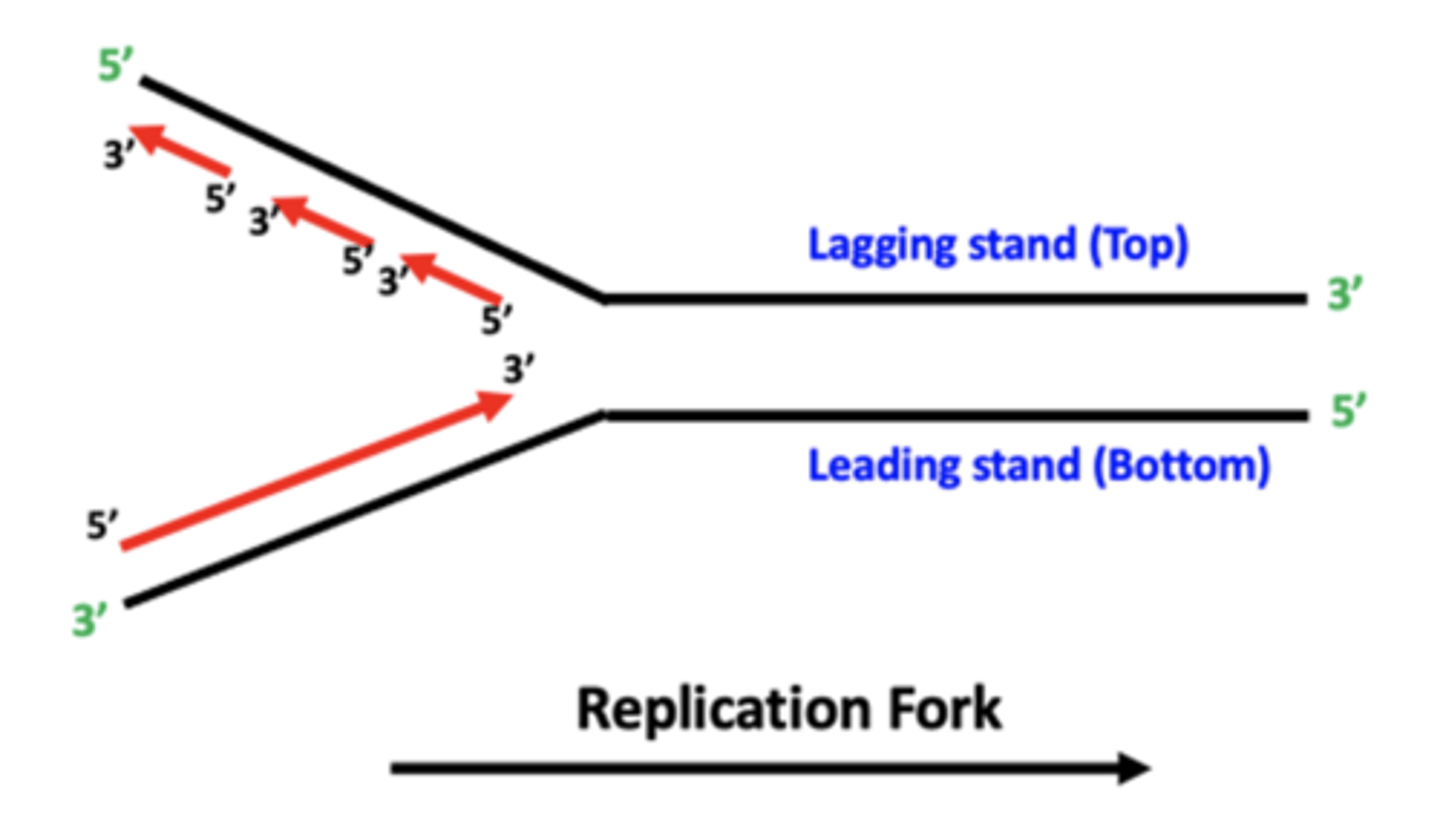
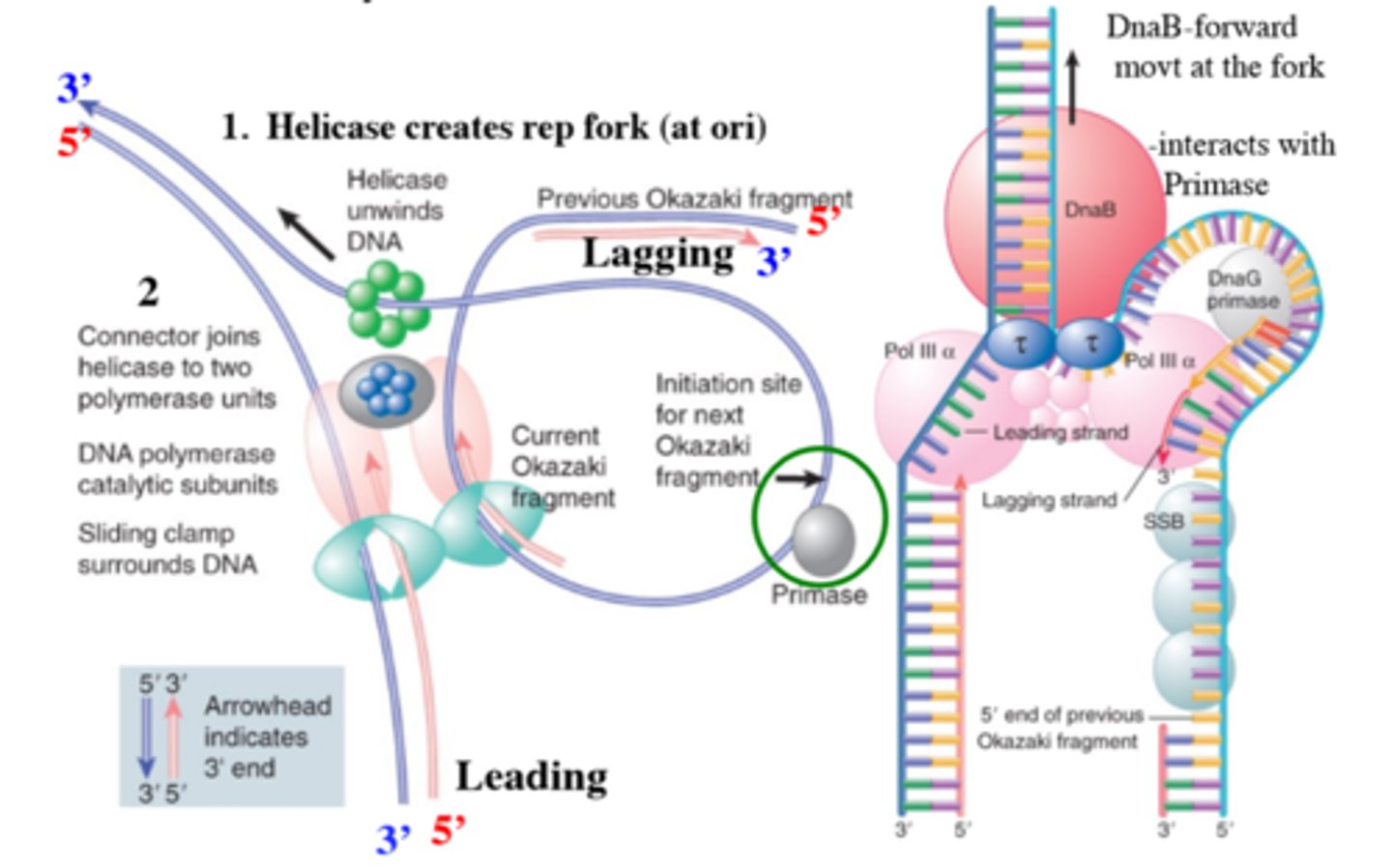
Describe synthesis of two DNA Strands
Replication is semi conservative and semi discontinuous, it is synthesized from 5' to 3' and the leading strand is continuous while the lagging strand is discontinuous.
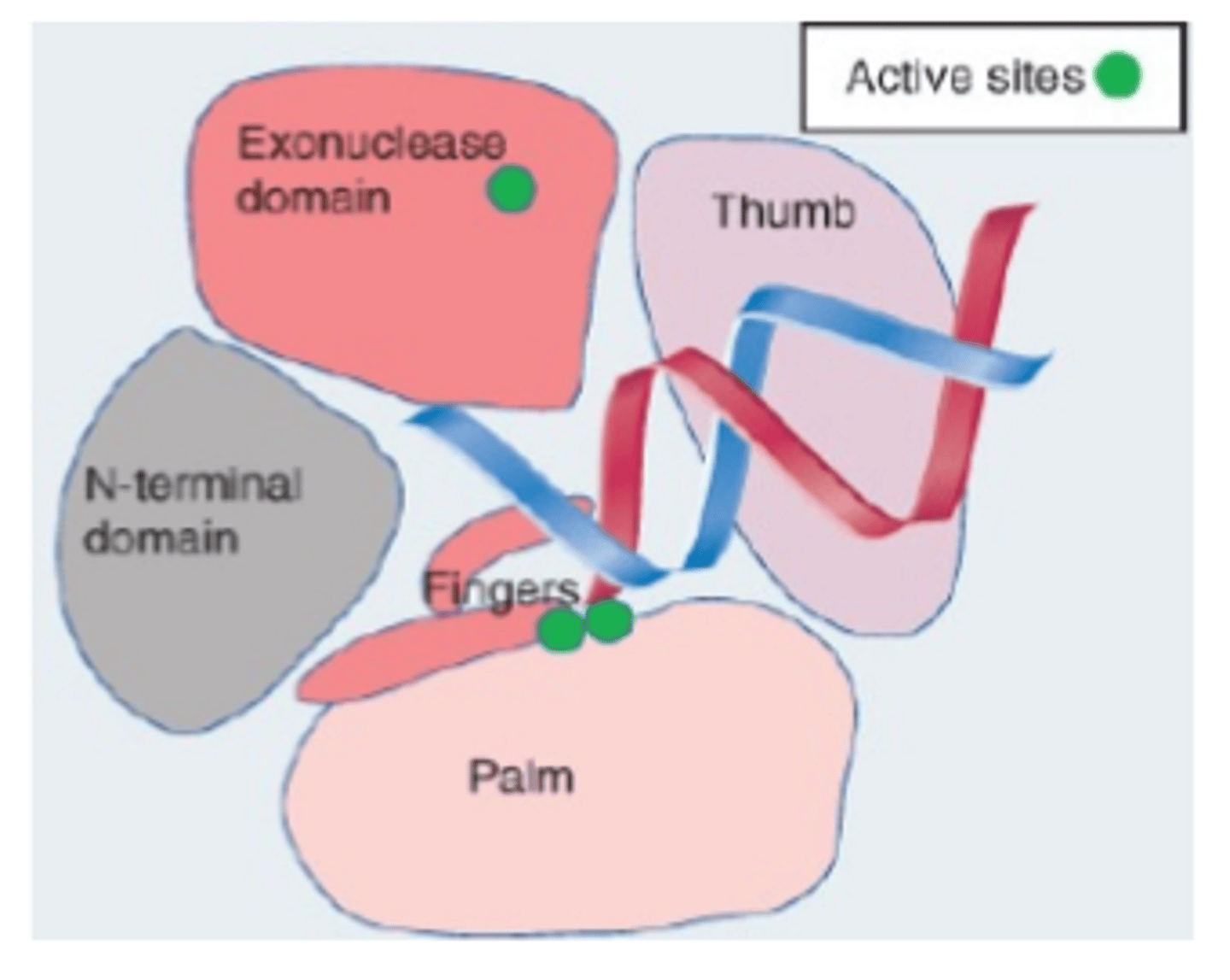
What is the common way to show Core Enzyme Domains of Polyermase?
Analogous to human right hand, Palm is the catalytic active site, Fingers are what positions the template correctly in the active site, and the Thumb binds DNA as it exits the enzyme Processivity.
What is Exonuclease Activity? How does it occur?
This is editing, it occurs in the 3 to 5 direction
What is the N-Terminal domain for during replication?
It acts as a spacer between Polymerase and exonuclease domains.
What is the Catalytic Core of DNA Pol 3 comprised of?
Alpha Subunit, Epsilon Subunit, and Theta Subunits
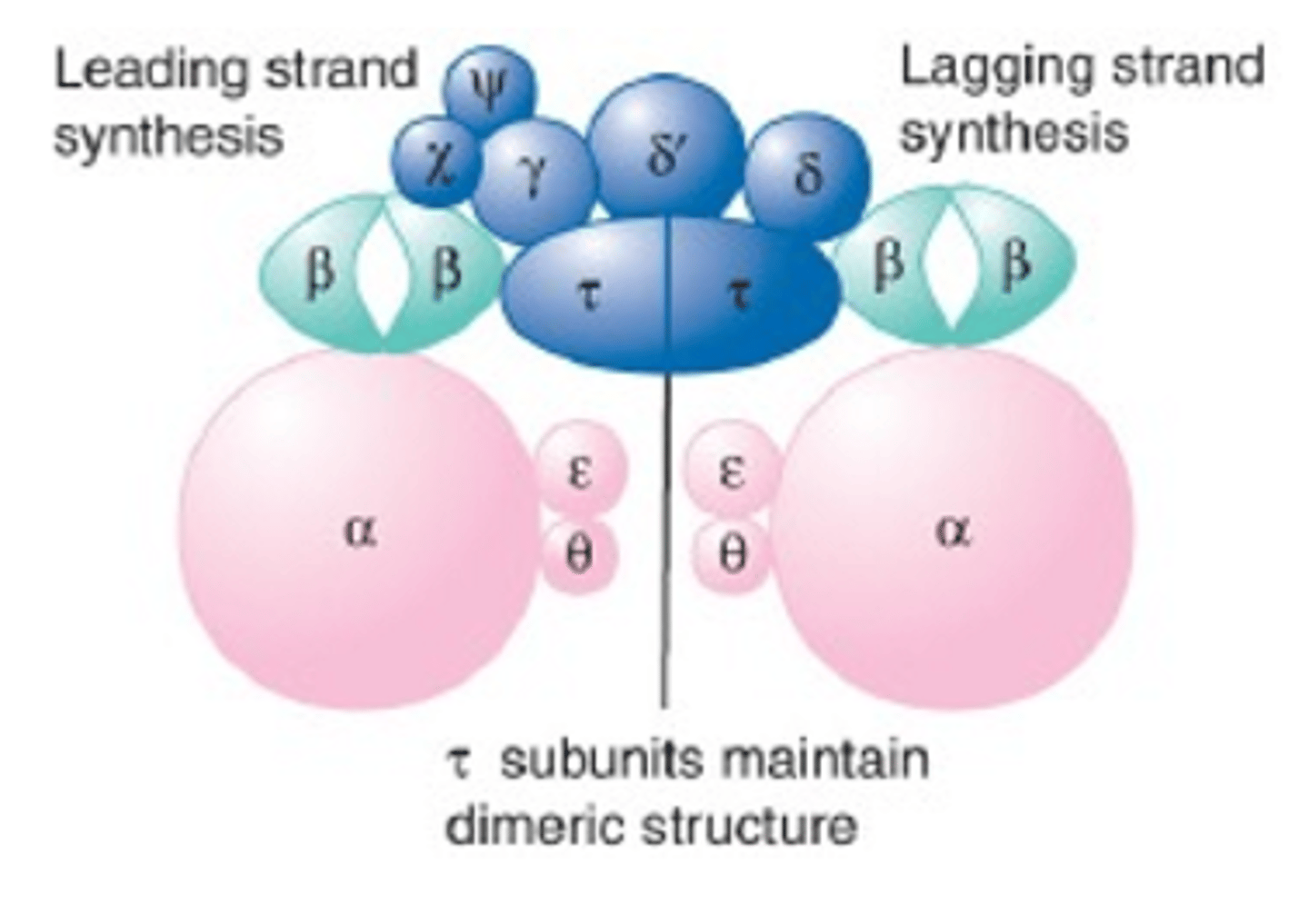
What is the function of DNA Pol 3 Alpha Subunit?
It is responsible for DNA Binding and Polymerase Activity (Palm Fingers Thumb and N Spacer)
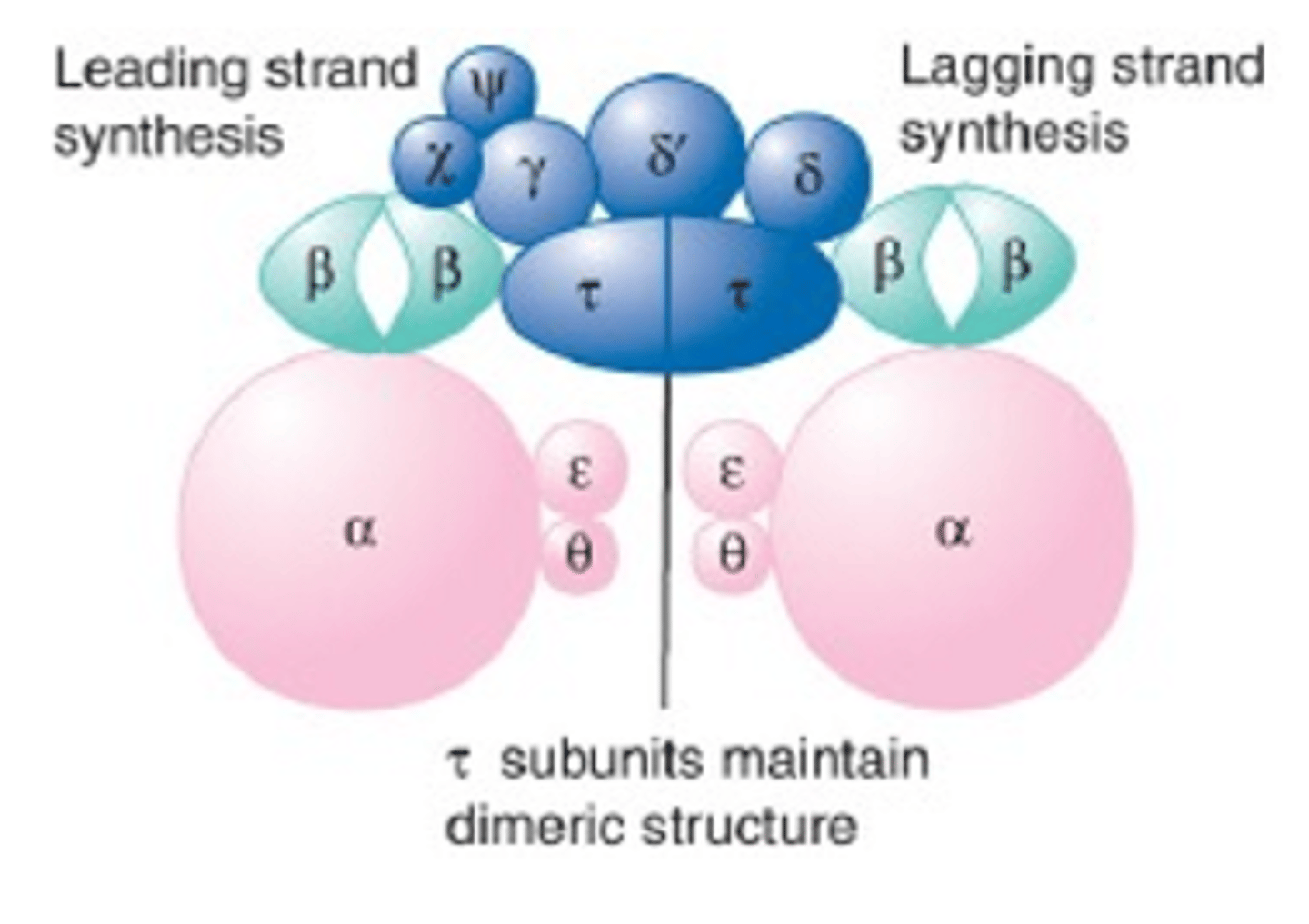
What is the function Dimerizing Subunit for DNA Pol 3?
AKA Tau Subunit, it links the two cores together
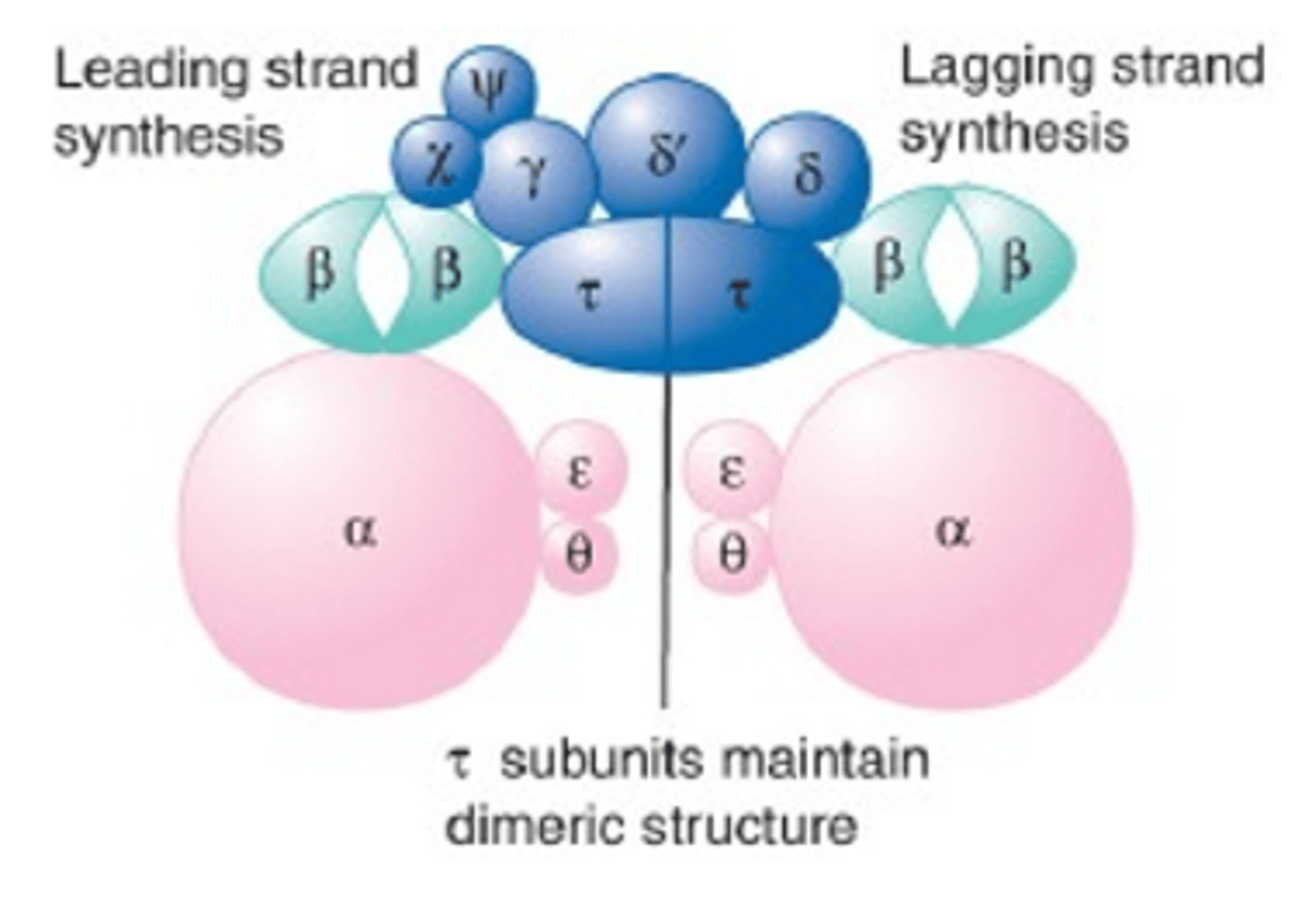
What does the Clamp do in DNA Pol 3?
It holds the Pol 3 Catalytic Core onto the DNA Template; they are Homodimers of the Beta subunit and binds around DNA ensuring processivity
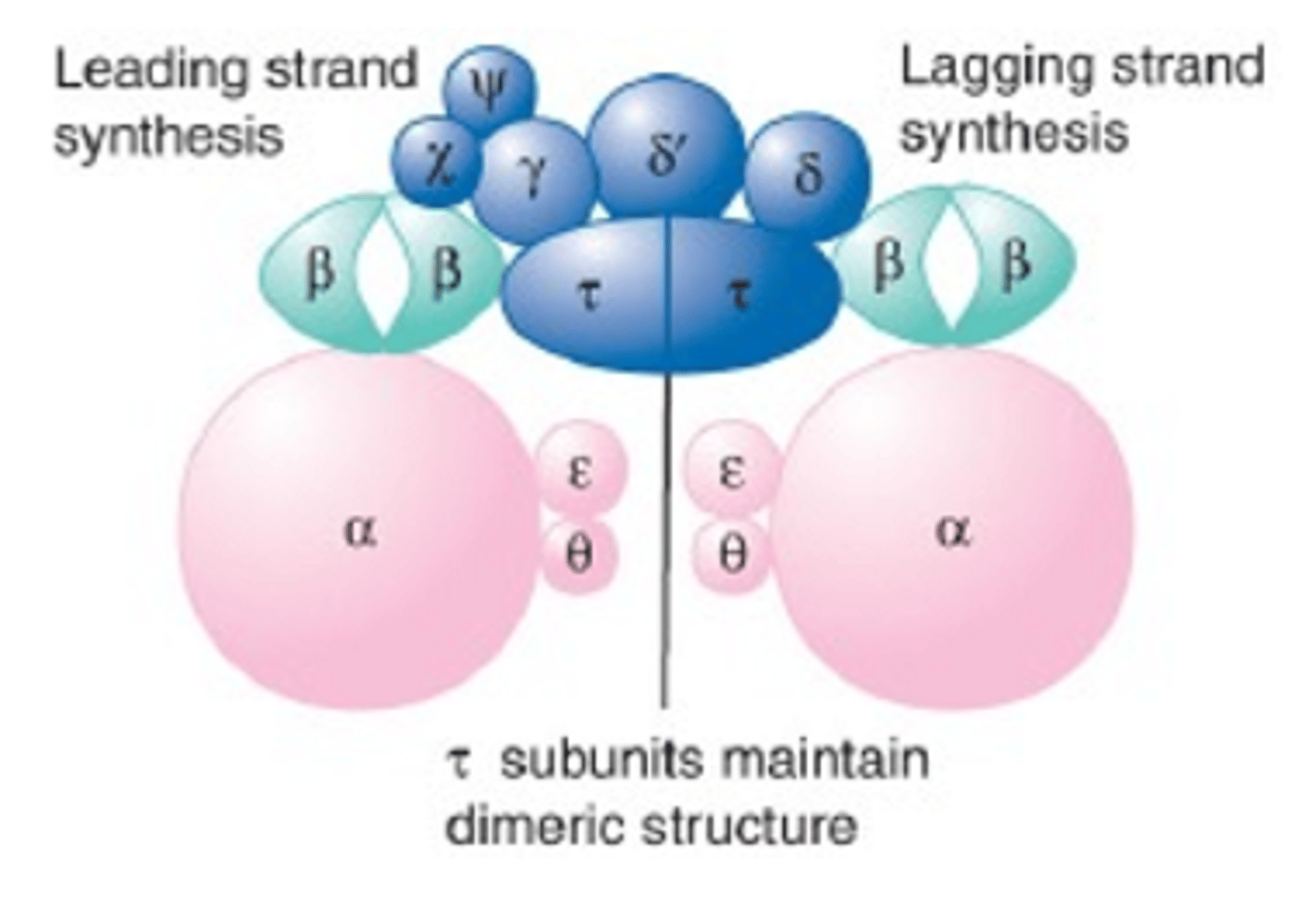
What is the Clamp Loader in DNA Pol 3?
AKA The Gamma Complex which consists of 5 proteins needed to place and release the clamp on DNA
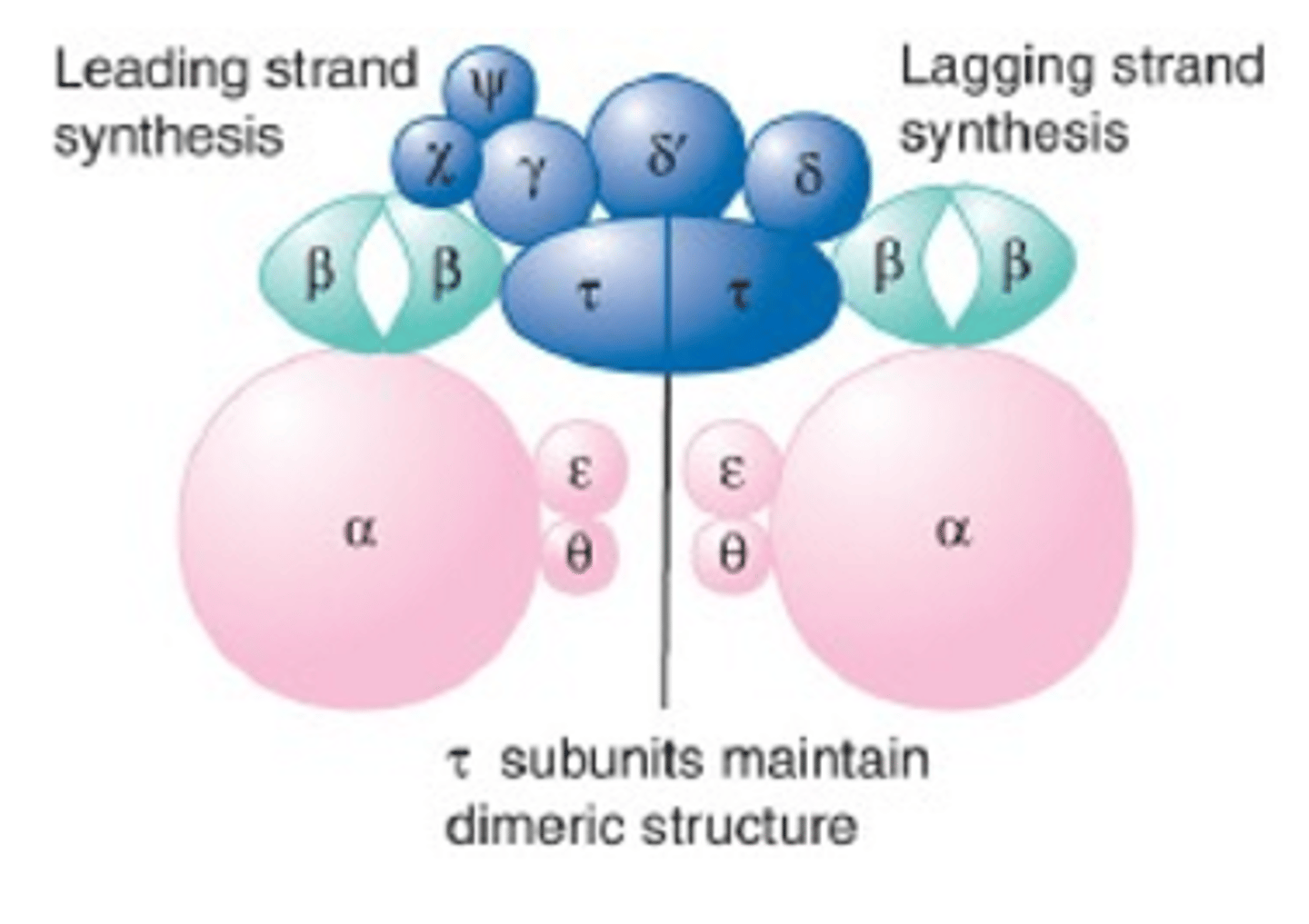
What are the three stages of the Holoenzyme Assembly?
1. Clamp loader Hydrolyzes ATP
2. Binding of DNA changed conformation
3. The Tau Dimer binds the core
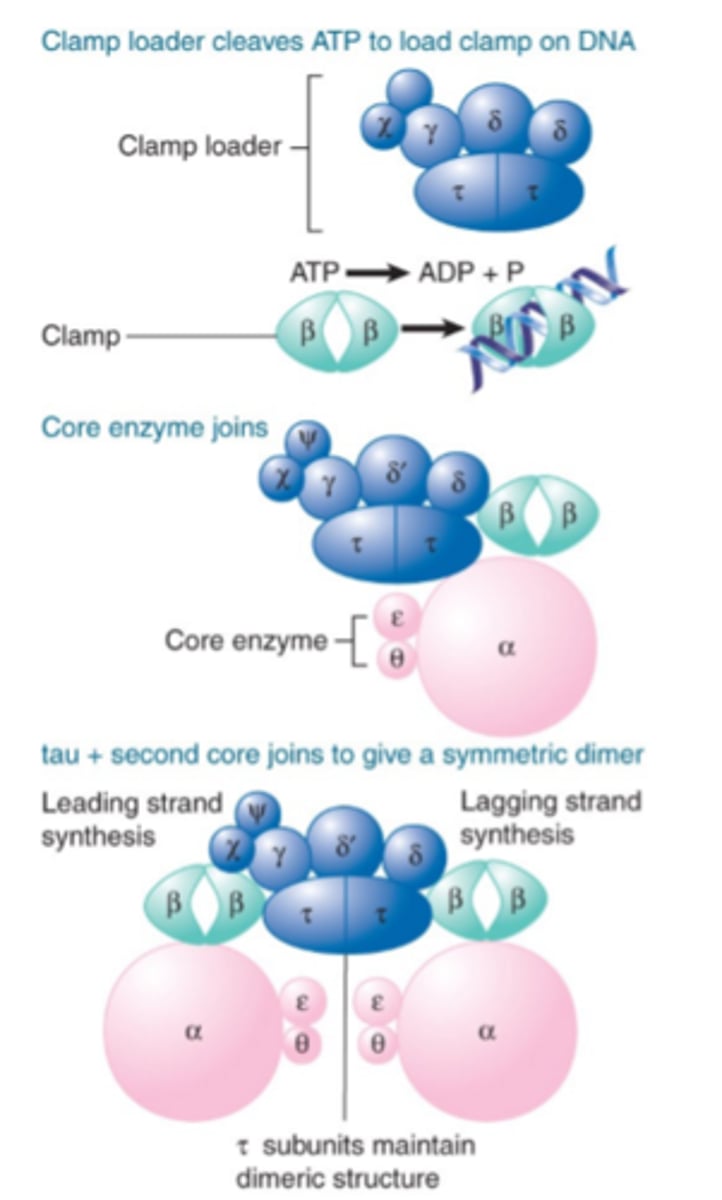
What is the Dipolymerase Model?
Explains how the leading strands and lagging strands are synthesized at the same time. Two Catalytic Cores
TERM
What Unwinds DNA at the replication fork?
DEFINITION
DnaB otherwise known as DNA Helicase.
TERM
What prevents Pol 3 dissociating from DNA?
DEFINITION
The DNA Clamp
TERM
What provides the RNA Primer?
DEFINITION
DnaG otherwise known as Primase