Cell Membrane Study Guide
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the Channel’s Function
Passing molecules through membrane
What is the Carrier’s Function
Transfer after changing shape to support substance
What is the Cell Recognition’s Function
Recognise cells to see if they are harmful or not
What is the Receptor’s Function
They contain a shape that only allows certain molecules to pass
What is the Enzymatic’s Function
Carry direct metabolic reaction
Hypertonic v. hypotonic solutions
Hypertonic makes cells shrink and hypotonic makes them grow and almost burst
What substance is analogous to a factory manager and In what organelle would this substance be found?
DNA/ Chromosomes and Nucleus
Which cell organelle controls the activities of the entire cell?
Nucleus
Which organelle generates energy to power cellular activities?
Mitochondria
Which organelle is responsible for assembling proteins?
Ribosomes
Once proteins have been assembled, to which organelle would they go next?
Rough ER
Into what organelle might the cellular products be placed?
Vacuole
The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration:
Diffusion
The movement of water across a membrane:
Osmosis
A solution that has more molecules (like salt) outside the cell is a _______ solution.
Hypertonic
Cells in a Hypertonic solution will gain or lose water?
Lose
A solution that has less molecules (like salt) outside the cell is a _______ solution.
Hypotonic
Cells in a Hypotonic solution will gain or lose water?
Gain
A solution that has the same number of molecules as the cell is an _______ solution.
Isotonic
This disease is caused by a failure of the cell membrane, which causes mucus to build up in the lungs:
Cystic Fibrosis
Cell membranes will let some things pass through them, this means they are:
Semipermeable
Type of transport that does not require energy:
Passive Transport
Type of transport that does require energy:
Active Transport
When molecules are even throughout a space, it is called:
Equilibrium
This organelle pumps out excess water:
Contractile Vacuole
The maintaining of a biological balance, or sameness:
Homeostasis
The outer boundary of all cells, its job is to move things in and out of the cell:
Cell Membrane
Type of transport where a cell takes in a large particle, like food:
Endocytosis
Type of transport where a cell pushes out large particles, like waste:
Exocytosis
Type of transport where proteins channels help move molecules across the membrane:
Facilitated Diffusion
When will Glucose Diffuse
If it is to big and polar
What order does the Endomembrane System occur in
Nucleus
Ribosome
Rough ER
Vesicle
Golgi Apparatus
Vesicle
Cytoskeleton
Cell Membrane
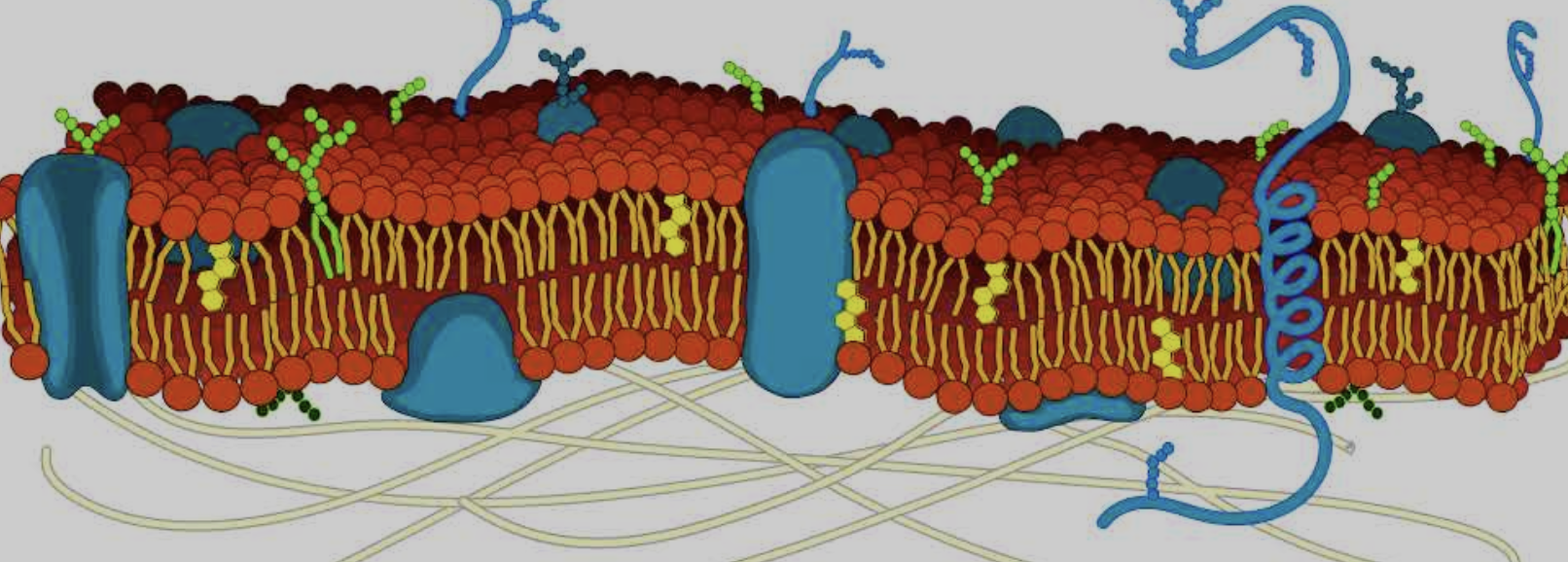
What is the cytoskeleton
Yellow lines on bottom
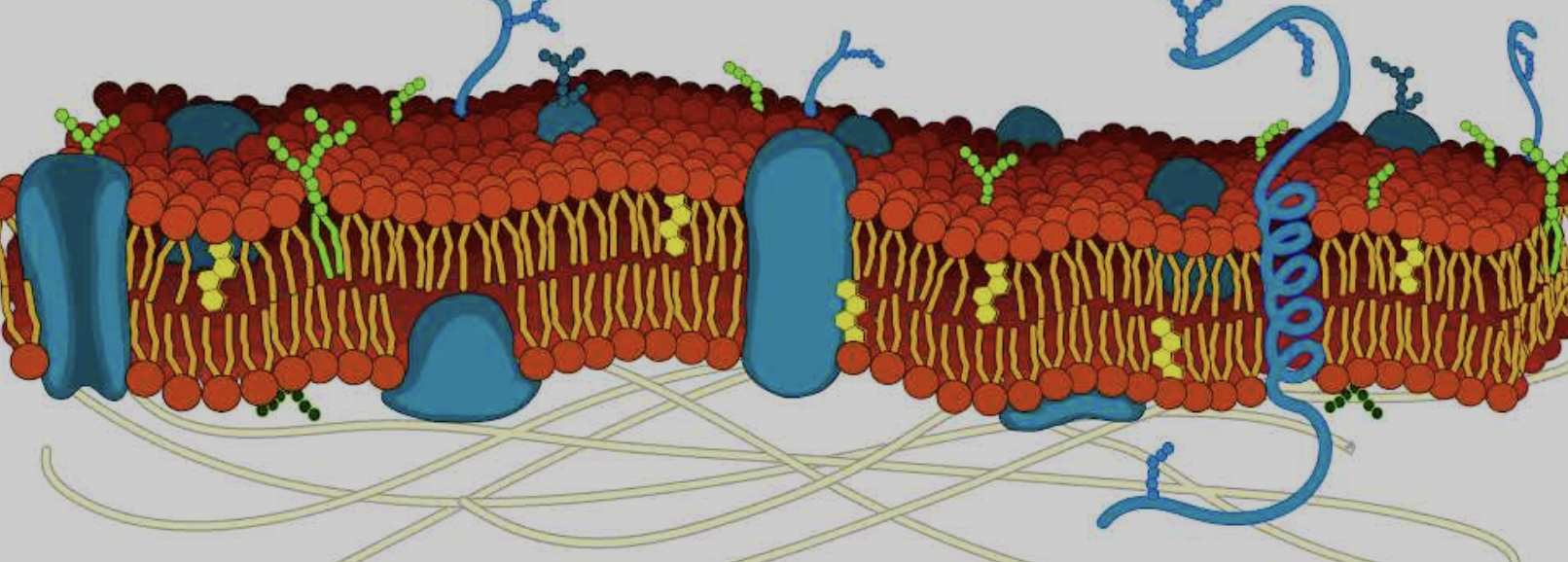
Where is the Integral and peripheral proteins
Big blue blobs
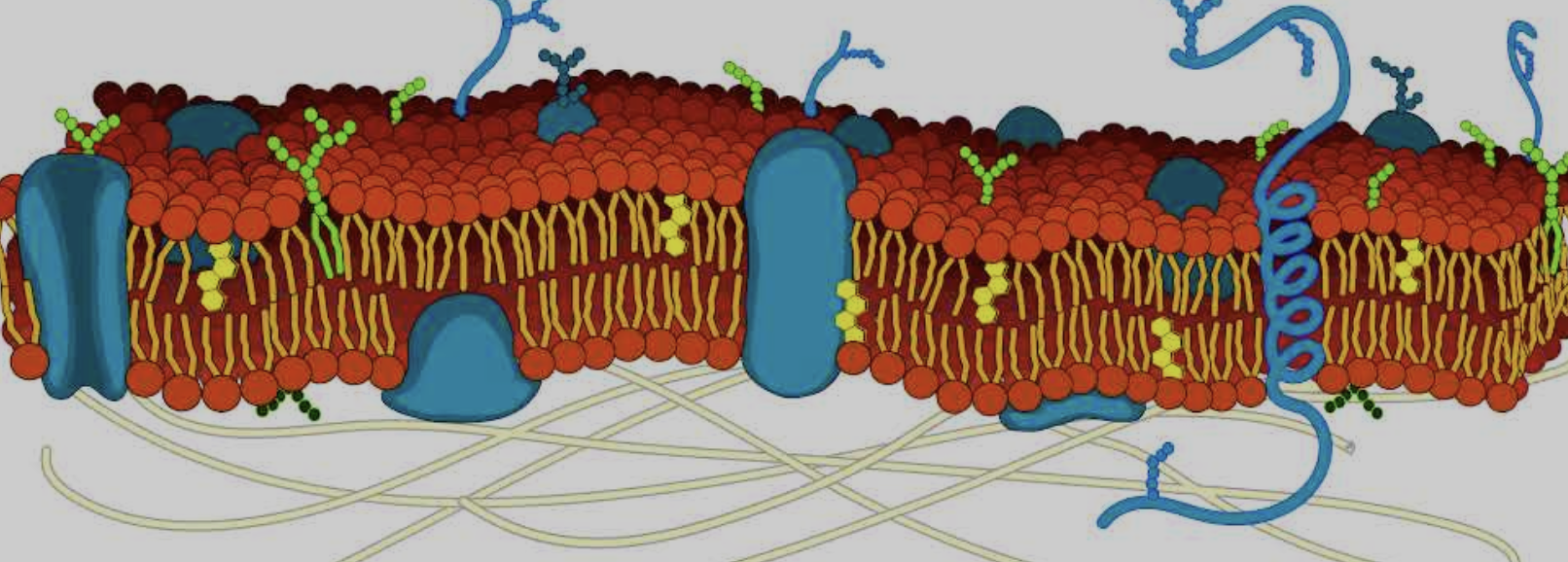
Where is the phospholipid bilayer
Red dots around the side
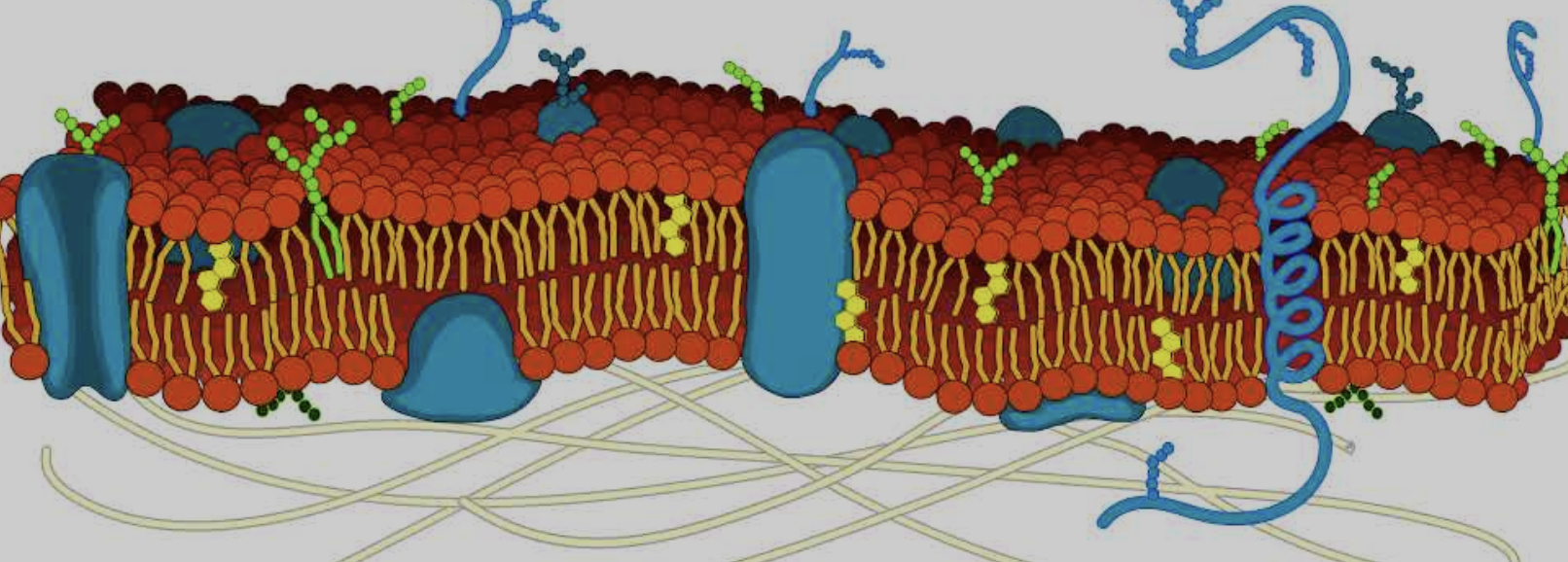
Where is the Cholesterol
Small yellow hexagons
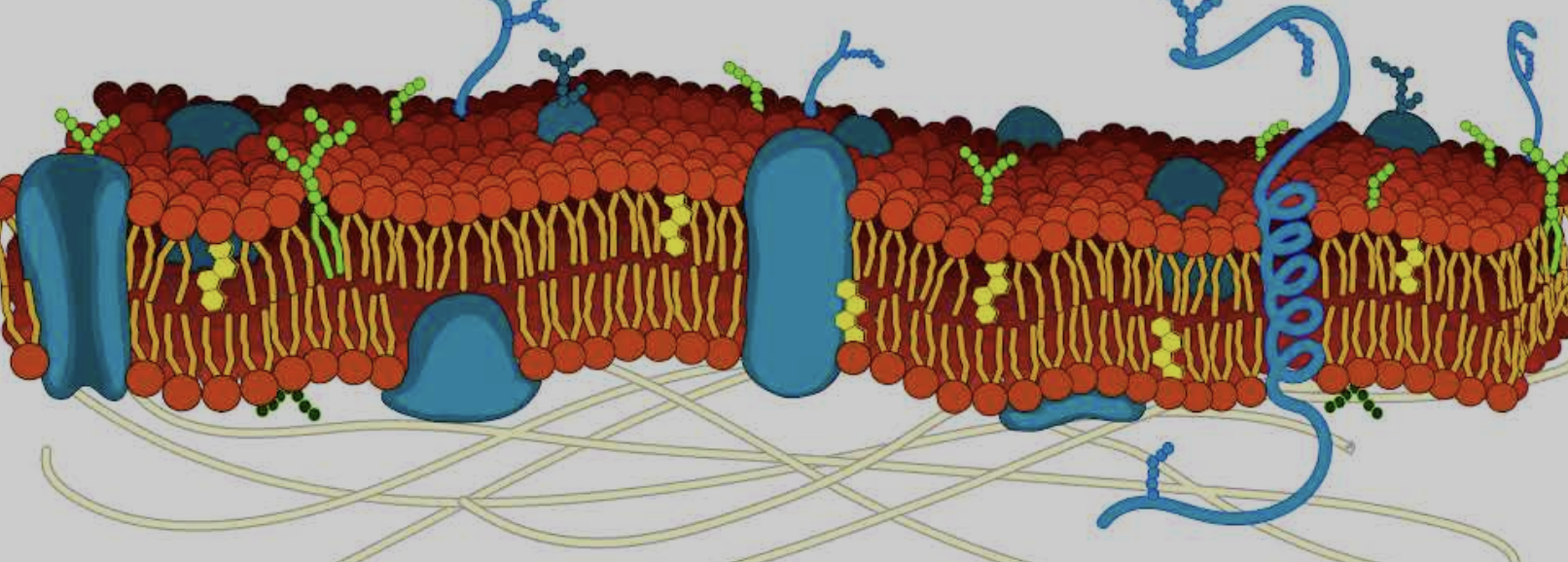
Where is the Carbohydrates
Dark blue strands on the top of glycoproteins
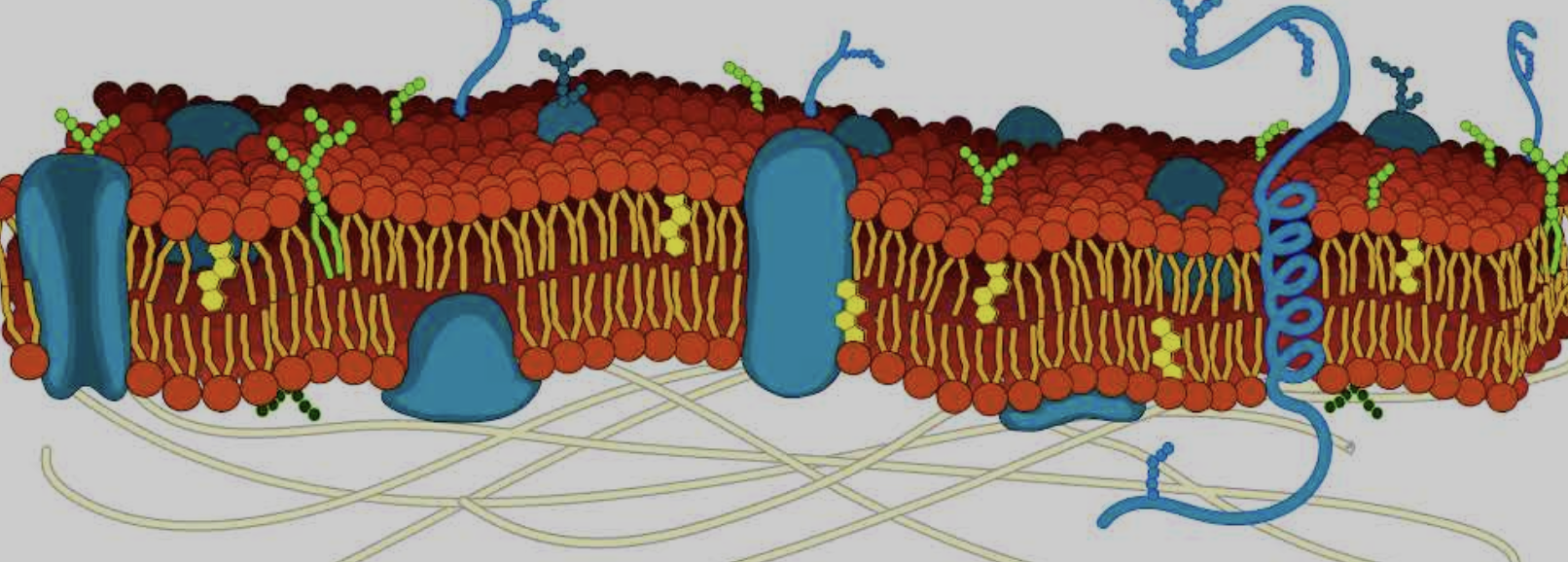
What parts are Hydrophilic and hydrophobic part in cell membrane
Hydrophilic is the head and hydrophobic is the tails
Why do the phospholipids form a bilayer
Because the hydrophilic heads face twords the water and teh hydrophobic tails face away from the water
What is the rule of concentrant gradient
substances naturally move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
What is a example of exocytosis
Nerve cells release nerotansmitter
What is a example of endocytosis
White blood cells engluf bacteria
Fluid Mosaic is…
The stuff inside the phosphorlipid bilayer that helps it move around
Semi permeable is…
How easy stuff can get through the cell such as small molecules