Neurons/Parts Of A Neuron
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Dendrite
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
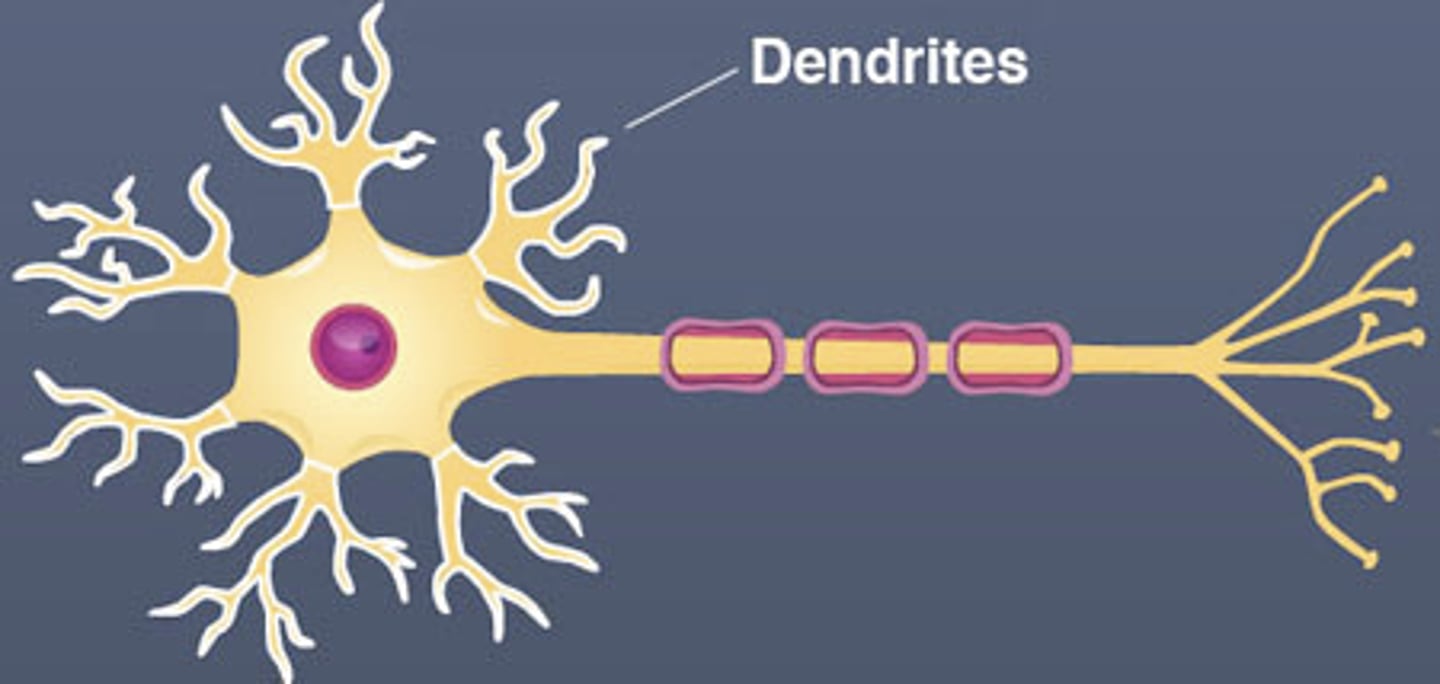
Axon
the extension of a neuron ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons
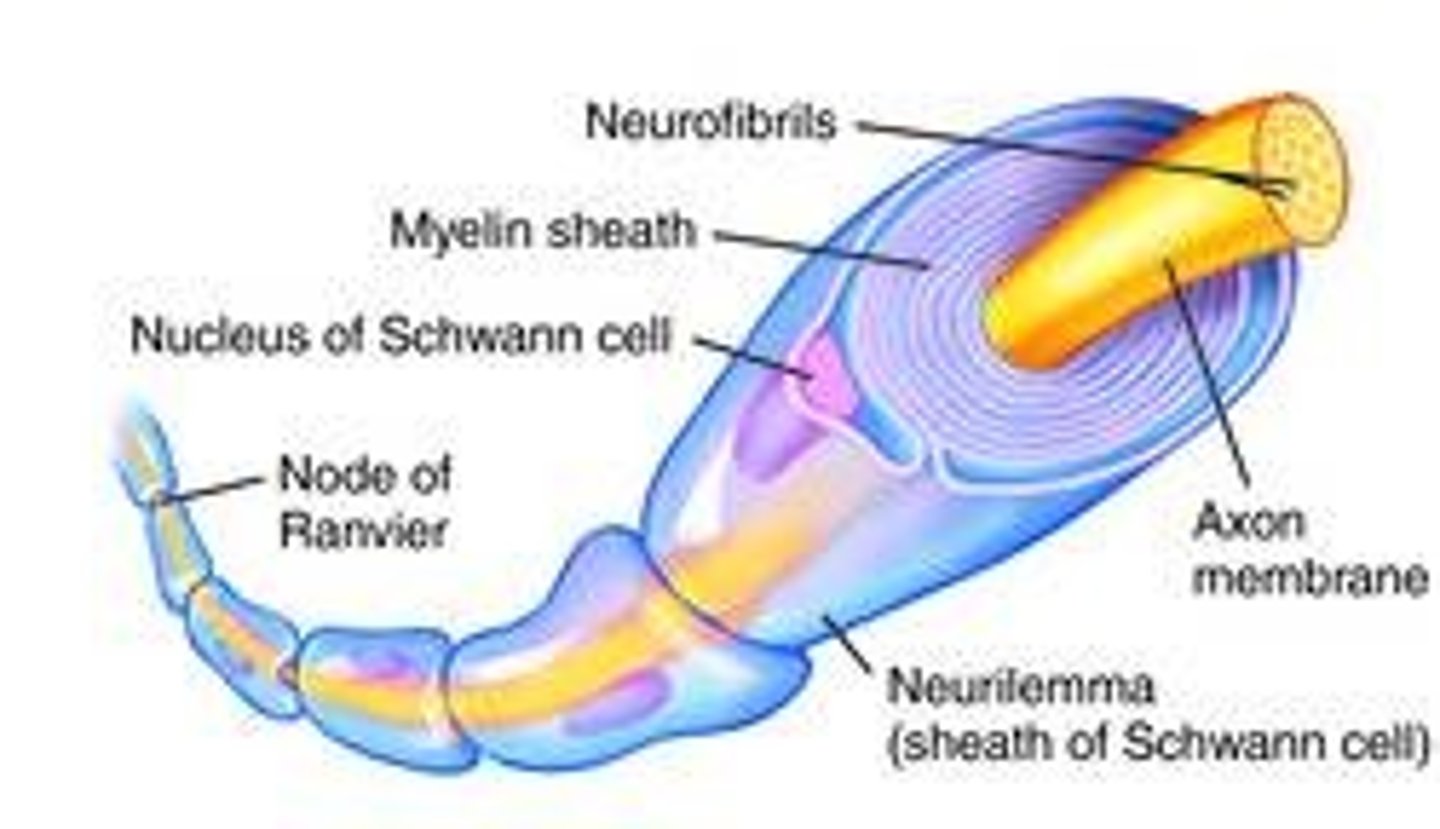
Myelin Sheath
a layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses
Action Potential
neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. The action potential is generated by movement of positively charged atoms in & out of channels in the axon's membrane
Threshold
level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
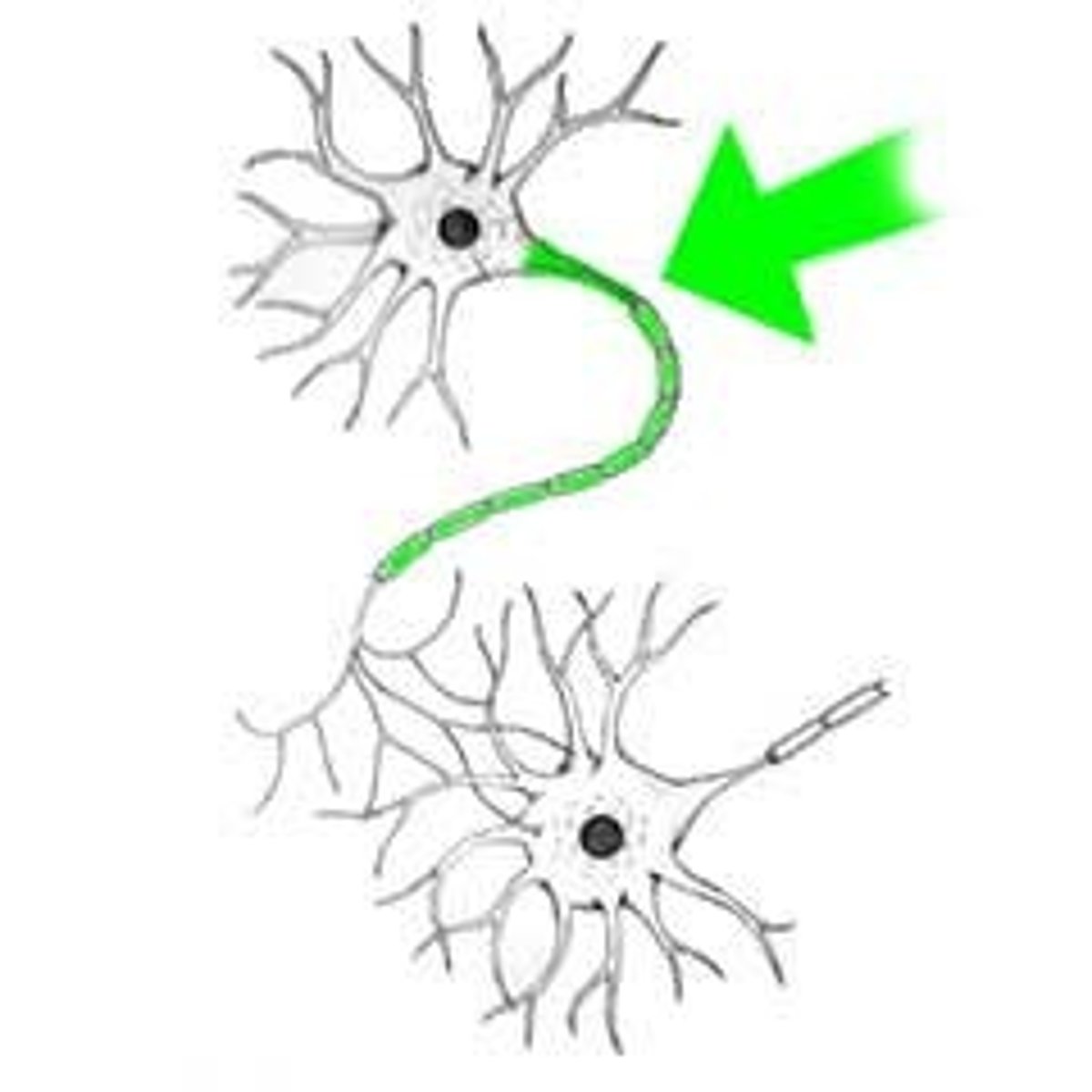
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that reverse the synaptic gaps between the neurons. when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse
Types Of Neurotransmitters
1. Acetylcholine
2. Dopamine
3. Serotonin
4. Norepinephrine
5. GABA
6. Glutamate
Soma
the cell body responsible for maintaining the life of the cell
Glial Cells
cells that provide support for neurons
-deliver nutrients
-produce myelin
-cleans up waste products
Acetylcholine
enables muscle action, learning & memory
Dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, & emotion
Serotonin
influences mood, hunger, sleep, & arousal
undersupply can lead to depression
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness & arousal
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, insomnia
Glutamate
a major excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in memory
too much can lead to seizures or migraines, some people avoid MSG inter foods
Afferent Neurons
a neuron carrying info from senses to the CNS
Efferent Neurons
transports messages from CNS to muscles of the body