Cognitive Orientation to Daily Occupational Performance CO-OP wk.8
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
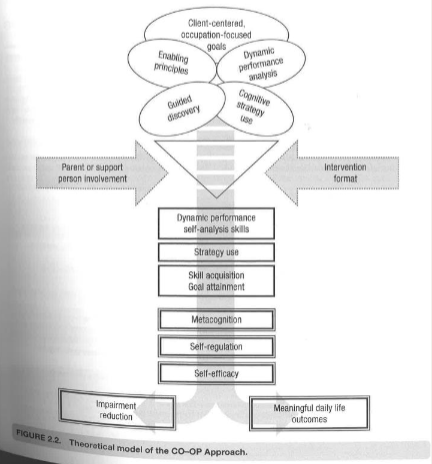
CO-Op Approach
1. Client-chosen goals
2. Dynamic performance analysis
3. Cognitive strategy use
4. Guided discovery
5. Enabling principles
6. Parent or caregiver involvement
7. Session structure and format
(Polatajko & Mandich, 2004)
History
developed in the 1990s for children with developmental coordination disorder (DCD)
now focus on the importance of cognition in skill acquisition
CO-OP Approach Goals
enables various populations with a variety of occupational performance issues, including motor-based performance issues, to use cognitive
strategies to attain their occupational performance goals
skills acquired can be generalized to real-worlk situations and transferred to novel tasks
5 Components
1. Client-centered
2. Performance-based
3. Problem solving
4. Strategy use
5. Guided discovery
Client Centered
collaborative partnership with client starting at goal setting and continuing through all aspects of the interaction
General Communication Strategies for Goal Setting
Be direct
ask for clarification… like “tell me more about___ “
open ended questions
address one topic at a time
don’t make assumptions
don’t think about the next topic while the client is still talking about topic at hand
Performance Base
when used to describe an intervention, indicates that the intervention is focused on goal-oriented performance; rather than on underlying processes
top down approach —> shifts from deficit driven models to learning models
Perspective is Performance Based
intervention is explicit, task-specific, and goal driven
CO-OP initiated w the identification by the client of 3 occupational performance goals using the COPM
uses the Performance Quality Rating Scale (PQRS) as a tool specifically designed for the CO-Op approach that rates performance on a scale of 1-10 scale
Dynamic Performance Analysis (DPA)
begin w performance based assessment
involves direct observation or reported observations in all aspects of the performance
a dynamic process that cannot be done in isolation of the actual performance
Focuses on the idiosyncrasies of the performance by a specific person in a specific context
Careful attention is paid to the various aspects of the performance, such as
movements performed relative to the skills required and the fit with occupational and environmental demands
Problem Solving
Problem solving is the ability to combine previously learned knowledge in a new way to solve a new problem.
◦ From a learning perspective, performance issues are viewed as a problem to be solved.
◦ Problem solving is a higher-order cognitive process. It is considered the most complex of all cognitive functions.
◦ Generally held that all people can become more effective problem solvers through the use of problem-solving strategies
Strategy Use
Strategies are tools or plans of action used for accomplishing a task or achieving a purpose; they are always goal directed (Toglia, Rodgers, & Polatajko, 2012).
Cognitive Strategy USe
GOAL-PLAN-DO-CHECK is a cognitive strategy!
involved in all activities that require thinking, planning, and decision making
throughout the Cognitive Orientation to daily Occupational Performance intervention, therapist and client are engaged in iterative exchange about goal, plan, implementation of plan, and checking
Global Cognitive Strategy
Include the GOAL-PLAN-DO-CHECK strategy
◦ Higher order strategies used to control or coordinate other strategies
Domain-specific (DSS)
Specific to a person, situation, task, or part of a task.
◦ Introduced to solve specific performance issues as they arise and are often used only for a short time.
◦ Not taught like global strategies, but discovered during the dynamic performance analysis DPA) process.
some DSS include task specification, verbal, mnemonic, body positioning, verbal self guidance, etc.
◦ Guided discovery ensures that the client is actively engaged in problem solving and identification of domain-specific strategies, becomes skilled at
the process, and feels ownership of the solutions and that the developed strategies are relevant to the client in his or her real-world context.
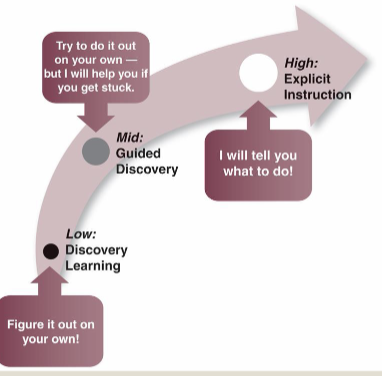
Guided Discovery
◦ A method of instruction designed to facilitate active learning
◦ Elicits the learner’s active involvement in the discovery of new learning
◦ Between direct ‘teaching’ and pure discovery learning
◦ More effective than discovery learning in supporting skill acquisition and transfer
◦ Using guided discovery ensures that the learner identifies the solutions that make sense, fit with existing knowledge, and have relevance to real-world context
Guided Discovery 4 Catchphrases
One thing at a time
ask, don’t tell
coach, don’t adjust
make it obvious
CO-OP Perspective of Human Occupational Performance
The unique perspective on occupational performance that is inherent in Cognitive Orientation to daily Occupational Performance is that the person’s individual cognitive process has primacy in occupational performance
It all starts with the person !
understand role cognition!