ecosystem apes 1
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
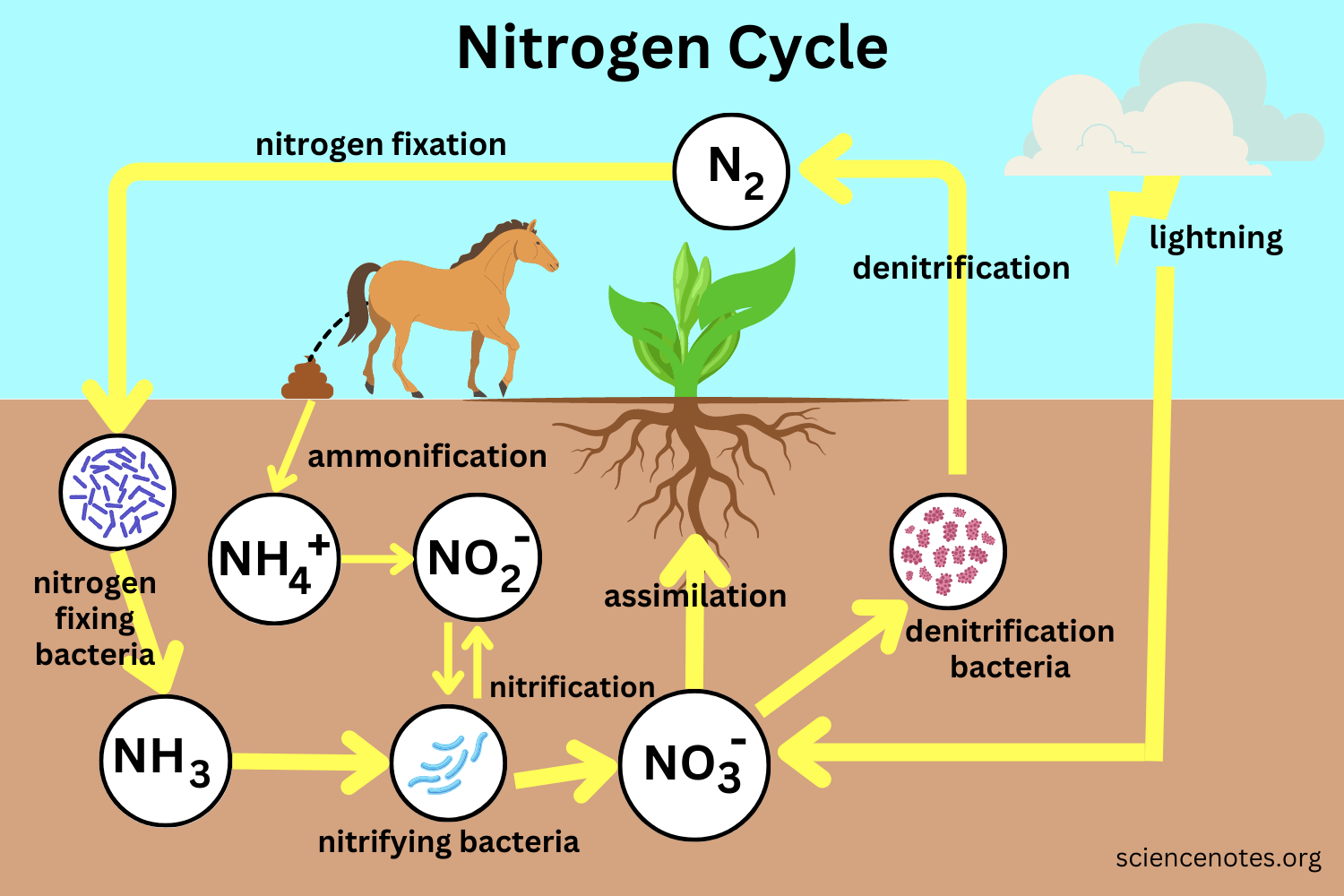
the nitrogen cycle
nitrogen fixation - N2 to NH4
ammonification - decomposer to NH4
nitrification - NO2 - NO3
assimilation - NO3 to autotroph
ammonium
(NH4) toxic to plants
nitrites
(NO2) toxic to plants
nitrates
(NO3) vital for growth and passed up through trophic levels, eventually absorbed by humans
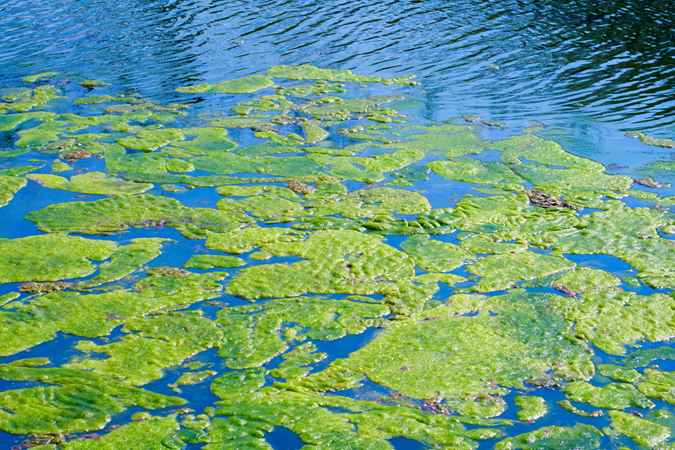
eutrophication
process where excess nutrients saturate the water near areas of terrestrial runoff, resulting in algae blooms
non-point source pollution
agricultural runoff is often linked to eutrophication
nitrogen (non point pollution)
synthetic fertilizer and animal waste runoff into streams and makes their way to larger bodies of water via watershed
phosphorus (non point source of pollution)
other fertilizers contain mineral phosphorus to further stimulate plant growth which can also run off into the watershed
deadzones
areas form in the water when aerobic bacteria decompose the dead plant matter
marine organisms die off due to decreased dissolved oxygen
algae blooms
surplus of nutrients cause rapid algae growth
produce toxins
deplete oxygen in water
blocking sunlight
disrupting food chains

species
group capable of mating with one another to produce fertile offspring
fundamental niche
overall niche of an organism
realized niche
actual part of the niche an organism occupies due to competition
r- selected
broad niche, pioneer species, many offspring, quickly mature for reproduction, high environmental tolerance, typically small size
K - selected
narrow niche, late successional species, fewer + larger offspring, low environmental tolerance, typically large adults
intra specific competition
comp. between members of the same species for resources
inter specific competition
comp. two different species for the same resources
competitive exclusion
niches of organisms can only overlap for a very brief time
resources partioning
division of limited resources by species to help avoid competition in an ecological niche
environmental tolerance
distribution of species in an ecosystem determine by levels of one or more physical / chemical limiting factors being with in range tolerated by that system
limiting factors
too much or too little abiotic factors that can limit / prevent growth of a population even if all other factors are at optimum level
exponential growth
J curve(r- selected)
logistic curve
S curve(K-selected)
mutualism
both species benefit
commensalism
one unaffected , one benefits
paratism
host is harmed, one benefits
native species
normally live and thrive in ecosystem
invasive
pathogens, likely cause harm
idicator species
if the species decline it is a warning, and vice versa
keystone species
without this the whole ecosystem would crumble.
ESA - endangered species act
federal law preventing the hunting and selling of certain species
CITES - convention of international trade in endangered species
regulations on the movement of proctected species
HIPPCO
Habitat
Invasive
Population growth
Pollution
Climate change
Overexploitation
major terrestrial biomes
taiga, temperate rainforests, temperate seasonal forests, tropical rainforests, shrubland, temperate grassland, savanna, desert, and tundra
taiga wildlife description
wildlife description: largest land biome, subarctic region, high latitude (50-70N)
taiga climate
climate: annual rain is 10-30 in, high latitudes mean longer winters
taiga biogeochemical cycles
carbon cycle: Trees are the biggest sink and the few forest fires that happen help to release the carbon cycle.
water cycle: Compacted snow builds up storing most of the water in the taiga biomes.
phosphorous cycle: Bogs (nutrient poor wetlands, spongy) traps organic material and help it decompose
nitrogen cycle: Natural sink is the soil where the nitrogen gets trapped and the soil and gets stuck below permafrost
desert wildlife descriptions
canyons
dunes
hamadas
oases
salt flat
15-35 latitude
canyon
caused by erosion of large sedimentary rock
dunes
casued by displacement and collection of sand
rocky areas of hamadas
formed by weathering of an area with a lack of vegetation
oases
created by groundwater coming up to the surface and creating a fertile area
desert climate
very low rainfall annually
scorching days and cool nights
subtropical in the north
tropical in south
10 in rainfall per year
temp. deciduous forest wildlife
broad array of deciduous trees
floor of shrubs, ferns moss
temp. deciduous forest climate
30-59 in rainfall
mid latitude: not extreme , moderate weather,
rainforest wildlife description
lush warm habitat
near equator
oldest biome
more than half worlds species, plants
Nearly all of the life-sustaining nutrients are
found in the plants and trees, not in the ground as in a northern, or temperate forest
rainforest climate
lots and lots of rain annually
These do not get too hot ever because they have a high level of cloud cover, making the hours of sunlight exposure minimal
One major role of rainforests is to help regulate global climate by storing excess carbon dioxide in the trees and soil
never gets too cold, plants keep growing
emergent layer
the uppermost layer of a rainforest, consisting of the extremely tall trees that tower above the dense canopy
canopy
the layer of interlocking trees, branches, and leaves that forms the "roof" of the rainforest, typically 100 feet or more above the ground
the understory
the layer beneath the dense canopy, characterized by darkness, high humidity, and a variety of plants like young trees, shrubs, and vines, which are adapted to low light conditions with large leaves to capture what little sunlight penetrates.
the forest floor
the dark, damp bottom layer of the forest, composed of leaf litter, roots, and decaying organic matter like fallen leaves and branches
coral reef wildlife
built upon polyps
underwater
supporting a vast array of marine life
coral reef climate
warm shallow waters tropical
high amount of sunlight for algae
estuary wildlife
brackish water
tidal
partially enclosed
sandy muddy bottoms
esturary climate
humid subtropical
mild winters
hot humid summers
steady rainfall year round
rocky intertidal coastal wildlife
The rocky intertidal coastline is a narrow area where the land and ocean meet, and it is exposed or submerged depending on whether it is high tide or low tide.
This zone supports a wide variety of life, including biotic organisms (like algae, barnacles, mussels, and crabs) that live in tide pools,
This area is also being shaped by abiotic factors (such as changing temperature, wave action, and salinity).
rocky intertidal coastal climate
extreme daily shifts between exposure to air and inundation by water, resulting in dramatic temperature fluctuations, wet/dry cycles, and variations in oxygen levels
kelp forest wildlfie
Kelp is a form of algae that uses the sun’s energy to grow (Hall 2024).
The Chilean kelp forest stretches thousands of kilometers along the Pacific Coast.
A dynamic underwater ecosystem that hosts some of the richest kelp forests in the world.
It provides a tiered habitat, similar to a forest on land: a canopy, an understory, and a floor. The uppermost layer, canopy, is formed by species like the giant kelp.
Beneath the canopy is the understory where kelp, fish, and invertebrates stay.
Lastly, the sea floor is the deepest and darkest part of the kelp forest and is where the plant is anchored.
kelp forest climate
cool, clear, and nutrient-rich temperate ocean waters, but are threatened by warming oceans, which can reduce nutrients and push kelp beyond its thermal limits, leading to declines in kelp populations.
ecotone
a transition zone between two different ecosystems or communities where they meet and integrate
groundwater
water held underground in the soil or in pores and crevices in rock
upwelling
a rising of seawater, magma, or other liquid.
carbon cycle
photosynthesis
consumption
respiration
decomposition
phosphorus cycle
weathering erosion
plant assimilation
animal consumption
decomposition
sedimentation - no gaseous phase
sulfur cycle
release of sulfur
mineralization
oxidation
assimilation
incorporation
reduction
return to atmosphere
ecozones
Small regions within ecosystems that have similar physical features
Pioneer Species
Organisms present in the first stages of either type of succession
● Have wide ranges of environmental tolerance
atoll
a ring-shaped reef, island, or chain of islands formed of coral.
hadely cell
a large-scale atmospheric convection cell in which air rises at the equator and sinks at medium latitudes, typically about 30° north or south.
Fringing reefs
- The most common habitat that is located near the land/shore
atoll
surround lagoons, far from land, and sometimes form near underwater volcanoes
patch reefs
Near sand or seagrass, or between islands