gcse physics - atomic structure
1/37
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
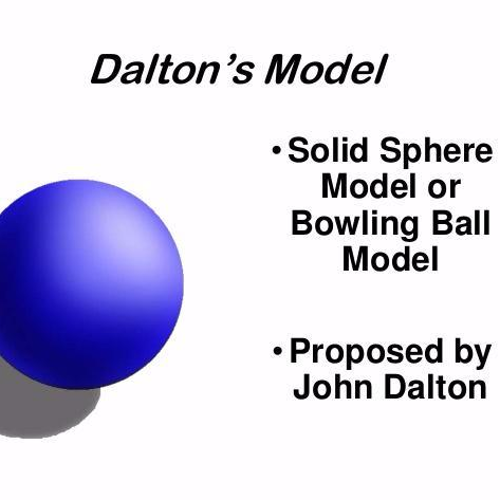
what did John dalton think the atom looked like?
a tiny, indivisible, solid sphere.
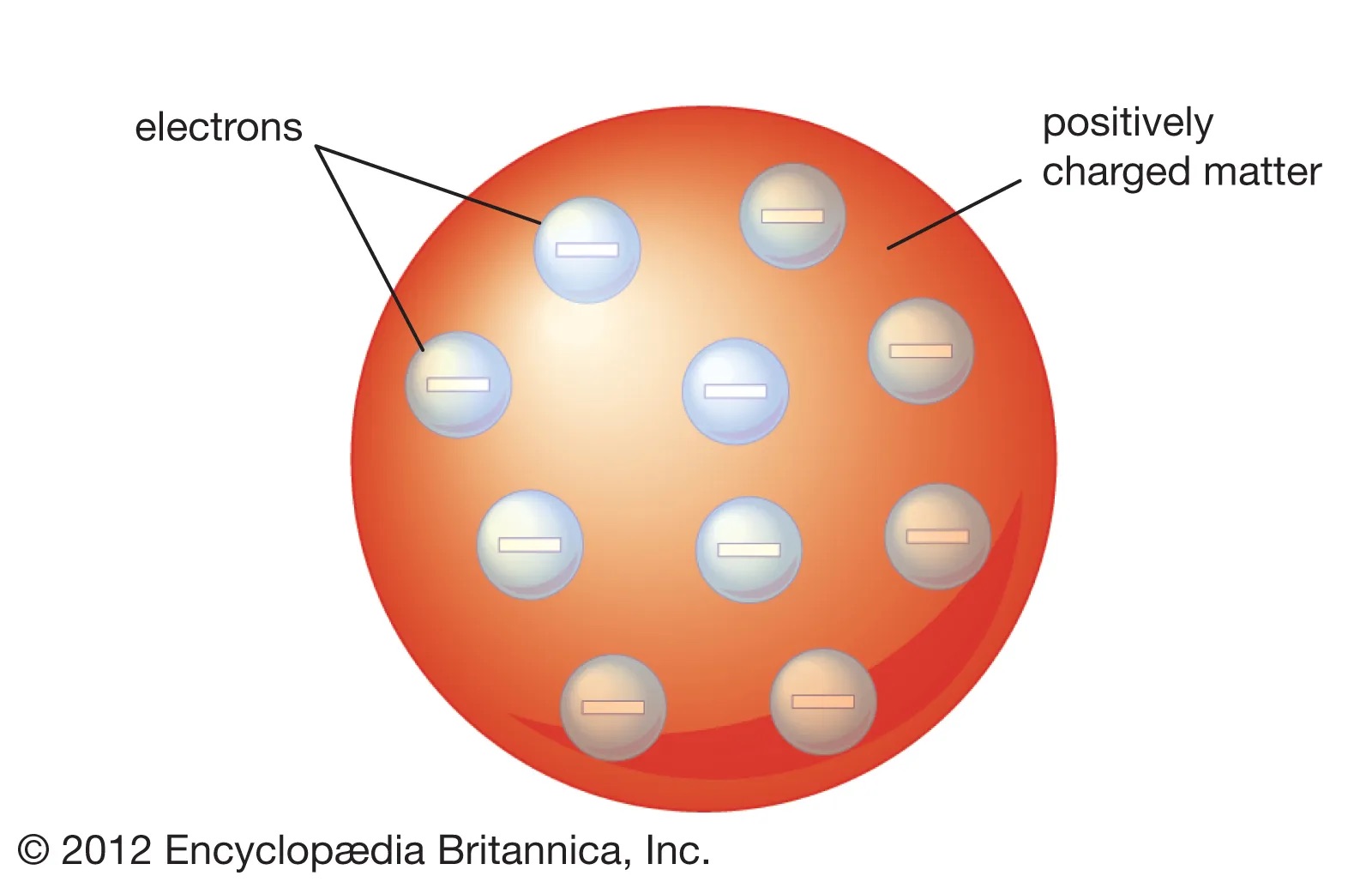
what did JJ Thompson think the atom looked like?
the plum pudding model.
A ball of positive charge with negatively charged electrons stuck in it.
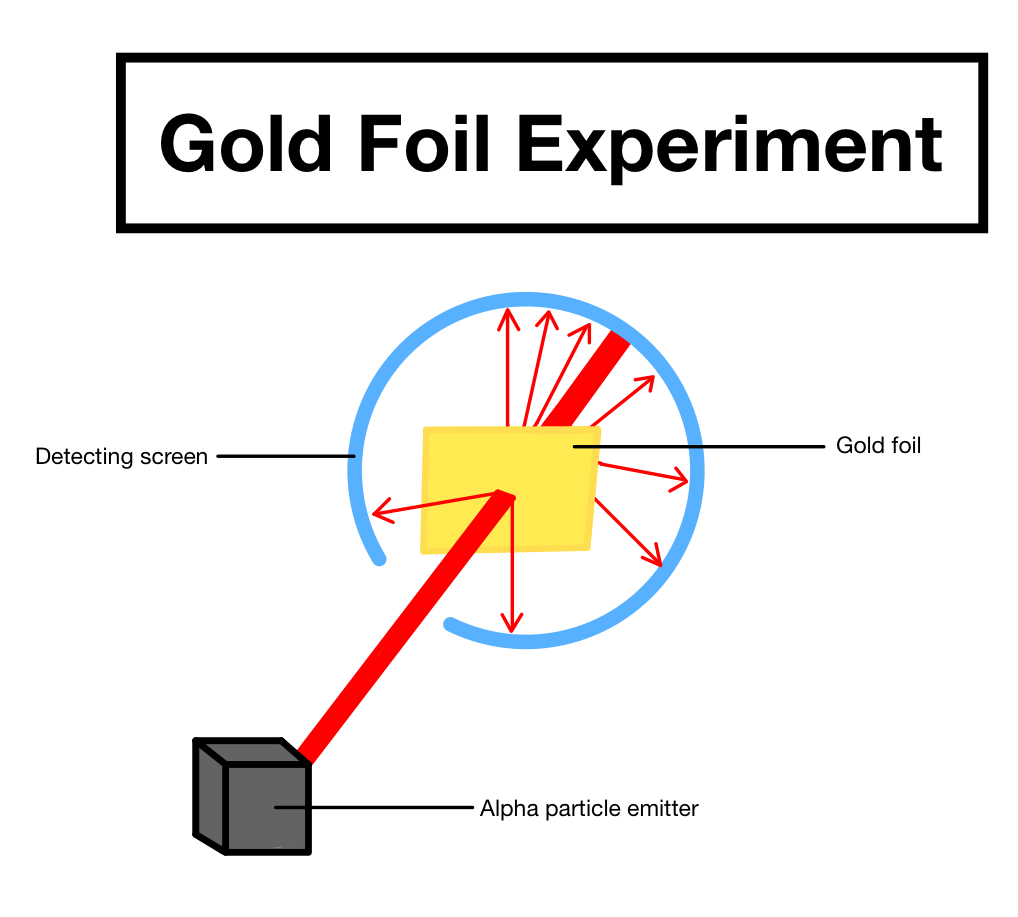
what experiment did Ernest Rutherford do?
He did the experiment where alpha particles were shot at gold foil. Most went through and some were deflected.
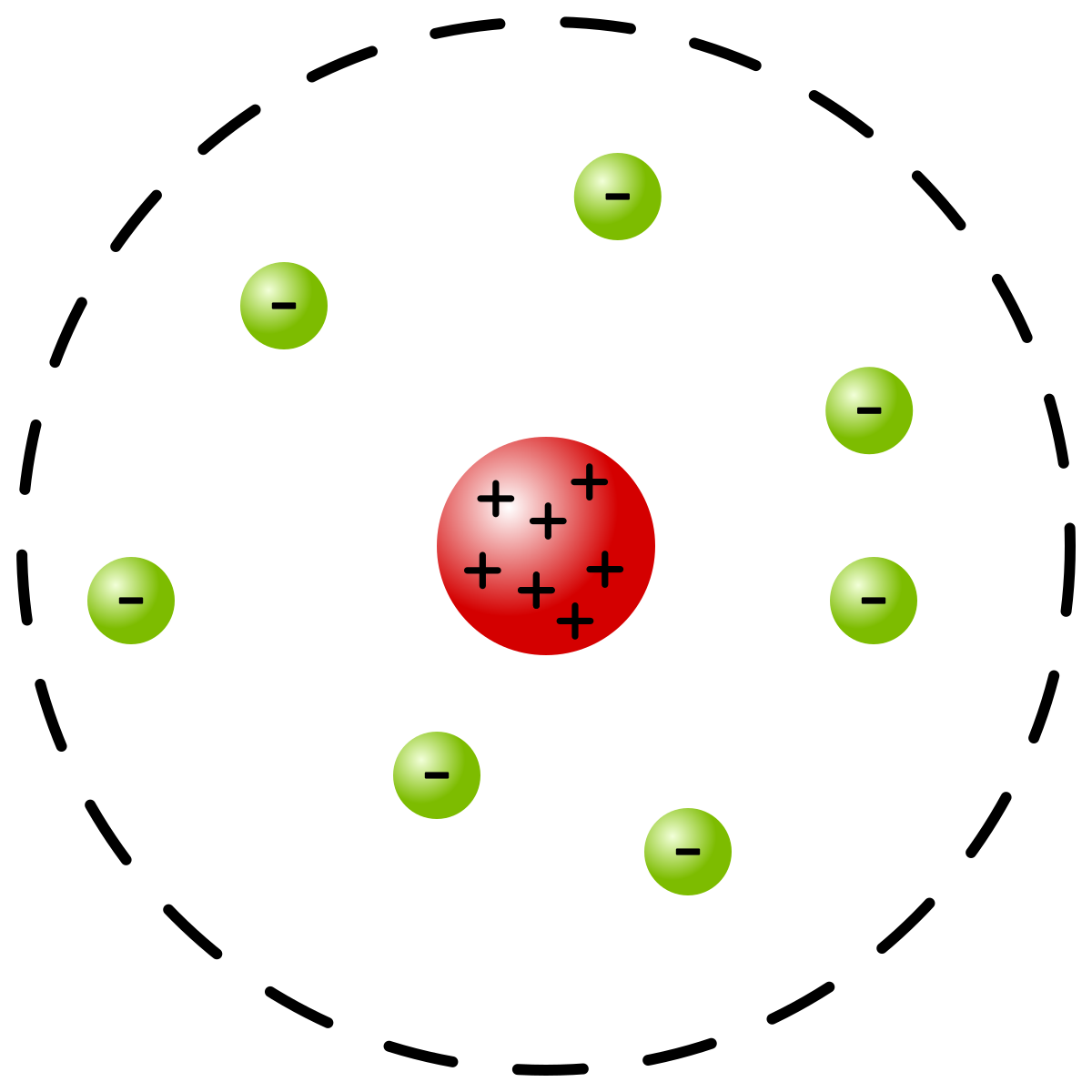
what did Ernest Rutherford think the atom looked like?
He thought atoms were mostly empty space with a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.
what did Niels Bohr think the atom looked like?
electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels
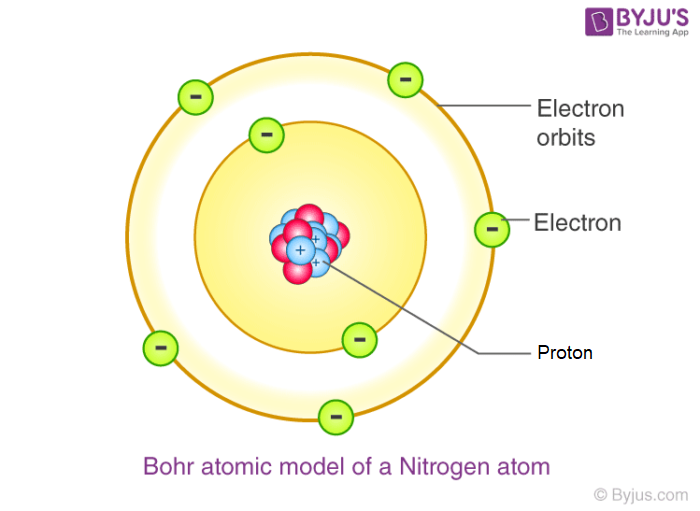
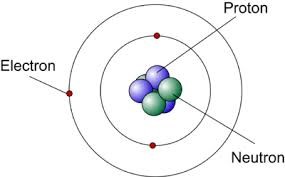
what did James Chadwick discover?
neutrons
what is an isotope?
same number of protons different number of neutrons
what do radioactive nuclei do to become more stable?
emit radiation
what does the random nature of radioactive decay mean?
you can’t predict which individual nuclei will decay and when
what is activity?
the rate at which a source decays
what is a higher activity?
radiation is emitted rapidly over a short time
what is a low activity?
radiation is emitted gradually over a long time
what is the unit of activity?
becquerels
what detects radiation?
Geiger-Muller tube
what is half life?
the average time it takes for the number of radioactive nuclei in an isotope to half
Cobalt-60 has a half-life of 5.3 years. If I have 0.25g now, how much was there when I originally bought the sample 10.6 years ago?
1 gram
what is ionisation?
when an atom loses or gains electrons it becomes an ion that has an overall charge
charge of alpha radiation
+2
charge of beta radiation
-1
charge of gamma radiation
0
mass of an alpha particle
+4
mass of a beta particle
negligible
mass of gamma radiation
0
penetration of alpha radiation
low
penetration of beta radiation
medium
penetration of gamma radiation
high
range of alpha radiation in air
3-5cm
range of beta radiation in air
30 cm
range of gamma radiation in air
over a km
what is alpha radiation?
a helium nucleus
what is beta radiation?
an electron
what is gamma radiation?
an electromagnetic wave
ionising ability of alpha radiation
high
ionising ability of beta radiation
medium
ionising ability of gamma radiation
low
what can stop alpha radiation?
a sheet of paper
what can stop beta radiation?
a few mm of aluminium
what can stop gamma radiation?
a few cm of lead