Bio-111 Exam 2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Central Dogma of Biology
DNA>RNA>PROTEIN
Beadles and Tatums Experiment
One gene-one enzyme , hypothesized that each gene encodes for a single enzyme. Discovered that genes provided instructions for making proteins. They used Neurospora crass which is bread mold, and produced genetic mutants using x-rays.
Genes and Proteins
A specific sequence of nucleotides on a strand of DNA, genes lead to the production of a specific protein product, blood type
Chromosomes
Long pieces of DNA that contain the DNA sequences of thousands of genes
Alternative Splicing
Genes have more than one coding regions (exon) and can be arranged in varying ways which will result in the development of different proteins.
Non-coding RNAs
rRNA,tRNA,siRNA etc.
Extra information regarding genes
Some genes encode a subunit of protein, not a whole protein, many proteins are composed of multiple, different polypeptides , a different gene encodes for each of those different polypeptides
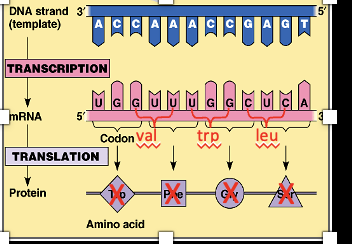
Codons
Our genetic information is stored in our sequence of nucleotides, the sequence is decoded by interpreting a series of non-overlapping base triplets.
How many amino acids are there?
20 amino acids
How many nucleotides are there?
Four Nucleotides: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine.
1 nucleotide codon
4 different codes
2 nucleotides codon
16 different codes
3 nucleotide codon
64 different codes
Degenerate or Redundant
multiple codons can code for the same amino acid or one amino acid can have more than one codon to make it
3 stop codons
U Are Annoying
U Go Away
U Are Gone
One start codon
A U G
Genetic code is nearly universal
Every living organism uses DNA, they all use the same A,C,G,T, or U in place of T when looking for RNA
Do all organisms use the same set of AA to build their proteins?
No, not all of them use them but the majority do
Reading Frame
The codons must be read in a certain way and it refers to which nucleotide starts the first codon in the coding region. It will always start with AUG which codes for the amino acid AA methionine.
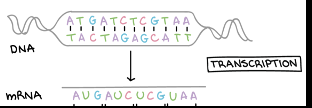
Gene Expression- Transcription
Synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA, produces the messenger RNA which is mRNA, produces the template for translation
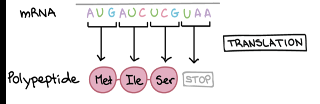
Gene Expression-Translation
The synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of an mRNA, occurs on ribosomes
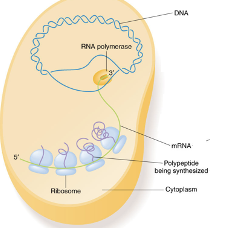
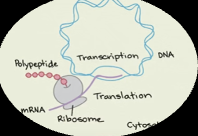
Gene Expression-Prokaryotes
NO NUCLEUS, transcription and translation take place in the cytoplasm and they occur at the same time
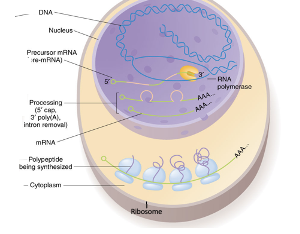
Gene Expression- Eukaryotes
Transcription occurs in the nucleus
Translation occurs in the cytoplasm
Unique Prokaryotes Features of Gene Expression
They do not require RNA transcript modification which means RNA transcripts can be translated immediately after being transcribed
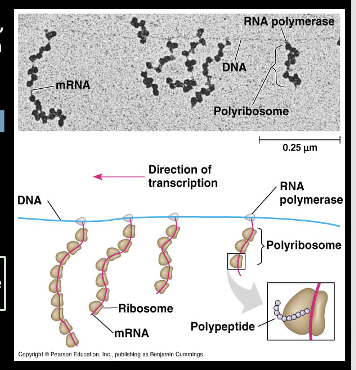
Prokaryotes RNA transcript
It can be translated as transcription progresses, meaning
Multiple polymerases can transcribe at a time
Numerous Ribosomes can concurrently translate the mRNA transcripts into polypeptides
This can allow a specific transcript and or a specific portion to rapidly reach high concentrations in a cell
Gene expression in a lab
Genes can be transcribed and translated after being transplanted from one species to another
Transcription
The gene sequence determines the sequence of bases along the length of a mRNA molecule
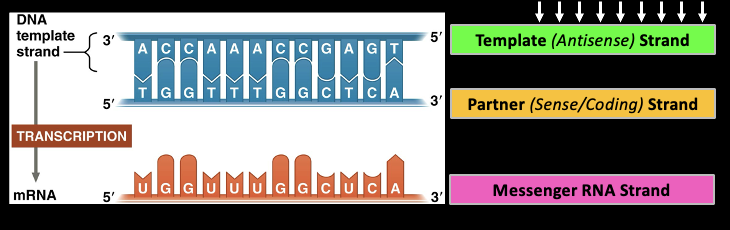
Transcription
DNA>mRNA
Transcription-Elongation
DNA>mRNA
Transcription-Terminiation
DNA>mRNA
What is RNA comprised of?
G, C, A, and U
Thymine is substituted for uracil in RNA
(G::::C and A::::U)
Where does transcription occur?
Nucleus-Eukayotic Cells
Cytoplasm-Prokaryotes
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme that carries out transcription
Template(Antisense) Strand
This is what is being transcribed
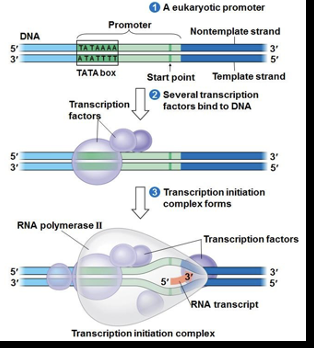
Transcription-Initiation Step 2
Transcription facttors recruit RNA polymerase and bind with it to form the initiation complex
Transcription-Initiaition Step 3
RNA Polymerase recognized the transcriptional start sequence and being synthesizing the RNA transcript in a 5 prime to 3 prime direction
Transcription-Initiation Step 1
Transcription factors bind to the promoter region of the gene to be transcribed
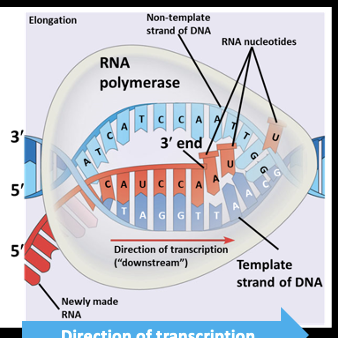
Elongation:Step 1
RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA (10-20 bases)
Elongation: Step 2
RNA polymerase reads the DNA nucleotide on the template strand and attaches the compliment RNA nucleotide
Elongation:Step 3
The RNA nucleotide is joined to the previous one on the 3 prime end via a phosphodiester bond along its backbone
Elongation; Eukayotes
The FACT complex removes and reassembles the nucleosomes as polymerase synthesizes the mRNA
FACT complex
facilitates chromatin transcription in elongation for eukaryotes
Terminator Sequences
A sequence of DNA at the end of a gene that is transcribed and signals the RNA that transcript is complete
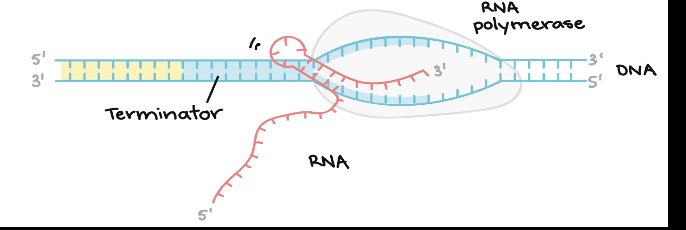
Prokaryotic Termination
Rho dependent termination- Rho protein travels along the mRNA and interacts with RNA polymerase terminating transcription
Step 1 of transcription termination
RNA polymerase reaches and transcribes the termination sequence
Step 2 of transcription termination
the RNA transcript is released by RNA polymerase
Step 3 of transcription termination
RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA officially ending transcription
Hair pin structure
a common example of a method helped to signal termination is the formation of this in the RNA transcript
Transcription Termination in Prokaryotes
RNA polymerase reads through a termination sequence and dissociates from the DNA , the RNA is immediately ready for translation
Transcription Termination in Eukaryotes
RNA polymerase reads through a polyadenylation sequence which is transcribed (AAUAA) and bound by proteins which causes the RNA polymerase to dissociate from the DNA and after termination the RNA needs additional processing
Transcription-Initiation overview
After RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, the DNA strands unwind and the polymerase initiates RNA synthesis at the start point on the template strand
Transcription-Elongation overview
The polymerase moves downstream unwinding the DNA and elongating the RNA transcript in a 5 prime to 3 prime direction. In the wake of transcription, the DNA strands reform a double helix
Transcription-Termination overview
Eventually the RNA transcript is released and the polymerase detaches from the DNA

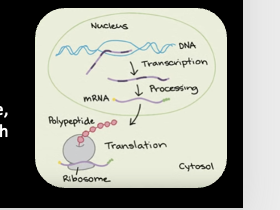
Post transcriptional processing in Eukaryotes
Eukaryotic cells must modify RNA after transcription and before translation
How do enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify pre-mRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm?
5 prime cap added
3 prime poly A tail added
Introns removed
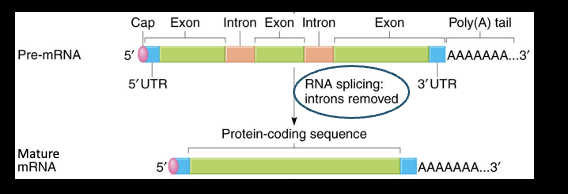
Post Transcription Processing: Caps and Tails
Alternation of mRNA Ends (5’ and 3’)
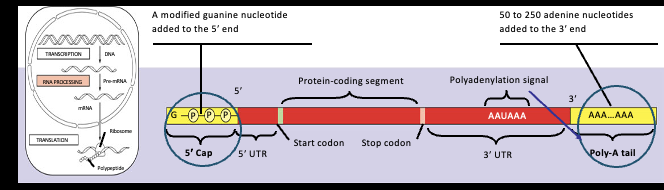
Each end of a pre-mRNA is modified in a particular way, this is the cap part
5’ end receives a modified guanine(5’- methlguanosine )
Each end of a pre-mRNA is modified in a particular way , this is the tail part
The 3’ end receives a poly-adenosine tail (3’ poly-A)
the cap and tail both protect the RNA as it enters the cytoplasm and undergoes translation
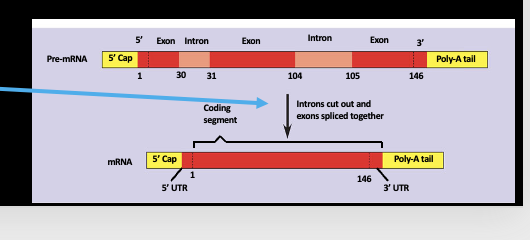
Post-Transcriptional Processing: RNA splicing
the process of removing introns and joining together exons to form a mature mRNA
What does RNA splicing ensure?
only coding sequences are translated (exons) and cuts out introns (coding sequences) and link together exons
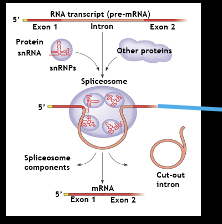
Spliceosomes
physically chops introns and removes them, and splices exons together and gives it to the RNA
Functional and Evolutionary Importance of Introns
allow for alternative splicing, process of selecting different combos of splice sites within a pre-mRNa to produce variable spliced m-RNA, Introns provide alternative cut sites for this
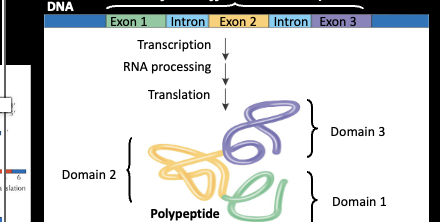
Domains
Polypeptides within proteins often have discrete structural and functional regions
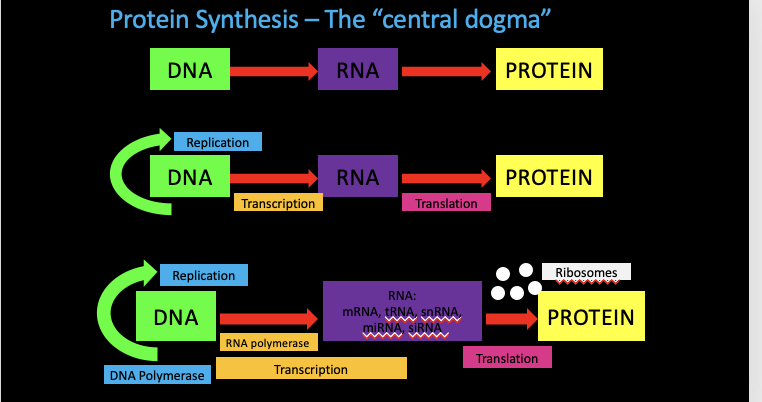
The Central Dogma
RNA-directed Synthesis of a polypeptide
During translation the mRNA sequence determines the sequence of amino acids in the primary structure of the polypeptide
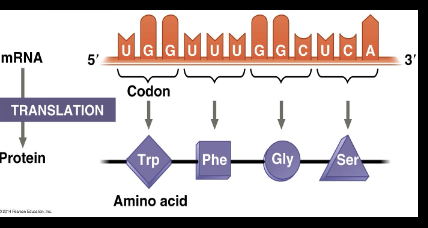
Translation
Occurs within the cytoplasm, mRNA reads as codons, codons are translated to amino acids and tRNAs are the deliverers
Molecular components of Translation
transfer RNAS, ribosome, mRNA, polypeptide
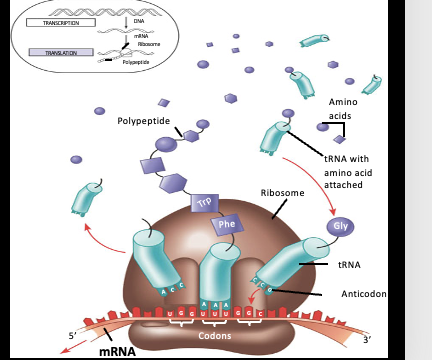
Translation Diagram
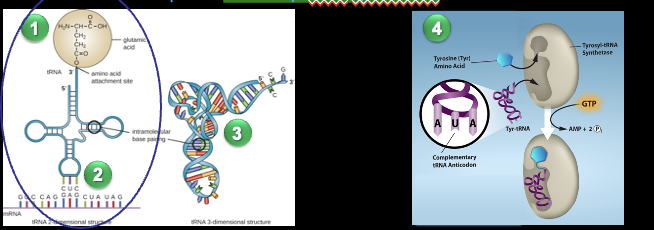
t-RNA: Transfer RNA
Not all identical, but they all
Carry a specific amino acid on one end
Have an anticodon on the other end
Single RNA stand that is about 80 nucleotides long
Utilize a specific Aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis to attach its amino
Function of tRNA
delivers amino acids to the ribosomes
Binding of tRNA
Carry a specific amino acid on 1 end and have an anticodon on the other end
Aminoacyl-tRNA syntase
The specific enzyme used to attach an amino acid to tRNA
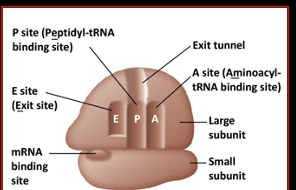
Ribosomes within Translation
protein and rRNA complex that facilitates the reading of mRNA and production of the corresponding polypeptide
Achieved through the pairing of mRNA codons with tRNA anticodons
Consists of 2 ribosomal subunits (vary between prokaryotes and eukaryotes)
tRNA
3 binding sites for tRNA
Ribosomes during translation
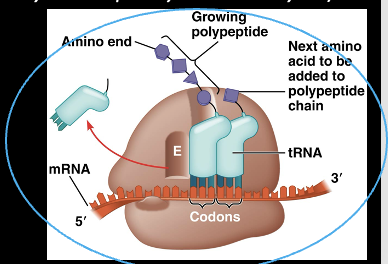
mRNA during translation
the molecule that directs the recruitment of tRNA molecules and production of the polypeptide, very specific sequence of RNA , unique to the polypeptide and will be used to create
Translation-mRNA in the ribosome
Reads in 3 base codons in a 5’ to 3’ fashion
AUG is the start of every codon in mRNA
Codon Bonding
Each codon in the MRNA is bonded to the anticodon of tRNA
mRNA in translation
Polypeptides
product of translation
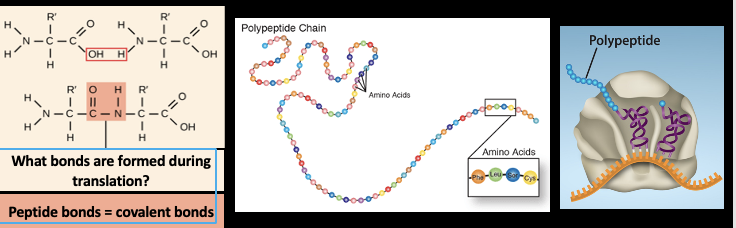
How are polpeptides’s produced ?
The assembly of amino acids bonded together in a specific sequence, achieved by the interaction of one tRNA in the p site with another tRNA in the A site. Occurs within the ribosome
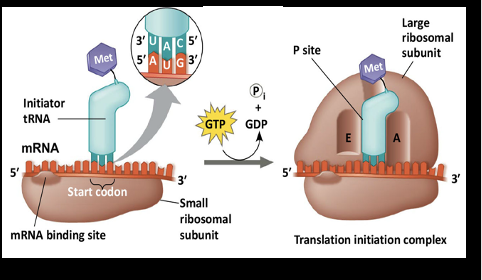
Translation Initiation Stage: Step 1
mRNA binds the small ribosomal subunit
Translation Initiation Stage: Step 2
Start codon is located
Translation Initiation Stage: Step 3
The initiator tRNA binds to the start codon
Translation Initiation Stage: Step 4
Energy is used to recruit and bind the large ribosomal subunit
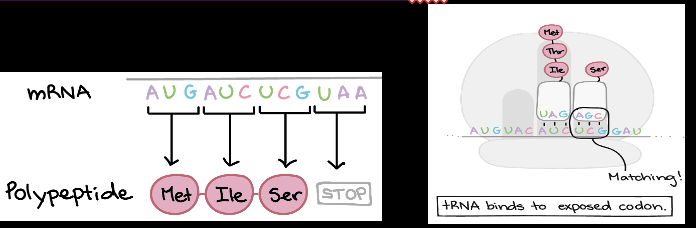
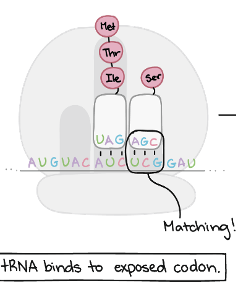
Translation Elongation:Step 1
tRNA binds to exposed codon
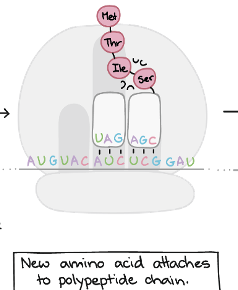
Translation Elongation:Step 2
New amino acid attaches to polypeptide chain
Translation Elongation:Step 3
Ribosome shifts one don over on the mRNA which will be the next codon read
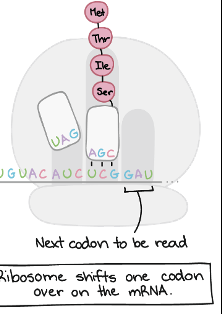
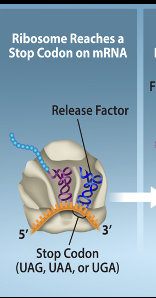
Translation-Termination Step 1
The stop codon in the mRNA is reached and reconginized
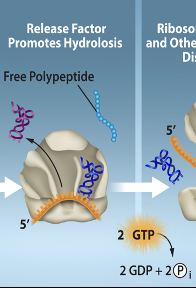
Translation-Termination Step 2
A release factor is recruited and binds to the stop condon causing the hydrolysis of the polypeptide from the tRNA
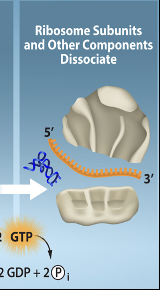
Translation-Termination Step 3
This bonding and some energy is utilized to cause the dissociation of the translation components
Protein Folding and Post Transcriptional Modification
After translation polypeptides/protiens may undergo modifications via the end-membrane system, this affects their 3 dimensional shape more specifically in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
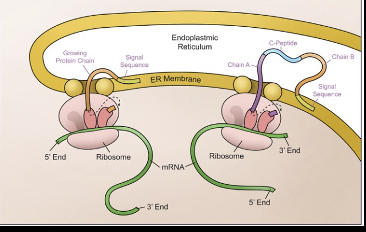
Where are ribosomes bound to in post transcriptional modifications
Ribosomes can be bound to the ER and produce the polypeptide into the ER