IB HL Biology Topic A - Unity and Diversity (incomplete)
1/99
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
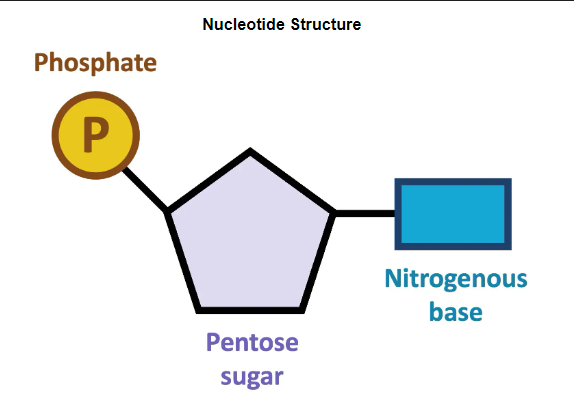
Nucleotide
Phosphate ester of a nucleoside with organic base, pentose sugar, and phosphate.
Cytosine
Pyrimidine base in DNA and RNA, pairs with guanine.
Guanine
Purine base in DNA and RNA, pairs with cytosine.
Adenine
Purine base in ATP, NADP, DNA, and RNA, pairs with thymine.
Thymine
Pyrimidine base in DNA, pairs with adenine.
Pentose
5-carbon monosaccharide sugar.
Condensation
Formation of larger molecules by removing water from smaller components.
Metabolism
when an organism undertakes essential chemical reactions
Reproduction
Produce offspring, sexually or asexually
Sensitivity
Responsive to internal and external stimuli
Homeostasis
Maintain a stable internal environment
Excretion
Produce waste
Nutrition
Exchange materials and gases with the environment
Growth/movement
Move and change shape or size
Cell theory
The cell is the smallest unit of life; cells only arise from pre-existing cells; all living things are made up of cells
Plasma membrane
Outer border maintaining internal chemistry to the exterior (homeostasis)
Genetic material
coded instructions (DNA) that control internal activities within a cell
Ribosomes
Translate the cell's coded instructions into functional elements
Cytosol
Internal fluid serving as a medium for metabolic processes
Sieve tube elements
elements in plants interconnected by plasmodesmata into supracellular assemblies, challenging the idea of independent cells → lacks nucelus
Red blood cells
Lack nucleus and mitochondria when mature, challenging the traditional definition of a eukaryotic cell
Striated muscle fibres
Fusion of muscle cells into long fibers, challenging the idea of discrete cell units
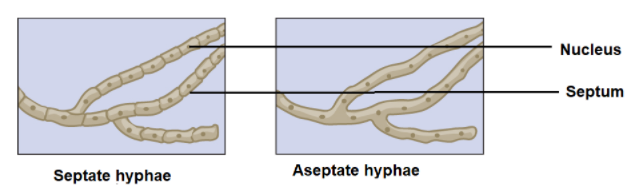
Aseptate Fungal Hyphae
Filamentous structures in fungi for nutrient absorption, challenging the idea of autonomous cells (cells connected without a cell wall between them)
Light microscopy
involves the use of glass lenses to bend light for magnification; can view living specimens in natural colors
Electron microscopy
When images are generated at higher magnification and resolution, but cannot be viewed as living specimens in natural color
Cryogenic electron microscopy
Involves freezing samples to determine molecular structures at near atomic resolution
Magnification
Image size divided by actual size; allows for the calculation of the enlarged image
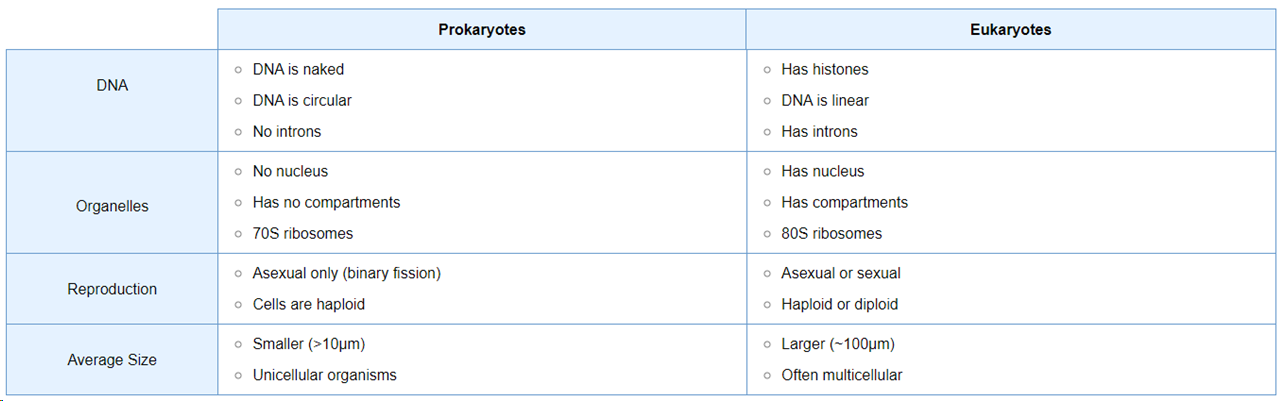
Prokaryotes
Single-celled organisms with simple cell structure; do not possess membrane-bound organelles; exhibit different shapes
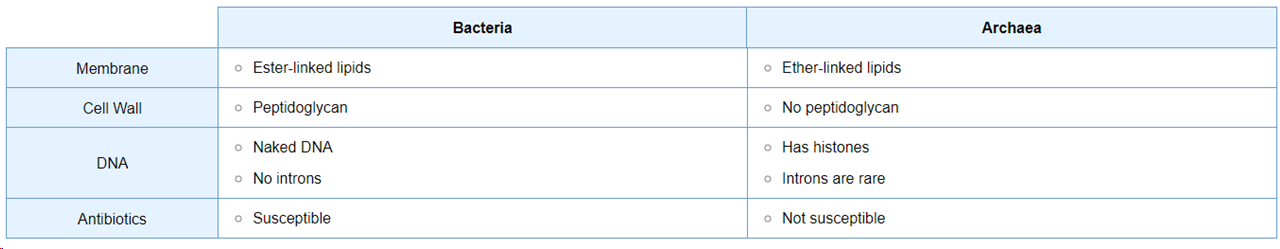
Archaea
prokaryotic; variety of extremophiles and organisms in normal habitats
bacteria
prokaryotic; Large and diverse range of organisms inc. pathogenic forms
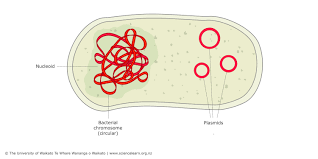
Genophore
Single DNA strand in the nucleoid of Archaea
Plasmids
Additional DNA molecules in Archaea, exchanged via bacterial conjugation
Ribosomes (Archaea)
Characteristically small (70S) responsible for protein synthesis in Archaea
Glycocalyx
Slime capsule covering in Archaea
Pili (Archaea)
Hair-like extensions aiding in adhesion or plasmid exchange in Archaea
Flagella (Archaea)
Whip-like projections facilitating movement in Archaea
Eukaryotes
Organisms with cells containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Endosymbiosis
Evolutionary process where one cell is engulfed by another, leading to assimilation (eukaryotic potential evolution from prokaryotic)
Mitochondria
Organelle responsible for energy production in eukaryotic cells
Cell Wall (Plant)
Made of cellulose, providing structural support in plant cells
Chloroplasts
Organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells
Cytoskeleton
Structural elements in eukaryotic cells, not considered organelles
Light Microscopes
microscopes with low magnification and resolution, view living specimens in natural colors
Electron Microscopes
microscopes which have high magnification and resolution, view dead specimens in monochrome
Prokaryotic Cell Drawing
Genophere as a loop, pili and flagella projecting from the cell wall, 70S ribosomes, appropriate shape
Eukaryotic Cell Drawing (Animals)
Double membraned nucleus, connected ER network, 80S ribosomes, sausage-shaped mitochondria
Eukaryotic Cell Drawing (Plants)
Large central vacuole, cellulose cell wall, double membraned chloroplasts with grana
Abiogenesis
the process of spontaneous emergence of cells from non-living material
Organic Compounds
Complex carbon-based macromolecules found in all cells and organisms
Self-Replication
Capacity for certain organic compounds to reproduce chemical processes in successive cells
RNA
a form of nucleic acid containing the pentose sugar ribose, and the organic bases adenine, guanine, uracil and cytosine.
Protocell Formation
Spontaneous formation of membranes from simple organic molecules
Role of Water
Essential for the formation of life, aids in maintaining stable internal environment
LUCA
Last universal common ancestor, shared source of all extant organisms on Earth
FUCA
first universal common ancestor
Biosignatures
Chemicals produced by cellular processes providing evidence of past or present life
Molecular Clock
Estimates evolutionary divergence timing using mutation rate of biomolecules
Hydrothermal Vents
Heat source interacting with fluid system, likely location of LUCA
Endosymbiosis Evidence
evidence of shared characteristics between organelles and bacteria, suggesting extracellular origins
Multicellularity
Organisms composed of multiple cells operating in unison to support the total lifeform
Emergent Properties
New functions arising from collective actions of individual cells in multicellular organisms
differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
differences between bacteria and archaea
differences between eukaryotes
Nucleotides
Monomeric units of nucleic acids with sugar, phosphate, and base
nucleic acid
polynucleotide chain of one of two types, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Strand Formation
Process of linking nucleotide monomers via condensation reactions
Base Sequence
Order of nitrogenous bases forming genetic instructions
Pentose Sugar
5-carbon sugar component in nucleotides
Phosphate Group
Component of nucleotides attached to the 5-carbon sugar
Nitrogenous Base
Component of nucleotides attached to the 1'- carbon atom
Condensation Reactions
Chemical reactions involving water linking nucleotide monomers into strands
Phosphodiester Bond
covalent bond between phosphate and 2 sugars (hydroxyl groups)
Polynucleotide Strands
Long strands formed by successive condensation reactions
Complementary Base Pairing
Hydrogen bonding between purine and pyrimidine bases
Chargaff
Scientist who studied nucleic acid composition and base pairing
Purine
Double-ringed bases like guanine and adenine
Pyrimidine
Single-ringed bases like cytosine, thymine, and uracil
Genetic Code
the order of bases in DNA (of a chromosome) that determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Tetranucleotide Hypothesis
Theory suggesting DNA composed of 4 repeating bases
DNA
a form of nucleic acid consisting of two complementary chains of deoxyribonucleotide subunits, and containing the bases adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine.
Variability in Base Sequence
Essential for DNA to function as genetic material
Chargaff's Data
Evidence disproving the tetranucleotide hypothesis
Chargaff's Experiment
Demonstrated uneven base frequencies, refuting tetranucleotide hypothesis
Purine-to-pyrimidine Bonding
Ensures DNA helix stability by pairing double-ringed purines with single-ringed pyrimidines
DNA vs RNA stability
DNA is stable, RNA is versatile for genetic information transfer
RNA Structure
Single-stranded nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis
DNA Structure
Double-stranded nucleic acid for hereditary information transfer
Directionality of DNA and RNA
Nucleotides form strands with 5' to 3' linkages, DNA is antiparallel
function of nucleic acids
DNA stores genetic instructions via base sequences, RNA aids in protein synthesis
Hershey-Chase Experiment
Proved DNA as genetic material using radioactive labeling of viruses
Nucleosome Structure
DNA wrapped around histone proteins for compacted structure
Organisation of Eukaryotic DNA
DNA complexed with histones forming nucleosomes, condensed into chromatin
nucleotide structure
mRNA
messenger RNA → encodes proteins
tRNA
transfer RNA → carries amino acids
rRNA
ribosomal RNA → forms the ribosome
histones
A type of protein found in chromosomes → bind to DNA, help give chromosomes their shape, and help control the activity of genes
nucleosome
help to supercoil the DNA, resulting in a greatly compacted structure that allows for more efficient storage
Supercoiling helps to protect the DNA from damage and also allows chromosomes to be mobile during mitosis and meiosis