physio- growth hormone
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH)
growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
what are the 2 hormones related with GH that are released from the hypothalamus- 1 and 2 in this diagram?
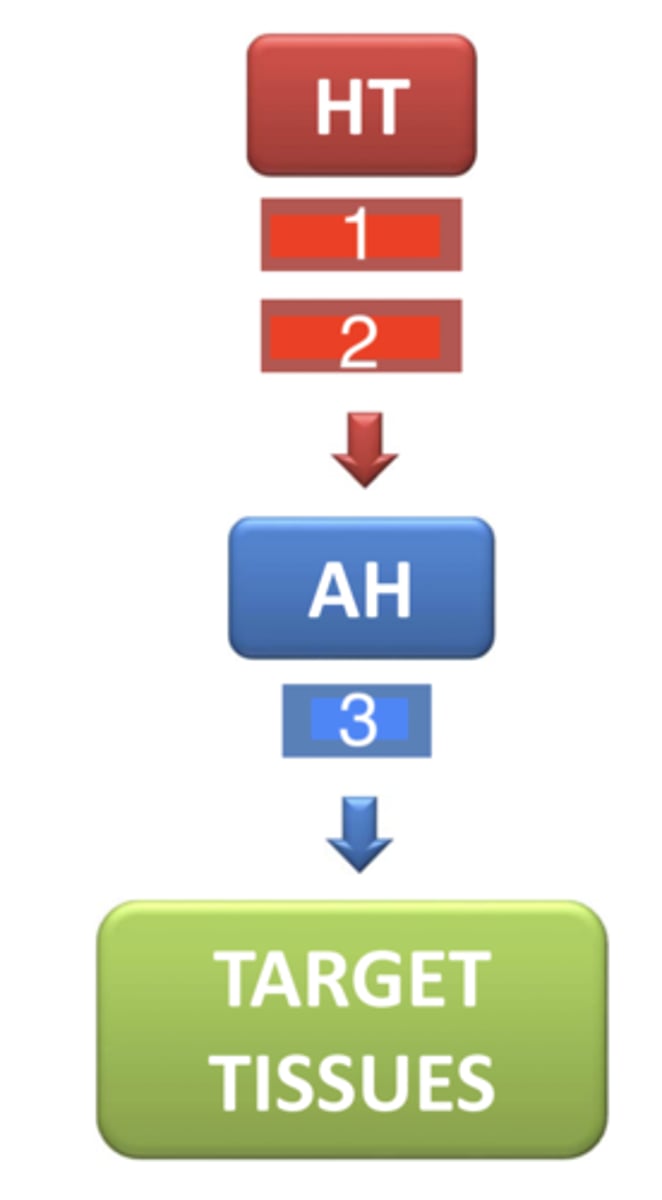
growth hormone (GH)
what is the hormone that is released from the anterior pituitary- 3 in this diagram?
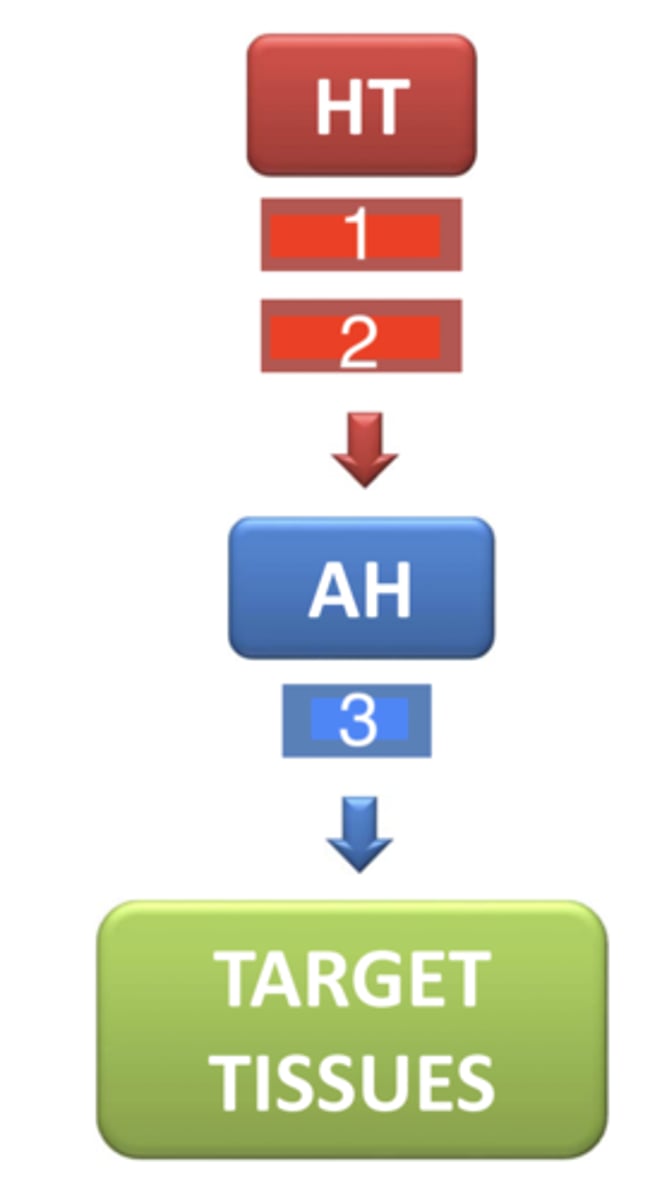
20 minutes
what is the half life of GH?
NON tropic- because it directly stimulates other tissues rather than another endocrine gland
is GH tropic or non tropic?
anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
what does the synthesis, storage, and secretion of GH?
the hypothalamus (with GHRH and GHIH)
what regulates the release of GH from the anterior pituitary?
with GHBP- growth hormone binding protein
how is GH transported through the plasma?
growth hormone binding protein- binds GH to transport it through blood plasma
what is GHBP and what does it do?
somatotropin
what is another name for GH?
hydrosoluble
is GH hydrosoluble or liposoluble?
by the kidneys
how is GH eliminated?
1. promoting cell differentiation
2. promoting protein synthesis
what are the 2 ways that GH regulates growth?
regulate growth
what is the main role of GH?
no, it is released in higher amounts during puberty and during the nighttime
is GH released equally throughout the life?
cell membrane (because it is hydrosoluble)
where is the receptor for GH located?
causes an intracellular cascade and phosphorylation, which ultimately triggers protein synthesis
what happens when GH binds to its receptor ?
metabolism
what is the direct effect of GH?
growth
if the direct effect of GH is metabolism, what is the indirect effect?
increases glycemia by:
- decreasing use of glucose
- increasing gluconeogenesis
- increasing glycogenolysis (catabolism)
what is the effect of GH on carbohydrates?
because it increases glycemia (amount of glucose), which stimulates the production of insulin. however, it does not allow insulin to act, producing resistance
why can GH have a diabetogenic effect?
once released from the anterior pituitary, it travels through the blood, bound to GHBP to its target cell. the receptor is on the cell membrane of the target cell. GH, once bound to the receptor, induces a cascade inside of the cell, which causes phosphorylation, ultimately triggering protein synthesis
what is the mechanism of action of GH?
increase
GH--->______ glycemia (increase or decrease)
decrease
GH--->______ glucose use (increase or decrease)
increase
GH--->______ gluconeogenesis (increase or decrease)
increase
GH--->______ glycogenolysis (increase or decrease)
increases free fatty acids by increasing lipolysis
increases free fatty acid conversion to acetyl CoA to produce energy
what effect does GH have on lipids?
increase
GH--->______ free fatty acids (increase or decrease)
increase
GH--->______ lipolysis (increase or decrease)
decreases
GH--->______ lipid synthesis (increase or decrease)
ketogenic
because GH increases FFA oxidation and mobilizes fat tissue, it is considered to have a ________ effect
it mobilizes fat tissue (allows its use for energy)
GH has a ketogenic effect. what does this mean?
increases proteins in body by:
- increasing amino acid transport
- increasing protein synthesis
- decreasing catabolism of proteins
what is the effect of GH on proteins?
anabolic- turns amino acids into proteins
GH has a _______ (anabolic or catabolic) effect on proteins
catabolic- breaks glycogen into glucose
GH has a _______ (anabolic or catabolic) effect on glycogen
increasing cell size
stimulating mitosis
promoting differentiation of stem cells
promoting proliferation
how does GH increase growth of tissues?
increases protein deposit in chondrocytes
increases speed of multiplication of cells
increases conversion of chondrocytes into osteogenic cells
how does GH effect the skeleton?
increases protein deposit in chondrocytes
increases speed of multiplication of cells
increases conversion of chondrocytes into osteogenic cells
how does GH promote bone growth?
increase in body mass and body tissues
what is the effect of GH reducing protein degradation and increasing protein synthesis?
during childhood, GH stimulates growth of ALL bodily tissue- organs, bones, etc
during adulthood, GH doesn't stimulate bone growth anymore
how does GH affect the body differently in childhood vs adulthood?
other substances that influence growth via external control of the cell cycle
what are growth factors and what do they do?
both
do growth factors act locally or do they go to other tissues via blood transport?
a type of growth factor that mediates the growth promoting actions of GH
what are somatomedins?
somatomedins
what is the major growth factor that is necessary for growth?
IGF-1 and IGF-2
what are the main types of somatomedins?
in the liver
where are somatomedins produced?
GH
what stimulates the production of somatomedins in the liver?
increase
GH---> _______ (increase or decrease) breast tissue development
increase
GH---> _______ (increase or decrease) milk production
increase
GH---> _______ (increase or decrease) immune response
increase
GH---> _______ (increase or decrease) erythropoeisis
increase
GH---> _______ (increase or decrease) glomerular filtration rate
increase
GH---> _______ (increase or decrease) salt retention
hyperglycemia- decreases secretion
hypoglycemia- increases secretion
high amount of amino acids- increases secretion
IGF-1- inhibits secretion
TRH- increases secretion
CRH- decreases secretion
high cortisol- increases secretion
other than GHIH and GHRH, what other factors can regulate the secretion of GH?
decrease
will hyperglycemia trigger an increase or decrease of GH?
increase
will hypoglycemia trigger an increase or decrease of GH?
increase
will high amount of amino acids trigger an increase or decrease of GH?
inhibits GH secretion
what is the affect of IGF-1 on GH secretion?
dwarfism, growth retardation
when there is not enough secretion of GH, what are the effects?
it reduces GH's response to stimuli
what effect does hypothyroidism have on GH?
decreases secretion of GH
what effect does Cushing's syndrome have on GH?
it decreases the secretion of ALL other anterior pituitary hormones
when there is a decrease of secretion of GH, how does this affect other hormones?
-diabetes
-gigantism (if it is before closure of epiphyseal plates)
-thick long bones and long membrane bones (if it is after closure of epiphyseal plates)
what are the effects of GH hypersecretion (too much secretion of GH)?
negative
does IGF-1 give positive or negative feedback to the anterior pituitary?