2.2.3 CASE STUDY - ETHIOPIA
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Where is Ethiopia located?
Ethiopia is located in east-central Africa, bordered on the west by Sudan and South Sudan, east by Somalia, south by Kenya and North-east by Eritrea.
This means that it is a landlocked LiDC.
How does Ethiopia’s location affect its development?
Landlocked + mountainous = no access to coast
trade by sea requires access via neighbouring countries which can be difficult
trade by land and air is more expensive than sea
will not make any capital to spend on developing its on economy and infrastructure
trade deficit - export = US $3 billion, import = US $11 billion
its neighbouring countries being LiDCs means that their infrastructure is limited and unreliable
Describe the landscape of Ethiopia.
Ethiopia has several high mountains, the highest being Ras Dashan at 4,620m.
How does mountainous land (landscape) affect Ethiopia’s development?
Mountainous land, up to 4500m mean that there are steep slopes and thin soils
difficult to build any infrastructure like houses
difficult to grow crops, farming is subsistence, no capital is made
fortunately, coffee, cotton and grains can still grow in lower valleys and be exported
however, they are exported in its raw form, meaning they are low value cash crops
little capital made and cannot be invested into building infrastructure like factories which could then manufacture its own goods
instead, EDCs and ACs make more profit by converting them into manufactured goods
How do lowlands (landscape) affect Ethiopia’s development?
Lowlands contain both livestock grazing and agriculture due to more flat and fertile land.
The land can be overgrazed and overcultivated, leading to soil erosion and desertification
those lead to crop failure over time and livestock become malnourished and people will soon experience famine
lowlands suffer from mosquitoes, malaria and unreliable rainfall
severe illness and loss of workforce, leads to loss of earnings and less development of economy
both then lead to people being too ill to work and country develops reliance on aid, getting into debt, further hindering development
How does climate affect Ethiopia’s development?
unreliable rainfall = altering monsoon and dry climates
higher risk of drought, soil erosion and desertification, lead to widespread famine
cattle face lack of food and water, so die
locals lose essentials of food and clean water, unable to develop
loss of workforce and increasing rate of poverty
How do natural resources affect Ethiopia’s development?
small reserves of natural minerals like gold, platinum, copper and natural gas
but only one large scale gold mine in operation, plans to develop more mines and oil & gas reserves
already 19% of exports that come from mining, however no manufacturing means that they are low value
they still generate income, boosts economy and can be invested into infrastructure and a manufacturing base
exported a higher cost = better economy
Describe Ethiopia’s political history and its political development.
1974 - 1987, military coup evicted the goverment, prompting the start of a civil war, killing 1.4 million people
During that, 1984 - 1985, severe drought and famine
government funds were focused on war, developing weapons instead of providing essentials for its citizens
1.4 million killed = workforce lost
years of political instability would require several years to recover from financial and social damage, setting them back from development
1993 Eritrea became independent, Ethiopia landlocked
need of good political links
trading, import and export becomes more expensive
hindering development
How does trade affect Ethiopia’s development?
trade deficit, import US$11 mil, export US$3 mil
major exports (80%) and 46% of national GDP is from agricultural
largest producers of food and flowers
economy is vulnerable due to unreliable rainfall, climate change and global price changes
however, economy has been growing at an average of 11% per year, less poverty and improving quality of life
however, trade deficit = debt, less income invested to development
How does international investment affect Ethiopia’s develoment?
TNCs like Hilton Hotels invest in Ethiopia, leading t growth in tourism, more jobs, above average wages in Ethiopia
could be poor treatment to workers
more businesses, boost economy, less poverty
H&M manufacture clothes and Siemens manufacture electrical equipment in Ethiopia
More income from trade of manufactured goods
could be poor working conditions
How does population affect Ethiopia’s development?
large population of over 94 million
high birth rate and a slowly falling death rate
natural increase, population growing by 2.6% per year
pressure on economy because of overpopulation
increase demand for food, clean water, clothes
need for imports
strain on economy due to shift in investments
little job opportunities = high rate of unemployment
How does employment structure affects Ethiopia’s development?
one of the world’s lowest levels of development , HDI of 0.435
reliant on agriculture (primary sector) is huge, 89% of all exports and 80% of all jobs
secondary is becoming more popular due to international investments
tourism and travel trade is taking off, meaning increasing numbers of tertiary service jobs
over 2.5 mil of tertiary jobs, contributing 4x as much to the national economy
How does education affect Ethiopia’s development?
poor education rate, especially girls, only 43% were in schools in 2000
education gender gap was still not closed
93% of girls are now in primary schools
government installed schemes like the national education development plan, ensuring that 96% of children join a primary school
however quality of education varies, adult literacy rate of just 36%
more males than females in primary education
very little females in secondary education
slow development
How does healthcare affect Ethiopia’s development?
risen by 50% since 1990, successful
now, 80% of population live 10 km within a doctor
one doctor was shared by 3333 people
malaria was leading cause of death
now, 100% of population have access to a mosquito net
child mortality reduced from 97/1000 to 45/1000, improvement of maternal health and child health
maternal mortality dropped 23% due to better before and after care
How does technology and innovation affect Ethiopia’s development?
Ethiopia is behind other African countries
have a state-owned monopoly, operated by just ethio telecom
lack of competition
slow technological developments
poor network coverage
no usage of credit cards or international banking systems, making online purchases inaccessible
less than 4% of population in 2015 were connected to internet
only 12% of population uses mobile phones
little online connection to the rest of the world
slowing development
How does Goat Aid affect Ethiopia’s development?
goats were mostly given to girls
able to sustain themselves and their families
sell their products like wool, milk, manure for money
support in education, status and security
less likely to be subjected to arranged marriage, prostitution and poverty
aid and debt relief from international communities
debt of 155% decreased to 21% by 2012
able to invest in services and infrastructure instead
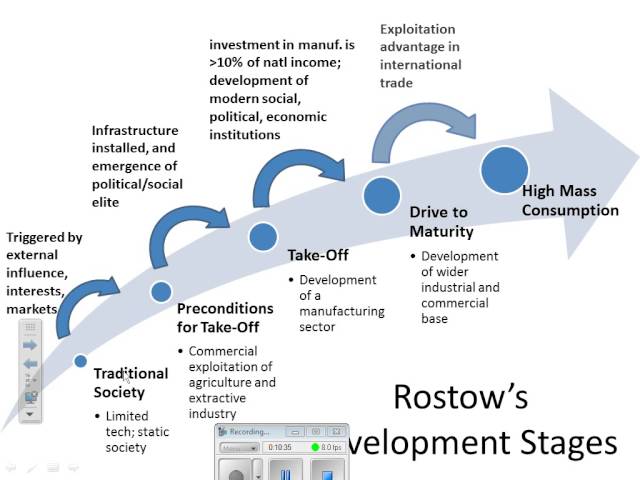
Determine where Ethiopia is according to the Rostow’s model and determine its future path.
It is most likely in between stage one and two (traditional society and preconditions for take-off) as only 12% of its population uses mobile phones, still a gender gap in education, 89% of all exports and 80% of jobs still come from agriculture, however with increasing international investments, Ethiopia' could take off soon.