Semester Final Rad pro 3 Fluoro, Reproductive, Skull, Mandible, Sinuses/Nasal
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
What are the primary sex organs called?
A. Testicles
B. Ovaries
C. Gonads
D. Zygotes
C. Gonads
Males testes secrete what hormone?
A. Estrogen
B. Testosterone
C. Prostaglandin
D. Progesterone
B. Testosterone
What is another term for eggs that develop in the ovaries?
A. Oocytes
B. Spermatizoa
C. Zygotes
D. Estrogen
A. Oocytes
At 9 weeks, the fertilized egg is considered to be a ______________.
A. Zygote
B. Embryo
C. Fetus
D. Baby
C. Fetus
What are the cornu?
A. Another name for fallopian tube
B. The lateral corners of the uterus where the fallopian tubes attach
C. The ruffled ends of the fallopian tubes
D. A portion of the male reproductive system
B. The lateral corners of the uterus where the fallopian tubes attach
The inner lining of the uterus, the __________________, is shed each month unless fertilization has occurred.
A. Omentum
B. Endometrium
C. Myometrium
D. Arboretum
B. Endometrium
A pregnancy located outside the uterine cavity, in the tubes or abdomen is called an ___________________ pregnancy, meaning outside normal location.
A. Ectopic
B. Endorphine
C. Ectomorph
D. Fimbrial
A. Ectopic
How many divisions of the uterus are there?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
C. 4
What type of glands are the Mammary glands/breasts?
A. Endocrine
B. Exocrine
C. Apocrine
D. Lactocrine
C. Apocrine
Breast cancer arises from which type of mammary tissue?
A. Adipose
B. Areolar
C. Glandular
D. Cooper's ligaments
C. Glandular
Amenorrhea means_______________________.
A. Early onset of menstruation
B. Late onset of menstruation
C. Abnormal bleeding
D. Absence of menstrual flow
D. Absence of menstrual flow
What is the medical term for fallopian tubes?
A. Vas Deferens
B. Salping/Salpinx
C. Mons pubis
D. Fundus
B. Salping/Salpinx
What does HSG stand for?
Hysterosalpingogram
What are HSGs primarily performed for?
A. All of these
B. Blocked tubes & tubal patency
C. Repeated miscarriage
D. Infertility
A. All of these
What is the ten day rule?
A. Exam scheduled after first ten days from LMP
B. Exam scheduled on 10th day following LMP
C. Exam scheduled within the 10 days from the first day of LMP
C. Exam scheduled within the 10 days from the first day of LMP
What type of contrast is used for an HSG?
A. Water soluble iodinated
B. Sinografin
C. Salpix
D. All of the above, one is type, two are brand names
D. All of the above, one is type, two are brand names
What is the term for a uterus that is divided/has 2 horns?
A. Duplicated
B. Bicornuate
C. Biphasic
D. Ectopic
B. Bicornuate
Non-descent of testes is known as _______________________.
A. Inguinal hernia
B. Epididymus
C. Impotence
D. Cryptorchidism
D. Cryptorchidism
What is the name of the external sac the testes are housed in?
A. Pupis
B. Scrotum
C. Vas Deferens
D. Prostate
B. Scrotum
The male urethra passes through the ________ gland and is _______________ long on average.
Prostate; 7-8 inches
What is the name of the antigen test for prostate enlargement or cancer?
PSA test
What is the name of the twisting of a testicle upon itself that can lead to loss of the testicle due to lack of blood supply and tissue death?
Torsion
What is the most common way to evaluate testicular and prostate abnormalities today?
Ultrasound
What is the primary male hormone?
A. Progesterone
B. Estrogen
C. PSA
D. Testosterone
D. Testosterone
What is an accessory organ to the male reproductive system?
A. Urethra
B. Prostate gland
C. Glans
D. Prepuce
B. Prostate gland
What is non-descension (failure to descend) of the male testes called?
A. Inguinal hernia
B. Scrotum
C. Epididymitis
D. Cryptorchidism
D. Cryptorchidism
What is the general term for sex organs of both males and females?
A. Ovaries
B. Testes
C. Gonads
D. Oocytes
C. Gonads
What is the medical term for fallopian tubes?
A. Vas Deferens
B. Salping/Salpinx
C. Mons pubis
D. Fundus
B. Salping/Salpinx
What is the initial stage of a fertilized ovum?
A. Zygote
B. Fetus
C. Embryo
D. None of these
A. Zygote
What are the primary sex organs of females?
A. Ovaries
B. Uterus
C. Testes
D. Fallopian tubes
A. Ovaries
What instruments are used to perform a hysterosalpingogram?
A. HSG tray, speculum, sterile drapes, contrast media, an acorn cannula or balloon-tip catheter, x-ray imaging
B. Speculum, knife, antiseptic, contrast medium, sterile equipment, and x-ray imaging
C. Speculum, a small tube, tenaculum, sterile equipment, an acorn cannula or a balloon-tip catheter, CT imaging
D. Speculum, contrast media, a small tube, a knife, sponge stick, and x-ray imaging
A. HSG tray, speculum, sterile drapes, contrast media, an acorn cannula or balloon-tip catheter, x-ray imaging
What are the contraindications of an HSG?
A. All of these
B. Pregnancy
C. Active uterine bleeding
D. Acute pelvic inflammatory disease
A. All of these
The uterus is situated between the _____________________ and the ________________________anteriorly.
A. Rectosigmoid colon; urinary bladder
B. Cecum; transverse colon
C. Urinary bladder; transverse colon
D. Symphysis pubis; transverse colon
A. Rectosigmoid colon; urinary bladder
Which of the following terms is used to describe the "degree of openness" of the uterine tube?
A. Patency
B. Gauge
C. Atresia
D. Stenosis
A. Patency
The contrast media preferred by most radiologists for an HSG is:
A. Water-soluble, iodinated
B. Oil-based, iodinated
C. Oxygen
D. Nitrogen
A. Water-soluble, iodinated
What is the name of the spongy depressions where the teeth embed from?
A. Coronal process
B. Turbinates
C. Alveolar processes
D. Diploe
C. Alveolar processes
What is another name for the Zygoma bones?
A. Maxillary bones
B. Antrum of Highmore
C. Pars Petrosa
D. Malar bones
D. Malar bones
Where is the CR for a Towne's view for mandible imaging?
A. At the Acanthion
B. At the Nasion
C. 2.5" above the Glabella
D. At the Glabella
D. At the Glabella
Where is the CR for a PA projection of the mandible?
A. Mental point
B. Acanthion
C. Junction of the lips
D. Nasion
C. Junction of the lips
What is the angle for the axiolaterals of the Mandible?
A. 20-25 degrees cephalic
B. 10 degrees caudad
C. 15 degrees cephalic
D. 10 degrees cephalic
A. 20-25 degrees cephalic
How is the mandibular body placed for an axiolateral view in relation to the IR to see it in profile?
A. Parallel
B. 20 degree rotation
C. Perpendicular
D. 45 degree rotation
A. Parallel
What position is described here?
Head true lateral, Angle Caudally 25-30 degrees to separate each TMJ from the other.
A. Towne
B. Schuller Method
C. Law's
D. Axiolateral mandible
B. Schuller Method
What is the name of the junction of the two halves of the mandible at the midline?
Mental point
Symphysis
Mental protuberance
Mentum
A. 1 and 2
B. 1, 2 and 3
C. 1 and 3
D. All of the above
C. 1 and 3
What is the name of the vertical portions on each side of the mandible?
A. Zygomatic processes
B. Alveolar processes
C. Condyles
D. Rami
D. Rami
Which process of the mandible forms the TMJ joint with the temporal bone?
A. Condyloid
B. Alveolar
C. Gonion
D. Coronoid
A. Condyloid
What is the name of the angle of the mandible?
A. Condyle
B. Coronoid
C. Rami
D. Gonion
D. Gonion
What bone does the zygoma join with to form the Zygomatic Arches?
A. Mandible
B. Temporal
C. Maxilla
D. Sphenoid
B. Temporal
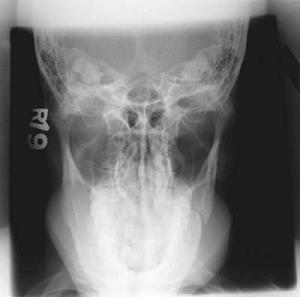
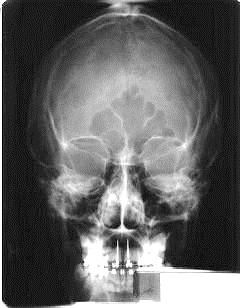
Which method is this image?
A. Towne Method
B. Modified Towne Method
C. Schuller Method
D. Waters Method
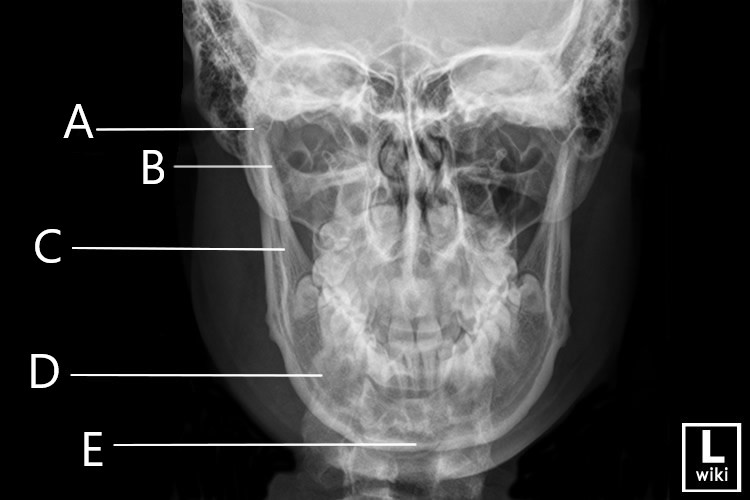
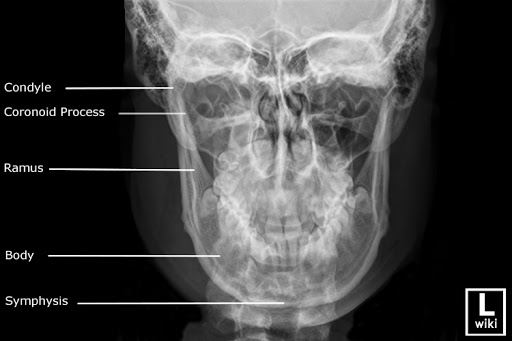
Match the letters with the following image:
A. Mandibular Condyle
B. Mandibular Coronoid Process
C. Mandibular Ramus
D. Mandibular Body
E. Mandibular Symphysis
Several methods are available to perform the axiolateral oblique projection of the mandible to demonstrate the symphysis, body, or ramus. What is the central-ray angulation for all of these projections?
A. 20-25 degrees caudad
B. 20-25 degrees cephalad
C. 15 degrees caudad
D. 15 degrees cephalad
B. 20-25 degrees cephalad
The axiolateral oblique projection is used to demonstrate the mandible. How is the head positioned to demonstrate the ramus of the mandible?
A. 45 degrees toward the IR
B. 30 degrees toward the IR
C. 30 to 45 degrees toward the IR
D. True lateral
D. True lateral
The axiolateral oblique projection is used to demonstrate the mandible. How is the head positioned to demonstrate the symphysis of the mandible?
A. 45 degrees toward the IR
B. 15 degrees toward the IR
C. True lateral
D. 30 degrees toward the IR
A. 45 degrees toward the IR
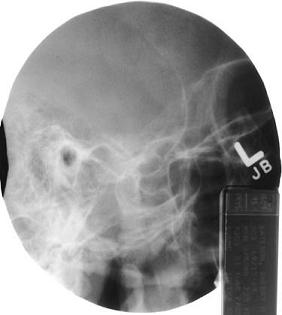
In the attached position of the TMJ, is the mouth opened or closed?
A. I am not sure this is a TMJ projection
B. It does not matter with this projection
C. Closed
D. Opened
D. Opened
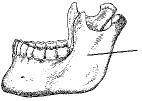
The portion of the mandible identified in the figure below is the:
A. Body
B. Alveolar portion
C. Ramus
D. Symphysis
C. Ramus
The zygomatic process creating the arches are a part of which bone?
A. Sphenoid
B. Frontal
C. Temporal
D. Parietal
C. Temporal
What angulation is used in this PA projection image?
A. 15 degrees cephalic
B. 15 degrees caudad
C. 25 degrees caudad
D. 0 degrees
B. 15 degrees caudad
What is the central-ray angulation to the IOML for the SMV projection?
A. 5 degrees cephalad
B. 5 to 7 degrees cephalad
C. 5 degrees caudad
D. 0 degrees
D. 0 degrees
What is the degree of angle and CR location for this mandibular image?
A. 15 degree caudal; Nasion
B. 0 degree angulation; center of lips
C. 0 degree angulation; Nasion
D. 15 degree caudal; center of lips
B. 0 degree angulation; center of lips
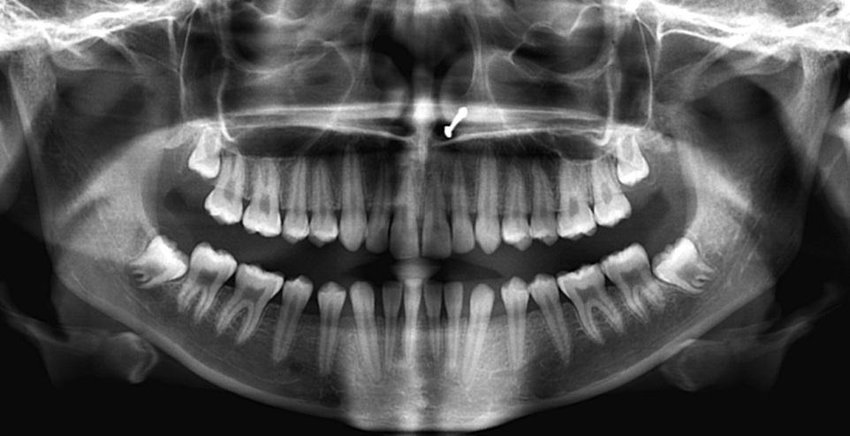
What is this image/procedure called?
A. Pinorex
B. Dentogram
C. Panorex
D. Penorex
C. Panorex
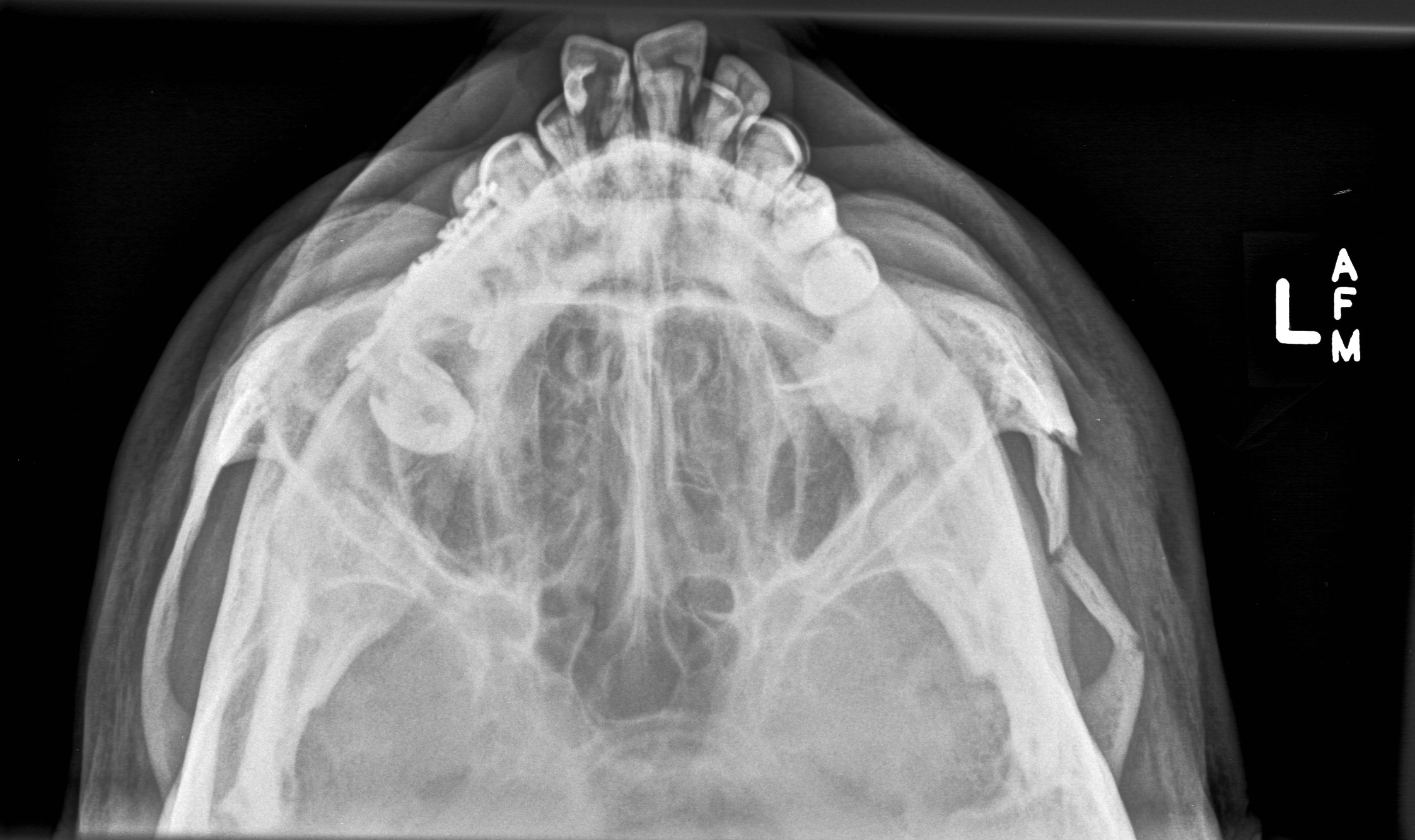
What pathology do you see in this image?
A. Depressed fracture of left zygomatic arch
B. There is no pathology
C. Sinusitis
A. Depressed fracture of left zygomatic arch
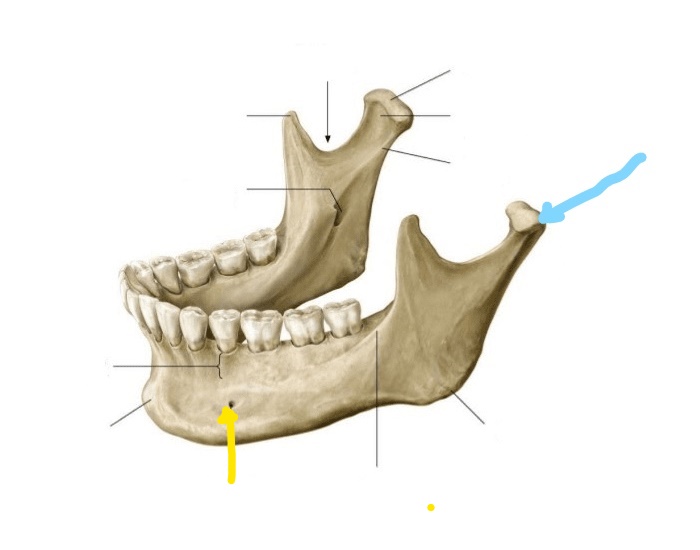
What is the yellow line pointing to in this image?
A. Symphysis
B. Alveolar processes
C. Mental Foramen
D. Menti
C. Mental Foramen
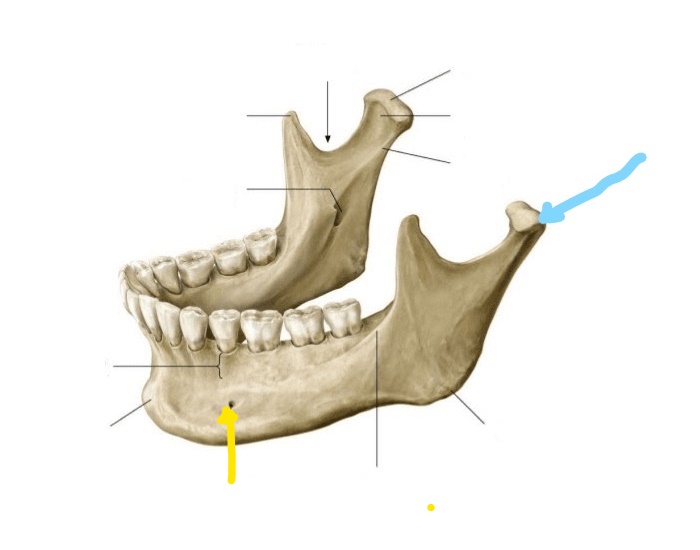
What is the blue line pointing to in this image?
A. Mandibular condyle
B. TMJ
C. Condyle
D. Coronoid process
A. Mandibular condyle
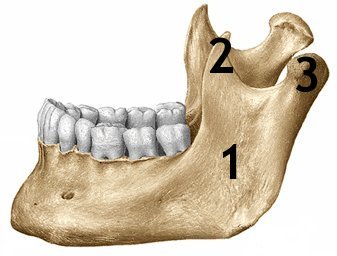
What is identified by the number 2 in this image below?
A. Condyloid process
B. TMJ
C. Coronoid process
D. Mandibular Coronoid process
D. Mandibular Coronoid process
What portion of the mandible would be imaged/featured/parallel to the IR on an axiolateral with the face rotated toward the table/IR 30 degrees from lateral?
A. Condyle
B. Rami
C. Mentum
D. Body
D. Body
Which medication treats angina?
A. Levophed
B. Nitroglycerine
C. Coradrone
D. Pronestyl
B. Nitroglycerine
Which medication is an anticoagulant?
A. Heparin
B. Metformin
C. Isoptin
D. Decadron
A. Heparin
Which medication is an anticoagulant?
A. Adenocard
B. Benadryl
C. Warfarin
D. Nitroglycerin
C. Warfarin
Which medication treats high blood sugar?
A. Glucagon
B. Epinephrine
C. Glucophage
D. Sodium bicarbonate
C. Glucophage
Which medication treats high blood sugar?
A. Metformin hydrochloride
B. Lasix
C. Benadryl
D. Xylocaine
A. Metformin hydrochloride
Which medication treats spastic colon?
A. Isoptin
B. Heparin
C. Glucagon
D. Dobutrex
C. Glucagon
Which medication(s) treats allergic reactions?
A. Diphenhydramine
B. Epinephrine
C. Decadron
D. All of these
D. All of these
Which premedication(s) can reduce the risk of reaction?
Antihistamine
Corticosteroids
Benadryl
A. C only
B. 1, 2 and 3
C. 2 and 3
D.
B. 1, 2 and 3
The radiography examination in which a contrast medium is introduced into a joint space and radiographs are made of the joint is called:
A. Arthrosis
B. Arthrography
C. Arthrogenesis
D. Arthroendoscopy
B. Arthrography
Which imaging modality has prompted a major reduction in the number of arthrograms performed in radiology?
A. Computer radiographyt
B. Computed tomography
C. Magnetic resonance imaging
D. Nuclear medicine
C. Magnetic resonance imaging
After the injection of contrast for myelography and the radiologist takes "spot films," what additional imaging may be requested immediately after?
"Overhead" Radiographs
Computed Tomography
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Sonography
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 only
C. 2 only
D. 1, 2, and 3 only
E. 3 only
F. 2 and 3 only
G. 1, 2, 3, and 4 (ALL)
A. 1 and 2 only
An alternate term for injections into the subarchnoid space is:
A. Intrathecal Injections
B. Interthecal injections
C. Intravenous injections
D. Percutaneous injections
A. Intrathecal Injections
Contrast used in myelography is injected into:
A. The Subarachnoid Space
B. The Subdural Space
C. The Ventricular System
D. The Pia Mater
A. The Subarachnoid Space
During Myelography, which should be performed to prevent contrast medium from entering the cerebral ventricles?
A. Place Table in Trendelenburg Position
B. Instruct Patient to Hyperextend Neck
C. Instruct patient to Hyperflex Neck
D. Place patient in the Lateral Recumbent Position
B. Instruct Patient to Hyperextend Neck
For which exam is the contrast injected directly into the fibrous cartilage between 2 vertebral bodies?
A. Diskography
B. Myelography
C. Ventriculography
D. Angiography
A. Diskography
Imaging of the Spinal Cord and CSF using _______ have reduced the number of myelograms performed in radiology.
A. MRI
B. CT
C. Fluoro
D. US
A. MRI
"Overhead" Lateral Projections of the Lumbar Spine post-myelography are usually performed in what manner?
A. Patient Prone, Horizontal Beam
B. Patient Supine, Horizontal Beam
C. Patient Left Lateral Recumbent, Vertical Beam
D. Patient Prone, Vertical Beam
C. Patient Left Lateral Recumbent, Vertical Beam
The brain and spinal cord are enclosed by three protective membranes called the:
A. Meninges
B. Arachnoidarachnoid
C. Subarachnoid layer
D. Pia mater
A. Meninges
What is the PRIMARY reason that the spot-imaging/fluoro carriage is locked into place with a Myelogram lock before the radiologist begins a myelogram?
A. To prevent the spot-filming device from accidentally contacting the spinal needle
B. To make sure all spot films are taken at the same SID
C. To minimize motion that can occur during radiography exposures
D. To allow the patient freedom of movement during the examination
E. So the spot films and the overhead films taken afterwards have the same SID
A. To prevent the spot-filming device from accidentally contacting the spinal needle
What is the purpose of tilting the table during myelography?
A. To control the flow of contrast medium
B. To facilitate the removal of CSF
C. To prevent the patient from having an aspiration
D. To keep from angling the tube for spot films
E. To get weight-bearing images of the vertebral bodies
A. To control the flow of contrast medium
Which of the following projections are performed during myelography?
PA
PA obliques
Lateral (decubitus)
A. 1 and 2
B. 1 and 3
C. 2 and 3
D. 1, 2, and 3
B. 1 and 3
Which of the following sites would NOT be an access site for myelography?
A. L2-L3
B. L3-L4
C. T7-T8
D. C1-Occipital Bone Junction
C. T7-T8
According to federal regulations, the source-to-skin (SSS) distance during mobile radiography may not be less than ______inches.
A. 10
B. 12
C. 15
D. 24
B. 12
During a mobile exposure, the radiographer should be how far from the patient or part being radiographed?
A. 4 Feet
B. 5 Feet
C. 6 Feet
D. 10 Feet
C. 6 Feet
During mobile radiography, shielding should be used on:
Children
Exams in which the gonads are near the primary beam
Patients of reproductive age
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
D. 1, 2, and 3
During mobile radiography, the least amount of scattered radiation will occur at what angle to the patient or part being radiographed?
A. 45 Degrees
B. 50 Degrees
C. 70 Degrees
D. 90 Degrees
D. 90 Degrees
During mobile radiography, the radiographer ideally should be standing at what degree of angle from the primary beam?
A. 0 Degrees
B. 45 Degrees
C. 90 Degrees
D. 45 to 90 Degrees
C. 90 Degrees
How long should the patient lie in the decubitus position before making the exposure during a mobile decubitus chest examination?
A. 1 Minutes
B. 2 Minutes
C. 3 Minutes
D. 5 Minutes
D. 5 Minutes
Mobile radiographic units can have direct digital capability with wired to the unit or wireless
A. True
B. False
A. True
Operative Cholangiograms are performed with a __________________________.
A. portable
B. C-Arm
C. specials dept
D. Stationary Fluoro unit
B. C-Arm
The most common radiolucent contrast agent used is ___________.
A. CO₂
B. Barium
C. Iodine
D. Room Air
D. Room Air
There are ______________ Rights of Medication Administration.
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 7
D. 7
What medication must be discontinued prior to injection with iodinated contrast media?
A. Warfarin
B. Glucophage/Metformin
C. Lasix
D. Decadron
B. Glucophage/Metformin
What does Urticaria mean?
A. Blisters
B. Reddening of skin
C. Severe SOB
D. Hives
D. Hives
What action by the patient can help facilitate the demonstration of Esophageal Varices?
A. Valsalva Maneuver
B. Holding their breath and bearing down
C. Trendelenburg position
D. A and B are the same and correct
A. Valsalva Maneuver
True or False: The fundus of the stomach lies posterior to the pylorus in the body.
A. True
B. False
A. True