EXS 407: Sensitivity and specificity
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
clinical measures of association
quantify the relationship between nominal outcomes/characteristics and the presence of an intervention or result of a test
What is a contingency table used for?
To display the relationship between two categorical variables, often used in clinical studies.

What does RR stand for in clinical measures?
Relative Risk
-Ratio of the rate of response in the intervention group to the rate of response in the non-intervention group
If the rate of the response is the same between intervention conditions, RR = 1.0• If RR > 1.0, then the rate of the response is greater in the intervention group (increased risk)• If RR < 1.0, then the rate of the response is less in the intervention group (decreased risk)
What does an RR of 1.0 indicate?
There is no difference in risk between the intervention and non-intervention groups.
What does it mean if RR > 1.0?
The rate of response is greater in the intervention group, indicating increased risk.
What does it mean if RR < 1.0?
The rate of response is less in the intervention group, indicating decreased risk.
hypothesis testing for relative risk
use confidence interval
if RR=1 is contained in the interval, then no significant difference exists between intervention groups at that alpha level
What is the formula for calculating Relative Risk?
RR = (A / (A + B)) / (C / (C + D))
What is Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR)?
The difference in rates of response between intervention conditions.
What does Number Needed to Treat (NNT) represent?
The number of individuals that must undergo an intervention to prevent one additional negative outcome.
NNT= 1/ARR
interpreting ARR and NNT
ARR=-0.13=for every 100 athletes, 13 knee injuries are prevented w/ stretches
NNT=8, 8 athletes need to do stretches to prevent 1 knee injury
What is an Odds Ratio (OR)?
The ratio of the odds of an event occurring in the presence of an intervention to the odds of it occurring in the absence of that intervention.
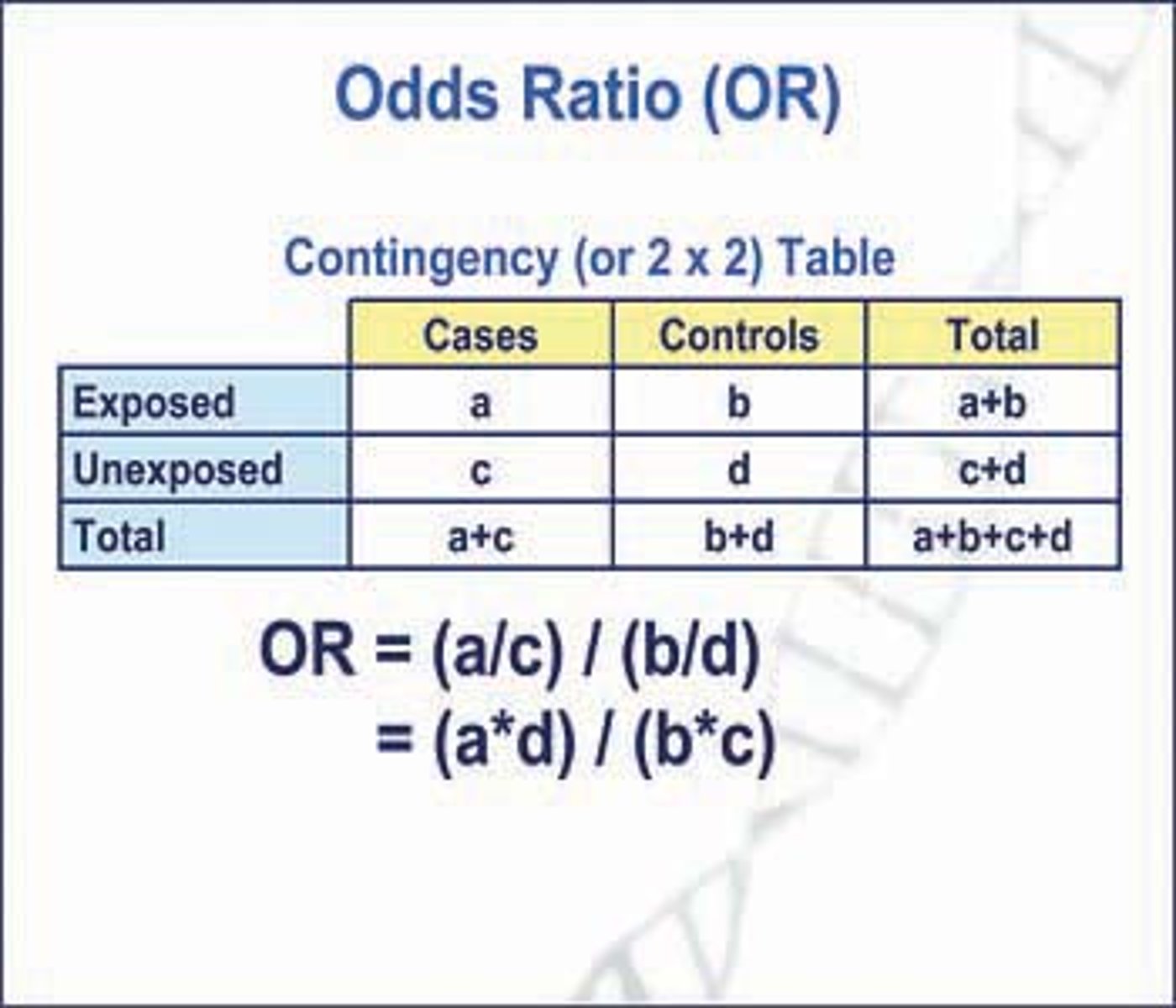
What does an OR of 1.0 indicate?
the odds of the response are the same between intervention conditions
If OR > 1.0, then the odds of the response are greater in the intervention group (increased odds)
• If OR < 1.0, then the odds of the response are less in the intervention group (decreased odds)
What is the formula for calculating Odds Ratio?
OR = (A / C) / (B / D)
-same interpretation as RR using C.Is
ex: Athletes who warm-up have 44% of the odds of injury as those who don't (Warm-up reduced the odds of a knee injury by 56% (1 - 0.44))
diagnostic tests
determine the presence or absence of a condition, and therefore generate nominal, binary data
-The validity of diagnostic tests can also be assessed using a 2x2 contingency table
What is sensitivity in diagnostic testing?
The true positive rate, indicating how well a test identifies those with a condition.
What is specificity in diagnostic testing?
The true negative rate, indicating how well a test identifies those without a condition.
formula for specificity and sensitivity
Specificity = D / (B + D)
Sensitivity = A / (A + C)
What is Positive Predictive Value (PPV)?
The proportion of individuals with a positive test that truly have the condition.
PPV = A / (A + B)
What is Negative Predictive Value (NPV)?
The proportion of individuals with a negative test that truly do not have the condition.
NPV = D / (C + D)
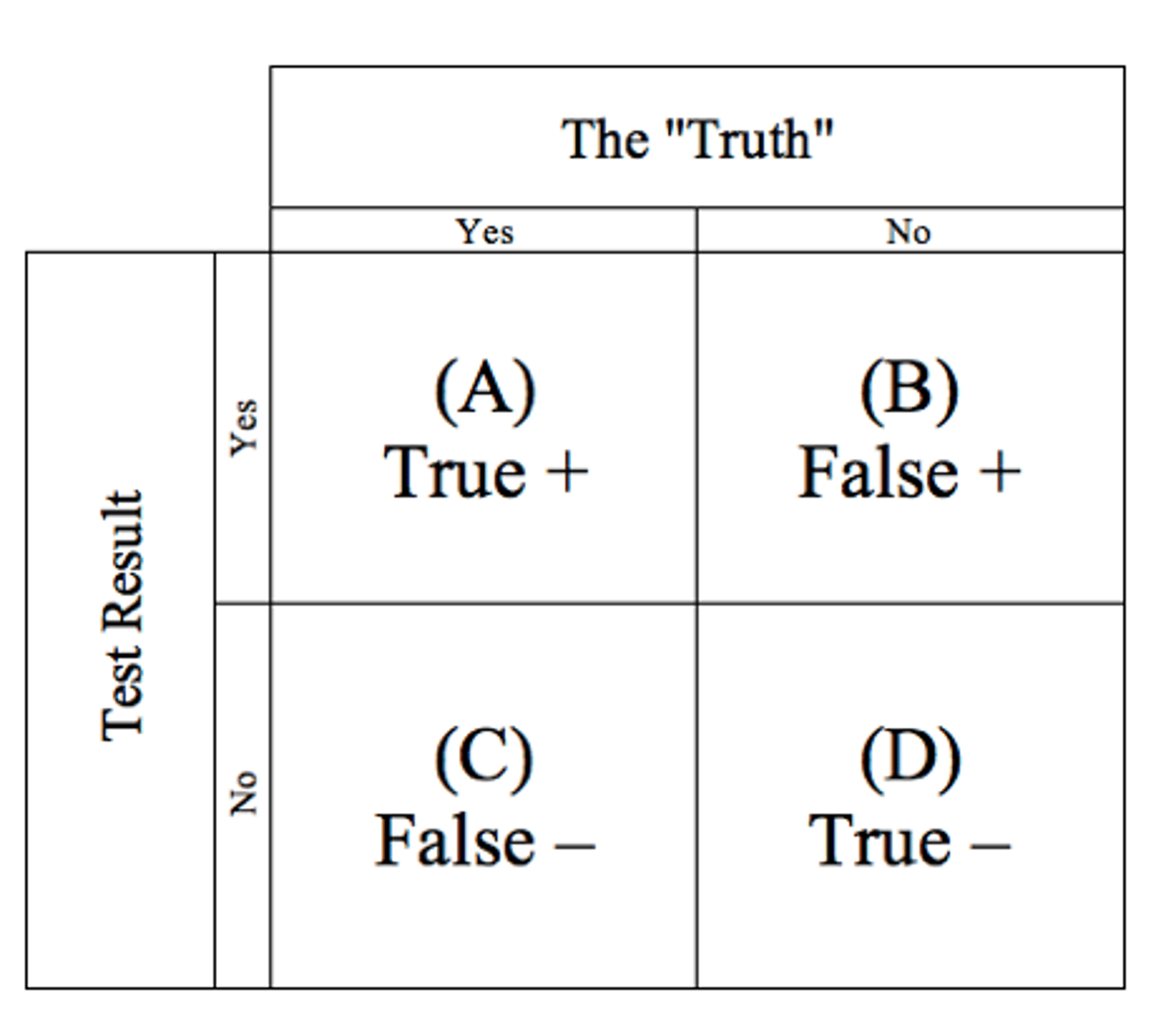
How does prevalence affect PPV and NPV?
-Higher prevalence increases PPV and decreases NPV.
-Sensitivity and specificity are not influenced by condition prevalence
What is a Positive Likelihood Ratio (PLR)?
The ratio of true positive rate to false positive rate.
-likelihood ratios aren't influenced by the prevalence of a condition
What is a Negative Likelihood Ratio (NLR)?
The ratio of false negative rate to true negative rate.
What does a high sensitivity indicate about a diagnostic test?
The test is good at identifying those who have the condition.
What does a high specificity indicate about a diagnostic test?
The test is good at identifying those who do not have the condition.